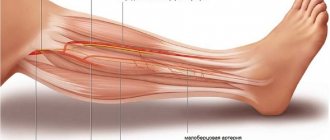
Occipital neuralgia is pain in the head that occurs due to compression of the nerve roots that form the occipital nerves, or the nerves themselves. The pain in this case has a “shooting” character and becomes constant as the disease progresses.
The causes of neuralgia of the occipital nerve can be different, and in accordance with them it is customary to distinguish:
- primary neuralgia, which occurs without obvious reasons;
- secondary neuralgia, which occurs as a result of injuries, neoplasms, etc.
Symptoms of occipital neuralgia can easily be confused with clinical manifestations of other diseases, so independent diagnosis is unacceptable. In order to undergo a course of treatment for occipital neuralgia, contact the CELT Pain Clinic!
At CELT you can get advice from a specialist algologist. Make an appointment
Causes of occipital neuralgia
Treatment of occipital neuralgia is prescribed depending on the reasons that caused this pathology, and they can be very different:
- mechanical damage to the spine resulting from trauma;
- hypothermia;
- prolonged muscle tension due to a sedentary lifestyle;
- consequences of osteochondrosis;
- severe stress;
- diseases of the spine of various nature;
- diseases of infectious etiology;
- inflammation of blood vessels;
- gout;
- diabetes.
Causes of the disease
This disease occurs in acute and chronic forms . The causes of the acute form have no explanation, despite the intense symptoms. But secondary (chronic) neuralgia develops due to pathological processes.
Its manifestation can be caused by these reasons:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Dystrophic changes in the discs affect the nerve processes.
- Injuries to the neck or upper back. In this case, the nerve endings are compressed.
- Frequent stress.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Muscle strain due to prolonged uncomfortable position.
- Draft or hypothermia. Complications of viral infections.
- Arthritis in the cervical vertebrae.
- Gout, which destroys joint tissue.
- Infectious diseases (meningitis or encephalitis).
- Spondylitis caused by tuberculosis infection.
- Intoxication of the body.
If the cause of inflammation is identified at the first stage of the disease, then it is possible to get rid of severe symptoms and restore damaged nerve processes.
Symptoms of occipital neuralgia
Primarily, neuralgia of the greater occipital nerve is characterized by headache. Her character is very specific:
- pain is concentrated behind the ears, in the occipital region, lower part of the neck, as well as in the eye area or above them;
- attacks occur unexpectedly when turning the head or touching the area of innervation, often when touching the skin of the head;
- painful sensations are localized on one side, although bilateral damage occasionally occurs;
- the pain looks like “lumbago” and disappears as suddenly as it begins;
- bright light causes pain in the eyes.
Treatment
You should immediately warn that it is better to avoid self-medication . Only the doctor selects the treatment regimen. The goal of traditional therapy is to eliminate pain.
Drugs
Did you know that...
Next fact
The following medications are usually prescribed:
| Anticonvulsants |
|
| Muscle relaxants to relieve muscle spasms |
|
| Anti-inflammatory drugs |
|
| Painkillers, antiepileptic drugs |
|
| Antidepressants |
|
Blockades
Nerve block is the fastest and most effective method to relieve pain. This is the most effective method of combating occipital neuralgia.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are used for injections:
- Metipred.
- Kenalog.
- Dextamethasone.
Treatment with blockades is highly effective . After a few minutes, the injected drugs begin to act and the neuralgia disappears.
After injections, subsequent attacks are much weaker. But you should know that you cannot constantly use this method, otherwise unpleasant consequences are possible.
Surgery
If the disease has become chronic and is accompanied by intense pain, surgical intervention is recommended.
It comes in two types:
- Microvascular decompression . The operation is performed using microsurgical equipment. During the procedure, pinched nerves are deactivated, which eliminates pain.
- Neurostimulation . The procedure blocks pain. The nerves are affected by electrical impulses. The method has no side effects, and possible damage is minimal.
Massage
To make the therapy more effective, massage is used, which is done in the area where the nerves exit. They are identified by painful points.
If the lesser occipital nerve is affected, massage the area behind the mastoid process. If a large nerve is damaged, the area between the upper vertebra of the neck and the mastoid process is rubbed.
Massage for neuralgia of the neck is performed after the pain has been eliminated. Massage of the back of the head involves a certain sequence of movements: stroking; squeezing; rubbing - zigzag, straight.
After the first 5 sessions, new techniques are added, for example, rubbing the neck.
