body .attr-article__date{ background: none; padding: 0; }
NEAD EAD SEAD South Administrative District South-Western Administrative District CJSC Central Administrative District SZAO Northern Administrative District 01 02 03 05 06 07 08 09 1 0 1 1 1 2 14 18 15 16 17 Babushkinskaya Prospekt Mira Pervomaiskaya Baumanskaya Paveletskaya Teply Stan Shipilovskaya Prague Academic University Barrikadnaya River Station Oktyabrskoye Bratislava Taganskaya Academician Yangelya October Field
The call center is open 24 hours a day
Ambulance 24/7
Home Health from A to Z Useful information Concussion: more than just a headache
Date of publication: 04/19/2017
until January 31
You get 10% cashback when purchasing a gift certificate More details All promotions
Symptoms of a concussion
A concussion occurs when an external impact or force causes a sudden movement of the head. In this case, the brain is displaced inside the skull, and brain tissue “impacts” against its walls, which leads to the development of concussion symptoms.
The most common symptoms of a concussion
:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- confusion;
- deterioration of concentration and memory;
- memory loss;
- irritability, personality changes;
- increased sensitivity to light and sounds;
- sleep disturbance;
- decreased mood;
- disturbances of smell and taste.
A concussion is not always accompanied by loss of consciousness!
Only less than 10% of people lose consciousness with a concussion.
You don't have to hit your head!
Damage to other parts of the body, as well as sudden acceleration or deceleration of movement, can also lead to a concussion.
All cases of concussions require seeking medical help!
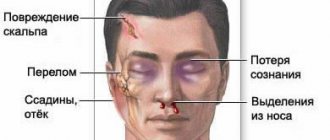
Possible symptoms of a concussion
- Brief confusion or loss of consciousness. With a strong blow, the moment of injury disappears from memory.
- Dizziness even at rest, and when turning, bending or other changes in body position, the symptom intensifies.
- Severe headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Double vision, inability to concentrate on one point.
- Increased sensitivity to light and sounds.
- Impaired coordination of movements.
- Reaction inhibition - the victim gives an answer to the question after some time.
- Pale skin, weakness, sweating.
Important! A concussion is not always accompanied by visible head injuries, so the absence of wounds does not exclude brain injury.
Danger can lurk at every step
In adults, a concussion often occurs against the background of alcohol intoxication: either he lost his balance, or he actively got involved in a fight, or he got into an accident. Alcohol in such cases becomes a factor that aggravates the patient’s condition and complicates early diagnosis,
because it obscures the clinical signs of the underlying pathology. It is difficult to figure out: lethargy and other manifestations are a consequence of intoxication or indicate the development of symptoms of a concussion. True, there are other options when an adult, completely sober person receives a TBI in transport, on the road, or at work due to circumstances beyond his control.
Head bruises often plague children and teenagers in games due to carelessness (slamming a book or briefcase on the head, other fun) or overestimation of capabilities when spending leisure time, because you really want to show off your adult prowess by riding an “iron horse” or jumping on roofs and fences.
Meanwhile, I would like to remind you that a concussion can occur without a blow. Sharp braking of a vehicle or attempts to maintain balance in winter ice sometimes also result in a known diagnosis.
Everyone knows that there are frequent cases of TBI and injury to other parts of the body among those for whom “sport is their life.” Chess does not sharpen an athletic figure and does not add physical strength, but “a person strives for perfection”, so he searches for new types of sports exercises, borrowing them from his peers overseas. What this could lead to - further.
The signs of a concussion in a child who can already speak and knows his “I” are practically no different from those in adults. But recognizing the symptoms of a concussion in infants can be very difficult even for a healthcare worker,
unless he is a pediatric neurologist, therefore, if this pathology is suspected, it is better for parents not to try to take responsibility and make a diagnosis on their own. The baby should be immediately shown to a doctor who is able to distinguish the normal behavior of the baby from the behavior of a sick child.
First aid for concussion
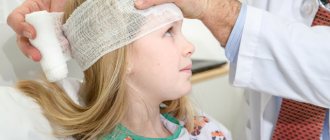
- If one or more symptoms are present, immediately call an ambulance or take the victim to a doctor.
- Treat a wound on the head if it appears as a result of an impact.
- For an hour or until the doctor arrives, it is important not to fall asleep, but to remain at rest.
- If you lose consciousness, lay the person on his side, bend his knees, and put his hands under his head.
- If symptoms of a concussion do not immediately appear, it is recommended to rest and not begin vigorous activity.
