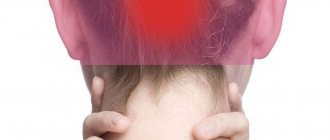
Sometimes we experience a special kind of discomfort - it seems that either our head or our eyes hurt. This pain occurs in the sinus area or at the back of the eye. Sometimes it is pulsating, sometimes it is constant. This condition frightens us very much and we want to know what causes this pain? What can be done to alleviate it? Could there be something wrong with my vision?
Let's first answer the last question.
Scientists from the American Academy of Ophthalmology defined "eye pain" as "physical discomfort caused by an eye or other disease." But scientists emphasize that “the location of the pain does not necessarily indicate the cause of the pain.”
In most cases, the cause of a headache felt in the eyes may be hidden in a completely different place. We feel pain in this particular location because of a network of interconnected sensory nerves that penetrate all tissues of the body.
“Almost every pain-sensitive structure in the head transmits the sensation of pain to the eye area,” says Dr. Mark W. Green, MD, professor of neurology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City. “Just because the eye hurts does not mean that the problem is in the eye itself. In fact, this happens quite rarely."
Green advises to remember one useful rule: if the white part of the eye (sclera) is not red, and there are no complaints about vision - a blurred or distorted picture, it is very unlikely that the headache is associated with the eyes themselves.
Causes of headaches in the forehead and eyes
Pain in the frontal part of the head and eyes is not a separate pathology, but a symptom of various disorders. It can also occur in the absence of any diseases, against the background of fatigue, stress, or prolonged work at the monitor. However, if it occurs frequently, you should undergo a full examination and receive recommendations for treatment.
Eye diseases
Acute and chronic eye diseases are one of the common causes of headaches. They have different development mechanisms and manifest themselves with different symptoms, so it is necessary to carry out their differential diagnosis. Ophthalmological diseases can be congenital or acquired in childhood or adulthood. They can progress, leading to partial or complete loss of vision, so treatment must begin in the initial stages.
- Glaucoma is a syndrome in which swelling occurs inside the eye. It is observed in various diseases, including can be caused by farsightedness and chronic hypertension. In the initial stages, peripheral vision deteriorates, headaches in the frontal part and eyes due to damage to the optic nerve. In the future, glaucoma can progress and lead to complete blindness.
- Myopia (myopia) is a disease in which the image is not on the retina, but in front of it. Objects located at a far distance are difficult to distinguish. For myopia, vision correction is necessary with individually selected glasses or lenses. It is also necessary to perform special gymnastics for the eyes, avoid prolonged work at the monitor and concentration on small details.
- Inflammation of the optic nerve is the cause of acute headaches in the forehead and eyes, and visual impairment. Its cause is often infectious diseases, but a chronic, recurrent course of optic neuritis can be caused by diabetes mellitus. Timely treatment and the prescription of corticosteroids will restore vision, relieve pain and inflammation.
Deterioration of vision, pain in the frontal part of the head and eyes, lacrimation, redness of the conjunctiva, inability to concentrate on near or distant objects - this is a reason to consult an ophthalmologist for an examination. To select glasses or contact lenses, as well as to prescribe a medication regimen, you must undergo additional examinations.
Increased intracranial pressure
If you often have a headache in the frontal area or put pressure on your eyes, you should consult a doctor to diagnose intracranial pressure. It is impossible to measure this indicator at home, since it is determined by indirect methods. Normally, it consists of three components: blood pressure, spinal fluid and the brain tissue itself. An increase in any of them leads to an increase in intracranial pressure and the following symptoms:
- headaches in the temples, forehead and eyes;
- dizziness, weakness, frequent fainting;
- deterioration of hearing and vision, the appearance of various hallucinations;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased or decreased blood pressure, slow heartbeat;
- development of convulsive syndrome.
Increased intracranial pressure is a common diagnosis in both adults and children. It is diagnosed based on the clinical picture, as well as indirect diagnostic methods. The cause of this disorder may be congenital vascular anomalies, traumatic brain injuries, poisoning and other factors. If the pressure rises slightly and can be corrected with medications, it is enough to take them and undergo periodic examinations. The operation is prescribed only in difficult cases when excess fluid causes oxygen starvation and necrosis of brain cells. This condition is one of the predisposing factors for ischemic stroke and therefore cannot be ignored.
Infectious diseases
One of the most common reasons why the eyes and frontal part of the head hurt is viral diseases. The pathogens most often affect the upper respiratory tract and are transmitted by airborne droplets. Headache becomes one of the first symptoms, after which weakness, fever, and other characteristic signs develop. However, a viral infection can spread to the bronchi and lungs and affect brain cells. There are a huge number of infectious diseases that are highly contagious. Diseases spread by contact of the pathogen with the mucous membrane of the mouth or nose, but a prerequisite for their development is a decrease in the body’s immune defense.
- ARVI (acute respiratory viral infections) is a group of diseases that manifest themselves with similar symptoms. They cause coughing, wheezing, sore throat, runny and watery nose, and fever. The patient often has headaches, forehead and eyes due to swelling of the mucous membranes.
- Sinusitis is inflammation of the maxillary paranasal sinus. If normally there is only air in it, then in case of illness it is filled with liquid or purulent contents. More often, sinusitis is one of the complications of ARVI and requires urgent treatment. Conservative methods include antibiotic therapy and rinsing with saline solutions. If they do not bring results, the doctor may prescribe a puncture of the maxillary sinus, removing its contents and rinsing with solutions containing antibiotics.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the lining of the brain. This is a dangerous disease that poses a threat to the patient's life. It is caused by viruses, bacteria, and meningitis can also have a traumatic origin. Treatment is carried out in a hospital, under 24-hour medical supervision.
