Article for the “bio/mol/text” competition: Cellular processes that enable the exchange of information between neurons require a lot of energy. High energy consumption has contributed to the selection of the most efficient mechanisms for encoding and transmitting information during evolution. In this article, you will learn about the theoretical approach to the study of brain energy, its role in the study of pathologies, which neurons are more advanced, why synapses sometimes benefit from not “firing,” and how they select only the information the neuron needs.
What are the rhythms?
The rhythms generated by the brain differ into five types depending on the amplitude and frequency of vibrations:
- The alpha rhythm is recorded in 95% of healthy patients at the moment of relaxation, when they close their eyes. Best expressed in the occipital regions. α-wave frequency 8-12 Hz. With visual stimuli, there is a deficiency of this radiation. At the same time, in people with congenital blindness or optic nerve atrophy, the α rhythm is absent.
- Beta rhythms are the fastest brain oscillations in the range of 12-40 Hz. They are associated with the processes of learning and concentration. Therefore, they are formed in a child during the development of logical thinking. Normally, this process ends by age five. Beta waves are generated naturally when you are awake. Under stress, their level increases, but a deficiency, on the contrary, is associated with absent-mindedness syndrome, depression and emotional disorders. Without β-activity, no meaningful human activity is possible.
- The gamma rhythm is clearly visible when solving complex problems. These are the highest frequency rhythms generated during an active thought process. Completely disappears in the deep sleep phase.
- The delta rhythm is characteristic of the recovery period and natural sleep. These are the slowest waves. They are formed in the prenatal period. Asynchronous delta waves appear during coma or drug intoxication.
- Theta activity manifests itself in the fetus already at 2-3 months and predominates in children under three years of age. They represent patterns of electrical activity in the range of 4-8 Hz. Normally, theta waves of an adult appear in the twilight state, during the transition from sleep to wakefulness. A significant number of them can be observed in a confused state, with mental disorders. A large amount of θ rhythm can signal a state of chronic stress.
Science and clinical practice
Physiology of the brain.
We often compare the human brain to a complex computer. This analogy is not very successful, but if we talk about the real capabilities and functions of the brain, then the number of logical processes that occur in it is amazingly large. The human brain consists of three main elements:
- Glial cells
- Neurons
- Dendrites
1) Glial cells
The name “glial” comes from the Greek word “glia,” meaning “to glue.” Although these cells have membrane potential, glial cells are largely nerveless and serve a supportive role for the brain and spinal cord.
7 types of glial cells have been identified, all of them perform different functions. Glial cells maintain high levels of ribonucleic acid (RNA), proteins, and enzymes. One of the enzymes produced by glial cells is acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Acetylcholinesterase is directly related to memory and the ability to process information. Some types of glial cells, especially astrocytes, provide nutrition for neurons. Others synthesize myelin, which is used to prevent nerves and neurons from crossing each other. Microglia and astrocytes are phagocytic, meaning that they clear the central nervous system of dead cells and waste products. Glial cells have the ability to divide and multiply throughout life. They have branches, but do not have axons or dendrites. Recent research has revealed that some glial cells can act as amplifiers, like transistors. Their purpose is to support neural connections and ensure the functioning of the nervous network connecting various areas of the cerebral cortex. The human brain is 5 times larger than the chimpanzee brain, but contains only 30-50% more neurons. It appears that the intellectual boundaries that separate humans from apes are a consequence of the action of glial cells in the human brain, which outnumber neurons by about 5 to 1. As a result of new technological developments in the creation of modern research instruments, scientists have been able to study the various types of activity that occur in glial cells. Research by neuroscientist Gary Lynch of the University of California at Irvine has shown that in the embryo, before the growth of neurons and axons, glial cells exhibit increased activity. Glial cells divide and move within the brain through intact tissue. They travel long distances in the brain to reach active areas of the brain, and those already present show incredible responses. They send out branches and become very large. All this happens before the axons grow from the neurons.
2) Neurons
Neurons are the nerve cells of the brain. They form the gray matter, which is the outermost 2 mm layer of the brain. Neurons consist of a cell body, an axon, and one or more dendrites.
The function of neurons is to create and conduct nerve impulses.
