Find out more about nervous diseases starting with the letter “N”: Sleep disturbance; Narcolepsy; Hereditary cerebellar ataxia of Pierre-Marie; Spinal circulatory disorders; Trigeminal neuralgia; Neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes; Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal node; Neuralgia of the ear ganglion; Neurasthenia; Neural amyotrophy of Charcot-Marie-Tooth; Acoustic neuroma; Neuroma; Optic neuritis; Pharyngeal neuritis; Neuritis of the facial nerve; Neuritis; Obsessive-compulsive neurosis; Pharyngeal neurosis; Neuroses; Neurosis-like stuttering; Femoral nerve neuropathy.
What is glossopharyngeal neuralgia?
If the cranial nerve is affected by a quarter on one side, and paroxysms of pain appear in the tonsils, soft palate, pharynx and ear, then the patient may have neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve. With this pathology, a violation of the taste perception of the posterior third of the tongue, on the affected side, is detected. Hypersalivation and decreased reflex of the palate and pharynx are also noted. To make a diagnosis, an examination by a neurologist or dentist is required. CT and MRI of the brain are indicated as hardware diagnostic methods. In most cases, treatment is conservative, including:
- Anticonvulsants;
- Analgesics;
- Sleeping pills and sedatives;
- Vitamin therapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- General strengthening procedures.
Where is surgical treatment for paralysis of the facial muscles performed?
Specialists from the Department of Maxillofacial and Reconstructive Surgery of the Federal State Budgetary Institution NKCO FMBA of Russia, together with the Department of Ear Diseases, have developed and put into practice a unique method of surgical treatment of patients with paralysis of the facial muscles. The first operations on patients with this pathology in Russia were performed by specialists from the Federal State Budgetary Institution NCCO FMBA of Russia - otosurgeon, MD. Hassan Diab and maxillofacial surgeon Ekaterina Orlova.
A healthy person rarely thinks about how important facial expressions are and what role they play in our lives, especially a smile... Smile more often!
Structure of the glossopharyngeal nerve
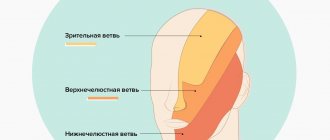
N. glossopharyngeus or glossopharyngeus nerve begins in the nuclei of the medulla oblongata. It is based on motor, sensory and autonomic parasympathetic fibers. Moreover, the sensory fibers begin in the sensory nucleus common to the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves. They innervate the mucous membrane of the pharynx, soft palate, tongue, tonsils, and Eustachian tube. The sensation of taste in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue is provided by taste fibers emerging from the nucleus of the tractus solitarius. The taste fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve are responsible for the taste sensations of the posterior third of the tongue and epiglottis.
The motor fibers originate in the nucleus ambiguus and innervate the stylopharyngeal muscle, which is necessary for raising the pharynx. Together with the vagus nerve, they form the reflex arcs of the pharyngeal and palatal reflexes.
Parasympathetic fibers originate in the salivary nucleus. Being part of the tympanic and lesser petrosal nuclei, they reach the autonomic ganglion, and with the branch of the trigeminal nerve they regulate salivation of the parotid gland.
Since the pathways and nuclei of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves are common, isolated pathology n. Glossopharyngeus. But more often symptoms of combined lesions are observed.
Pathogenesis
There are cases of idiopathic Sicard syndrome. At the same time, it is almost impossible to establish the etiology of the disease. Provoking factors may be:
- Acute or chronic intoxication;
- Otitis;
- Pharyngitis;
- Tonsillitis;
- Sinusitis;
- Atherosclerosis;
- Viral infections incl. flu.
Secondary neuralgia occurs due to:
- Arachnoiditis, encephalitis and other infectious lesions of the posterior cranial fossa.
- TBI.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Meningiomas, gliomas, medulloblastomas and other intracerebral tumors of the cerebellopontine ganglion.
- Compression and irritation of any part of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Nasopharyngeal tumors.
- Intracerebral hematomas;
- Carotid artery aneurysm;
- Hypertrophy of the styloid process.
- Overgrowth of osteophytes of the jugular foramen.
- Ossification of the styloid ligament.
In some cases, pathology may be the first symptom of cancer of the larynx or pharynx.
Causes of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes
The following factors can provoke the development of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes:
- physical impact - prolonged or regular hypothermia of the ganglia;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the oral cavity - stomatitis, multiple caries, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- infectious pathologies - viral diseases, sepsis, syphilis, tuberculosis;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system and pelvic organs;
- negative consequences of surgical interventions - removal or prosthetics of teeth;
- foci of infection in nearby organs - sore throat, otitis media, sinusitis.
Often neuralgia can appear due to intoxication of the body with poisons, salts of heavy metals, and low-quality alcohol. It can also develop against the background of allergic and endocrine diseases, and be one of the manifestations of hypovitaminosis.
Symptomatic picture
Clinical signs include painful paroxysms lasting from a few seconds to three minutes. A sharp acute pain originates at the root of the tongue and instantly spreads to the tonsils, soft palate, ear and pharynx. May radiate to the eye, neck and lower jaw. Pain can be triggered by coughing, chewing food, its temperature, yawning, swallowing and even talking. During paroxysm, dry mouth is noted, immediately after hypersalivation. But dryness is not a mandatory sign of diagnosis, because the secretory insufficiency of the parotid gland can be compensated by the remaining salivary glands.
