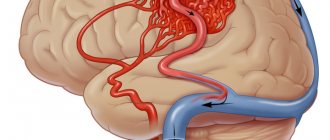
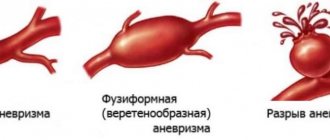
Symptoms of cavernous angioma
The patient may have no symptoms, although headaches, seizures, or other focal symptoms, such as motor or sensory disturbances, are common. Most often, the occurrence of symptoms is associated with hemorrhages, which can occur both inside the cavernous angioma and in the surrounding brain tissue. Depending on the severity of the hemorrhage, conservative treatment or surgical intervention is used, which will be discussed below.
Cavernous angioma of the right frontal lobe. A CT scan without contrast enhancement shows a large heterogeneous mass in the right frontal lobe. The formation is characterized by high X-ray density in its central part and diffusely increased density in the periphery due to the presence of calcifications and small hemorrhages in the formation.
General symptoms of the disease
Newly formed cells exert pressure on neighboring ones.
The initial symptom of the disease is mild headaches and slight dizziness. The characteristic pathology begins to manifest itself as follows:
- Headaches of various types;
- Frequent dizziness accompanied by nausea;
- Epilepsy attacks;
- Paralysis of individual areas;
- Fainting;
- The vestibular apparatus malfunctions;
- Speech disruptions;
- Convulsive twitching;
- Distortion of information reading by taste buds;
- Changes in visual perception;
- Decreased mental activity;
- Noise hallucinations in the head;
- Disease of the venous system.
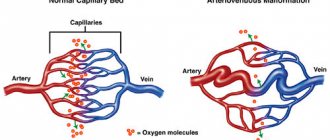
Vascular malformations of the brain
Types of vascular malformations differ based on their macroscopic and microscopic characteristics. Typically, intracranial vascular malformations are divided into the following 4 groups:
- Capillary malformations (or telangiectasias)
- Cavernous malformations (cavernous angiomas/hemangiomas)
- Venous malformations
- Malformations with arteriovenous shunts
According to the newer classification, 2 more categories have been added: arterial malformations (without the formation of an arteriovenous shunt) and mixed malformations.
Cavernomas can be found in any area of the brain because they can arise anywhere along the vascular bed. Intracranial extracerebral cavernous angiomas sometimes occur, but they are quite rare. Cavernous angiomas are also sometimes found in the spinal cord, most often in association with multiple vascular lesions of the brain.
Detection of cavernous angiomas
Despite the fact that cavernous angiomas are visualized using computed tomography (CT), this method is not the method of choice: the fact is that the identified signs in a CT study may correspond not only to cavernous angioma, but also, among other possible options, poorly differentiated tumor.
The sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is much higher, due to its higher contrast resolution, as well as its greater ability to image flowing blood and its breakdown products. The combination of different MRI pulse sequences has largely solved the problem of misdiagnosis or under-detection of cavernous angiomas, since these lesions have quite specific features on MRI.
Get an MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg
CT and MRI can be used for follow-up of patients with already diagnosed cavernous angiomas, especially in cases where there is a risk of hemorrhage. Although the MR image of cavernous angiomas does not predict the occurrence of bleeding, MRI is the method of choice for long-term follow-up of patients with cavernous angiomas, as well as for the evaluation of family members of the patient who are at risk of having such malformations. In addition, MRI is extremely useful in planning surgical intervention, as it allows you to assess the size of the formation, its boundaries, and thus determine the type of operation and surgical approach.
With classical angiography, most cavernous malformations are not visualized, and even when signs are detected, they are extremely nonspecific. If the lesion develops in combination with other vascular malformations, which occurs in approximately 30% of patients with venous malformations, then its MR characteristics become much more complex and less specific. In such patients, angiography may be useful to further clarify the diagnosis.
What can provoke hemorrhage?
According to neurosurgeons, the risk of hemorrhage in the case of venous angioma is quite low. It is found in 0.22–0.34% of patients. But when analyzing information from pathologists, it turns out that among all vascular causes of death in patients, rupture of brain angiomas accounts for 60%.
Increase the risk of hemorrhage:
- arterial hypertension;
- physical activity (for women – labor);
- sudden bends, jumps;
- turning the head;
- minor head injuries (bruises);
- stressful situations.
