Article for the “Bio/Mol/Text” competition: The amygdala (amygdala, amygdala) is a region of the brain that plays a central role in the formation of emotions. This small pair structure makes us experience fear, anxiety, concentrate attention on the most significant environmental stimuli, and remember emotional moments. There is a lot to be said for the incredible number of other processes to which the amygdala contributes in one way or another. It is not surprising that a significant part of them allows us to feel good in society and successfully interact with it.
General information.
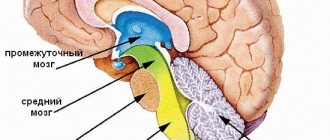
The white matter in the temporal part of the brain contains the amygdala. In front is the hippocampus. The body is called the amygdala. The amygdala consists of 2 parts in both hemispheres of the brain. In this regard, the organ is called a pair and belongs to the limbic system.
The subcortical nuclei contain the tonsils. The amygdala is capable of connecting the limbic system with the autonomic nervous system. The main function of the limbic system is to recognize and reproduce emotions. The Amygdala is a body that has been sufficiently studied by scientists and neurophysiologists, but there are still unknown facts. Composition of the amygdala:
- cortical nuclei;
- medial nuclei.
- basolateral nuclei.
Gustatory and olfactory information is obtained through the functions of the cortical and medial nuclei. Emotional behavior is regulated by the basolateral nuclei. Scientists claim that it is this feature that connects emotions with taste.
Elements of the brain that are interconnected with the amygdala:
- cingulate gyrus;
- frontal cortex;
- taste system;
- olfactory system;
- brain stem.
One of the tonsils' jobs is to maintain attention. Recognition of emotionally significant phenomena, with the ability to recognize danger and favorable conditions. According to scientists' theories, the received information enters a part of the brain - the thalamus. The next stage of distributing this information towards the cortex and into the amygdala. The difference between the actions of the cortex and the amygdala in this case makes a big difference. The cortex, receiving information, ponders and makes a verdict on rational decision-making. The amygdala, on an emotional level, gives an assessment of the situation according to past experience. For example: if you are preparing breakfast and suddenly you are photographed using flash. First of all, you will get scared and twitch, thinking that this is a problem with electric current, and then you will realize what the point is. The amygdala helps a person recognize their emotional states. Scientists have argued that the amygdala is involved only in negative emotions, such as:
- fear;
- excitement;
- anxiety.
This belief has been dispelled by new data, because the amygdala has a wider range of emotional reactions.
Scientists conducted an experiment: sick animals underwent surgery to remove the amygdala. After the removal of one tonsil, emotional feelings disappeared in one hemisphere and fear disappeared. Aggressive animals became calm. If two tonsils are removed, team cohesion is disrupted. The animal leaves and tries to hide from the herd; the leaders become much lower in the hierarchy than their position and do not try to return it. Improper functioning of the amygdala leads to the following diseases:
- tendency to depression;
- excessive anxiety;
- stress disorder.
If unpleasant moments impacted the amygdala, pessimism appeared. The importance of proper functioning of the tonsils is undeniable.
Social distance
We have heard the phrase “social distance” quite often lately. During a pandemic, it is recommended to maintain a distance of 1.5 meters - but what comfortable distance do people choose on average during social interaction and how is this regulated? Let's try to figure it out.
Let's return to patient S.M. Researchers from California decided to measure her comfortable communication distance and compare it with a control group [25]. During the experiment, S.M. asked to approach the stranger at the closest possible distance, which, in her opinion, would not cause inconvenience to either her or the stranger. For the patient, this distance was approximately 0.3 meters. In the control group, the comfortable distance was twice as large - 0.6 meters (Fig. 3). Moreover, S.M. understood the concept of personal space and said that she would come even closer, but thought that the participant in the experiment would feel discomfort.
Figure 3. Comfortable distance between the experimenter and S.M. compared to the control group. a — The results of S.M. are shown in red, the results of a healthy subject are shown in blue. b — Illustration of the experiment.
