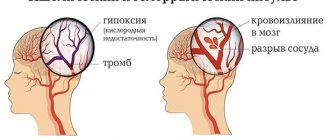
This condition was first described by Thompson and Kopell in 1959. Damage to the suprascapular nerve, as a cause of pain in the shoulder joint and dysfunction, often remains unrecognized and accounts for 1 to 3% of all complaints relating to the shoulder.
Anamnesis
The age of patients with suprascapular nerve entrapment varies from 20 to 50 years. Patients most often experience deep aching pain in the posterior and outer sections of the shoulder of the dominant limb. Symptoms are sometimes associated with trauma, but they usually develop and worsen with activity above the head. There may be weakness in external rotation or abduction. Often, in the presence of a pathological focus in the area of the spinous glenoid beard, there is an isolated decrease in the strength of the infraspinatus muscle, since most of the sensory branches branch more proximally.
Clinical examination
Proximal nerve injuries at the suprascapular notch result in atrophy of both the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles. In the area of the projection of the suprascapular notch, pain is often detected, localized behind the clavicle in the trapezius muscle covering the spine of the scapula.
of external rotation and abduction is often determined in comparison with the opposite side. Compression of the distal suprascapular nerve in the spinoglenoid groove leads to isolated atrophy of the infraspinatus muscle. Posterior shoulder over the spinoglenoid groove and isolated loss of external rotation strength may occur.
Visualization
Pathological changes on radiographs of the cervical spine and shoulder joint are usually absent, but radiography is necessary to exclude other conditions that may cause pain in the shoulder joint .
MRI has sufficient diagnostic effectiveness in identifying signs of fatty infiltration and atrophy of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles that develop as a result of denervation. Posterior ganglion cysts arising from the shoulder joint are also visible on MRI as high-intensity T2 and low-intensity T1 signals.
When diagnosing associated posterior capsulolabral lesions, MRI is less sensitive, but MR arthrography increases sensitivity for this pathology to 91% and specificity to 93%.
Electromyography can help determine the level of nerve entrapment based on the difference in combined values from the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles and in isolation from the infraspinatus muscle. Fibrillations and positive sharp waves can be detected as early as three weeks after injury.
The main causes of pain under the right shoulder blade
Let's look at the main causes of back pain in the area of the right shoulder blade. Do not forget, the presence of this symptom may indicate a serious surgical disease that requires emergency medical attention.
Gallbladder diseases
Back pain in the area of the right shoulder blade is a common symptom in acute or chronic cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). Thus, local pain in the area of the inner corner of the right scapula, which increases with pressure, is called Kharitonov’s symptom - this is one of the specific signs of acute inflammation of the gallbladder. Similar points are present on the inside of the scapula in its lower part, and in the area of the transition of the scapula to the collarbone, on the right.
If there are stones in the gall bladder, which interfere with the flow of bile, intense abdominal pain occurs, radiating to the right shoulder blade, right shoulder, and interscapular space. The nature of the pain in the back is aching, pulling, while the pain in the abdomen is sharp, cutting, paroxysmal. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for examination and to exclude acute surgical pathology.
Subphrenic abscess
Subphrenic abscess is an acute surgical disease, a complication of acute cholecystitis, appendicitis, and other surgical pathologies of the abdominal organs, in which pus accumulates. Most often, an abscess forms on the right, above the liver, and is accompanied by pain in the abdomen, lower back, and the right side of the back under the shoulder blade. Subphrenic abscess can also occur after surgery on the abdominal organs as a complication.
Bronchopulmonary diseases
Diseases of the bronchi and lungs, such as pleurisy, pneumonia, bronchopulmonary cancer, are almost always accompanied by pain in the chest and back. Due to the large number of pain receptors in the pleural cavity, pain can be sharp, acute, and intensify with breathing, coughing, and sneezing. The localization of pain is different and depends on the location of the focus in the lungs or pleural cavity.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Kidney diseases
Kidney diseases such as acute pyelonephritis, renal colic, kidney stones, abscess, cancer may be accompanied by pain in the shoulder blades. If the right kidney is affected, the patient will experience back pain under the right shoulder blade. If left, then left. The nature of the pain is sharp, pulling, cutting, paroxysmal, pain occurs simultaneously with pain in the lower back and hypochondrial areas in front. Fever, pain when urinating, nausea and vomiting are possible.
