November 10, 2009
Tobacco use is not so much a bad habit as a serious physiological and psychological addiction. You smoke a cigarette, get a dose of good mood, and a few hours later you go for a new one.
Tobacco use is not so much a bad habit as it is a serious physiological and psychological addiction. You smoke a cigarette, get a dose of good mood, and a few hours later you go for a new one. The tobacco industry readily offers us different options for delivering happiness. So what makes you take out your wallet and go to the nearest stall?
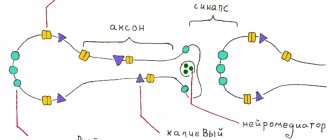
Reward system
Nicotine is addictive
– one of the components of tobacco smoke. It enters the brain approximately 10-15 seconds after the first puff, which is comparable in speed to intravenously administered drugs.
In the brain, nicotine acts on dopamine structures
– this way the “positive” effect of tobacco is consolidated and a desire is formed to repeat it again. The fact is that dopamine is involved in the formation of motivation for behavior and regulates emotions from what has been done. Simply put, dopamine makes us feel good and makes us want to repeat it.
Treatment of tobacco smoking in the Skvir center
"Skvira" is one of the leading medical organizations specializing in the treatment of addictions. The company's mission is not just to relieve people of this or that craving, but also to make a person free from any bad habits.
To start treatment, you need to do very little: consolidate the desire to get rid of “slavery,” refrain from smoking for 12 hours and consult a specialist. The work will be organized according to the original methodology of Ivan Mikhailovich Skvir, physician and doctor of medical sciences. The complex impact will be ensured by the use of psychotherapy, psychocorrection, and reflexology. A person will be able to completely get rid of cravings and restore health.
Deciding to quit smoking is already half the battle. But this process is so complex and time-consuming that it is almost impossible to overcome it alone, without knowing all the techniques and techniques. To achieve an effective result, complex work between the patient and the specialist is necessary.
“Squira” helps to maintain motivation by working with the physical, social and spiritual spheres of activity. Each patient works according to an individual scheme, working through both the physical and psychological aspects of the issue. It is very important to consolidate the result so that at the end of treatment the patient does not return to cigarettes.
Treatment methods are very different. Behavioral ones involve self-regulation and reading specialized literature, but they can only help with a little tobacco experience. Psychological ones include psychotherapy and hypnosis, allowing you to work through the problem at a very deep level and avoid breakdowns. The physiological process is supplemented with medications, replacement therapy, reflexology, dietary nutrition and special breathing exercises.
Success is near
It often seems to us that in order to achieve any goal, especially if it is liberation from something, we need to apply titanic conditions and adhere to the decision made for years, overcoming incredible difficulties that stand in the way. In fact, overcoming yourself, even in such an issue as getting rid of cigarettes, can become a pleasant and uncomplicated process with the competent support of a specialist. “Skvira” can offer its patients exactly this kind of help.
I want more
The rapid development of tobacco addiction is due to the fact that nicotine is very quickly destroyed in the body. About 50 percent in two hours. The concentration of dopamine and endorphins changes, so you have to take another smoke break
. The real withdrawal syndrome manifests itself after three to four hours, and reaches its peak after a day or two.
If you have already developed a severe nicotine addiction
, then irritability, insomnia, and difficulty concentrating are expected. After two to three weeks it usually gets better, but it will still be uncomfortable for a few months.
Experts believe that an attempt to get rid of nicotine addiction is successful if a person has not smoked continuously for six months
.
Psychological addiction to smoking
The first experience of smoking cigarettes is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and sometimes acute nicotine intoxication. A person develops the following symptoms:
- cough;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- increased salivation;
- nausea;
- vomit.
With regular intake of small doses of nicotine into the body, resistance to its effects gradually develops. After one cigarette, you no longer experience nausea, vomiting or dizziness.
Psychological dependence on nicotine develops first. It is associated with the ritual of smoking and certain situations when the need for tobacco arises. At first, this is a company in which the majority are smokers, nervous tension in which cigarettes are used to distract thoughts. Many men start smoking during military service, when there is a long wait or a long gap to fill. Tobacco use is then associated with drinking a cup of coffee, driving a car, and other situations.
At the stage of psychological dependence there is no acute need for nicotine; the process itself is important. Narcologists call this stereotypical behavior. Therefore, a person can easily quit smoking and not experience withdrawal symptoms if they manage to break the psychological model.
To start smoking and form an addiction, special conditions are required. Some researchers believe that the cause of the bad habit is heredity. 50% of children from families where parents smoke also become addicted. In non-smoking families, 25% of children develop a bad habit. But this feature points more to the memorization of adult behavior patterns and the greater availability of cigarettes.