[25]
Another observation was made in this area using fMRI [24]. The participants in the experiment were placed in a tomograph, and during the research the experimenter either approached or moved away from them, about which the subjects were warned in advance. The fMRI data showed that amygdala activation was attenuated when people knew that the experimenter was far away from them, and increased when the experimenter approached.
Little is known today about the neurobiology of the processes that determine the boundaries of a comfortable personal space. However, there is no denying that the amygdala plays an important role in this component of social interaction.
Structure of the amygdala
- The amygdala is round in shape.
- The basal ganglia, which are located in the right and left hemispheres of the brain, are part of the amygdala complex.
- The amygdala is the subcortical part of the limbic system.
- There are 2 parts on the right and left side of the brain.
- Located near the temple in the white matter environment.
- The amygdala complex is located behind the temple at a distance of 2 cm.
- The hippocampus is located next to the amygdala.
There are 3 groups of nuclei:
- Central. Vegetative control is carried out.
- Basolateral (to the cerebral cortex)
- Corticomedial. Functions of smell.
Neurons in the amygdala are responsible for defensive behavior. When an animal loses its tonsils, it becomes calm, without aggression, devoid of fear. Eating behavior directly coordinates the digestive system. Take for example a cat, the deprivation of its tonsils leads to obesity and an excessive desire for food. In the case of removal of the animal's body, hypersexuality occurs, which can only be eliminated by castration. This is proof that hormones and the amygdala are closely interconnected. This part of the brain contains neurons that calculate probability.
Polysensory nuclei
The electrical activity of the amygdala is characterized by fluctuations of different frequencies and amplitudes. Background rhythms correlate with heart contractions and breathing rhythm. The tonsils are capable of responding to cutaneous, olfactory, interoceptive, auditory, and visual stimuli. In this case, these irritations cause changes in the activity of each of the amygdala nuclei. In other words, these nuclei are multisensory. Their reaction to external stimuli, as a rule, lasts up to 85 ms. This is significantly less than the reaction to the same irritations characteristic of the neocortex.
It should be noted that the spontaneous activity of neurons is very well expressed. It can be inhibited or enhanced by sensory stimulation. A significant portion of neurons are polysensory and multimodal and are synchronized with the theta rhythm.
Development
The amygdala changes dramatically throughout life. It takes several years for the tonsils to change. Women's tonsils develop faster than men's. The difference in development directly depends on body size: men’s tonsils are larger, and accordingly they take one and a half years longer to develop. The amygdala contains nuclear receptors that bind testosterone. Sexual differences are highlighted accordingly. It is due to different hormonal levels. Gene expression depends on DNA synthesis and amygdaloid receptors. Since the amygdala of men contains gray matter, the amygdala itself will accordingly be increased in size.
The presence of testosterone in women is also observed, but it is significantly less than in men, and the development of the amygdala directly depends on the abundance of testosterone. There are differences not only based on gender. It is important to note that in different hemispheres, the tonsils develop differently. For example, the right body is responsible for recognizing faces and feelings of fear, and increases in duration longer. The left is responsible for the feeling of danger and succeeds in development two years faster than the right. This is due to the need to distinguish danger from an early age. During puberty, the difference in response increases noticeably.
What it is?
What is standard hypertrophy of the pharyngeal tonsil in humans?
This condition is called adenoids, and it is a proliferation of the tissue of the above-mentioned tonsil.
The pharyngeal tonsil (also called the nasopharyngeal tonsil) is developed only in childhood. This is why adenoids are most often diagnosed in children aged 5 to 16 years.
In adults, this problem almost never occurs (more precisely, it does happen, but extremely rarely and only in men 25-30 years old and in elderly people 70-75 years old), but residual effects in the form of complications occur quite often.
If the lymphoid tissue is only hypertrophied, then the disease is called hypertrophy or adenoids (in Latin "adenoides"). This tissue can also become inflamed and this is another disease - adenoiditis. How to distinguish one disease from another? This is also discussed in this article below.
The problem develops gradually, at the initial stage it is almost invisible, but then it can be easily identified even without medical diagnosis using the symptoms described below.