Concussion is one of the forms of TBI
Usually, by concussion, people mean any traumatic brain injury, and this, of course, cannot be reproached, since all these TBIs are the competence of doctors. In medical circles, a concussion is a mild form of traumatic brain injury.
which is not characterized by focal neurological symptoms, there are no signs of vascular damage, and the functional disorders that follow the injury are reversible. However, taking into account the readers’ interest not only in this form of pathology, we will try to stop and explain the essence of those head injuries that are popularly considered to be a concussion, since everyone interprets this term in their own way and is often confused with the concept of a brain contusion or the formation of an intracranial hematoma from compression.
As experience shows, each of us may find ourselves in a situation where determining the degree of damage becomes very important, since not only a person’s life, but also its quality in the future often depends on it. Symptoms of a concussion can range from few to very varied, depending on the force of impact or the strength of the person's head.
Thus, a concussion is the result of the shaking of a soft substance and its impact on the hard skull,
within which it is located. As the brain moves to the bones of the skull, the cells (their processes) stretch and experience some discomfort, which affects their functional abilities, which are temporarily lost.
Doctors have still not come to a consensus on what actually happens in the head at the moment of impact, so there are several versions of possible events that throw the central nervous system out of its normal rut:
- Neurons lose connection with each other.
- Disturbances in the nervous tissue of the brain occur at the molecular level.
- A sharp spasm of microcirculatory vessels makes it difficult to nourish the brain.
- Imbalance of interaction between the cortex and other brain structures.
- Changes in the chemical composition of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Short-term increase in intracranial pressure due to physicochemical disorders and colloid imbalance.
- Disruption of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, which, upon impact, leaves the cavities of the ventricles of the brain and is directed into the interventricular spaces.
Which of these hypotheses is probably correct is probably not for us to judge, but the important thing is that they all agree on one thing - with SHM, reversible functional disorders occur, but the brain structures do not suffer, and no morphological changes are noted in them. The veracity of this statement is also evidenced by data from computed tomography, which is usually prescribed for head injuries.
Recommendations for the treatment of concussions
If hospitalization is not required, with the permission of a doctor, a mild concussion can be treated at home:
- Bed rest and rest are required, no work. Long sleep is very important.
- You cannot read, watch TV, play computer games or use gadgets.
- Under no circumstances should you play sports.
- You are allowed to listen to music, but not through headphones.
- You can use herbal sedative drops or herbal infusions.
- In your diet, you should give preference to dairy and plant products, limit salt intake - to prevent increased pressure, including intracranial pressure.
If the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and all recommendations are followed, recovery will occur quickly and without complications.
Diagnosis and treatment is the task of the hospital
As a rule, a neurologist will suspect a mild TBI, that is, a concussion, even based on 2-3 signs.
However, in order to properly treat the patient, it is necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis by conducting a series of studies:
- Craniography (survey R-graphy of the skull) to exclude skull fractures;
- Examination of the blood vessels of the fundus (consultation with an ophthalmologist);
- Lumbar (spinal) puncture to study the composition of cerebrospinal fluid;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT);
- Electroencephalography (EEG);
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the head (ultrasound, ultrasound).
The patient is in the hospital mainly for the purpose of monitoring him, where he is given preventive and symptomatic treatment:
- Analgesics (baralgin, sedalgin, ketorol).
- Sedatives (tinctures of valerian and motherwort, tranquilizers - Relanium, phenazepam, etc.).
- For dizziness, bellaspon, bellataminal, and cinnarizine are prescribed.
- Magnesium sulfate is good for relieving general tension, and diuretics are helpful for preventing cerebral edema.
- It is advisable to use vascular drugs (Trental, Cavinton), nootropics (Nootropil, Piracetam) and B vitamins.
The victim, if everything goes well and manages only a concussion, will spend about a week in the hospital, but this does not mean that all questions are closed, and he can consider himself completely healthy. He will be observed by a neurologist for another whole year, visiting the clinic every quarter and receiving treatment prescribed by the doctor.
Thus, it is not recommended to treat a concussion on your own or take any medications.
Moreover, often patients, reacting to all external influences (people’s voices, light, etc.), become even more irritated and lose the ability to correctly assess their condition. They have a negative attitude towards hospitalization and believe that they themselves know how best to cope with an unexpected problem. This should be taken into account by relatives or people who happen to be nearby.
Classification of pathology
The disease occurs in three degrees of severity, which are divided into:
- Mild form - passes without short-term loss of consciousness. The patient experiences spatial disorientation, cephalalgia, dizziness, and nausea. Symptoms are recorded within 20 minutes after the injury and can be supplemented by an increase in temperature up to 38 degrees. Subsequently, the signs of pathology spontaneously disappear and the condition stabilizes.
- Moderate – the injury does not cause fainting and manifests itself with a standard clinical picture. Unlike a mild concussion, symptoms last more than 20 minutes, and the disease can provoke short-term memory loss. Retrograde amnesia is characterized by the absence of events that occurred a few minutes before the TBI.