The desire to start smoking, and subsequent addiction, develops under the following conditions:
- the desire to seem like an adult, increasing one’s social status and self-esteem;
- frequent stress and the feeling of relaxation that smoking gives;
- establishing interpersonal contacts, smoking for company;
- reduction of withdrawal symptoms in other types of addiction.
Psychological dependence on smoking is a special type of conditioned reflex. The brain remembers and then learns the conditions under which it receives a dose of nicotine. If a person often ends lunch with a cigarette, then gradually each time after eating the desire to smoke will appear.
Is it possible to jump off?
Addiction develops in different people over different periods of time, and usually ranges from several months to a year. At the stage of its formation, a person can stop using tobacco on his own.
The longer you smoke, the more likely it is that you are addicted. For example, it is manifested by an increase in the number of cigarettes smoked. This is due to the fact that the brain develops a tolerance to nicotine and the dopamine effects - you can never have too much of a good thing.
Degrees of dependence
Nicotine addiction, like any chronic disease, goes through several stages in its development. You can assess how dependent you are on nicotine by answering the Fagerstrom Psychological Test.
Fagerstrom psychological test
| Number | Question | Answer options | Points |
| 1 | How soon after you wake up do you smoke your first cigarette? | In less than 5 minutes | 3 |
| After 6 – 30 minutes | 2 | ||
| After 31 -60 minutes | 1 | ||
| More than 60 minutes later | |||
| 2 | Do you find it difficult to abstain from smoking in places where smoking is prohibited (for example, in a church, cinema, train, restaurant, etc.)? | Yes | 1 |
| No | 0 | ||
| 3 | Which cigarette would be most difficult for you to give up? | From the first | 1 |
| From the second | 0 | ||
| 4 | How many cigarettes per day do you smoke? | 31 or more | 3 |
| 30 — 21 | 2 | ||
| 11 — 20 | 1 | ||
| 10 or less | 0 | ||
| 5 | Do you smoke more often in the first hours after waking up than during the rest of the day? | Yes | 1 |
| No | 0 | ||
| 6 | Do you also smoke when you are so sick that you spend most of the day in bed? | Yes | 1 |
| No | 0 |
The results are evaluated depending on the number of points2. Nicotine addiction2:
- absent or low - the total number of points does not exceed 2;
- average or moderately expressed - if you scored 3-6 points;
- strongly expressed - if you have 7-10 points.
to come back to the beginning
The same... Only in profile
In an attempt to get rid of addiction, people often switch to “light” cigarettes. This is the most successful trap of the tobacco industry. In this situation, everyone is happy: tobacco manufacturers, since you continue to buy their products, and you yourself, since you seem to have switched to something more “healthy.”
But you never know, there is a lot of nicotine in these cigarettes. Along with resins and other toxic substances. Most often, when switching to a “light” brand, a person either increases the number of cigarettes or begins to puff much harder. And this leads to an increase in nicotine intake and even greater irritation of the larynx with hot smoke.
The health risks of nicotine
Smoking affects several key systems of the body at once: nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine, respiratory. Let's consider the main consequences: increased excitability, decreased reaction, decreased appetite, increased and then a sharp drop in blood pressure, vasoconstriction, blood oxygen saturation worsens, a severe cough occurs, breathing becomes difficult, the voice becomes rough and hoarse. Smoking is the main cause of lung cancer and becomes one of the factors in the development of atherosclerosis and hypertension.
Let's imagine a portrait of a classic smoker? He is irritable, inattentive, sleeps poorly and eats a lot. His health is gradually deteriorating, and the rate of this process is much faster than that of non-smokers. In addition to lung cancer, he may encounter an oncological process in the bladder, blood, cervix, intestines, esophagus, kidneys, larynx, liver, oral cavity, pancreas and stomach, trachea, etc. His heart can no longer withstand the previous loads, sports or simply climbing stairs becomes a difficult undertaking.
Reasons to quit smoking
- the flow of toxic substances will stop, the pulse will return to normal;
- blood circulation will improve, the “eternal cold” in the extremities will go away;
- the blood will be saturated with oxygen, and carbon monoxide, on the contrary, will decrease to normal;
- forgotten tastes and smells, long suppressed by receptors, will return;
- shortness of breath will subside;
- the craving for tobacco will disappear, the body’s endurance will increase;
- sleep is normalized, the condition of the skin, hair, and teeth improves.
There are, obviously, a huge number of reasons that can motivate us to quit smoking. And to the benefits that this liberation will bring to health, you can easily add caring for those around you (riding them from second-hand smoke) and preserving a certain share of finances. But, the main thing is to gain true freedom, life without being tied to any substance.
