General description of the disease
It is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity and postural instability.
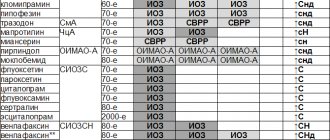
This disease shares symptoms with Parkinson's disease, from which it takes its name. However, “Parkinsonism” is a separate set of symptoms, which is still different from the progressive and neurodegenerative Parkinson’s disease. The latter is the most common cause of parkinsonism. However, a number of other reasons can lead to its development, including toxins, certain metabolic diseases, and neurological conditions. This will be discussed in more detail below. In 7% of people with parkinsonism, this syndrome developed after taking specific medications. It can manifest itself as a side effect of neuroleptic antipsychotics, thioxanthenes, phenothiazines, and sometimes antidepressants[1].
Causes that provoke the occurrence of parkinsonism
Not everyone with parkinsonism has Parkinson's disease. There are many other causes of parkinsonism, including:
- medications, such as those used to treat psychosis, underlying mental disorders, and nausea;
- exposure to toxins such as carbon monoxide, cyanide and organic solvents;
- certain brain lesions such as tumors or fluid accumulation;
- metabolic and other disorders such as chronic liver failure and hypoparathyroidism;
- brain injury;
- diffuse Lewy body disease;
- encephalitis;
- HIV AIDS;
- meningitis;
- multiple system atrophy;
- progressive supranuclear palsy;
- stroke;
- Wilson's disease.
Other causes of secondary parkinsonism include:
- brain damage caused by drugs used for anesthesia;
- carbon monoxide poisoning;
- poisoning with mercury and other chemicals;
- drug overdose[3].
Symptoms of Parkinsonism
Most often, parkinsonism is characterized by the same symptoms as Parkinson's disease. Among its symptoms are the following:
- 1 Tremor. Tremor or shaking usually begins in a limb, most often in the hand or fingers. One of the characteristic features of Parkinson's disease is tremors of the hand in a relaxed state (at rest).
- 2 Slow movement (bradykinesia). Over time, Parkinson's disease can reduce a person's ability to move and slow them down, making simple tasks difficult and time-consuming. A person's steps may become shorter or it may be difficult for them to rise from a sitting position.
- 3 Tight muscles. Muscle stiffness can occur in any part of the body. Tight, tense muscles can limit your range of motion and cause pain.
- 4 Poor posture and balance. A person's posture may become slouched, or as a result, coordination may be impaired.
- 5 Loss of automatic movements. With Parkinson's disease, a person may have decreased or completely lost the ability to perform unconscious movements, including blinking, smiling, or swinging their arms while walking.
- 6 Changes in speech. A person with Parkinson's may speak softly, quickly, sloppily, or feel embarrassed before speaking. In most cases, speech becomes more monotonous[2].
Other symptoms that may also occur with parkinsonism include the following:
- marked memory loss that occurs during the first year of the disorder (including dementia);
- low blood pressure, difficulty swallowing, constipation, and problems urinating (sometimes due to multiple system atrophy);
- hallucinations and visual-spatial problems (for example, with orientation in the house or in the parking lot early in the development of the disease);
- abnormalities in eye movement[2].
Types of parkinsonism
Parkinsonism can be divided into three different types. This:
- 1 Primary parkinsonism. It is caused by Parkinson's disease. Includes sporadic and familial cases and accounts for about 80% of parkinsonism cases.
- 2 Secondary parkinsonism. This form of parkinsonism can be caused by a number of problems. These include drug addiction, infections, toxins, brain injury or tumors, normal pressure hydrocephalus, hypoxia, and metabolic dysfunction.
- 3 Atypical parkinsonism. This is a type of disease that includes additional neuropsychological and neurological deficits such as hemiatrophy-hemiparkinson syndrome, juvenile form of Huntington's chorea, corticobasal degeneration and others[4].
Complications of parkinsonism
Parkinsonism resulting from Parkinson's disease may be accompanied by additional complications. In most cases, they require separate treatment. Among them are the following:
- Difficulty in thinking. A person suffering from Parkinson's may experience cognitive problems (dementia) and difficulty thinking, which usually occur in the later stages of Parkinson's disease. Such cognitive problems are not very responsive to medications.