Paresis of the levator pharyngeal muscle does not cause swallowing disorders. But difficulties in chewing and swallowing associated with impaired proprioceptive sensitivity, which is responsible for the position of the tongue, may be noted by patients.
The disease has a wave-like course, worsening in autumn and winter.
Results of surgical treatment of paralysis of facial muscles
The result of these operations (with the exception of static correction) does not appear immediately. As a rule, the result appears after 4-8 months - the first weak movements appear, which gradually intensify with mandatory adherence to the specialist’s recommendations. This is due to the fact that nerves re-grow, according to the literature - up to 1 mm per day. First, sensations appear in the form of “lumbago”, “running goosebumps”, etc. This indicates the growth of the nerve along the nerve fibers. The first movements are quite weak, since the muscles have been without load for a long time, so it takes time for their functional restoration, and it is necessary to constantly load them rationally. Thus, rehabilitation plays a very important key role in the final outcome. And the patient must be prepared for daily exercise and not immediate results.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist, who, if necessary, can involve an otolaryngologist and dentist. During the examination, the doctor determines analgesia, that is, the absence of pain sensitivity at the base of the tongue, upper parts of the pharynx, and tonsils. Taste sensitivity is also studied, for which a taste solution is applied to symmetrical areas of the tongue. The diagnosis is confirmed by isolated unilateral taste disorder in the posterior third of the tongue. Bilateral disruption is typical for diseases of the oral mucosa, such as chronic stomatitis.
The pharyngeal reflex needs to be checked. To do this, touch the back wall of the throat with a paper tube, which provokes a swallowing movement and occasionally a cough. Normally, touching the soft palate should be accompanied by a lifting of the palate and uvula. Sicard syndrome is characterized by the absence of reflexes on one side. But a similar symptomatic picture can occur with damage to the vagus nerve. If the pharynx and pharynx are strewn with herpetic rashes, the doctor can diagnose ganglionitis of the ganglionitis of the glossopharyngeal nerve nodes, which differs in almost identical n. Glossopharyngeus clinical picture.
To establish the root cause of symptomatic neuritis, neuroimaging diagnostics is needed:
- MRI or CT scan of the brain;
- Electroencephalogram;
- Echo-EG;
- Ophthalmoscopy with consultation with an ophthalmologist.
It is necessary to distinguish between neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve and diseases that cause painful paroxysms of the face and head. These include:
- Neuralgia of the ear ganglion;
- Trigeminal neuralgia;
- Oppenheimer's syndrome;
- Glossalgia;
- Ganglionitis of the pterygopalatine ganglion;
- Retropharyngeal abscess;
- Tumors of the pharynx.
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Facial nerve neuropathy requires the fastest and most accurate diagnosis and comprehensive, comprehensive treatment. Only in this case can a rapid restoration of impaired functions be achieved. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic use the most effective techniques:
- modern drug regimens that affect the cause of the disease and relieve symptoms;
- physiotherapy courses for tissue restoration;
- massotherapy;
- training in facial gymnastics techniques;
- taping the affected areas;
- observation throughout therapy, adjustment of dosages and medications if necessary;
- a full range of measures for quick and complete rehabilitation;
- organization of sanatorium-resort treatment for the most complete recovery.
Therapy
To treat neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve, conservative therapy is prescribed. The only exception is if the underlying cause is tumors and hypertrophy of the styloid process, leading to compression of the nerve. In these cases, surgery is indicated.
To relieve pain, a 10% solution of cocaine is prescribed, which is applied to the root of the tongue and pharynx. This allows you to eliminate paroxysms for 6-7 hours. If this remedy turns out to be ineffective, a 1-2% novocaine solution is injected into the root of the tongue. Non-narcotic analgesics and anticonvulsants are also prescribed internally. If the pain syndrome is pronounced, it is advisable to prescribe sedatives, hypnotics, antipsychotic medications and antidepressants. AFT, multivitamin complexes and FiBS are used as general strengthening agents.
Among the physiotherapeutic procedures that have proven effectiveness are:
- SMT on the area of the larynx and tonsils;
- Diadynamic therapy;
- Galvanization.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic provides each visitor with medical care of the highest level, regardless of his age and reason for visiting. We offer:
- screening diagnostic programs to assess health status;
- accurate and quick diagnosis of obvious and hidden pathologies;
- modern methods of drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage;
- minor surgical operations within the walls of the clinic;
- course treatment of chronic diseases in comfortable day care wards;
- organization of hospitalization in a specialized hospital if necessary;
- preparation of documents for sanatorium-resort treatment, selection of sanatorium;
- remote consultations with foreign doctors to obtain an alternative opinion;
- modern rehabilitation programs.
Facial nerve neuropathy is a fairly common pathology. To prevent it from leading to irreversible facial asymmetry, contact a specialist as soon as possible. Neurologists at the Energy of Health clinic will always come to the rescue.