Functions.
With the help of the cerebellar bodies, people can remember their emotional reactions to different events over time. The possibility of unconscious learning arises in a person thanks to the limbic structure, which includes the amygdala. Several species of animals have this difference.
Incidents associated with global events (at the survival level) are remembered due to strong emotions and the special structure of the brain. The human brain cares about its survival, thus, emotion acts on internal mechanisms for remembering global events at the survival level. Long-term memory contains this information.
The formation of conditioned reflexes depends on unconscious learning, which is carried out in an automatic way. Rationalizing human reflexes is difficult because thinking does not interact with reflexes.
Cerebellar amygdala. What happens if you remove the cerebellar tonsil?
The amygdala is a specific part of the brain that visually resembles the shape of a regular amygdala. Its dislocation is located deep in the temporal lobe of the brain; in Latin, “lobe” is called Lobus temporalis. Each hemisphere of the brain has its own amygdala. The importance of these tonsils is difficult to overestimate, because they are involved in the formation of emotions and are an integral element of the limbic structure.
In humans and many species of animals, it is this part of the brain that is responsible for the production of positive and negative emotions - pleasure, fear, anger and others. The size of the cerebellar amygdala has a direct relationship with respect to aggressive actions. This part of the brain is sexually dimorphic. For example, if a man has been castrated, the cerebellar tonsils decrease in size by 30%.
Doctors have proven that many mental illnesses are associated precisely with disruption of the normal function of the cerebellar tonsils. In particular, the following diseases:
increased anxiety; autism; schizophrenia; bipolar disorder; various phobias.
In fact, a number of separately acting nuclei are called tonsils. Doctors combine them because these nuclei are close to one another. The main cores are:
basal lateral nuclei; medial central complex; medial cortical complex.
The basal lateral nuclei are necessary for the formation of the fear reflex. Signals to the nuclei come from sensory structures. But medially, the central complex is the output of the basal lateral nuclei and is necessary for the formation of emotional arousal.
Until recently, doctors were confident that with Urbach-Wiethe disease, the patient did not have such an emotion as fear. It is known that in patients with this disease, the cerebellar tonsils are destroyed. But more modern studies and experiments have proven that such patients can still be frightened. This is possible through exposure to air and large amounts of carbon dioxide through inhalation. However, the gas to air ratio must be at least 35%.
This amygdala is responsible for a large number of different responsibilities, for example:
The amygdala is responsible for motivation, i.e. motivation to action. waking up; fear and its emotional manifestations; various types of emotions; hormonal secretions; memory.
Thanks to the cerebellar bodies, a person is able to quickly and permanently remember emotional reactions to various kinds of events. And since the amygdala is part of the limbic structure, a person has the ability to learn unconsciously. This feature distinguishes some types of animals.
The brain has a special structure, for this reason, incidents that are significant in terms of survival are recorded with the help of strong emotions. After all, the main job of the brain is to care about survival. Accordingly, such an emotion activates the internal mechanism necessary for a person not to forget this event. This information is located in long-term memory.
Unconscious learning can control the formation of conditioned reflexes. This learning occurs automatically and on an unconscious level. Because human reflexes are located in parts of the brain that are independent of thinking, they are difficult to rationalize. In carrying out its duties, the amygdala interacts with the hippocampus and basal ganglia. As a result of this interaction, incoming data is assimilated at a higher level.
Dystopia of the cerebellar tonsils is a specific descent of the cerebellar amygdala into the large foramen magnum. This pathology can be called Chiari malformation; it occurs when there is a caudal dislocation of the amygdala on the right or left side of the brain. The disease is characterized by decreased position of the amygdala.
Such standing of the tonsils in no way affects the patient’s life and does not cause concern. This disease is found extremely rarely in children; adults between 30 and 40 years of age are more susceptible to it. It is diagnosed by chance, during routine examinations or treatment of other problems.
This condition occurs due to congenital abnormalities when the volumes of the foramen magnum and the brain do not match. Ectopic tonsils may have another explanation and be secondary. This situation is likely with a large number of injuries or with incorrectly taken lumbar punctures.