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system are the main cause of pain in the shoulder blades. Among them are diseases such as spinal osteochondrosis, intervertebral disc herniation, scoliosis, spondyloarthritis and spondyloarthrosis. The source of pain can be a pathological muscle spasm that occurs due to instability of the spinal column, overstrain of the back muscles trying to compensate for the load on the sore back. It is characterized by constant aching pain that subsides with rest. With hernias and protrusions, pain can be caused by pinching of the spinal cord roots. The pain is sharp, acute, radiating to the shoulder blades, upper limbs, chest, and intensifies with physical activity and heavy lifting.
The immediate cause of pain behind the right or left shoulder blade from behind from the back may be associated with the shoulder blade itself, as happens with glenohumeral periarthritis. The disease occurs with degenerative-dystrophic damage to the shoulder joint, and is accompanied by inflammation of nearby soft tissues - muscles, ligaments and tendons. At the beginning of the disease, the pain is episodic in nature and occurs during physical activity, maximum elevation or abduction of the arm, and when throwing with the arm. Then they take on the character of constant pain, and bother you even at rest, sharply intensifying when you move your hand.
Muscle strain and inflammation
Muscle strain and inflammation (myositis) are common causes of pain in the shoulder blade, right or left. Pain occurs as a result of excessive physical activity, when playing sports, or lifting weights. As a result, microscopic ruptures of muscle fibers occur in the affected muscles, and minor hemorrhages are possible. Swelling and inflammation occurs at the site of injury. The pain is sharp and intensifies with movement and physical activity.
Myositis or muscle inflammation can be an independent disease that occurs due to hypothermia, draft, or intoxication due to acute respiratory viral infections. Less commonly, the disease is a consequence of autoimmune or rheumatic diseases. The pain is aching, prolonged, and intensifies with movement. The scapula area is affected quite often due to the presence of developed muscles.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Intercostal neuralgia
Neuralgia is attacks of sharp acute pain along the nerves, arising due to hypothermia, inflammation or irritation of the spinal cord roots in diseases of the spine. With intercostal neuralgia, pain spreads along the intercostal spaces and can be localized both under the right and left shoulder blades, behind the back, or on the sides and front of the chest. The pain is sharp, sharp, and worsens with breathing, movement, coughing or sneezing. The patient has to spare himself in attempts to relieve the pain, limiting the depth of breathing, trying not to cough or sneeze. In some cases, the pain can be so severe that it is necessary to resort to novocaine blockade of the intercostal nerves.
Diseases or injuries of the scapula
Diseases of the scapula that lead to pain include bruises, fractures and cracks of the scapula, benign and malignant tumors (sarcomas, osteochondromas, osteomas, etc.). Injuries occur due to direct physical impact (impact, falling on your back, traffic accident). A characteristic sign is pronounced swelling of the soft tissues in the area of the scapula, sharp acute pain, intensifying when moving the hand, crunching (in case of fractures, occurs due to friction of moving bone fragments).
With tumors, pain can be of a different nature, from aching, arching pain to severe pain. The pain is constant and not relieved by rest. Visually or by touch, a foreign dense and immovable formation in the area of the scapula associated with it can be determined.
Diagnostics
Pain under the right shoulder blade occurs in diseases of various organs and systems, which requires the involvement of several specialists and a careful differential diagnosis. During a physical examination, the doctor will look for skin manifestations, signs of injury, or spinal curvature that may cause tenderness in the subscapular area. The most informative instrumental methods for diagnosis are:
- CT scan of the spine.
In orthopedics and traumatology, standard radiography is also used, but computed tomography provides clearer and more detailed visualization of bone formations. In the photographs, the specialist determines postural disorders, damage to the vertebrae, and signs of ankylosing spondylitis. Neurological complications of osteochondrosis can be detected by MRI of the spine. - Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Given the high prevalence of hepatobiliary disorders, standard diagnosis includes ultrasound examination of this area. On ultrasound, biliary stones, thickening of the gallbladder wall, and inflammatory changes in the liver are clearly visible. To assess the contractile function of the bladder, a test is done with a choleretic breakfast. - ERCP.
Invasive endoscopic examination of the biliary tract is the main method for diagnosing cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, cholangitis and functional disorders. The study is carried out for contrast visualization of the ductal system, finding filling defects and inflammation. - X-ray of the OGK.
Diagnosis of pulmonary diseases is impossible without a standard x-ray in 2 projections. The doctor pays attention to focal infiltrates in the lungs, effusion in the pleural cavity, and symptoms of pneumothorax. It is extremely rare that x-rays confirm dextrocardia - then the pain under the right shoulder blade may be of cardiac origin. - Additional invasive methods
. To detect problems with bile secretion, duodenal intubation is prescribed. For difficult to diagnose pulmonary pathologies, bronchoscopy, pleural puncture, and transthoracic biopsy are recommended. Gastrointestinal diseases with an atypical course require diagnostic laparoscopy.