How does nicotine addiction manifest?
A symptom of nicotine addiction is the formation of a persistent habit. If you imagine this clearly, then the habit will be the tip of the iceberg - this is what is visible to others and the person himself, and a huge invisible part will be hidden under the water - mental and physical nicotine addiction.
Habit
- these are actions brought to the point of automatism; at the physiological level, this is the establishment of strong neural connections that give us the opportunity to quickly respond to environmental influences without involving consciousness. Breaking a habit is quite difficult because breaking or rebuilding the formed neural connections will require a lot of additional energy and motivation.
How to improve your condition during withdrawal
It’s not enough to just want to quit smoking, you also need to be ready to change your lifestyle and get ready for a speedy recovery. The following measures can help improve your condition:
- Compliance with the daily routine and rest. It is important to sleep at least 8 hours a day, eat right, and rest when symptoms of fatigue occur.
- Walks in the open air. You can walk, ride a bike, or run. It’s good if the walks take place in a forested area. Endorphins produced in the body during walks have a positive effect on metabolic reactions.
- Breathing exercises. It increases blood circulation and fills the lungs with oxygen.
- Herbal teas. Decoctions of lemon balm, mint, motherwort, and valerian are very soothing. You need to prepare them according to the instructions and drink two or three times during the day.
These measures alone are not enough to feel good during the period of weaning from cigarettes. Therefore, the narcologist additionally prescribes drug therapy and psychotherapy sessions to the patient.
Literature:
- Bogoslovsky, Vladimir Alekseevich. About the dangers of smoking / V. A. Bogoslovsky. – 2nd ed., rev. and additional – Moscow: Center. scientific research Institute of San. education Ministry of Health of the USSR, 1998. – 37 p.; 22 cm. – (To help the lecturer).
- Ulanov, Vladimir Ivanovich. The harm of smoking / Vladimir Ulanov. – [Velsk]: Povazhye, [2012]. – 239 p. : ill.; 21 cm.
- Barabash, Pavel Ivanovich. How to quit smoking: (Practical guide to quitting smoking) / Pavel Barabash. – Khabarovsk: Publishing house DVAGP, B. – 56 p.; 20 cm. – (Modern psychotechnologies).
The effect of smoking on the body
Let's talk in more detail about the negative effects of cigarette smoke on the body:
Circulatory organs
With an increase in nicotine concentration, the load on the heart increases, tachycardia occurs and peripheral vasospasm occurs. With a constant flow of nicotine into the blood, the stage of relaxation and recovery does not have time to occur and this leads to damage to the vascular wall. Manifests itself in the form of the following violations:
- blood viscosity increases
- the risk of developing thrombosis increases
- tissues constantly experience a lack of oxygen, the heart suffers from hypoxia due to spasm
- cholesterol accumulates, which leads to the formation of vascular plaques
- hypertension occurs
- the risk of heart attack, stroke, arrhythmia increases significantly
People with nicotine addiction are five times more likely to die from cardiac necrosis.
Digestive organs
Some of the components of tobacco smoke enter the stomach along with saliva. This leads to irritation of all mucous membranes - the oral cavity, esophagus, and stomach. The teeth turn yellow, their enamel becomes fragile, gum disease begins, the intestines suffer, as well as the liver, kidneys and gall bladder. Due to smoking, the process of digesting food slows down, it remains in the stomach longer than it should, which provokes additional release of hydrochloric acid and enzymes.
For experienced smokers, the following symptoms are typical:
- chronic gastritis
- peptic ulcer
- colitis
- decreased immunity due to intestinal dysfunction
- disturbances in the functioning of the liver, which is the main filter of the body and which works in an enhanced mode
Note! The appearance of a smoker suffers greatly - brittle nails, falling out dull hair, weak skin turgor, unhealthy complexion.
Respiratory system
The main target of tobacco smoke is the respiratory system. Tobacco smoke passes through the oral cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles. Constant exposure to nicotine on the inner surface of the alveoli leads to a decrease in their elasticity and swelling, which is why smokers almost always develop:
- chronic form of bronchitis
- asthma
- emphysema
- laryngitis, tracheitis
- hoarseness of voice
- lungs' cancer
Harmful substances, settling on the respiratory organs, accumulate, causing the so-called smoker's cough, which usually intensifies after waking up in the morning. This is how the body tries to cleanse itself of harmful compounds.
Sexual function and childbearing
Many people start smoking in adolescence without particularly thinking about future children, and in vain. In men, smoking disrupts sperm production, reduces potency, and creates predisposing factors for the development of prostate cancer. Women experience changes in the menstrual cycle and an imbalance in hormone levels. The result of these pathological processes is infertility. All these factors tend to accumulate, and the earlier a person starts smoking, the more severe disorders of the reproductive system await him by the time he thinks about having a child.