- Severe – manifested by short-term fainting. Events are erased from memory under the influence of retrograde amnesia, clinical signs of a concussion persist for several weeks. The condition is accompanied by sleep and appetite disturbances, nausea, problems with orientation in space, cephalgia, and fatigue.
Traditional medicine
Non-traditional methods of treatment for injury should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, so as not to provoke the development of various complications. To eliminate pathological symptoms of a concussion, soothing decoctions are used based on:
- Ivan-tea.
- Melissa.
- Eleutherococcus.
- Medicinal valerian root.
As well as other medicinal herbs that have a calming, sedative effect on the nervous system during a concussion.
The patient must follow a special diet after a TBI after completing hospital treatment for a long time. It is necessary to gradually include familiar foods in the diet; it is better to avoid spicy and salty foods. You should not get carried away with sweets. In case of a concussion, the victim should be observed by a doctor until the central nervous system and general condition are completely restored.
What is recommended for the victim to eat?
- In the first days after injury, the patient often experiences nausea, vomiting and other signs of injury. There is something hard about these times. The diet includes only a solution with glucose or broths made from lean meat.
After your condition improves, you can add other products to the menu.
- Preference in the diet of a person who has suffered a concussion is given to protein foods:
- beef,
- poultry meat;
- seafood and fish;
- eggs, legumes, etc.
Carbohydrates from vegetables and fruits will be a good addition. These products will help you gain strength faster.
- All dishes must be cooked gently. Fried, smoked, spicy foods are excluded. Cooking, stewing and baking are recommended. Too sweet, fatty foods should also be postponed until better times.
- Vitamin B is of great importance in the nutrition of a weakened body. It is contained in:
- liver;
- asparagus;
- potato;
- seafood (oysters);
- nuts;
- fish;
- whole wheat bread;
- milk;
- buckwheat;
- egg yolk.
- To improve digestion, you need to eat soups every day: vegetable, chicken, fish or beef broth. They improve digestion and promote better absorption of nutrients.
- Iron helps the absorption of B vitamins, these are:
- cereals (buckwheat, oatmeal, barley);
- poultry (included in the menu every day), liver;
- spinach;
- legumes
- The most important products in the patient’s diet are milk and products made from it. The calcium they contain has a beneficial effect on metabolism, the health of the immune system, and digestion.
- Vitamin C fights stress. Products containing it are recommended to be included in the patient’s diet.
- Magnesium (there is a lot of it in milk porridges and legumes) stabilizes brain function.
- If the patient is prescribed medication, such as diuretics, the body will need more potassium, which is found in dried fruits, baked potatoes and other foods.
- To improve brain activity, glucose-containing foods (fruits, dried fruits) are needed.
Food containing honey will be very useful at this time. For example, a mixture of walnuts and this healing product is not only incredibly tasty, but also extremely nutritious.
In order for a person to receive all the necessary vitamins, it is recommended to include more fresh fruits and vegetables in the diet. Doctors often prescribe additional dietary supplements so that the body does not lack nutrients.
Foods you should avoid eating
Experts agreed that it is necessary to exclude some foods from the daily menu in case of a concussion of varying severity. The list of main dishes that you should avoid if you have a concussion includes:
- food with a lot of fat, which impairs blood flow,
- various seasonings and spices are contraindicated for concussion: they irritate the central nervous system,
- sweets, buns and various confectionery dishes,
- when the “gray matter” is shaken, it is not recommended to eat salty, spicy food,
- alcoholic drinks: they not only contribute to the destruction of neurons, but also have a negative effect on the blood circulation of the brain, nervous system,
- coffee cocktails, strong tea drinks: increase blood pressure.
All of these products can significantly worsen the patient's condition during the recovery period after an injury.
A proper diet for mild concussions is an integral part of a comprehensive recovery. It should be realized that adequate therapy and compliance with all the doctor’s advice leads to the recovery of the victim. It is important not only drug treatment, but also good nutrition, a positive attitude, rest and walks in the fresh air.
Moderate TBI requires treatment in a hospital setting, where the patient is constantly under the supervision of doctors. Only this approach guarantees complete recovery of the body.
Alcohol abuse when the “gray matter” is affected
With a concussion, the clinical picture is similar to the symptoms of severe alcohol intoxication. If the victim abuses alcohol-containing cocktails during therapy, there is a risk that signs of the pathological syndrome will recur. The patient may experience hysterical attacks, hallucinations, and irritability.
Due to a small amount of alcohol consumed after a blow to the head, mental disorders and delirium tremens are observed, which can appear even after a glass of beer.
When the “gray matter” begins to recover after the blow, the “recreational” cocktails cause attacks of headaches, hypertension, and sudden mood swings. Symptoms of a concussion intensify, and swelling of the brain is sometimes observed. As a result, the patient may lose consciousness or fall into a coma. Drinking alcohol during therapy often provokes a stroke.