Cavernous angioma or tumor?
Brain scanning using CT and MRI in most cases allows one to clearly distinguish a cavernoma from other brain formations, including tumors of varying degrees of malignancy. However, in some cases, differentiation of these formations represents a diagnostic problem, the solution of which requires extensive experience. In this regard, the ability to attract a highly qualified diagnostician is critical. In addition, high-quality interpretation of CT and MRI images provides a solution to other diagnostic problems: exclusion of surrounding cerebral edema, identification of the severity of hemorrhage, description of details affecting the operability of the cavernoma. If you are in doubt about the diagnosis, you should consult a radiologist from a leading center specializing in brain pathology. A second opinion from such a diagnostician can be very valuable in the differential diagnosis of angiomas and other pathological conditions.
Cavernous angiomas on CT
When using visualization methods, it is useful to separate the cavity into 3 components. These include (1) a peripheral pseudocapsule, consisting of glial tissue impregnated with hemosiderin, (2) an irregularly structured intermediate connective tissue separating the cavities, and (3) a central vascular part, consisting of vascular cavities with slow blood flow.
On CT images without contrast enhancement, a cavernoma appears as a focal formation of an oval or nodular shape, characterized by slightly or moderately increased X-ray density and does not have a volumetric effect on the surrounding parenchyma. Areas of calcification and hemosiderin deposition in the walls of fibrous septa, along with stagnation of blood in the cavities, contribute to increased x-ray density on non-contrast-enhanced images. On CT images, calcifications are detected in approximately 33% of all cavernomas. If the formation is old, then it may contain central non-contrasting areas of reduced density, which corresponds to cysts from resorbed hematomas.
Contrast enhancement can be minimal or maximal, although 70-94% of cavernous malformations are weakly or moderately enhanced after intravenous contrast. In most cases, good contrast is the result of increased blood flow in the vascular component of the mass. The heterogeneous “speckled” enhancement is caused by intravascular fibrous septa, and the low-density rim along the periphery is caused by a pseudocapsule of glial tissue surrounding the formation.
Mass effect is not typical for cavernomas, unless they are associated with recent hemorrhage. On CT images without contrast enhancement, cavernomas may not be detected at all. In hemorrhages and the formation of intracerebral hematoma, cavernomas are visualized as areas of focal signal enhancement in the area adjacent to the hematoma.
Any hemorrhage detected on CT in a relatively young patient should be carefully investigated, and cavernous angioma should always be considered as a possible cause. When evaluating a patient with a seizure disorder, cavernous angioma should also be considered as a likely etiological factor, especially if the patient is between 20 and 40 years of age.
Cavernous malformations identified by CT may also include other rare vascular malformations (thrombosis of arteriovenous malformation, capillary telangiectasia), glioma (poorly differentiated astrocytoma or oligodendroglioma), and metastatic melanoma.
Prevention
We can only talk about secondary prevention for patients with an already established diagnosis, since primary prevention does not exist. Recommended:
- control blood pressure;
- stop smoking and do not indulge in alcohol;
- women should be careful when choosing contraceptives, oral hormonal drugs contribute to circulatory problems;
- take painkillers and antipyretics only after consulting a doctor; all tablets containing Aspirin increase the risk of hemorrhage;
- avoid severe stress and physical tension;
- organize a good rest.
Cavernous angiomas on MRI
Cavernous angiomas represent about 1% of all intracranial vascular lesions and 15% of cerebrovascular malformations. With the development and introduction of MRI, cavernous angiomas have become the most commonly detected vascular malformations of the brain. In early studies on autopsy material, the frequency of their occurrence was 0.02-0.53%. Using MRI, the incidence of formations similar to cavernous hemangiomas was 0.39-0.9%, and the detection of previously unidentified asymptomatic formations using MRI increased their incidence to 0.45-0.9%.
Get an MRI of the brain in St. Petersburg
On MRI, parenchymal cavernous angiomas are represented by a characteristic “popcorn”-type formation, clearly defined, with a smooth border. The internal part is represented by multiple foci of signal of varying intensity, which correspond to hemorrhages at different stages of resolution.
MRI signs of cavernous angioma. Large cavernous angiomas of the right frontal lobe and left occipital lobe on T1-weighted axial section. These two heterogeneous space-occupying lesions have a central mesh structure with alternating areas of high and low signal intensity, surrounded by a hypointense rim of hemosiderin.
