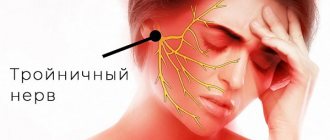
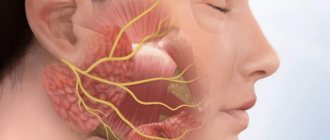
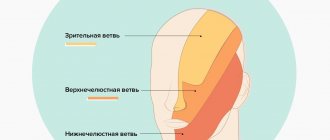
The trigeminal nerve is a ganglion that gives rise to three “branches” that exit directly from the brain stem. Three “branches” reach directly to the human face, supplying it with nerves and connecting it with the central nervous system.
The trigeminal nerve exits the skull through three different foramina. The first “branch” comes out through symmetrical points that are located slightly above the person’s eyebrows (the so-called ocular process). The second, emerging, passes along both sides of the nose (just below the eye area and close to the cheeks) and is therefore called the maxillary, the third “branch” exits in the lower jaw (mandibular) in the direction from the corners of the mouth to its center.
With inflammation of various processes of the trigeminal nerve, pain is observed, localized in various places of the face. When the first “branch” is inflamed, pain occurs above or below the brow ridge, in the forehead and in the front part of the temporal region of the head. When the second and third “branches” of the trigeminal nerve become inflamed, pain occurs in the upper and lower jaws, respectively, which, in turn, causes severe toothache.
Next, we will talk about the types of neuralgia, causes and methods of treatment. But if you are experiencing unbearable pain right now, make an appointment with us. When making an appointment, tell the administrator that you need emergency assistance, and they will find an appointment for you as soon as possible. An appointment with a dentist can be made by calling 8 or using the online appointment form.
Types of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is divided into two types. The first, the so-called true trigeminal neuralgia, is a holistic disease caused in most cases by compression of the nerve or disruption of the blood supply. The second type - secondary trigeminal neuralgia - is a symptom of a general disease of the body. It could be a tumor or a serious infection.
In most cases, doctors diagnose inflammation of one of the processes of the trigeminal nerve, but in some situations inflammation of two or three processes occurs at once. Inflammation can affect either one side of the face or both, and in different combinations.
Real life examples
Some famous people, whose fame sometimes trumpets all over the world, were also hostage to the pathology of the facial nerve.
Sylvester Stallone, who is known for his enchanting roles, was injured at birth. The actor's mother had a difficult birth and he had to be pulled with forceps. The result is damage to the vocal cords and paresis of the left side of the face. Because of this, Stallone had problems with speech, which became a reason for ridicule from his peers.
The actor grew up as a difficult child. But, in spite of everything, he managed to overcome his defect and achieve considerable success, although partial immobility of his face remained.
Domestic showman Dmitry Nagiyev received facial asymmetry, which was nicknamed “Nagiyev’s squint”, due to paresis of the facial nerve. The illness happened unexpectedly. As a theater student, one day he felt that his face was not moving.
He spent 1.5 months in the hospital to no avail. But one day in his room a window broke due to a draft. Fright provoked a partial return of mobility and sensitivity of the facial part, but the left part retained its immobility.
Causes of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Doctors believe that the main cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is compression of it either inside the skull or outside it. Inside the skull, the trigeminal nerve can be compressed as a result of the formation of tumors, in most cases resulting from some kind of head injury.
Also a fairly common cause of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is internal venous or arterial displacement.
Other causes of trigeminal neuralgia include:
- the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, viral or bacterial infection in the body;
- herpes infection (herpes);
- a brain tumor;
- scarring in the brain stem;
- failure of anesthesia during treatment or tooth extraction.
Most often, inflammation of the trigeminal nerve affects women at pre-retirement and retirement age (usually from fifty to seventy years). If trigeminal neuralgia is diagnosed in a young man or girl, then most likely its cause is a change in the arteries of a sclerotic nature or a strong dilatation of blood vessels.
Unusual sensations
It happens that a person can feel phenomena in the face and head that are unusual for the usual state. They are called paresthesias and are manifested by the following symptoms:
- tingling;
- burning;
- "goosebumps"
- numbness;
- itching and rashes.
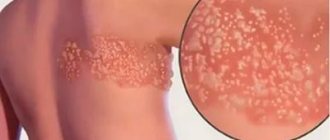
Often facial paresthesias have an organic basis and become a sign of the disease:
- neuritis, neuralgia of the cranial nerves;
- multiple sclerosis;
- stroke and other circulatory disorders in the brain;
- shingles;
- migraine;
- diabetes;
- epilepsy;
- hypertension.
In certain cases, unusual sensations are observed in certain parts of the face. For example, similar manifestations in the language may appear for the reasons listed above, but often have a different etiology. They are provoked by cancer of the tongue and larynx, as well as trauma by a splintered tooth or denture.
Dental procedures cause numbness and other unusual feelings, especially after tooth extraction. Another reason for their appearance may be an uncomfortable position during sleep or an unsuitable pillow. But the sensations caused by such phenomena usually pass soon.
Another group of provoking factors consists of psychogenic and neurogenic disorders.
How does inflammation of the trigeminal nerve manifest?
The main symptom of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is severe pain that occurs in the facial part. The pain really has a powerful force and shooting character, so it is very difficult for the patient to calmly endure painful attacks. The pain intensifies when performing the slightest actions with the facial muscles and jaws - yawning, chewing, laughing, and performing daily oral hygiene. At the same time, the sensitivity of the skin on the inflamed side of the face decreases.
The next painful attack is accompanied by a rapid dilation of the patient’s pupils and the same rapid contraction of facial muscles. Increased tear production may begin.
Pain with trigeminal neuralgia is severe, but not constant. The pain occurs for a few seconds and is interrupted for a while. But if the intervals between painful attacks are short, then it seems that the pain is constant. Trigeminal neuralgia is dangerous because the interval between attacks can be several weeks, and sometimes even several months. But after this period, the pain will certainly return. A long break does not mean that the disease has passed, so if you have already noticed symptoms of neuralgia once, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Symptoms of neuralgia
- Facial pain (prosopalgia). A characteristic sign of neuralgia. Sharp and sudden, reminiscent of an electric shock. Usually lasts from 5 to 15 seconds, is paroxysmal in nature and can occur at any time. During periods of remission, the number of attacks decreases. Most often, pain occurs in the area of the cheekbones and lower jaw (both right and left), and can be localized in almost all areas of the face.
- Impaired sensitivity. A severe form of neuralgia can lead to partial or complete loss of sensitivity of the skin.
- Nervous tic of the eyelid (nystagmus), spasms and twitching of facial muscles.
- Loss of coordination and motor skills are rarer manifestations of severe forms of the disease.
- Headaches, fever, chills and weakness are syndromes caused by viruses and infections.
Why do teeth hurt when the trigeminal nerve is inflamed?
How is inflammation of the trigeminal nerve related to teeth? The connection here is the most direct. Firstly, severe pain during attacks “radiates” to the upper or lower jaw (depending on which nerve extension is inflamed), and sometimes to both jaws. This causes severe and unbearable toothache.
Secondly, those nerves that are found in the upper and lower teeth and gums are directly connected to the trigeminal nerve. The second branch of the trigeminal nerve innervates the upper teeth and gums, and the third, respectively, the lower jaw and gums.
The trigeminal nerve can also be damaged during a number of dental manipulations. Unsuccessful tooth extraction or improper filling, surgical intervention in the jaw structure that ended unsuccessfully, and injuries can cause trigeminal neuralgia.
It is very important to distinguish inflammation of the trigeminal nerve from other diseases of the oral cavity, in particular pulpitis - inflammation of the internal dental tissues. A characteristic sign of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is that, despite severe pain, the sensitivity of the teeth does not increase when they come into contact with cold and hot foods, and hypothermia or heating does not provoke the onset of a new pain attack. Acute tooth sensitivity is a symptom of pulpitis.
When the trigeminal nerve is damaged in the jaw area, acute toothache, pain in the chin, ears and sometimes in the lower lip occurs. The pain may become increasingly intense, and often the patient continues to feel a dull ache after the attack.
Neuritis causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention methods
The pathology is classified into types according to the affected nerve, the location of the affected area and the causes of its occurrence.
Along a damaged nerve
Neuritis of the facial nerve is an inflammatory lesion of the nerve innervating the facial muscles of half the face, which is manifested by piercing pain and asymmetry;
Solar plexus neuritis is a lesion of an inflammatory, less often degenerative nature, in which sensitivity decreases, motor disturbances occur, and in severe cases, paralysis;
median nerve neuritis - damage to the nerve innervating the palm and the first three fingers of the hand, which is accompanied by impaired flexion function of the fingers, piercing pain and sensory disturbances;
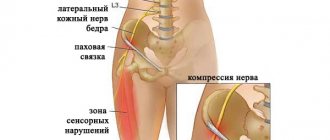
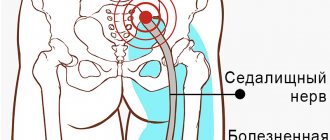
sciatic nerve neuritis - inflammation of a large nerve passing through the buttocks and back of the leg, which occurs with infections and degenerative changes in the spine, intervertebral hernias;
ulnar nerve neuritis is an inflammatory lesion characterized by impaired sensitivity of the little and ring fingers, tingling, paralysis of the muscles of the hand and forearm;
neuritis of the radial nerve - an inflammatory process, compression or pinching of the nerve ending with decreased sensitivity of the dorsum of the hand from the thumb to the middle finger, tingling in this area, paralysis of the extensor and flexor muscles of the forearm and hand;
Acoustic neuritis is an inflammation due to chronic or acute infection, toxin poisoning or long-term medication use, which is accompanied by general hearing loss, imaginary noise, ringing in the ears, and decreased sensitivity to high or low frequency sounds.
According to the affected area
Axial - occurs when the axial nerve cylinders are damaged;
autonomic - associated with pathology of peripheral fibers of the autonomic nervous system;
ascending - develops after injury to the peripheral part of the limbs;
Gombeau's neuritis - associated with the disintegration of the myelin sheath in a limited area of the fiber;
interstitial - occurs when connective nervous tissue is damaged and atrophied.
For reasons of defeat
Vibration - associated with constant exposure to vibration, develops mainly in the feet and hands;
hypertrophic Dejerine-Sotta neuritis is a genetic disease that progresses and leads to degeneration of the nerve fiber;
infectious - a complication of previous infectious diseases;
professional - caused by the negative impact of external factors in the workplace, for example, heavy metals and other toxins.
Treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
The first stage of treatment for inflammation of the trigeminal nerve is medication. It is aimed at reducing the strength and frequency of pain in the patient. Most often, doctors prescribe anticonvulsants to a patient suffering from trigeminal neuralgia. Sedatives are also used.
Physiotherapeutic procedures, as well as resorption therapy to relieve the inflammatory process, have a good therapeutic effect. Next, the doctor may recommend the use of laser treatment, in which the laser is directed cutaneously to the area where the processes of the trigeminal nerve exit the skull.
Our clinic is located in the same building as the multidisciplinary clinic “Diamed on Shchelkovskaya”, where special conditions for receiving physiotherapeutic procedures are organized for dental patients. The clinic’s physiotherapy room is equipped with modern equipment, including a laser physiotherapy device, with which you will feel relief after the first procedure. The pain will go away and you can return to normal eating. Make an appointment with a dentist by calling 8 or using the online appointment form. The doctor will make an accurate diagnosis and refer you for treatment.
If you are in severe pain, but for some reason you have not yet made an appointment with us, then it can be relieved with folk remedies. Take one tablespoon of yarrow, pour a glass of boiling water, let it brew for one hour and strain. The tincture should be taken one tablespoon before meals three to four times a day.
How to treat neuropathy
There is no point in looking for a cure for neuropathy on your own. This is a consequence, not a cause. The disease that caused it needs to be treated. In each specific case, its own therapy is prescribed. Therefore, you cannot do without the help of a doctor.
Vasoactive drugs and B vitamins will help maintain the condition, especially in cases of alcoholic or toxic damage. Means to improve blood circulation, restore fiber conductivity and light sedation will not be superfluous.
It’s a mistake to drown out sensations with painkillers. They only relieve discomfort, but do not cure. And the disease that has become the root cause of neuropathy remains unattended.
A healthy lifestyle is not an alternative to therapy. Changing your diet, quitting smoking and exercising are all helpful and will improve your overall well-being. But these measures are secondary and do not replace treatment.
Complex methods of treatment are used to treat polyneuropathy. In some cases, observation by a neurologist and several specialized specialists is necessary - for diabetes - an endocrinologist, for kidney pathology - a urologist, alcoholism - a narcologist.
Tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants help reduce unpleasant painful sensations, convulsive contractions and a burning sensation. (Here we need a link not to Finlepsin, but to Gabapentin) With infectious causes of polyneuropathy, especially those caused by HIV infection, it is impossible to completely recover from the pathology, but with proper treatment of the underlying disease, its progression can be stopped.
Some patients with autoimmune, toxic or metabolic disorders are prescribed plasmapheresis. Blood purification allows you to get rid of substances that cause damage to nerve trunks. At the recovery stage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy are used: electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, acupuncture.
There is no need to put off visiting a neurologist. It is better to select adequate treatment as early as possible, get rid of unpleasant symptoms and prevent further negative effects on the body.
How to remove teak yourself
If a nervous facial tic is situational and is not too intense, but at the same time obsessive, you can try to get rid of it using physical methods.
One way is to try to disrupt the pathological muscle rhythm by overexerting it. For example, if your eye twitches, try to close your eyes tightly.
It is possible to calm an overexcited muscle through a light massage. Or apply cold to it. The temperature difference will also help. Wash your face alternately with cold and warm water.
How to get rid of nervous tics
In order to free yourself from unpleasant sensations, you must first eliminate their problem. Sometimes all it takes is a good night's sleep. In another case, you need to change the situation for a while, get out of the destructive environment.
Among the auxiliary methods used are herbal soothing teas, baths with the addition of aromatic oils, swimming, walks in the fresh air or sports: running, yoga.
Add ingredients with a high content of calcium and magnesium to your menu. These include fermented milk products, buckwheat, bran bread, red fish, eggs, and meat. Vegetables and fruits include beets, currants, dried fruits, nuts and parsley.
If these foods do not fit into your diet, consider taking appropriate vitamin supplements. Do not overuse strong tea and coffee.
And most importantly: remain optimistic and calm in any situation!
In cases where the condition worsens, psychotherapy is sought. Cognitive behavioral therapy is especially effective in helping to stop tic disorders at the stage of their precursors.
Habit reversal therapy teaches patients movements that help prevent the development of neurological facial symptoms.
Medications include anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants, Botox injections, and antidepressants.
If the above methods are ineffective in combating nervous tics, they turn to deep brain stimulation. A device is installed in the GM that controls electrical impulses.
Dermatillomania
Neurosis of the face and scalp can manifest itself in a behavioral disorder such as dermatillomania.
Its main manifestation is scratching the skin of the face and head, not because of itching, but because of dissatisfaction with its appearance. This also includes an obsessive zeal to squeeze out pimples, scratch off scabs, and pull out hair. Self-injurious actions cause a short-term feeling of pleasure, followed by feelings of shame, frustration, and dissatisfaction.
The face of such patients is covered with scars and scars due to constant trauma to the skin. This process is uncontrollable and can occur at any time of the day. But most often traumatic actions are carried out in front of a mirror.
Symptoms of the disorder also include the habit of biting the lips and mucous membranes of the cheeks. Patients are not deterred by the prospect of redness, bleeding, and scarring of the skin. They repeat the ritual day after day. It lasts from a few minutes to an hour.
Such actions can be provoked by feelings of fear, anxiety, and close examination of one’s skin because there is nothing to do.
Dermatillomania has been described as a state of addiction. It begins with concentrating on what the patient thinks is a skin defect. Gradually, attention is increasingly focused on this detail. A person begins to think that he is sick with something serious. This provokes irritability and nervousness in him, leading to obsessive actions.
The root cause of the disease is rooted in the psychological state of a person and lies in self-dissatisfaction, anger, feelings of shame and malice. Traumatic rituals are a way of punishment, self-flagellation.
Treatment of this pathology requires the intervention of a psychotherapist and a dermatologist.
The main method of treating addiction is psychotherapy, in particular cognitive behavioral therapy.
Yoga, physical exercise, relaxation procedures, as well as any hobby that absorbs a person and helps redirect attention will help reduce anxiety, distract and relax.
The help of a dermatologist is necessary to eliminate skin lesions in order to prevent infection and reduce the degree of dermatological defect.