In the modern world there are almost no unique substances; any category of objects is represented by a broad group. From an evolutionary point of view, the more different creatures in an ecosystem, the more resistant it is to adverse factors. In the environment of human interaction, the phenomenon when one product has many options, forms and manufacturers is called competition. Thanks to this, better representatives remain on the market, and the rest disappear.
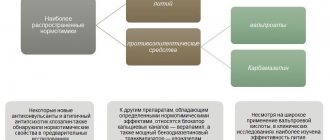
Cortexin and Cerebrolysin are nootropics. Nootropics are medications that improve brain function and stimulate cognitive processes (learning, memory, thinking). They also protect neurons from damaging influences and promote faster recovery of central nervous system structures in neurological diseases.
pharmachologic effect
Cerebrolysin contains low molecular weight biologically active neuropeptides that penetrate the BBB and directly enter nerve cells.
The drug has an organ-specific multimodal effect on the brain, i.e. provides metabolic regulation, neuroprotection, functional neuromodulation and neurotrophic activity. Metabolic regulation:
The drug Cerebrolysin increases the efficiency of aerobic energy metabolism of the brain, improves intracellular protein synthesis in the developing and aging brain.
Neuroprotection:
the drug protects neurons from the damaging effects of lactic acidosis, prevents the formation of free radicals, increases survival and prevents the death of neurons under conditions of hypoxia and ischemia, and reduces the damaging neurotoxic effect of excitatory amino acids (glutamate).
Neurotrophic activity:
Cerebrolysin is the only nootropic peptidergic drug with proven neurotrophic activity similar to the action of natural neuronal growth factors (NGF), but manifested under conditions of peripheral administration.
Functional neuromodulation:
The drug has a positive effect in cases of cognitive impairment on memory processes.
Indications
Both drugs have common indications for use:
- Encephalopathy
- Brain infarction
- Cerebrovascular disease
- Intracranial trauma
There is a fairly large number of studies that prove the positive effect of neuropeptides (which contain Cortexin and Cerebrolysin) on the healing of nerve structures after damage.
However, there are also differences. Cortexin can be used if:
- Asthenic (emotionally labile) disorders.
- Disorders of speech, language, learning skills.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Intellectual-mnestic dysfunctions.
- Delayed developmental stages.
- Malaise and fatigue.
The fact is that Cortexin has a strong influence on cognitive processes associated with the transmission of impulses in the central nervous system.
Cerebrolysin is used in the following cases:
- Dementia of various etiologies.
- Alzheimer's disease.
- Depression.
- Excessive activity (pathological motor activity).
Studies have revealed the ability of Cerebrolysin to normalize the ratio of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters, which is now actively used in medicine.
Speaking about indications for use, it is important to say that Cerebrolysin appeared quite a long time ago - in the 1970s. During its existence, a fairly large amount of information has accumulated about its effects in clinical trials and in practice.
Cortexin is a newer drug, it appeared about 20 years ago, but the experience of its use is already quite large and contains enough data on positive effects.
Dosage
The drug is used parenterally. The dose and duration of use depend on the nature and severity of the disease, as well as the age of the patient. A single administration of the drug in a dose of up to 50 ml is possible, but a course of treatment is more preferable.
The recommended course of treatment is daily injections for 10-20 days.
| Indication | Dose |
| Acute conditions (ischemic stroke, traumatic brain injury, complications of neurosurgical operations) | from 10 ml to 50 ml |
| In the residual period of cerebral stroke and traumatic injury to the brain and spinal cord | from 5 ml to 50 ml |
| Psychoorganic syndrome and depression | from 5 ml to 30 ml |
| Alzheimer's disease, dementia of vascular and combined Alzheimer's-vascular origin | from 5 ml to 30 ml |
| In neuropediatric practice | 0.1-0.2 ml/kg body weight |
To increase the effectiveness of treatment, repeated courses can be carried out as long as the patient's condition improves as a result of treatment. After the first course, the frequency of injections can be reduced to 2 or 3 times a week.
Cerebrolysin is used parenterally in the form of intramuscular injections (up to 5 ml) and intravenous injections (up to 10 ml). The drug in a dose of 10 ml to 50 ml is recommended to be administered only through slow intravenous infusions after dilution with standard solutions for infusion. The duration of infusions ranges from 15 to 60 minutes.
Comparison of addiction between Cerebrolysin and Cortexin
Like safety, addiction also involves many factors that must be considered when evaluating a drug.
So, the totality of the values of such parameters as “syndrome o” in Cerebrolysin is quite similar to the similar values in Cortexin. Withdrawal syndrome is a pathological condition that occurs after the cessation of intake of addictive or dependent substances into the body. And resistance is understood as initial immunity to a drug; in this it differs from addiction, when immunity to a drug develops over a certain period of time. The presence of resistance can only be stated if an attempt has been made to increase the dose of the drug to the maximum possible. At the same time, Cerebrolysin has a fairly low value of the “syndrome”, however, the same as Cortexin.
Side effects
The frequency of adverse reactions was determined in accordance with WHO recommendations: very often: (≥1/10); often: (from ≥1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (from ≥1/1000 to <1/100); rare (from ≥1/10,000 to <1/1000); very rare, including isolated reports (<1/10,000).
From the immune system:
very rarely - increased individual sensitivity, allergic reactions.
Mental disorders:
rarely - the expected activation effect is accompanied by agitation, manifested by aggressive behavior, confusion, and insomnia.
From the nervous system:
rarely - too rapid administration of the drug can lead to dizziness; very rarely - isolated cases of generalized epilepsy and one case of seizures were associated with Cerebrolysin.
From the cardiovascular system:
very rarely - too rapid administration of the drug can lead to increased heart rate and arrhythmia.
From the digestive system:
very rarely - dyspepsia, diarrhea, constipation, nausea, vomiting; rarely - loss of appetite.
For the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
very rarely - skin reactions; rarely - with excessively rapid administration, a feeling of heat, sweating, and itching may occur.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site:
very rarely - redness, itching, burning at the injection site, pain in the neck, head and limbs, fever, mild back pain, shortness of breath, chills, collapsing state.
One study reported an association between rare use (>1/10,000 to <1/1,000) with hyperventilation, hypertension, hypotension, fatigue, tremor, possible depression, apathy and/or somnolence, and flu-like symptoms. (cold, cough, respiratory tract infections).
Since Cerebrolysin is used mainly in elderly patients, the above symptoms of diseases are typical for this age group and often also occur without taking the drug.
It should be noted that some undesirable effects (excitement, arterial hypertension, arterial hypotension, lethargy, tremor, depression, apathy, dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, diarrhea, nausea) were identified during clinical studies and occurred equally in patients treated with Cerebrolysin and in patients in the placebo group.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions are aggravated or any other side effects not specified in the instructions are noted, the patient should inform the attending physician.
Notification in case of suspected side effects
It is important to report side effects after drug approval to ensure ongoing monitoring of the drug's risk-benefit profile. Healthcare professionals are asked to report all cases of adverse reactions observed with the drug through national adverse reaction reporting systems and/or to the company's representative office.
Comparison of side effects of Cerebrolysin and Cortexin
Side effects or adverse events are any adverse medical event that occurs in a subject after administration of a drug.
Cerebrolysin's side effects are almost the same as Cortexin's. They both have few side effects. This implies that the frequency of their occurrence is low, that is, the indicator of how many cases of an undesirable effect of treatment are possible and registered is low. The undesirable effect on the body, the strength of influence and the toxic effect of Cerebrolysin are similar to Cortexin: how quickly the body recovers after taking it and whether it recovers at all.
Drug interactions
Taking into account the pharmacological profile of the drug Cerebrolysin, special attention should be paid to possible additive effects when co-administered with antidepressants or MAO inhibitors. In such cases, it is recommended to reduce the dose of the antidepressant. The use of Cerebrolysin in high doses (30-40 ml) in combination with MAO inhibitors in high doses can cause an increase in blood pressure.
Cerebrolysin and balanced solutions of amino acids should not be mixed in the same solution for infusion.
Cerebrolysin is incompatible with solutions containing lipids and with solutions that change the pH of the medium (5.0-8.0).