It works like this::
- With your fingertips pointing straight ahead.
- Also with the pads of the fingers, but in a circular manner.
- Rubbing the affected area with the phalanges of the fingers, alternately with each hand.
You can also add a slight vibration. The session lasts no more than 15 minutes, and the total course is 14 procedures.
Treatment of occipital neuralgia
Sympathetic blockade
- Cost: 8,200 rub.
- Duration: 15-30 minutes
- Hospitalization: 2 hours in hospital
More details
At the CELT Pain Clinic, medical and surgical treatment methods are used to treat occipital neuralgia:
Drug treatment
Drug treatment methods are aimed at reducing pain. For this purpose, anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants are prescribed. In addition, massage and rest are prescribed.
A procedure called nerve block has proven itself well in our Pain Clinic. It consists of injecting the drug directly into the affected area, thereby achieving a long-lasting pain relief effect.
Surgery
If pain lasts a long time, is pronounced, or if conservative treatment does not bring the desired result, our specialists will recommend the following:
- pulsed radiofrequency ablation of the occipital nerves;
- stimulation of the occipital nerves - involves conducting electrical impulses through the nerves that block pain;
- microvascular decompression - involves the use of microsurgical techniques that eliminate compression of the nerves, and therefore the pain itself.
It is worth noting that occipital nerve stimulation is a minimally invasive method that does not have similar effects and is absolutely painless.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Features of the treatment of cervical neuralgia
Drug therapy is based on the use of drugs that relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms. For this purpose, patients are prescribed painkillers. To eliminate muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed.
Patients are also prescribed anticonvulsants, steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, sedatives, and B vitamins. In cases of extremely severe pain due to inflammation of the occipital nerve, novocaine blockades can be used.
Physiotherapy helps to achieve good results:
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- special massage;
- spinal traction;
- ultrasound therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy.
When treating scalp neuralgia, physiotherapy is combined with medications. This allows you to quickly get rid of pain and neurological manifestations.
In addition to relieving symptoms, it is important to pay attention to the root cause of neuralgia and eliminate it.
If the pain persists for a long time, is severe, and conservative treatment of occipital neuralgia does not bring results, radical measures may be resorted to. For this purpose, use:
- stimulation of the occipital nerves in the projection of the nerve exit (electric current is used);
- pulsed radiofrequency ablation of the occipital nerves;
- microvascular decompression (microsurgical technique to eliminate nerve compression).
Treatment with folk remedies
You can try to treat this disease using traditional medicine recipes.
These recipes will help alleviate the condition:
- Sleep-herb tincture . The raw materials are poured with boiling water and kept for 24 hours. I use the product once a day. The infusion is also very effective for neurasthenia and insomnia.
- Lilac ointment . Boil lilac buds and add pork fat. The resulting ointment is rubbed into areas of the neck and head that are inflamed.
- Willow bark decoction . Pour boiling water over dry bark. Then simmer over low heat for 20 minutes. The product is taken one spoon 5 times a day.
- Horseradish compress.
It is necessary to take into account that all folk remedies are used only after consultation with the attending physician.
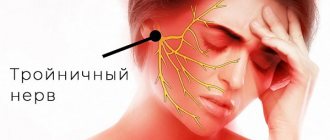
Trigeminal neuralgia: symptoms and treatment
After the first painful attack, you can grimace as much as you like, feel every millimeter of facial skin and even pat yourself on the cheeks approvingly. Everything is fine! But the fear of the next attack has already settled in my soul forever... This is how most of my patients describe the debut of a painful and difficult-to-treat disease called “trigeminal neuralgia” (trigeminal neuralgia, Fothergill’s disease).
Waiting for the pain
Unlike tension headaches, trigeminal neuralgia is characterized by sudden, short-term, intense, recurring pain in the area of innervation of one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve, usually on one side of the face, but can affect both sides, and can (in an atypical form) manifest as a burning sensation , pressing, aching, bursting, constant or wave-like pain or a feeling of goosebumps running across the face.
Attacks of these pains in the face (lip, eye, nose, upper and lower jaw, teeth, gums, tongue) can occur spontaneously or be provoked by talking, chewing, brushing teeth, touching certain areas of the face (trigger points that trigger an attack; usually located in area of the nasolabial triangle). Their frequency varies from single to tens and hundreds per day! During the period of exacerbation, more often in the cold season, attacks become more frequent.