A fresh hematoma containing deoxyhemoglobin is isointense on T1-weighted images and significantly hypointense on T2-weighted images. A subacute hematoma containing extracellular methemoglobin is hyperintense on both T1- and T2-weighted images due to the paramagnetic effect exerted by methemoglobin.
Intermediate fibrous elements are characterized by a weakly hypointense signal on T1- and T2-weighted images, since they contain calcifications and hemosiderin. The heterogeneous interior of the mass is surrounded by a hemosiderin rim, which has low intensity on T1-weighted images. The hypointensity of this rim becomes more pronounced, resembling a halo, on T2-weighted and gradient-echo images due to the higher sensitivity of these sequences to changes in the magnetic field.
Axial gradient-echo MR images provide better visualization of large cavernous angiomas in the right frontal and left occipital lobes. The hemosiderin rim appears as a halo due to the increased magnetic susceptibility of hemosiderin.
Smaller cavernomas appear as low-intensity nodules on T1- and T2-weighted images.
Small lesions are better visualized on gradient echo images due to the increased sensitivity to changes in the magnetic field that is inherent in such pulse sequences. It has also been shown that in sequential gradient echo images, small punctate formations are better visualized with longer echo times; these data suggest that such formations contain paramagnetic substances.
Gradient-echo MR imaging shows multiple bilateral small, punctate and round, low-intensity lesions in the periventricular and subcortical white matter. The largest lesion is visualized in the periventricular white matter of the frontal lobe anterior to the anterior (frontal) horn of the left lateral ventricle near the genu of the corpus callosum. Multiple smaller lesions are visible anterior and posterior to it.
On time-of-flight angiography images, methemoglobin in the center of a cavernous malformation may resemble moving blood. However, on a subsequent phase-contrast MR angiogram obtained with a low blood flow speed setting during encoding (10-20 cm/s), blood flow or pathological vascularization is not visualized, which makes it possible to exclude vascular lesions.
Typically, cavernous angiomas do not have a bulking effect on adjacent tissue or cause edema, and they do not have a feeding artery or draining vein unless they are associated with other similar vascular malformations. Cavernous angiomas are often associated with venous malformations, which are characterized by the presence of a draining vein. In such mixed cases, standard angiography may be useful.
T2-weighted image of a cavernoma of the pons.
Cavernous malformations detected on MRI include other occult vascular malformations (AVM/aneurysm thrombosis, capillary telangiectasia), hemorrhage in a primary or secondary tumor (metastasis of melanoma, choriocarcinoma, thyroid or kidney cancer), amyloid angiopathy, treated or primary infection (toxoplasmosis or cysticercosis), multiple hemorrhages associated with damage to the blood system (disseminated intravascular coagulation, leukemia), as well as the consequences of diffuse axonal damage.
Treatment of the disease
Brain angioma can only be treated with radical methods.
Medicines cannot unravel the congestion of blood vessels and bring them back to normal. Conservative therapy is exclusively auxiliary in nature to mitigate the clinical manifestations of the disease.
For these purposes, patients are prescribed painkillers, antihypertensive and sedative medications.
Surgery is not prescribed for small venous angiomas that do not threaten the life and health of the patient.
For medium and large angiomas and rapid development of small tumors, surgery is indicated.
Treatment is carried out in one of the following ways:
- removal of vascular accumulation - surgery is performed when the neoplasm is located relatively close to the surface of the skin; other methods are used to eliminate deep angiomas;
- radiosurgery - gamma knife or cyber knife is used to eliminate internal angiomas; with the help of a directed beam of radiation, doctors clog the vessels formed into a ball, blood does not enter the formation;
- sclerotherapy - during the procedure, a sclerosing drug is injected into the vascular tangle using a special catheter, it leads to blockage of the vessels.
Modern methods of treating cerebral angioma:
- angioplasty is a method of vascular reconstruction that allows you to restore the lumen of veins and arteries;
- embolization is a method of blocking blood vessels by introducing a platinum spiral into the vascular lumen;
- Liquid embolization is a treatment method during which a substance is injected into a collection of veins that disconnects angiomas from the general blood flow; after some time, the vessel is replaced by connective tissue.
You will learn more about the radiosurgical treatment method in the following video: