Head spin
Probably, each of us at least once in our lives experienced dizziness, noise or ringing in the ears, and even more so, nausea.
But if these symptoms:
- are combined without obvious reasons (trauma, poisoning, etc.);
- periodically repeat, intensifying (even if this periodicity occurs once a year, then it may be more often);
It makes sense to see a doctor. You may be experiencing Meniere's disease.
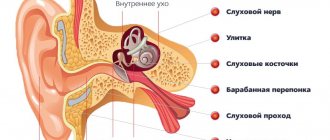
In simple terms, this is a disease of the inner ear when fluid begins to accumulate in the parts of the inner ear called the labyrinth (where the parts responsible for balance and the cochlea are located).
This may be due to many reasons:
- metabolic disorders, namely water-salt balance;
- vascular disorders;
- genetic autoimmune conditions;
- complication of a viral infection;
- allergic diseases.
General – only the main symptoms:
- dizziness;
- noise, ringing and/or fullness, mainly in one ear;
- hearing loss.
They should be alert first!
There may also be: nausea, vomiting, sweating, disruption of the cardiovascular system, fear of light and sound, inability to focus on one object.
These symptoms occur in attacks that sometimes last several hours, sometimes up to 12.
Several years may pass after the first one, therefore, once faced with the manifestations of Meniere’s disease, a person may put off visiting a specialist about this for a very long time. Like, just think, my head was spinning, my ears were ringing... it doesn’t happen to anyone. Until the attacks become frequent (even daily) and begin to significantly worsen the quality of life. They are very difficult to bear! Finally, deafness can be a consequence of Meniere's disease.
Therapy methods
Having found out why the patient has pressure on his ears, the doctor develops a treatment regimen.
It all depends on the true causes of the pathological process. For high blood pressure, which can cause severe headaches and stuffy ears, Captopril helps. Nootropic drugs are also used that strengthen the walls of blood vessels and normalize blood circulation: Vertizin, Disiron. Osteochondrosis requires complex treatment using ointments and creams (Diclac gel, Clodifen, Diclofenac), anti-inflammatory drugs, Noofen, which improves cerebral circulation, drugs that strengthen blood vessels, for example, Ginkgo Biloba. When the cause of the malaise is sinusitis, the patient is prescribed a procedure for clearing the nasal passages of accumulated pus, which is called “cuckoo”. In severe cases, the nasal septum is punctured or a Yamik catheter is inserted. In addition to treatment, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, for example, Zinnat, Amoxil, vasodilating drops, and herbal medicines.
Purulent otitis media is treated with antibiotics for both internal and external use. The patient drinks pills, drips medicine into his ears, and takes vitamins. In case of atherosclerotic changes, thinning medications (Aspirin) are prescribed, as well as drugs that reduce the risk of blood clots (Wobenzym). Migraine attacks cannot be cured, but they can be controlled with painkillers. It is important to take the pill at the very beginning of the headache, otherwise it will not help the patient.
Meniere's disease: rare, but accurate
Of course, suspecting and diagnosing any disease is the prerogative of a specialist.
Meniere's disease is considered quite rare. In different countries, according to statistics, it affects from 20 to 200 people per 100,000 population. Women are almost twice as likely as men. The average age of patients is 40 years, and it almost never occurs in children.
But for whom does this make it easier if you are faced with the symptoms described above? In addition to Meniere's disease, they can signal other unhealthy and downright dangerous conditions, for example:
- benign positional paroxysmal vertigo;
- vestibular migraine;
- vestibular neuronitis;
- bilateral vestibulopathy;
- functional dizziness;
- stroke;
- brain tumors.
Therefore, if there are obvious disturbing symptoms, without delay, you need to make an appointment at the clinic with a therapist, ENT specialist, or directly at a specialized center. Establishing a diagnosis is not difficult for a specialist, but only after a set of diagnostic examinations.
When is it due to nerves?
At the time of panic attacks or as they approach, patients often experience increased blood pressure, which can cause severe discomfort in the ears, temples and head. It is known that hypertension provokes the occurrence of severe spasms.
We recommend that you read: What is depersonalization?
Often, floaters appear before the eyes - various spots, stripes, dots.
Other accompanying symptoms include:
- tachycardia, interruptions, body tremors, fever or chills;
- respiratory disorders (shortness of breath, suffocation);
- frequent urination;
- pain, tension, tightness in the chest area;
- nausea, diarrhea;
- the appearance of red spots on the skin, “nervous” allergies;
- numbness of the limbs.
Types of otitis
Depending on the direction of the pain, it is customary to distinguish 3 types of otitis: external, middle and internal otitis.
Otitis externa most often appears as a result of mechanical damage to the auricle or external auditory canal. The following symptoms are characteristic of external otitis of the ear: aching, dull pain, swelling of the ear, and a slight increase in temperature.