Neurophysiological features of functioning.
A number of discoveries have been made in the field of neurophysiological features of the amygdala. The integrity of a healthy body is compromised if the amygdala is damaged.
- Sexual orientation. Scientists have proven that homosexual men have a more developed female part of the amygdala - the left one. For homosexual women, on the contrary, it is the right.
- Social interaction. The amygdala influences the ability to remember; the larger it is, the greater the ability to remember people. We are able to recognize emotions with ease. The intelligence to recognize emotions is proportionally intertwined with the tonsils. Scientists have proven that the larger the amygdala, the better orientation in space and society. In case of violation of personal space, the amygdala is involved at the forefront of events. This is why people often feel uncomfortable when their personal space is violated.
- Aggression. The arousal of sexual and aggressive behavior has been proven experimentally by scientists. But if you remove the tonsils, all these functions disappear.
- Fear. If two tonsils are removed, the feeling of fear completely disappears. Scientists have conducted experiments on this matter, and it has been proven
- Alcoholism. Drinking and introducing toxins from drinking alcoholic beverages into the body negatively affect the amygdala. It is damaged by alcohol abuse. In case of damage, a person’s senses become dulled, as this part of the brain suffers. Therefore, lovers often drink, explaining that it is due to emotional damage.
- Anxiety. When feeling fear and aggression, the amygdala is activated. The fight reflex is the main task of the amygdala. In the event of an irritant or a panic attack, the tonsils are activated. The feeling of anxiety depends on external factors and stimuli. This classification includes: negative feelings; smell; inner feelings.
- Post-traumatic stress device. Research shows that tonsil function is closely linked to post-traumatic stress disorder. If you show a person with this disorder photographs of people experiencing fear, the tonsils begin to activate.
Social anxiety
Let's step back a couple of steps from the norm and touch on such a pathology as social phobia. Characteristic symptoms of this disease include the individual’s excessive anxiety about what others will think of him, fear of judgment, public speaking, and communication with strangers [31]. Moreover, this fear often turns into severe physiological manifestations: stuttering, panic attacks, fainting. The etiology of the disease is not fully understood; it is only clear that genetic factors and environmental elements are involved [32]. Social phobia, along with other phobias, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), belongs to the anxiety spectrum. And on this spectrum, the leading neurobiological correlate is (drum roll!) the amygdala [33].
For example, one of the reasons for the development of social phobia is considered to be previously experienced negative social experience [31]. Let's imagine that a young man did something ridiculous in a large company, for which he was ridiculed and harshly criticized. He is very ashamed, and the last thing he would like is a repetition of this. Subsequently, he formed the connection “a big company - the opportunity to be ashamed,” he showed himself less and less in such companies, and then completely pulled away from them. Repeating the same unpleasant thoughts is very similar to that of depression and PTSD. The dominant role here is occupied by the mechanism of “learning fear.” Its neurobiological basis is the interaction of the BLA and certain parts of the hippocampus [34]. By reminding ourselves over and over again about negative experiences, we reinforce these connections and try to avoid situations that could have similar consequences for us. Stimulation of the BLA-ventral hippocampus pathway caused animals to avoid social contacts, while inhibition did the opposite [35].
Different phobias are based on different stimuli. If you put an arachnophobe in a CT scanner and show him a spider, the fMRI image will show significant activation of the amygdala. However, what stimulus will cause a similar reaction in a person with social phobia? In studies, subjects were compared with a control group (healthy individuals) by showing them images of human faces with different emotional valence (fear, anger, happiness) [36–38]. It turned out that in patients with social phobia, the reaction of the amygdala was enhanced in relation to angry and fearful faces, but not happy ones. Moreover, this reaction depended on the degree of anger and fear expressed on the face (scientists were able to calculate this and take reliable photographs on this basis). The experiment revealed that people suffering from social phobia have a lower threshold for perceiving a face as threatening or frightened than the control group [38].