What's best for a child?
Increased demands are placed on medications in pediatric practice in terms of safety and effectiveness. Both Cortexin and Cerebrolysin have found their use in children. Cortexin has shown the best effect for the treatment of epilepsy (as part of complex therapy), convulsive syndrome, cerebral palsy and delayed development of certain brain functions (speech, learning skills). Due to the risk of side effects of Cerebrolysin, the drug is contraindicated for status epilepticus in a child.
Each tool has its own strengths and weaknesses. It is necessary to choose a medicine strictly individually, taking into account the nature of the disease, concomitant pathologies and individual characteristics of the person. There is no ideal universal “pill”; any drug will be effective only in cases where the indications for its use are met.
special instructions
If injections are performed too quickly, a feeling of heat, sweating, and dizziness may occur. Therefore, the drug should be administered slowly.
The compatibility of the drug has been tested and confirmed (within 24 hours at room temperature and light) with the following standard solutions for infusion: 0.9% sodium chloride solution, Ringer's solution, 5% dextrose (glucose) solution.
The simultaneous use of Cerebrolysin with vitamins and drugs that improve cardiac circulation is allowed, but these drugs should not be mixed in the same syringe with Cerebrolysin.
Only clear Cerebrolysin solution should be used and only once.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Clinical studies have shown that Cerebrolysin does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and use machinery.
Comparison of ease of use of Cerebrolysin and Cortexin
This includes dose selection taking into account various conditions and frequency of doses. At the same time, it is important not to forget about the release form of the drug; it is also important to take it into account when making an assessment.
The ease of use of Cerebrolysin is approximately the same as Cortexin. However, they are not convenient enough to use.
The drug ratings were compiled by experienced pharmacists who studied international research. The report is generated automatically.
Last update date: 2020-12-04 13:47:57
Release form, composition and packaging
Injection
yellowish-brown, transparent.
| 1 ml | |
| Cerebrolysin concentrate (a complex of peptides* obtained from pig brain) | 215.2 mg |
* molecular weight not more than 10,000 daltons.
Excipients:
sodium hydroxide, water d/i.
- 1 ml - brown glass ampoules (10) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs.
- 2 ml - brown glass ampoules (10) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs.
- 5 ml - brown glass ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs.
- 10 ml - brown glass ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs.
- 20 ml - brown glass ampoules (5) - contour cell packaging (1) - cardboard packs.
- 30 ml - brown glass bottles (1) - cardboard packs.
- 30 ml - brown glass bottles (5) - cardboard packs.
Compound
Both drugs have a similar composition - they are polypeptides from the cerebral cortex of animals. Cerebrolysin is made from the nerve structures of pigs, and Cortexin is made from cattle.
There are some differences in the manufacturing process. Cerebrolysin is obtained by breaking down brain proteins into their components. The disadvantage of this method is that the likelihood of destruction of the necessary aminopeptides increases. In the manufacture of Cortexin, lyophilization (freezing and vacuum processing) is used. Due to this, a direct transition of a substance from a solid to a gaseous state is achieved, which reduces the destruction of proteins and amino acids.
Place of drugs in therapy in children
A common question that is asked when prescribing Cerebrolysin or Cortexin is which is better for children. The effectiveness of Cortexin has been confirmed by studies in the treatment of infants on the second day after birth with cervical trauma. The medication did not have a stimulating effect on the body, which distinguishes it from other nootropics.
For newborns, this medication is a priority in cerebroprotective therapeutic treatment.
Cerebrolysin is recommended for children with the following symptoms:
- frequent pain in the head and cervical region;
- increased feeling of fatigue;
- irritability and nervousness;
- impaired concentration and inattention;
- memory loss;
- sleep disturbance.
Side effects of drugs on the body
The development of side effects (Table 1) occurs in rare cases, and usually disappear on their own after a few days.
| Body systems | Negative effects |
| Blood flow system and cardiac organ |
|
| CNS |
|
| The immune system |
|
| Digestive system |
|
| Respiratory system |
|
| Leather |
|
| General negative reactions of the body |
|