Otitis of the middle ear is an inflammatory disease of the air cavities of the middle ear: the tympanic cavity, the auditory tube and the mastoid process.
Internal otitis is untreated otitis media of the middle ear. With internal otitis, inflammation of the inner ear occurs and the entire vestibular apparatus is damaged.
Diagnosis of ear congestion
Standard examinations for any ear pathology:
- video endoscopy or microscopy of the ear;
- video endoscopy of the nose and nasopharynx;
- audiometry;
- tympanometry;
If necessary, additional studies are prescribed:
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the temporal bones and brain;
- culture of nasal discharge and external auditory canal for flora and sensitivity to antibiotics;
- general blood test, blood glucose (other additional laboratory tests are possible after consulting a doctor);
- Doppler ultrasound of neck vessels;
- consultations with other specialists.
Causes of headaches and ear congestion
Constant pain in the head, which causes blocking of the ears, is an alarming symptom for which you should seek medical help. It may indicate physiological changes that do not require therapy, including water entering the ear canals or fatigue. However, in some cases, this sign will help identify dangerous diseases in the early stages and begin treatment on time.
High blood pressure
Chronic hypertension is a disorder in which the pressure in the arteries exceeds normal levels. In a healthy person at rest it is 120/80 mmHg, but it is important to take into account individual characteristics. Blood pressure is considered high if it is 140/90 mmHg. and more. The condition can be caused either by an increase in circulating blood volume or by vascular spasms.
Blood pressure is easy to measure yourself using a tonometer. If the readings are too high, you should seek medical help. Without timely treatment, hypertension poses a danger to the patient and can cause the following complications:
- angina pectoris - acute pain in the chest;
- myocardial infarction - a sharp disruption in the supply of oxygen to the heart muscle;
- chronic heart failure – deterioration of the heart valve apparatus caused by increased load on it;
- arrhythmia is a disturbance in the heart rhythm that can cause a heart attack.
When blood pressure rises, the patient has a headache and pressure on the ears. Symptoms such as dizziness, nausea, hearing loss and poor coordination of movements also occur. With a sudden attack, fainting is possible. Hypertension can be triggered by an increase in atmospheric pressure, physical activity, stress, disruption of the daily routine and other factors. For chronic hypertension, it is necessary to take medications in a course, including to remove excess fluid.
Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses. With this disease, the nose and ears are blocked, the head hurts, and the overall body temperature rises. The process can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, and cold weather is often the trigger. Sinusitis occurs in acute or chronic forms and may recur after some time. In addition, the disease can manifest itself as a complication of seasonal colds.
The paranasal sinuses are cavities formed by the bones of the skull. In a healthy person, they are not filled with anything, and their walls are lined with mucous membrane. During the inflammatory process, pathological contents appear in them, which causes headaches. Sinusitis can be serous (with clear liquid contents), catarrhal (cavities filled with mucus), purulent and mixed. Depending on the location of the process, there are several types of this disease:
- sinusitis - inflammation of the maxillary sinus, often occurs as a complication of a cold;
- frontal sinusitis - the process affects the frontal paranasal sinus;
- ethmoiditis - inflammation of the mucous membrane located in the ethmoid labyrinth;
- sphenoiditis - damage to the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus.
At home, you can conduct an initial diagnosis of sinusitis. If you sharply tilt your head forward and down, a sharp pain occurs in the forehead. This indicates fluid accumulation in the sinuses. Also, with inflammation of the maxillary sinuses, headaches intensify at low temperatures and decrease in a warm room.
Diseases of the hearing organ
If your ears are blocked due to pain in your head, you should undergo an examination by an otolaryngologist. Chronic diseases of the organ of hearing cause a sharp deterioration in health, increased body temperature, impaired balance and coordination of movements, as well as other symptoms and complications.
- Otitis is an inflammation of the ear in any of its parts. Depending on the location, they distinguish between external, middle and internal, and according to the nature of the course - acute and chronic otitis. The process can be caused by hypothermia or herbs, as well as viral and bacterial infections. Internal purulent otitis is the most dangerous because it can spread to the membranes of the brain and cause meningitis.
- Acoustic neuroma is a benign neoplasm. Its first symptoms include constant headaches and dizziness, as well as hearing loss. Over time, nausea, loss of coordination of movements, and atrophy of the masticatory muscles appear. Neuroma does not disappear on its own and may increase in size. To treat it, surgical techniques, radiation therapy, or combined methods are prescribed.
- Mechanical damage or blockage of the ear canals is another reason why headaches and blocked ears occur. You can get injured even at home, if you do not properly clean your ears or if sharp objects get into your ear canals. The cause of the blockage is often cerumen plug - after its surgical removal, headaches disappear and hearing is restored.