Treatment of infectious diseases is selected individually. Mild forms can be cured at home; all you need to do is stay in bed and take vitamins. However, with meningitis, severe forms of influenza and sinusitis, hospitalization will be required. In a hospital setting, antibiotics, supportive medications, and symptomatic medications are prescribed to reduce fever.
Traumatic brain injuries
One of the reasons why headaches occur in the temples, forehead and eyes is traumatic damage to brain tissue. They can be open or closed. In the first case, the integrity of the skin, skull bones and brain tissue is violated, so treatment is carried out surgically. Even after a long time after such an injury, the patient may experience headaches in the forehead and eyes, as well as various disorders of brain activity.
Closed head injuries are more common. They are no less dangerous for the victim and can cause long-term complications. There are several types of injuries that differ in the mechanism of development and types of damage to brain tissue.
- A concussion is a temporary, reversible disturbance of consciousness due to a bruise, blow or fall. No organic damage is diagnosed, so treatment can be carried out at home. For several days, the patient experiences symptoms such as headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, hearing and vision impairment.
- Brain contusion is the result of an unintentional or intentional blow to the head. Light bruises cause temporary impairment of consciousness and headaches. However, treatment must be carried out in a hospital, under the supervision of doctors. Bruises can cause swelling of the brain, increased intracranial pressure and cause a stroke.
- Hematomas are an accumulation of blood in the brain tissue or in the space between the membranes. Their main cause is damage to blood vessels during bruises. Hematomas pose a danger to the patient's life and cause acute impairment of brain function.
Traumatic brain injuries can cause headaches even many years later. Many patients complain that they have a headache in the frontal part, pressure on the eyes during sudden changes in weather conditions or during physical exertion. Treatment is symptomatic and consists of eliminating pain and reducing stress.
Other reasons
Headaches that affect the forehead and eyes can be a sign of various conditions and diseases. When diagnosing, it is important to exclude the possibility of both the most common and rare causes of this symptom. These include:
- physical, emotional fatigue, prolonged lack of proper rest;
- disturbance of sleep and wakefulness, night shift work;
- frequent alcohol consumption, poor diet;
- an increase or decrease in the concentration of certain hormones in the blood.
The cause of headaches can be both common human conditions and dangerous diseases in the early stages. So, during diagnosis, a tumor in the brain or an aneurysm may be detected. Another dangerous disorder that must be taken into account during diagnosis is stroke, an acute disorder of cerebral circulation. Help during an attack is most effective in the first 2–4 hours. Then irreversible changes occur in the functioning of the brain, which can lead to disruption of vital functions, even death.
VSD in faces
This page contains excerpts from patient histories, covering the main complaints with which people turn to us for help. This is done with the goal of showing how different and “complex” the symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia can be. And how closely it is sometimes “fused” with disturbances in the functioning of organs and systems. How it “disguises” itself as “heart”, “pulmonary”, “stomach”, “gynecological” and even “psychiatric” problems that people have to live with for years...
To learn more
Examination methods
If your eyes and head in the forehead area often hurt, you need to undergo an examination to determine the cause of this symptom. The initial examination is carried out by a therapist, then additional examinations are prescribed according to indications. They may include consultations with a neurologist, traumatologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist, as well as a number of tests and instrumental diagnostic methods:
- general and biochemical blood tests - make it possible to determine inflammatory processes, acute and chronic diseases of internal organs;
- MRI, CT scan of the head - a method for detecting tumors, hematomas, pathologies of the structure of the brain;
- blood pressure measurement;
- determination of eye pressure, methods for diagnosing visual acuity.
The Clinical Brain Institute has modern equipment for diagnosing diseases that are accompanied by headaches. The ability to make an accurate diagnosis, as well as many years of experience of specialists, allow us to prescribe the most effective treatment in a timely manner.
Optic neuritis
The pathology is an inflammation of the second cranial nerve. The general clinical picture is similar to the manifestation of papilloedema, but without the characteristic increase in intracranial pressure. The most common cause is pathology of the central nervous system (selective damage to the myelin sheath), less often - sinusitis, inflammation of the orbital contents.
Pain inside the eye is the main symptom of the pathology, intensifying with its movement. Additionally, the patient complains of changes in the perception of shades, deterioration of vision, and the appearance of pointless images before the eyes.
Diagnosis of the disease is quite difficult; instrumental research methods cannot always reveal characteristic changes in the fundus. The task is to determine the presence of multiple sclerosis, which is a provoking factor of the disease.
Treatment of headaches in both eyes and eyes
The main condition for effective treatment of headaches is timely consultation with a doctor. It is impossible to choose the right regimen on your own, since only painkillers that relieve the symptoms of the disease are available at home. Additionally, the following methods may be prescribed:
- drugs for the correction of increased intracranial and blood pressure, including systemic use of diuretics;
- Antibiotic therapy is the basis for the treatment of inflammatory diseases;
- medications to improve blood supply to the brain;
- selection of glasses or lenses by an ophthalmologist, drops to eliminate dryness and inflammation of the mucous membrane;
- symptomatic treatment for additional manifestations of diseases - may include antipyretics, vitamins and other drugs.
The Clinical Brain Institute offers individual programs for diagnosing and treating headaches in the forehead and eyes. The main advantages of the center are the possibility of inpatient and outpatient observation, highly qualified specialists, accurate and modern equipment.