Instrumental studies are complemented by laboratory methods. In the hemogram, special attention is paid to leukocytosis and increased ESR as nonspecific signs of infection. A biochemical blood test is informative for verifying the syndrome of cytolysis and cholestasis in pathological processes in the liver and gall bladder. An increase in acute phase parameters confirms the presence of active inflammation.
Detection of kidney damage is based on the results of a clinical urine test, a study of concentration function according to Zimnitsky, and a study of cellular composition according to Nechiporenko. If necessary, the diagnostic complex is supplemented with a bacteriological method - culture of sputum, feces, urine or other biological material is carried out on nutrient media.
Physical therapy for back pain
Types of pain under the shoulder blade on the right
Pain varies in severity and nature. Depending on the characteristics of the pain syndrome, it can be assumed what the underlying cause is. Thus, with intercostal neuralgia, the pain is almost always acute, intensifies with movement and coughing, turning into sharp shooting pains. Myositis is characterized by aching pain that can intensify with movement. Knowledge of the characteristics of pain syndrome in a particular pathology simplifies diagnosis.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Aching pain in the right shoulder blade
Aching pain in the area of the shoulder blades is characteristic of diseases of the musculoskeletal system, osteochondrosis, hernias and protrusions of intervertebral discs, myositis, and glenohumeral periarthritis in the initial stage. Similar pain can occur with diseases of the abdominal and thoracic organs, with neurological pathologies and pathologies of the spinal cord.
Acute pain under the shoulder blade on the right
Acute pain under the scapula on the right or left is a symptom characteristic of injuries, fractures, muscle strains, and tumors of the scapula. The cause of acute pain may be a hernia or protrusion of the intervertebral disc with radicular syndrome.
Sharp pain in the area of the right shoulder blade
Sharp pain in the area of the right shoulder blade is possible with intercostal neuralgia, diseases of the lungs, bronchi and pleura. Similar symptoms are observed with advanced glenohumeral periarthritis, severe myositis, and injuries.
Stitching pain behind the right shoulder blade
Stitching pain behind the right or left shoulder blade can be a symptom of diseases of the lungs and pleura (with pleurisy), myositis. Volatile stabbing pains are characteristic of radicular syndrome, when pain occurs due to pinching of the spinal cord roots, intercostal neuralgia.
Nagging pain in the right side of the back under the shoulder blade
A nagging pain in the right side of the back under the scapula is a symptom characteristic of acute or chronic cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and cholelithiasis. Similar symptoms can occur with kidney pathologies. Nagging pain in the right shoulder blade with a feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium may be a sign of subdiaphragmatic abscess, cirrhosis of the liver, or urolithiasis
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Constant pain on the right side under the shoulder blade
Constant pain on the right or left under the scapula is a possible sign of a benign or malignant tumor of the scapula. Constant pain can also occur with chronic diseases of the spine, such as spondyloarthritis, spondyloarthrosis, osteochondrosis or intervertebral disc herniation.
Burning pain on the right side of the shoulder blade
Burning pain in the scapula area is a characteristic sign of herpes zoster before the appearance of rashes, intercostal neuralgia, and neuritis of the intercostal nerves. This symptom can occur with diseases of the spinal cord, such as multiple sclerosis, spinal cord tumors. Infringement of the spinal cord roots by a hernia in the thoracic spine can also lead to burning pain in the scapula area.
Principles of treatment
Pain relief is aimed at reducing pain and eliminating muscle spasms in the affected area. If taking NSAIDs orally or by injection does not help, blockades are performed. This is the introduction of drugs into the most painful points, which are projections of the exit of nerves. Local anesthetics, hormones, NSAIDs, and muscle relaxants are used. Diuretics reduce swelling of the compressed nerve and eliminate pain. Drugs are prescribed that improve the conductivity of nerve tissue.
In addition to relieving acute pain, it is necessary to influence the cause of pinching of the intercostal nerve in the thoracic region. Medicines, massages, manual therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures, reflexology, and physical therapy help reduce the destruction of bones and joints. Medicines prescribed:
- vascular drugs - improve blood circulation;
- chondroprotectors – restore the properties of the cartilage layer between the vertebrae;
- calcium supplements, vitamin D fight osteoporosis;
- multivitamin complexes with minerals.
Acupressure, lymphatic drainage and classic types of massage are used. The impact on the back muscles helps eliminate spasms, improves blood flow and tissue nutrition. Thanks to this, it is possible to break the pathological circle, when pain causes muscle contraction, which compresses nerve fibers and blood vessels, disrupting blood supply and increasing pain.
In some cases, surgical treatments may even be necessary. For example, to eliminate the consequences of an injury, remove a significant hernia, tumor, or perform spinal stabilization.
Every person should be attentive to their health and not ignore the symptoms of a pinched nerve in the thoracic region if they appear. It is important to seek qualified help immediately. After all, the earlier the problem is identified, the greater the chances of achieving complete restoration of the function of the nerves and all structures of the spinal column, and of avoiding another pinching under the breast in the future.
How to relieve pain under the right shoulder blade
If pain in the scapula area is associated with diseases of the spine, muscles or injury, then painkillers should be taken as first aid. For this purpose, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are most often used. They effectively fight pain of any origin, suppressing inflammatory reactions. However, uncontrolled and long-term use of NSAIDs increases the risk of side effects of this group of drugs, such as stomach ulcers, gastric bleeding or kidney failure. Therefore, without a doctor’s prescription, it is permissible to take analgesics for no more than 5 days, after which you must consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Local remedies in the form of distracting and analgesic ointments, gels and patches do not have such side effects, since this dosage form is limited to the area of application. They help especially well with myositis, muscle strain, attacks of neuralgia and other diseases with chronic pain syndrome. In diseases of the spine, pain can be relieved by rest, limiting physical activity and prohibiting heavy lifting.
It is strictly forbidden to use painkillers if you suspect acute cholecystitis, pancreatitis and other diseases of the abdominal organs that require emergency surgery. Taking painkillers in such patients can lead to temporary relief of symptoms and a false sense of improvement, which ultimately contributes to late presentation and serious condition of the patient due to extensive inflammation of the peritoneum or peritonitis.
If pain in the area of the shoulder blade on the right occurs against the background of severe abdominal pain, accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting, you must seek medical help as quickly as possible.
Shpidonov Gennady Stanislavovich
Neurologist
Rostov State Medical University (neurology)
10 years of experience
Pain in the heart area radiates to the shoulder blade. Diagnostics
If your heart hurts and radiates under your shoulder blade, then you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. At the KDS Clinic, patients undergo a comprehensive examination using modern equipment and new technologies. After the initial examination, the patient informs the doctor about the nature and frequency of pain. The patient is referred for tests and examinations. When your heart hurts and radiates to your shoulder blade, visit a cardiologist, neurologist and orthopedist. Undergo ultrasound diagnostics, electrocardiogram and Holter examination. Call the clinic at number.
Treatment of pain on the right side of the shoulder blade
Pain treatment must begin with diagnosis, since effective pain management is only possible if you know its cause. Symptomatic therapy based on the use of analgesics does not treat the cause of pain, but only temporarily alleviates the most severe symptom. After making an accurate diagnosis, it is possible to treat the underlying disease by influencing the factors that led to it.
This is also important because without knowing the cause of the pain, it is difficult to choose the right treatment. Thus, attempts to treat pain in the scapula on the right side with analgesics in acute cholecystitis can lead to complications in the form of gangrene of the gallbladder, its perforation and extensive peritonitis, with a high risk of death. Painkillers are strictly contraindicated for acute surgical diseases of the abdominal organs.
Treatment of lesions (neuropathy) of the suprascapular nerve
Treatment of any suprascapular nerve injury should begin with four to six weeks of conservative measures that include anti-inflammatory medications, limited overhead activity, and physical therapy that includes exercises to strengthen the scapular stabilizers and rotator cuff.
Even ganglion cysts of the spinous glenoid sulcus can dissolve spontaneously, but such patients should be closely monitored to monitor the dynamics of symptoms.
Surgical treatment is indicated when conservative measures are ineffective or nerve compression is confirmed by electromyography. Decompression of the nerve helps to significantly reduce the intensity of pain, but recovery of the atrophied muscle is difficult to predict.
Surgical treatment of suprascapular nerve damage:
- Open release of the transverse scapular ligament and spinoglenoid ligament
- Arthroscopic release of the transverse scapular ligament
- Percutaneous release of the transverse scapular ligament
- Elimination of compression of the distal parts of the suprascapular nerve, which developed as a result of the formation of a ganglion cyst
- Endoscopic release of the spinoglenoid ligament
Open ligament release
The open release technique of the transverse scapular ligament and spinoglenoid ligament is rarely used. The intervention can be performed through a single skin incision using superior or posterior approaches. To perform it, the operated limb is draped loosely with surgical linen, and the patient is positioned in a position midway between the position on the side and on the stomach.