Published: 10/11/2018 Updated: 06/23/2021
With prolonged exposure, stress triggers a cascade of physiological reactions that negatively affect health. The heart rate and breathing rate increase, and body temperature rises. All this can lead to problems with the heart and blood vessels, exacerbation of chronic diseases, and decreased immunity.
Learning to cope with the normal stresses of life will help you maintain strength and a positive attitude for productive work and communication with your loved ones. Below are recommendations to help you get rid of stress.
Evening yoga for stress
If you like yoga, two simple poses will allow you to achieve complete relaxation and help you calm down after a busy day.
- Pose 1 . Sit on the floor with your legs crossed. Place your hands on your knees. Try to focus all your attention on the pose you have taken. The base of the spine should be as close to the floor as possible, and the head should be raised high. Imagine that your spine is stretching.
- Pose 2 . Lying on your back with your legs wide apart, place your hands, palms up, about 15 cm from your torso. Slowly rotate your limbs, first outward, then inward. Turn your head from side to side. Imagine that your legs are separated at the knee joints, that your head is separated from your shoulders. Breathe with your stomach, imagine that you are being pressed to the floor by the force of gravity and with each inhalation it becomes stronger and stronger.
What is stress
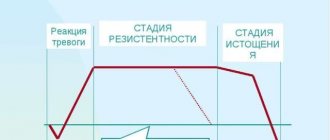
Stress is a normal reaction of a healthy body to threat or overwork. In this way, he tries to resist high stress, fear, excessive physical and psychological activity. As a result of such protection, the nervous system is primarily affected.
If the overload protection works normally, this is not a problem. This way a person remains cheerful, efficient and fit for a long time. However, such loads are often prohibitive. This has a detrimental effect on health and causes chronic diseases.
Stress is an abnormal state of the body. When a person is exposed to it for a long time, the body intensively spends energy.
What other procedures affect the state of the brain?
The brain is the central control system.
The first and fastest link in any stress response is the perception and assessment of the threat by the brain, which determines the type of response to the stressor. Once the brain has identified a situation as threatening, it takes direct control of the endocrine, immune, cardiovascular and digestive systems through complex communication networks: hormones, neurotransmitters, chemicals associated with the immune system. Chronic post-stress disorders are associated primarily with dysregulation of the central nervous system (CNS), which occurs after stress and leads to changes throughout the body. A stable, but no longer capable of adaptation, system is formed with a central link in the central nervous system and peripheral links in other organs.
Is anxiety normal?
It’s normal to worry, because worry is our defensive reaction, which does not pose a danger to health. People worry when faced with something unfamiliar because the brain at such moments calculates and evaluates the situation in order to adapt to it, hedge its bets and ultimately cope.
But if a person is constantly worried, then stress hormones have a negative effect on the body. Increased heart rate and breathing, increased blood sugar levels, and altered blood circulation in a regular manner can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the heart.
Training in planning, tactics and strategy
A stressful situation always seems confusing and insoluble at first, but after rethinking, a way out is found, unless one goes deeper into suffering. Very often, troubles are the consequences of impulsive, thoughtless or emotional actions. And stress acts as a kind of brake, it makes you stop, think, and understand what the mistake is. And also the fact that only a plan, taking into account general circumstances (strategy) and the sequence of actions (tactics), gives the highest probability of victory. Remember that only a well-organized business is successful.
What are the causes of stress?
There are many causes of stress. Each person has an individual body and psyche. The same factor may not affect one of us at all, but cause a violent reaction in another. The most common factors in the development of stress:
- conflict situations at work or at home;
- discontent;
- lack of money;
- long absence of a full vacation;
- routine life with no change;
- death of a relative or loved one;
- lack of vitamins, poor nutrition;
- problems in sexual life;
- fears;
- loneliness;
- sudden change in environment;
- other reasons that can hook a person.
Who can benefit from stress?
Those who suffer first are those who consider stress to be an inevitability associated solely with external circumstances. At first glance, this is so: in most such critical situations do not depend on the person himself and it is impossible to influence them. But in similar circumstances, some people experience stress, while others see it as simply an obstacle, a difficulty, and begin to look for ways to solve the problem. It all depends on the person himself: to accept the inevitable, to blame something or someone and suffer, or to figure it out and change his attitude towards the situation.
People who are accustomed to seeing only negative things in everything almost always suffer from stress..
Such thinking further aggravates the situation, making it insoluble and hopeless. This means there is no need to try to resolve it, to direct energy in a constructive direction instead of useless suffering.
Another category of people suffering from the consequences of stress are those who turn even a banal stressful situation (for example, the loss of something) into a global event, stressing themselves out even more. This also includes those who believe that troubles have a catastrophic effect on their health; any experience leads to terrible diseases and shortens their lives.
The main benefit is belief in good, positive thinking.
A depressed state, a gloomy defeatist mood, and lack of self-confidence are the main obstacles to success and a direct path to failure. Stress acts as a reminder that it’s time to switch to a different evaluation approach, to a different way of thinking. How to relate to what is happening - positively or negatively - is solely the choice of the individual. Optimistic people almost always win, since they use positive attitudes in solving the most difficult situations, while pessimists are doomed to failure in advance.
***
As a result of all that has been said, I would like to wish everyone who is experiencing stress to find the strength to change their attitude from a negative to a constructive positive, not to indulge in suffering and self-flagellation, not to look for those to blame, but to do something, change and move on with the experience gained, not making mistakes again.
leave a comment
Stress teaches you to understand people and find the right connections
Even strong people find it difficult to cope with stress on their own; they have to seek support, advice, and help. But not everyone can give them, only those who are confident in themselves, have achieved success and can cope with difficulties themselves. Admitting your mistakes, incompetence or inability, asking for help is a reason to want to help and support. This is how useful and necessary people appear in life. And in addition, communication in them acts as psychotherapy, eliminating the likelihood of emotional burnout.