- Depression and emotional changes. The latter includes changes in emotional state such as fear, anxiety or loss of motivation. Doctors often prescribe additional treatment in such cases.
- Swallowing problems. A person may have difficulty swallowing as the disease progresses. Saliva can accumulate in the mouth due to slower swallowing, leading to drooling.
- Sleep disorders. People with Parkinson's disease often have trouble sleeping, including waking up frequently at night, waking up early, or falling asleep during the day.
- Bladder problems. Parkinson's disease may cause an inability to control urination or difficulty in doing so.
- Constipation. Many people with Parkinson's disease develop constipation, mainly due to a slow digestive tract.
- Changes in blood pressure. A person may feel dizzy due to a sudden drop in blood pressure (orthostatic hypotension).
- Fatigue. Many people with Parkinson's disease lose energy and become tired easily.
- Pain. It can occur in specific areas of the body or throughout the body[5].
Prevention of parkinsonism
The most common cause of parkinsonism, as we wrote above, is Parkinson's disease. Because the cause of Parkinson's disease is unknown, proven methods of preventing the disease have not yet been developed.
However, research has shown that caffeine, which is found in coffee and tea, may reduce the risk of developing Parkinson's disease. Regular aerobic exercise is also beneficial. Equally important is a healthy lifestyle, avoiding the use of drugs and alcohol[6].
Diagnosis of parkinsonism
Diagnosis of this disease includes an assessment by a doctor - the doctor conducts a conversation with the patient, asks him about complaints and lifestyle. Tries to determine whether a person's body has been exposed to toxins, drugs, or other substances or factors that could trigger the onset of parkinsonism.
In some cases, neuroimaging, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), is prescribed. They are needed to look for a structural disorder that may be causing parkinsonian symptoms.
If the diagnosis is unclear, doctors may give the person a special drug used to treat Parkinson's disease to rule it out. If the drug leads to a clear improvement, then this helps to establish that the probable cause of parkinsonism is Parkinson's disease[2].
Treatment of parkinsonism in official medicine
In official medicine, the treatment of parkinsonism includes measures to treat the original source of the disease, as well as taking medications to relieve symptoms and general measures.
So, if parkinsonism occurs as a result of taking medications, then stopping them can help eliminate the disorder.
Often, the medications used to treat Parkinson's disease are not effective in eliminating the signs of Parkinson's disease. But general measures to help people with Parkinson's disease maintain mobility and mobility can be helpful. For example, the patient should try to be as active as possible, simplify the daily routine, and, if necessary, use assistive devices for movement. It is also very important to secure the environment in the house - for example, remove rugs that could cause a person with difficulty moving. It is also important to undergo physical therapy and maintain proper nutrition[2].
General rules
Parkinson's disease is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that is associated with the degeneration (destruction) of certain neurons (dopamine neurons) and dysfunction of the central nervous system.
The cause of the disease is unknown. Research has proven the role of many factors, including hereditary ones. It is believed that neuronal degeneration is caused by oxidative stress of neurons and apoptosis (death). There is an accumulation of calcium and iron in the cells, with a simultaneous lack of zinc. Clinical symptoms appear when 50-80% of neurons die. Parkinson's disease is characterized by a complex of symptoms that includes tremors (shaking of hands, head), muscle stiffness, stiffness of movements, decreased facial expressions, autonomic and mental disorders. Parkinson's disease cannot be cured. However, thanks to medications and nutrition, it is possible to slow down the progression of the disease, reduce its manifestations and improve the patient’s quality of life.
The role of nutrition should not be ignored. Considering that atherosclerosis is a risk factor for the onset and progression of the disease, it is clear that the diet for Parkinson's disease must meet the requirements of a cholesterol-lowering diet . It involves eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, greens, legumes, various seeds and nuts, whole grain bread, low-fat dairy products and lean meats (no more than once a week). The basis of the diet is fish and seafood, as well as olive, linseed, and sesame oil.
of ketogenic diets , a type of low-carbohydrate diet program, has also been confirmed The mechanism of ketosis is triggered by consuming carbohydrates at a level of 100 g per day or less, which is 3, 5, 4 times less than the daily requirement of a healthy person. Due to the deficiency of carbohydrates, fats are actively included in metabolism . When they are actively broken down, fatty acids and ketone bodies are formed and energy is released. Ketogenic diets are widely used for epilepsy , Dravet syndrome , Douse syndrome and other diseases of the nervous system and are considered as an alternative non-drug treatment option.
Ketone bodies affect brain structures: the production of antioxidants , the production of free radicals decreases, and neurodegenerative changes are inhibited. This is the basis for the use of this diet for Parkinson's disease . If the hypocholesterol diet can be used by everyone without restrictions, then the ketogenic diet can only be used on the recommendation of the attending physician. First of all, because it has many contraindications ( diabetes , heart disease, high cholesterol , kidney pathology). Then, it is very important to be able to correctly calculate the amount of nutrients in the diet. Another disadvantage is that it is difficult for patients to tolerate and is often accompanied by decreased ability to work.
Considering some of the pathogenetic aspects of this neurological disease, nutrition for Parkinson's disease should include:
- Antioxidant vitamin C , which slows the progression of the disease. Patients have an increased need for ascorbic acid, therefore, in addition to consuming foods containing it (rose hips, red peppers, sea buckthorn, Brussels sprouts, dill, wild garlic, cauliflower, red rowan, oranges, papaya, kohlrabi, strawberries), it is recommended to take dose 3000–6000 mg per day.
- B vitamins are very important for this disease. The production of dopamine in the body depends on the intake of vitamin B1 in the body. Pyridoxine is contained in potatoes, oat and buckwheat cereals, nuts, carrots, and spinach. The tablet drug should not be taken while taking Levodopa .
- Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) is important for preventing the progression of neuronal damage and depression . Its suppliers are kidneys, liver, yeast, eggs, dairy products, cabbage, rose hips.
- We get vitamin B6 Sources of B12 are offal, fish, soy, seaweed, oysters. Folic acid (B9) is found in dark green vegetables (lettuce, spinach, asparagus), avocados, wheat, beans, liver, and the least in egg yolks.
- Vitamin B3 (nicotinic acid) supports the immune system, prevents depression and irritability. Contained in brewer's and bread yeast, cereals, bran, animal liver, peanuts.
- Berries, fruits and vegetables as sources of vitamins and minerals. Cherries, cherries and barberries are useful for this disease. If possible, consume all fruits and vegetables raw.
- Tocopherol (vitamin E) and lipoic acid have neuroprotective properties and antioxidant effects . High levels of lipoic acid are found in beef, liver, cream, sour cream and beans. Sources of vitamin E are nuts (almonds come first, hazelnuts, cashews, pistachios, walnuts), vegetable oils, wheat sprouts, dried apricots, prunes, sea buckthorn, rose hips, salmon, squid, pike perch, eel, oatmeal and barley. Taking vitamin E in high doses has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease. The recommended intake of this vitamin is 200 IU per day.
- Vitamin D , whose role has also been proven. We get this vitamin from fermented milk products, cottage cheese, vegetable and butter, cheese, raw yolks, seafood, fish liver (halibut and cod), fish oil, herring, tuna, mackerel, oatmeal, potatoes. The drug can be taken at a dose of 400-800 IU per day.
- Calcium for the prevention of osteoporosis . It is found in dairy products and sesame seeds. Magnesium provides neuromuscular impulse transmission (wheat bran, pumpkin seeds, sesame seeds, almonds, pine and walnuts, peanuts, spinach, beans, dates, sunflower seeds), potassium (honey, bee bread, apple cider vinegar, potatoes, soybeans, beans, peas, watermelon, melon, bananas, dried apricots, almonds, pine nuts) and sulfur as an antioxidant (the highest content in rabbit and chicken meat, pike, sea bass, sardine, pink salmon, flounder, peas, eggs, average content in lamb, beef, soybeans, peanuts, pork and duck liver).
- Coenzyme Q10 , which promotes the production of cellular energy, slows down the death of neurons and the progression of the disease. Coenzyme A ( vitamin B5 acts synergistically with coenzyme Q10 , balancing cell metabolism, reducing fatigue and eliminating depression. Suppliers of these vitamins are beef, lamb, chicken, liver, heart, sardines, mackerel, eggs, legumes, fresh vegetables and fruits, and brown rice.
It has been proven that caffeine has a positive effect on the neurological status of patients. Drinking coffee daily (no more than one cup per day) strengthens the blood-brain barrier, which reduces the toxic effects of various substances. There is another explanation for the reduced risk of parkinsonism: caffeine blocks adenosine A2A receptors , which regulate the release of glutamate , which damages motor neurons. Taking into account frequently occurring vegetative disorders ( constipation , stomach dysfunction, urinary disorders), adjustments are made to the diet.
It is recommended to drink one cup of coffee per day
In the treatment of constipation , a diet high in dietary fiber (vegetables and fruits in any acceptable form, wheat bran, flax seed) plays an important role. When consuming bran and flax seed, you must not forget about parallel drinking load (1.5 liters of liquid per day). Flax seeds can be consumed ground, 1-2 tsp. 2-3 times a day, after filling them with 100 ml of water. The diet should include foods that have a laxative effect and enhance intestinal motility: beets, prunes, peaches, apricots, apples, strawberries, plums. Increasing physical activity is of no small importance in the treatment of constipation.
In case of dysfunction of the stomach associated with deterioration in the evacuation of its contents, patients experience nausea, vomiting, pain in the stomach and a feeling of fullness. In this case, it is recommended to eat light meals in small portions: soups, vegetable purees, boiled rolled meat, boiled fish.
Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) is also quite common in Parkinsonism. To correct this condition, additional culinary processing of food (for example, chopping or pureeing) is used. Rough and fried foods that are difficult to swallow are excluded, and boiled food with a creamy consistency is introduced. If vegetables and fruits are difficult to swallow raw, you need to switch to stewed and finely chopped or pureed. Fruits need to be peeled from hard skins. Any food should be taken in small pieces, chew it thoroughly and not take the next portion until the previous one has been swallowed. You need to eat more often and in small portions.
Reduce consumption:
- Squirrel. Low protein intake optimizes drug treatment with levodopa . Certain amino acids may compete with this drug at the blood-brain barrier and in the intestine, reducing its effectiveness. In this regard, the drug should be taken 40-60 minutes before meals. Plant foods contain little protein, but more carbohydrates, and animal foods contain a lot of fat, protein and cholesterol .
- Milk and dairy products. If they are limited, elderly patients need to take calcium supplements (1200 mg per day) and vitamin D (400–800 IU).
- Zhirov. Excessive fat intake has been shown to be a risk factor for developing the disease. In this regard, it is recommended to replace saturated animal fats with polyunsaturated and vegetable fats. Some authors note a deterioration in the condition of patients with increased consumption of arachidonic acid (lard, butter, red meat, fish, game meat, eggs). Because arachidonic acid is a polyunsaturated fat, it is mistakenly considered a “healthy fat.” But as we see, it enters the body as part of animal fats; if consumed excessively, it does more harm than good. In addition, it is a precursor of prostaglandins - mediators of inflammation and allergic reactions. Fatty foods also slow down the absorption of levodopa and its entry into the blood.
- Simple carbohydrates and salt.
- Products containing iron. Based on the role of iron in neuronal damage, some authors propose limiting the intake of this trace element in the diet.
- Certain food additives ( monosodium glutamate , aspartate , cysteine , hydrolyzed vegetable protein) can worsen the manifestations of the disease, and therefore it is recommended to avoid products containing them (these are industrially produced products).
- Avoid drinking alcohol. Many drugs do not combine with it. In addition, tremors may increase after drinking alcohol.
The relationship between medications and food intake
The basic drug for Parkinson's disease is Levodopa. It belongs to dopamine derivatives and is an isomer of tyrosine acid. It is taken orally and is well absorbed in the initial and middle sections of the small intestine (duodenum, jejunum). If Levodopa tablets are delayed for any reason in the stomach, it increases acidity, increases appetite and overeating.
Important! Diet and nutrition for Parkinson's disease is compared with the medication regimen, otherwise the bioavailability of the drug is reduced significantly.
Levodopa is an amino acid, so when you eat food and take the drug at the same time, there is a kind of competition. Food breaks down into small molecules consisting of similar amino acids. These elements are absorbed in the small intestine and transported by the same blood proteins. In this regard, doctors recommend taking Levodopa for Parkinson's pathology 1.5-2 hours before eating.
It is more rational when the diet and menu for Parkinson’s disease are distributed so that in the morning a diet poor in proteins prevails in order to avoid competition between Levodopa and other amino acids. However, you cannot completely abandon plant and animal proteins. In the afternoon, eggs, meat and fish are allowed.
Similar to the example of Levodopa, other medications are prescribed. For example, it is not recommended to combine iron supplements with antiparkinsonian medications and dairy dishes.
Authorized Products
- The weekly diet should consist of fish and seafood dishes. This could be tuna, mackerel, cod, sardines, saury, flounder. Sea kale is useful, which can be finely chopped and added to salads or stewed vegetables.
- If possible, use fresh vegetables. If eating them is difficult, switch to stewed or boiled and crushed. Restrictions on coarse vegetables - radishes, radishes, turnips. If tolerated well, legumes should be a mandatory component of the diet. They can be included in your diet daily. Green peas and green beans do not cause bloating. Beans and spinach have been shown to contain natural dopamine . Beans can be eaten as grain or green beans.
- Fruits and berries, as they contain fiber and pectins (especially citrus fruits, apples, viburnum, grapes, cranberries, dried dogwood berries). Pectins improve intestinal motility, reduce cholesterol , and cleanse the body of harmful substances (radioactive substances, pesticides, toxic metals).
- Bran, sesame seeds, fenugreek and flax are additional sources of fiber and healthy oils. They should be administered additionally if there is constipation .
- Vegetable soups (cabbage soup, beetroot soup, borscht) with vegetable broth. Vegetables are well ground when swallowing is difficult. Cereal soups are also good when boiled or pureed. You can prepare puree soups into which pureed meat or fish is added.
- Choose low-fat varieties of meat and poultry (give preference to turkey or chicken). It is enough to eat meat dishes once a week. Meat dishes should be cooked boiled and then chopped. You can cook steamed cutlets, pates and airy meat soufflé.
- Rye and bran bread. It may be easier to consume it in the form of soaked crackers.
- Milk, cottage cheese, fermented milk drinks low in fat and limited. Every day you can include up to 2 whole eggs, from which you can prepare omelettes (steamed and baked).
- Any cereal, but it is better to exclude pearl barley, as it is the coarsest cereal. Porridge is cooked in water and with the addition of milk. Dry and crumbly porridges are difficult to swallow, so you need to prepare “smear porridges” - boil well and add water to a semi-viscous consistency.
- To season ready-made dishes, use unrefined vegetable oils (olive, sesame, corn, flaxseed).
- All nuts and seeds contain healthy monounsaturated fats. You need to eat 30-50 g daily, but they are difficult to eat in their natural form, so you can grind them in a blender, add honey and get a tasty and healthy dessert. It’s a good idea to add chopped prunes and dried apricots here (especially if you are prone to constipation).
- Rosehip decoction, herbal teas, juices, still mineral water (up to 2 liters per day). Anti-stress and neurotrophic effects are exerted by herbal decoctions of catnip, skullcap, passionflower, and valerian root.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| cashew | 25,7 | 54,1 | 13,2 | 643 |
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Sausages | ||||
| boiled diet sausage | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 170 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Fight constipation
A diet for Parkinson's disease does not imply an absolute abstinence from certain types of foods, but rather a balanced diet. Often, elderly and senile patients are prone to constipation. This may be due to impaired motility of the digestive tract due to Parkinson's pathology, taking medications, prolonged sitting, a decrease in saliva volume due to drooling, or physical inactivity. Nutrition and fluid balance algorithm:
- It is recommended to drink 1 glass (150-200 ml) of water at room temperature on an empty stomach. The drinking regime is regulated at the rate of 25-30 ml per 1 kg of person’s weight per day. With caution - in case of heart failure or kidney disease with excretory failure due to the possible development of edema.
- Foods for Parkinson's disease should be rich in fiber and coarse fibers for the productive formation of feces (brown bread, rice, corn, bran, oatmeal).
- Inclusion in the diet of foods that help softly loosen stools: prunes, dried apricots, raisins, baked apple, boiled beets, strawberries.
- Stimulation of the intestines through pectin-containing fruits and berries: apples, peach, banana, orange, cherry, grapes; vegetables: eggplant, carrots, cucumbers, peppers, tomatoes, pumpkin.
In addition to correcting nutrition, it is recommended to maintain physical activity during the day, perform abdominal massages and gymnastic exercises.
Fully or partially limited products
The following should be excluded from the diet:
- fatty pork, duck and goose meat, sausages, cooking fats, smoked meats, canned fish, fish caviar, margarine;
- products containing monosodium glutamate (it negatively affects the basal structures of the brain);
- all types of broths, fried foods;
- fatty dairy products.
It is recommended to significantly limit the consumption of sunflower oil, chocolate, ice cream, cocoa, strong tea and coffee, confectionery products, pastry products, cakes, cream pies, sugar, jam and jam.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 11% | 16,0 | 11,0 | 1,0 | 170 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Menu (Power Mode)
5-6 meals a day are provided in small portions. The food menu can be varied, since there are no serious restrictions. Breakfast may consist of: porridge - “mix” with fruit or dried fruits, a piece of unsalted cheese (tofu is the most suitable) and tea. You can prepare an omelette with filling (zucchini or pumpkin, grated carrots, boiled cauliflower), which are added to the omelette mixture.
Second breakfast includes cottage cheese soufflé or natural cottage cheese with kefir or yogurt. For lunch you can prepare various soups - fish, cereals, vegetables. Meatballs, pieces of chopped chicken or minced meat are added to vegetable soups if swallowing is difficult. The second courses are meat or fish, if there was no meat in the first courses. For a side dish, choose any well-cooked or pureed porridge and vegetable additives (any boiled or stewed vegetables that the patient tolerates well). Unrefined vegetable oil is added to cereals and vegetables.
An afternoon snack may contain fruit and berry soufflé, cottage cheese or cottage cheese casserole, and juice. For dinner - light fish dishes and steamed puddings or pureed vegetables (zucchini, green peas, potatoes, cauliflower, carrots).
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
| Breakfast |
|
| Lunch |
|
| Dinner |
|
| Afternoon snack |
|
| Dinner |
|
| For the night |
|
Diagnosis of Parkinson's disease
Clinical diagnosis of the disease takes place in three stages.
Stage I
Parkinsonism syndrome is recognized and its symptoms are compared with other psychopathic and neurological pathologies that manifest themselves in a similar way. The main symptom of the disease is hypokinesia, combined with muscle rigidity, resting tremor or postural instability. However, it is not associated with visual, cerebellar and vestibular disorders.
Stage II
Provides for the exclusion of the presence of other diseases manifested by parkinsonism syndrome. The doctor pays attention to a number of criteria:
- prolonged remission;
- oculogyric crises (gaze convulsions);
- use of antipsychotics before the onset of the first symptoms of the disease;
- clear manifestation of dementia;
- Babinski reflex;
- manifestation of autonomic failure;
- cerebellar symptoms;
- unilateral manifestation of pathology for more than 3 years;
- supranuclear gaze palsy;
- lack of effect from taking Levodopa;
- detected open hydrocephalus/brain tumor;
- a history of strokes with progression of symptoms of Parkinson's disease;
- repeated traumatic brain injuries.
Stage III
Symptoms are identified that allow an accurate diagnosis to be made. To do this, you must have at least three criteria from the list:
- presence of rest tremor;
- greater severity of symptoms on the side of the body on which the disease debuted;
- presence of a reaction to taking Levodopa;
- effectiveness of Levodopa for at least 5 years;
- duration of illness from 10 years;
- progressive course of the disease.
When evaluating patients with symptoms of Parkinson's disease, the following are used:
- Electroencephalography (EEG). Biological signals coming from brain cells are recorded. The functional activity of the brain is assessed, and pathological disorders present in it are diagnosed.
- MRI of the brain. It makes it possible to see brain structures and visualize the pathological formations present in them, evaluate the parameters of pulse blood flow in the capillary arteries, and identify functional areas of the brain.
- CT scan of the brain. During the examination, the structure of the brain tissue and the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid system are studied. The technique allows you to recognize abnormal processes occurring in the brain and carry out dynamic monitoring of the course of the disease and the effectiveness of the treatment.
- Rheoencephalography. The method is aimed at studying the blood supply to the veins of the neck and head. Makes it possible to study the parameters of pulse blood flow in the arteries of the brain, venous outflow from the cranial cavity.
Differentiation of diagnosis
It is very important during diagnostic measures to differentiate Parkinson's disease from other pathologies manifested by parkinsonism syndrome. This means:
- parkinsonism plus;
- secondary parkinsonism;
- pseudoparksinsonism.
Advantages and disadvantages
| pros | Minuses |
|
|
Reviews and results
The diet contains foods that are healthy for the body and is a healthy diet, so it should be followed constantly. It does not have any strict restrictions and from time to time patients can allow themselves to eat their favorite foods, including sweets. Limiting simple carbohydrates and fats does not adversely affect health. As a result of therapeutic nutrition, patients lose weight and improve their health.
- “... My father has had this disease since he was 55 years old. In addition to becoming helpless, he also became nervous and irritable. Everything on his part is expressed by shouting, anger and reproaches. We always try to pay attention to him and do not let him relax and withdraw into himself. We often go outside and find something interesting for him to do at home. He takes pills, the doctor said that the more active he is, the better - inaction will ruin him. He also mentioned that diet for Parkinson’s is also important”;
- “... Mom’s tremor starts when pressure surges, so we try to keep it at the same level. She also has high cholesterol, so she began to take her diet seriously: she switched to fish, seaweed, eats a lot of vegetables, and adds bran to all her dishes. I eliminated animal fats completely and switched to olive and corn oil. I'm not very sure that these measures will help reduce cholesterol, but overall my health has improved. She became cheerful, active, and interested in life. During those periods when his hands are not shaking, he even knits socks, hats and scarves for his grandchildren. It gets worse if she gets nervous, so we protect her from all troubles. We all live together, so I force her to do physical therapy and flexibility exercises every day, to prevent speech disorders - to read aloud, for memory - to learn poetry. And her grandchildren constantly support her interest in life”;
- “...Mom has been suffering from this disease for 10 years. I won’t say it’s critical, but the deterioration is noticeable every year. The main problem is periodic depression. Sometimes it drags on for a long time and there is no way to get it out. She is overcome by complete emptiness and hopelessness. The doctor prescribed Fefarin and it helped. Now fears and anxiety have disappeared and my mood has improved significantly. They didn’t make any special changes in her diet, since she had long ago switched to vegetable oils, inexpensive fish, stewed vegetables and legumes (though she rarely eats due to bloating). Dairy is limited - a glass of kefir at night, cottage cheese 2-3 times a week. She was never fond of sweets. In general, the usual diet of an elderly person.”
Contraindications in nutrition
The Parkinson's disease diet and proper nutrition exclude the consumption of certain types of foods. It is recommended to avoid fast food (jellied noodles, mashed potatoes, minute porridge) and snacks (chips, croutons, etc.). They contribute to an increase in low and very low density lipoproteins, disrupt the lipoprotein balance with an increase in triglycerides and cholesterol. With such a diet, there is a high risk of progression of atherosclerosis of the vessels of the heart, head and neck.
The menu for Parkinson's disease does not include alcohol-containing and sweetened carbonated drinks, as they lead to a decrease in cognitive abilities, increased gas formation in the intestines, and artificially cause a feeling of hunger. The amount of salt consumed per day is limited to 4-5 grams. Thus, it is possible to avoid retaining excess fluid in the body and exacerbating diseases of the cardiovascular system. Fasting and severe dietary restrictions are unacceptable.