Smoking during pregnancy has an extremely detrimental effect on the fetus:
- oxygen starvation of the brain
- chronic asphyxia
- cell mutations and the appearance of structural abnormalities
- death in the womb
- stillbirth
- premature birth
- developmental delay
Women who smoked before conception and during pregnancy have a much higher likelihood of having a child with physical disabilities or premature birth. Later, they lag behind their peers in development and are characterized by lability of the nervous system.
Central and peripheral nervous system
Since nicotine is integrated into the biochemistry of the brain, its harmful effects cannot be ignored; it leads to the excitation of impulse transmission between neurons, and with a significant intake of the toxin, inhibitory processes begin to predominate. The regulation of the production of neurotransmitters is disrupted, and other functions of the central nervous system are affected.
Other toxic substances contained in tobacco smoke cause vasospasm, which contributes to the development of ischemia, and lack of oxygen leads to hypoxia and death of brain cells.
Smokers are 3-4 times more likely to be hospitalized with cerebral hemorrhages and stroke. The same thing happens with the peripheral nervous system. Problems with it can manifest themselves in:
- irritability
- apathy
- migraines
- drowsiness
- decreased performance and physical activity
- memory impairment
- fatigue even with light exertion
The effect of nicotine leads to poisoning and disruption of all organs and systems of the body. And even after quitting smoking, a person will need several months to completely remove this substance and even more time to restore health.
What is nicotine withdrawal?
Nicotine withdrawal is a withdrawal syndrome that occurs as a result of constant use of nicotine and subsequent refusal of it or reduction of the dose. During the intake of nicotine, the metabolic processes in the smoker's body change and, with a sharp refusal of it, a lack of it occurs, and, as a result, withdrawal without cigarettes occurs. This is clearly expressed on a physical level in painful and unpleasant symptoms.
Nicotine withdrawal symptoms
- cough accompanied by dark sputum;
- unstable blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- gastrointestinal problems, constipation;
- increased appetite;
- irritability, depressed mood;
- sleep disturbance, insomnia.
Causes of nicotine withdrawal
The reason for the deterioration of health during the period of quitting smoking is the cessation of the nicotine dose entering the body. It takes time for the body to learn to live again without the stimulation of nicotine. This period has several stages.
Stages of nicotine withdrawal
Cigarette withdrawal occurs quickly when quitting smoking.
Already on the first day, a heavy smoker, 2 hours after consuming nicotine, feels a strong desire to smoke a cigarette.
After 2 hours, a headache and a feeling of severe discomfort may occur; after 6-9 hours, a person may feel irritable, anxious and restless.
On the second or third day of quitting smoking, the apogee of nicotine withdrawal occurs, which can last 3-4 weeks. During this period, a person is in constant doubt whether to smoke or not to smoke.
At this time, the psychological state of the smoker ranges from a state of irritability and hot temper to falling into deep depression, and suicidal thoughts may arise.
About a month after stopping the use of cigarettes, the apogee of nicotine withdrawal passes, and with it the symptoms of physical illness, but it is difficult to answer the question of how many days after you don’t want to smoke, since the psychological craving for cigarettes is still present.
Consequences of nicotine withdrawal
During a smoker's nicotine withdrawal, the physical symptoms are unpleasant, but they can be survived. Pressure changes, dizziness, gastrointestinal upset, dry mouth, and general malaise are observed.
Much greater discomfort is created at this time by the patient’s psychological state, when the desire to smoke can turn into an obsession. And as a consequence of this, irritability, aggressiveness, insomnia, fatigue, and sometimes increased or lack of appetite appear.
Does nicotine withdrawal go away on its own?
A person independently decides to quit smoking, and the outcome of the decision largely depends on his moral and volitional qualities and the strength of the smoker’s motivation. To help yourself survive the period of withdrawal from nicotine, you can go to a special clinic, where specialized psychologists with the necessary experience and knowledge will help remove and alleviate difficulties on the path to a healthy lifestyle.
What is nicotine hunger?
In the first week after quitting cigarettes, the body continues to eliminate nicotine. Nicotine hunger sets in. The restoration of the mucous surfaces of the intestines, bronchi and lungs begins, in which, during the use of cigarettes, a large amount of mucus and soot has accumulated. Expectoration occurs. Intestinal tone is reduced, and, as a result, constipation may occur. The functioning of the stomach and pancreas improves, and taste sensations become more vibrant. During this period, you may be worried about high blood pressure, tinnitus, lack of appetite, bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, and poor sleep.