The functioning of the amygdala has a huge impact on life in society. A detailed study of individual structures of the “social brain” helps scientists understand the mechanisms of our everyday interactions. In addition, it provides insight into the origins of certain mental conditions and allows the development of approaches to treat diseases in which these interactions are disrupted.
The importance of the amygdala for the human body.
The amygdala plays an important role for a person’s full life. The vital functions necessary for everyone are performed by part of the brain. Gustatory and olfactory information, emotional behavior, nervous system: all this exists thanks to the amygdala, the main function of which is to remember emotions and feelings.
The amygdala (amygdala) is a small part of the brain, named for its external resemblance to the nucleus of an almond. Sometimes in Russian-language literature it is called the amygdala, but this is not a completely correct direct transliteration of the English name. The amygdala is a paired section; the tonsils are located in the temporal lobes of both hemispheres. They belong to the limbic system - an ancient part of the brain that controls autonomic functions, some physiological reactions and emotions. The tonsils are involved in the formation of the latter. In addition, they are associated with memory functioning and decision making.
Names: amygdala, tonsil
English name: amygdala
Latin name: corpus amygdaloideum
The amygdala consists of three groups of nuclei. The basolateral ones are associated with emotions, the cortical ones are associated with taste, and the medial ones are associated with the sense of smell. Their joint work can play a protective function - for example, an unpleasant taste or smell makes a person experience negative emotions and stay away from what causes them - spoiled food, which can be poisoned, or waste products, which may contain dangerous bacteria.
The amygdala is shown in purple
In addition, the amygdala is connected to the hippocampus, which is responsible for long-term memory. Therefore, after meeting something scary or unpleasant, its image will be fixed in memory, and subsequently it will be possible to recognize it in time and avoid new contact.
Interestingly, depending on its location, the amygdala produces different emotions. In a study by specialists from the University of Provence, it was found [1] that electrical stimulation of the right amygdala causes negative emotions - sadness, fear, anxiety. And stimulation of the left one often brings happiness and only sometimes unpleasant experiences.
Amygdala nuclei
It is usually said that men’s amygdala is larger than women’s, but develops more slowly [2] – women’s reaches the peak of its development on average 1.5 years earlier. In fact, it is not very clear whether this is so.
For example, a 2021 meta-analysis [3] based on 46 studies and data from 6,726 people says that, on average, the amygdala in men is 0.3 cubic centimeters larger than in women. This gives us a 10 percent increase in volume. But if we renormalize to the fact that the brain itself in men is on average 11-12 percent larger than in women (this has nothing to do with the fact that men are smarter - they are just slightly larger than women, and the spread of normal volume parameters the human brain as a whole differs not by percentages, but by several times - from just over 1000 cc for Anatole France to just over 2000 cc for Ivan Turgenev), it turns out that there is no difference by gender in relative volume the amygdala is not observed.
A 2014 meta-analysis [4], using 126 studies, on the contrary, indicates an increase in the relative volume of the left amygdala in men (among other differences we see the hippocampus and insula).
Illustration from [4]. Blue shows areas that are larger in men than in women.
In addition, regardless of gender, the left amygdala matures 1.5-2 years faster than the right. Early development of the left amygdala provides the ability to respond to danger in childhood.
The size of the amygdala is related to the number of social contacts a person maintains, the social groups to which he belongs - the larger the amygdala, the more complex the network of social interactions. In particular, the size of the amygdala is associated with the ability to remember the appearance of other people and recognize their emotions.
In Urbach-Wiethe disease, an extremely rare genetic disorder described in 1929 by Erich Urbach and Camillo Witte (about 400 cases are known to date), the amygdala can be destroyed. For a long time it was believed that this makes patients completely fearless, but in 2013, American scientists found out that it is still possible to scare such people [5]. This requires inhalation with a high carbon dioxide content, about 35 percent. Such concentration caused not just fear, but a panic attack in three subjects.