Do the oxygen capsules that are so popular in Japan really work?
Such capsules were first created in Japan, but now they are appearing all over the world - not only in medical institutions, but even in fitness centers.
The procedure is called normobaric oxygenation. A higher concentration of oxygen is created in the oxygen capsule - 30% (oxygen content in atmospheric air is almost 21%) with a minimal increase in pressure (1.1–1.5 ATA). During the session, organs and tissues are enriched with oxygen. According to modern research, 30 minutes in such a capsule is equal to 24 hours in a pine forest. The procedure has a powerful neuroprotective effect, helps neutralize the effects of hypoxia of various natures, including after a Covid-19 infection, and increases the body’s adaptive capabilities.
Acute and chronic stress, according to a psychologist
The experience of stress can be either acute or develop into a chronic form. Acute stress usually occurs in response to a short-term stressor, such as a car accident or an argument with your spouse. Acute stress can be very unpleasant, but it passes quickly and is usually well managed with coping techniques such as deep breathing tips.
The chronic form occurs when stressors do not subside and affect you permanently. The roots of chronic stress can vary widely, from situations that people can control or avoid (such as a toxic family) to difficulties that cannot be resolved (poverty, racism or other discrimination, caring for a sick family member). Because people respond differently to stressful circumstances, a situation that one person may find tolerable may be a source of severe stress for another. Psychologists suggest that simple tips relieve stress and allow you to relieve most of the tension.
Chronic stress harms both mental and physical health. This heaviness makes you feel tired, undermines your ability to concentrate and adds headaches and problems with digestion, cardiovascular system and immunity. Unfortunately, we can’t always get rid of stress factors easily and quickly; some of us have to live with for quite a long time. Maintain your mental and physical health - use our simple and effective tips and see how your ability to cope with stress will increase and your health will improve .
The information presented in this material is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional advice from a physician. If you notice signs of stress or depression, consult a specialist!
Author: Editorial staff of the Help-Point.net portal
Start working with a psychologist right now
Start a consultation
Tags: emotional burnout consultation with a psychologist cost of consultation with a psychologist psychologist online
Share
Comments
- Comments
Loading comments...
Previous article
How to improve your memory
Next article
Why do we panic
Any unpleasant, potentially dangerous or simply incomprehensible situation always causes severe anxiety, that is, stress. This is how it happened evolutionarily: negative thinking once helped humanity survive. Imagine an ancient monkey sitting in the bushes - and then there’s a rustling sound. What behavior model is safest for her? Positive - a ripe banana fell from a branch, you need to go look, or negative - a saber-tooth tiger is sneaking and you need to run? Pessimists survived more often.
Therefore, when something goes wrong, it is human nature to expect bad things. This is fine. Our psyche has a whole arsenal to combat anxiety and stress. For example, isolation, denial or rationalization of what is happening (searching for reasons why an unpleasant situation can be useful).
When anxiety is too strong, the deepest mechanism is activated - “fight or flight”. The body prepares for this reaction - tension is transferred to the muscles. But in modern life, as a rule, it is not clear who to hit and who to run away from. And then the only desire is to hide, but it doesn’t work. There is no immediate solution. The stress gets even worse.
As a result, due to severe and prolonged stress, panic sometimes begins. We are either on edge, or frantically rushing around the room, or falling into a stupor and crying, huddled in a corner. The more panicking people there are, the stronger the panic.
Symptoms of stress
Each person reacts to stress differently. What all reactions have in common is a negative impact on the psyche and physical state. The person becomes aggressive and his mood worsens. It happens that stress also causes other reactions - silence, detachment, passivity and isolation. It all depends on the type of temperament.
Typical signs of stress are:
- inability to concentrate on any one type of activity;
- causeless attacks of irritability, anger, dissatisfaction with others;
- lethargy and weakness, depression;
- insomnia, nightmares;
- inability to completely relax and unwind;
- panic attacks, constant feeling of fear;
- desire to cry, melancholy;
- lack of trust in yourself and the people around you;
- lack of appetite or, conversely, the desire to eat a lot;
- sudden appearance of bright and strong emotions (for example, laughter, which quickly gives way to tears and vice versa);
- increased sweating, excitability, itchy skin and headache;
- dizziness, rapid breathing;
- numbness of the limbs;
- nervous tics, desire to bite nails or lips;
- interest in alcohol or drugs;
- chronic fatigue that does not disappear even after a night's rest.
Diagnostics and therapeutic procedures
That is why modern medical anti-stress programs must necessarily include diagnostic techniques and a set of therapeutic procedures to restore the state of the brain. You should always start with diagnosis - it is important to determine what kind of dysregulation of the central nervous system a person has. The rapid development of neuroscience (primarily neurophysiology) has made it possible to study deep physiological mechanisms, explaining from a scientific perspective the formation of stress-related disorders.
How do you know when to see a doctor?
The goal of the stress response is to adapt to life events and return, physiologically and psychologically, to its original state. If usually it was enough for you to change your environment for a couple of days, add spa treatments or massages, streamline your sleep, but now this does not help, your performance decreases or new symptoms appear, your mood changes, anxiety appears, sleep is disturbed, your appetite decreases or increases, If your resistance to colds decreases, if you have problems with the cardiovascular or digestive systems, or if any other symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a doctor. However, it is important to note that in modern conditions it is inappropriate to test the strength of your adaptation systems and wait for them to become exhausted and for complaints to appear. The goal of adaptive medicine is to increase resistance to stress factors, identify maladaptive reactions, and prevent the formation of stress-related disorders. Talk to your doctor and find your own program to keep your stress response systems in optimal condition.