If you suspect a disease of the hearing organ, you must undergo an examination by an otolaryngologist. It uses a special device - an otoscope, which allows you to detect various disorders in the auditory canals. The inner ear is difficult to access for diagnosis and has a complex structure, so it is important to prevent the spread of infection from the external parts.
Other reasons
Headache and ear congestion are common symptoms for a large number of diseases and conditions. They are not necessarily related to hearing health, so it is important to pay attention to associated signs. A more detailed examination reveals the following pathologies:
- cervical osteochondrosis is a chronic disease of the spine in which blood circulation and innervation of the tissues of the head are disrupted;
- viral diseases - influenza, ARVI also manifest themselves as headaches and hearing impairment;
- consequences of traumatic brain injuries , which can manifest themselves many years later.
These symptoms can also occur in a healthy person. So, they often bother you during a flight or in other cases of changes in atmospheric pressure, when water gets into the ear canals, during fatigue or prolonged work at the monitor. However, if they occur regularly, doctors at the Clinical Brain Institute recommend undergoing an examination and determining the exact cause.
Symptoms of ear congestion
Associated symptoms for various ear diseases:
| Cause | Symptoms | |||||||
| Pain | Ear discharge | Itching | Hearing loss | Autophony | Noise | Sensation of fluid transfusion | Manifestations of general intoxication | |
| Sulfur plug | No | No | Not really | Yes | Not really | Not really | No | No |
| Otitis externa | Yes | Not really | Yes | Yes | Not really | No | No | Not really |
| Tubootitis | Not really | No | No | Yes | Yes | Not really | No | Not really |
| Otitis media | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Not really | No | Yes |
| Suppurative otitis media | Yes | Yes | Not really | Yes | Not really | Not really | No | Yes |
| Exudative otitis media | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Not really | Yes | No |
| Sensorineural hearing loss | No | No | No | Yes | Not really | Yes | No | No |
Treatment
Treatment for ear congestion and otitis media involves treating the underlying cause of the disease:
- in case of an inflammatory process in the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, antibacterial therapy is prescribed, in addition, lavage of the nasal cavity is prescribed, which eliminates the discharge of discharge into the auditory tube during self-washing, treatment with a YAMIK catheter, puncture of the maxillary sinuses, physiotherapy;
- if a chronic pathology of the nasal cavity or nasopharynx is detected, leading to the closure of the mouth of the auditory tube, surgical treatment is performed (adenotomy, vasotomy, septoplasty, etc.);
- To remove wax plugs or foreign bodies, the doctor performs lavage (under visual control) or instrumental removal of the foreign body;
- for external otitis, the outer ear is washed and its walls are treated with antifungal and antibacterial drugs;
- in case of dysfunction of the auditory tube or exudate in the tympanic cavity, medical procedures are necessary: pneumomassage of the tympal membrane, blowing of the ears according to Politzer, catheterization of the eustachian tube, paracentesis or shunting of the eardrum;
- for sensorineural (sensorineural) hearing loss, a course of vascular and vitamin therapy is prescribed to improve the nutrition of the inner ear and brain.
Basic treatment regimens for ear pathology*
| Pathology | Basic treatment methods |
| Sulfur plug | Removal by rinsing or instrumental removal. |
| Otitis externa | Toilet of the external auditory canal, treatment with medications, ear drops, vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, systemic antibacterial or antifungal therapy, FTL**. |
| Tubootitis | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, blowing of the eustachian tubes according to Politzer, pneumomassage of the eardrum, FTL**, catheterization of the auditory tubes if necessary. |
| Otitis media | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, systemic antibacterial therapy, ear drops, Politzer ear blowing, pneumomassage of the eardrum, FTL**, if necessary, catheterization of the auditory tubes, lavage of the nasal cavity using the moving method. If necessary, surgical treatment - eardrum bypass or paracentesis. Complemented by the treatment of diseases of the ENT organs. |
| Suppurative otitis media | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, systemic antibacterial therapy, ear drops, Politzer blowing, if necessary, transtympanic injection of drugs, catheterization of auditory tubes, nasal lavage using the displacement method. If necessary, surgical treatment - eardrum bypass or paracentesis and other operations, FTL**. It is supplemented by treatment of pathologies of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses, if indicated. |
| Exudative otitis media | Vasoconstrictor nasal sprays, mucolytics, Politzer blowing, catheterization of auditory tubes. If necessary, surgical treatment - eardrum bypass or paracentesis, FTL**. It is complemented by the treatment of pathologies of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses. |
| Sensorineural hearing loss | Catheterization of auditory tubes, systemic vascular and vitamin therapy. |
*These treatment regimens are not a recommendation for self-treatment and serve to familiarize patients with basic treatment methods. The final decision on treatment and examination methods is made by the doctor after the examination!
** FTL – physiotherapeutic treatment.