Role in emotionality
The relationship between the amygdala, the reticular nuclei of the thalamus and the orbitofrontal cortex determines the rationality and appropriateness of certain emotions
Scientists have recently been able to figure out exactly what neurophysiological properties connect emotions with attention. Researchers have discovered the directions and contacts of individual axons, processes of nerve cells that transmit information to the next neuron, which leave the amygdala and are concentrated in the reticular nuclei of the thalamus, which is involved in the primary processing of signals from sensory organs
The signal transmitted from the amygdala to the thalamus is extremely powerful, which dampens other impulses that might distract the thalamus from emotional information. Such a powerful communication channel is more than important when detecting a threat of danger. Let's say, if a large snake comes into view, then the impulse of fear from the amygdala should muffle all the others. Excessive anxiety may be a consequence of excessive activation of the leading pathway between the amygdala and thalamus, when absolutely everything that happens around is perceived as a potential danger. Conversely, with depression, this connection can be weakened so much that the person stops noticing anything.
The amygdala is known as the “fear zone”, although it is involved in the formation of all emotions. Fear is one of the most powerful emotions not only in humans, but also in mammals. Scientists have been able to prove that the protein stathmin, the highest concentration of which is observed in the amygdala, is responsible for the functioning of innate and the development of acquired forms of fear. A deficiency of this protein leads to a weakening of long-term synaptic connections between neurons in parts of the nerve networks leading to the amygdala.
General characteristics of the amygdala
This small part of the brain gets its name due to its shape and size, which make it resemble the kernel of an almond. The amygdala is often called the amygdala or amygdala in Latin.
We have two amygdalae; they are located in different hemispheres of the brain, more precisely, in its temporal lobes. The tonsils belong to the limbic system - an ancient part of the brain that is responsible for autonomic functions, simple physiological reactions and elementary emotions: fear, anger, rage, pleasure.
- basolateral – responsible for emotional behavior;
- cortical – associated with taste sensations;
- medial – associated with the sense of smell.
By the way, we need to say a few words about white matter. The gray matter of the brain is better known; it is a collection of nerve cells and is responsible for higher mental functions. To put it simply, we think with it. But the white matter performs auxiliary, but very important functions - it ensures the transmission of signals between neurons and supplies them with nutrients.
It is the environment of the white matter that provides the amygdala with communication with different parts of the brain and instantaneous receipt of information. And despite its small size compared to the volume of the brain, the amygdala performs very important functions.
Structure of the limbic system
The LS consists mainly of thirteen main entities. Take, for example, the amygdala nuclei. These two identical almond-shaped areas of the brain are located in the temple area, in different hemispheres. The amygdala forms emotions and also plays an important role in decision making and remembering information. A negative effect on the tonsils affects the activity of the heart, peristalsis functions, hormone production and gastric secretion. From experiments on animals it follows that the removal of some parts of the almond leads to uncertainty and anxiety.
In humans, on the contrary, electrical stimulation of these areas causes aggression and nervous breakdown.
Cingulate gyrus. This cortical portion of the LS runs along the lateral walls of the sulcus that separates the left and right hemispheres. Anterior perforated substance. This is the part of the hemisphere located below and extending posteriorly from the olfactory triangle. Blood vessels pass through it. Next come the reticular formation of the midbrain and the piriform gyrus. Parahippocampal gyrus. Transverse temporal gyri. Located inside the lateral groove.
Hippocampus and hypothalamus
Hippocampus This part is responsible for the consolidation of memory (the transition from short-term to long-term), the realization of emotions and the generation of the theta rhythm with increased attention. Inside there is a dentate gyrus, smoothly turning into a ribbon gyrus.
Hypothalamus. Science does not have clear enough boundaries defining this zone. But it is generally accepted that the hypothalamus is a small region in the diencephalon, just below the thalamic region. Despite their small size, its neurons form 30–50 groups of nuclei that regulate the secretion of various hormones. Next comes the mastoid body.
Group of olfactory formations
Olfactory bulb. It looks like a slight thickening and is located along the edges of the longitudinal fissure of the brain under the temples. There are several of these bulbs. They are located next to each other and are closely connected to the brain by nerve tissue. The olfactory receptor of the bulb only needs one molecule of a substance with an odor to create a complete sensation. Olfactory tract. Olfactory triangle.