By the second trimester of pregnancy, the developing brain is already capable of producing about a hundred neurons per minute. By the age of two, a child may already have a hundred million neurons in the brain. People may lose neurons over time, especially in the part of the brain that is least used, but the loss of neurons is more than offset by the increase in the number of dendrites. . The outer surface of the brain, on which neurons are located, consists of convolutions and grooves (folds and convolutions of the brain). These gyri and sulci increase the surface area of neurons.
If we straighten out the furrows and convolutions of the brain, we get a surface approximately one and a half square feet in area.
3) Dendrites
This word comes from the Greek tree. Axons and dendrites serve to connect different neurons. Dendrites are formed due to processes in the protoplasm of neurons, and transmit impulses to the cell body of the neuron. Typically several hundred dendrites are involved. They form connections, called “synapses,” with other neurons. As a result, dendrites are the brain's "wire" system. They are shaped by thought processes, environmental influences, learning and life experiences. It is estimated that an educated adult develops approximately 1 trillion dendrites in the brain, which in physical measurement would be approximately 100,000 miles (160,934.4 km). Figure 1 shows a neuron and its dendrites.
BRAIN WAVE ACTIVITY
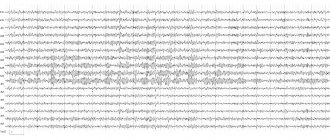
A typical neuron takes 1 microsecond to respond to a stimulus, but when millions of neurons respond in unison, they produce “swinging” electrical discharges. These discharges create a rhythm called a “brain wave.” These rhythms are observable via EEG. EEG records and measures huge numbers of neurons responding simultaneously. These rhythms of brain activity waves are formed into several groups, depending on their frequencies:
Beta, Alpha, Theta and Delta.
Michael MacKenzie
The electrical activity of the brain can be determined through an EEG (electroencephalogram), which measures the frequency of the electrical potential. This frequency is measured in cycles per second or Hz (Hertz). At any given time, these frequencies determine your mood. Frequency speed allows us to group our brain waves into four categories.
Beta waves are the fastest brain waves, ranging in frequency from 13 to 100 Hz. During Beta wave activity we are in a normal state of wakefulness, alertness and concentration. When we feel anxious or anxious, these are fast beta waves (30 Hz). When we feel threatened, in extreme danger, or in fight or flight, these are super fast beta waves.
If you close your eyes, relax, become passive and unfocused, your brain wave activity will slow down and alpha waves will appear. They range in frequency from 8 to 12.9 Hz. We enter a state of “overlearning” within the higher end of Alpha waves, and we begin to produce calming neurochemicals. The deeper structures of the Alpha rhythm are characteristic of traditional meditation.
As calm and relaxation deepen into sleepiness, the brain shifts toward slower theta waves. The frequency range of theta waves is from 4 to 7.9 Hz. Theta waves are often accompanied by unexpected, dreamlike mental images. Quite often these images can be accompanied by vivid memories; as a rule, childhood memories predominate. Theta brainwave activity is associated with healing, increased creativity, sudden insight (eureka) when everything suddenly becomes clear. Even very advanced meditators can achieve the theta state within a short period of time.
Delta waves are the slowest brain waves, ranging in frequency from 0.1 to 3.9 Hz. Typically, people sleep during delta waves, but there is evidence that it is possible to remain conscious in this extremely deep trance-like state. Also, within the delta wave activity of the brain, the production of healing somatotropin increases significantly.
Each of these groups represents a specific type of cortical activity and is associated with states of consciousness such as anxiety, calm, dreaming, or sleep.
We constantly produce a certain amount of all these frequencies at the same time. Therefore, the state of our consciousness reflects the mixed activity of the rhythms of different waves of brain activity and their localization. The rhythm of waves of brain activity is characterized by the highest power of wave activity of a certain category. For example, a person with his eyes closed produces a large amount of alpha and a small amount of beta waves in the visual cortex, because it does not process visual information.
When the eyes are open, the production of alpha waves is sharply reduced, and the power of beta waves increases as a result of the processing of incoming visual information in the visual cortex. Each of the rhythms of brain waves and different states of consciousness corresponding to each type of waves. The classification of brain wave rhythms changes as scientists learn more about the brain and states of consciousness. For example, many of these categories now have different subgroups.