The pain is so severe that patients cannot concentrate on anything else and are in constant tension, all the time waiting for the next attack (they do not touch the painful side of the face, do not brush their teeth, do not chew on the affected side). There have been cases where patients, unable to bear the pain any longer, committed suicide.
What really hurts
The main cause of true trigeminal neuralgia is compression (squeezing) of the trigeminal nerve root by an arterial and, less commonly, venous vessel directly at the brain stem, from where this nerve actually exits.
The trigeminal nerve, on the one hand, is the main sensory nerve of the face and oral cavity, on the other, it also contains motor fibers that innervate the masticatory muscles. Therefore, in addition to transmitting information to the brain about what our face is doing at any given time, the trigeminal nerve carries impulses to some of its own facial muscles, which is why pain is often accompanied by a tonic, long-term (trismus), or short-term (tic) contraction of these muscles.
There are several hypotheses to explain why nerve compression leads to the development of trigeminal pain, but none of them is yet generally accepted. In all cases, confirmation of a neurovascular conflict is carried out only with the help of MRI, so the doctor will definitely refer you to this study. Unfortunately, in 15% of patients, even an MRI is not able to accurately establish a diagnosis. Then electromyography (EMG) or electroneurography (ENG) can help doctors.
Diagnostic problems
But alas, most often after the first attacks a person is sent not to a neurologist’s office, but to a dental clinic. This is due to the fact that the area of pain is located not only on the face, but also in the oral cavity. Very often, healthy teeth are removed by mistake on the affected side, sometimes this “attraction” lasts for months and years, and only after losing half of the “emergency reserve” of teeth does the patient begin to suspect something...
The standard for diagnosing classical trigeminal neuralgia, according to the diagnostic criteria of the International Headache Society (IHS, ICHD-II), is the presence of at least 4 points out of the 5 below:
- The pain occurs in the form of attacks lasting from several seconds to 2 minutes in areas of the face corresponding to the zones of innervation of the trigeminal nerve.
- The pain is sudden, intense, sharp, similar to an “electric discharge”, caused by irritation of various areas of the face and oral cavity when eating, talking, washing the face, brushing teeth.
- Attacks of pain are stereotypical for each patient.
- There are no neurological symptoms during the interictal period.
- Taking carbamazepine causes pain relief at the onset of the disease.
Conservative therapy
Treatment always begins with conservative therapy, the basis of which is anticonvulsants (in particular carbamazepine). Their use at the onset of true trigeminal neuralgia leads to regression of the pain syndrome in 90% of patients. That’s why it’s so important not to delay seeing a doctor! However, with long-term use, the effectiveness of the drugs sooner or later decreases, toxic damage to the liver, kidneys, and changes in the cellular composition of the blood may develop, so conservative therapy can only be considered temporary.
In turn, patients prefer vascular drugs, antispasmodics, sedatives, ointments with anesthetics, physiotherapeutic procedures, acupuncture, laser therapy, and are happy to use traditional medicine methods and efferent methods of therapy (plasmapheresis, hemosorption).
In my experience, all this does not bring any particular relief, but it significantly distracts from the anxious anticipation of an attack. And... the time before examination and surgical treatment is delayed, which sometimes leads to tragic consequences. Meanwhile, the operation cannot be delayed.
Neurosurgical treatment
As for surgical treatment, today neurosurgeons have two main methods at their disposal:
Vascular decompression.
The essence of the method, as the name suggests, is to eliminate compression, i.e. compression of the nerve by the adjacent vessel. The method is indicated for all types of vascular compression of cranial nerves. To use it, an established diagnosis of classical trigeminal neuralgia is sufficient. A contraindication is the presence of severe concomitant pathology that makes it impossible to perform a neurosurgical operation.
Stereotactic radiosurgery, or “gamma knife”.
To achieve the effect, the trigeminal nerve root is irradiated with a dose of ~ 90 Gy and the affected cells are “burned out”. Indications for the use of this method are aggravated somatic status (presence of chronic diseases, mainly cardiovascular and endocrine) and the patient’s categorical refusal of surgical intervention. The use of the method is justified by the non-invasiveness of the technique, which significantly reduces the likelihood of complications, however, radiosurgery is less effective and has a higher number of relapses.
In general, the success of treatment for trigeminal neuralgia, just like the treatment of other diseases, depends on a clear diagnosis, strict adherence to surgical technologies and... your timely visit to the doctor!
Valentina Saratovskaya
Photo thinkstockphotos.com
Products by topic: [product](carbamazepine)