These groups overlap with almost all parts of the central nervous system. Neuroendocrine connections deserve close attention. They are the connecting link between the nervous and endocrine systems.
Functions of the amygdala
The amygdala, like the limbic system as a whole, is a very ancient formation that arose at an early stage of evolution, when vertebrate creatures first appeared. Therefore, the functions that this part of the brain performs are also associated with rather primitive reactions and behavior. But this does not mean that they are insignificant, especially since they are associated with the most important protective reactions of our body.
The main function of the tonsils is to control emotions, although not all of them. A person has different levels of emotional states, differing in the degree of rationality or meaningfulness. For example, when we hear an unexpected loud sound, we flinch, our muscles tighten, and our heart begins to beat faster. This is the most primitive feeling of fear, awakening an unconscious need to run and save yourself. This urge occurs before a rational thought appears or a meaningful intention is formed. This feeling of fear is generated by the amygdala.
What problems does disruption of the ganglia cause?
Emerging pathological failures and disorders in the basal ganglia quickly lead to a deterioration in a person’s condition. Not only his well-being suffers, but also the quality of mental activity. If the functioning of this part of the brain is disrupted, a person may become disoriented, suffer from depression, etc. This is due to two types of pathologies - neoplasms and functional failure.
Any neoplasms in the subcortical part of the nuclei are dangerous. Their appearance and development leads to disability and even death. Therefore, at the slightest symptoms of pathology, you should consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. The formation of cysts or other neoplasms is caused by:
- degeneration of nerve cells;
- attack by infectious agents;
- injuries;
- hemorrhage.
Functional impairment is diagnosed less frequently. This is due to the nature of the occurrence of such pathology. It appears more often in infants during the maturation of the nervous system. In adults, failure is characterized by previous strokes or injuries.
Amygdalae and sexual orientation
Sexual behavior, including the reaction of sexual dominance, also belongs to the most ancient forms of behavior. The amygdala plays an important role in the formation of sexual response, including the experience of emotions of pleasure.
Sexual behavior differs between men and women, as do physiological responses, and recent research has shown that the amygdala differs in both shape and size between the sexes. Moreover, its physical parameters and degree of activity depend on testosterone levels.
Thus, the amygdalae in boys develop more slowly than in girls; in fact, sexual maturation itself in boys occurs later than in girls. But adult men have larger tonsils than women.
The amygdala of the left hemisphere is responsible for the female type of sexual behavior, and the right hemisphere for the male type. It has been noticed that in homosexuals, it is the left, female amygdala that is enlarged in size, and in lesbians, the right, male amygdala is enlarged.
Communication with visual analyzers
The connection between the tonsils and the visual analyzers is carried out mainly through the cortex located in the area of the cranial fossa (posterior). Through this connection, the amygdala influences information processing in arsenal and visual structures. There are several mechanisms for this effect. We invite you to take a closer look at them.
One of these mechanisms is a kind of “coloring” of incoming visual information. It occurs due to the presence of its own high-energy structures. The information that goes to the cortex through visual radiation is superimposed with one or another emotional background. Interestingly, if the amygdala is oversaturated with negative information at this moment, even a very funny story will not be able to cheer the person up, since the emotional background will not be prepared to analyze it.
In addition, the emotional background associated with the tonsils has an impact on the human body as a whole. For example, the information that these structures return and which is then processed in programs forces us to switch, say, from reading a book to contemplating nature, creating one mood or another. After all, if we are not in the mood, we will not read a book, even the most interesting one.
Latest research
The amygdala is responsible for a person’s sense of comfort and personal space; set to activate the tonsils, just one thought is enough, regardless of whether the personal space is violated or not, so the person himself is able to choose his own measure of comfort. Research has established that damage to the amygdala is the cause of the disappearance of fear in a person and the identification of potential danger; also, reduced size of the amygdala is observed in criminals and people with an unbalanced psyche.