BETA WAVES
Beta waves are fast waves, low in amplitude, approximately 14 to 40 cycles per second (Hz). Beta waves are generated naturally when we are in the waking, alert state of consciousness. Initially, beta waves are a data processing process involving hundreds of small calculations between two nearby cortical areas that work together to achieve a result (“What was that sound or sight?”, “What is 2 + 3?”, “Is this dangerous?” ?”, “I'm afraid”, “What should I do?”). There are 3 main subgroups of beta waves: Gamma (35 to 40 Hz), Beta 2 (24 to 34 Hz) and Beta 1 (14 to 23). Gamma waves, the fastest, reflect the peak activity of consciousness. Excessive beta 2 activity is associated with heightened emotional states such as anxiety and fear. Beta 1 frequencies are associated with cognitive processes such as problem solving and reasoning.
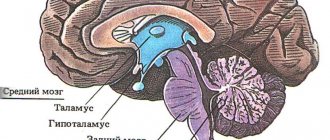
ALPHA WAVES Alpha waves vibrate in the range of approximately 8 to 13 Hz. Alpha activity is vibrations between fragments of the cortex and the thalamic thalamus, known as the corticothalamic lemniscus. Alpha waves occur during periods of sensory rest (for example, in a quiet room with eyes closed), mental relaxation, deep relaxation, meditation, or peaceful consciousness (dissociation). Alpha waves are the desired result of meditators. Traditional meditation methods require 10 years of practice to achieve ideal alpha wave production. The production of alpha waves is reduced when this part of the brain processes sensory information, as well as during problem solving and cognitive activity. Increasing the number of alpha waves gives:
- feeling of peace
- improved academic performance
- warmth in the extremities
- increased productivity in the workplace
- feeling of well-being
- decreased anxiety, improved sleep
- improvement of immune function.
It is believed that the most creative geniuses, such as Einstein, were constantly in an almost unchanged alpha state.
Most of these creative people had poor performance in school and were considered troubled students. Perhaps they were too focused on creative activities to pay attention to their studies. In the last few years, new subgroups of alpha waves have been identified. Mu waves (sometimes called Talpha) are borderline between Alpha/Theta waves (from 7 to 9 Hz). Their active production is associated with a healthy state of consciousness, giving exceptional intuition and the experience of personal transformation. Some researchers believe that “healthy” mu activity can reduce irrational anger and anxiety from hidden problematic childhood memories or past traumas. Examples of these waves of brain activity are Schumann resonance or the “fifth stage” of meditation. THETA WAVES Theta wave frequencies are from 4 to 8 Hz. Theta waves are associated with the sleep state, the twilight state, the hypnotic trance state, the REM sleep phase and the dream state. In this state, memory activity increases. Memory improves (especially long-term memory), access to the subconscious increases, the possibility of free associations increases, creativity increases, and unexpected insights occur. This is a mysterious, special state of consciousness. For a long time, scientists could not study this state of the brain, because... an ordinary person cannot remain in it for a long time without falling into sleep (which also produces a large number of theta waves).
DELTA WAVES Delta waves are the slowest waves of brain activity with frequencies ranging from 1 to 4 Hz. Delta waves are dominant when we fall asleep and continue to dominate during deep sleep. Some researchers are confident that delta waves are present in healers in a state of “healing” and in psychics while receiving information. The following table presents a summary of the positive waves of brain activity associated with the activity of different groups.
Positive Factors Categories of Brain Waves
Possibly associated with the peak of vital activity. Gamma 35 - 45 Hz Very active external attention. Beta 2 22 - 35 Hz Active external attention. Beta 1 15-22 Hz Relaxation, passive attention. Slow beta waves 12-15 Hz Relaxation, inner attention, meditation, healthy mental state. Alpha (Upper) 9-13 Hz Deep meditation, insight, Schumann Resonance, hypnosis Slow alpha waves - Mu/Talpha 7-9Hz Creativity, REM sleep phase, hypnagogic state Theta 5-7Hz Improved sleep. Delta 1 -4 Hz
Within a few minutes, the brain usually produces a certain amount of all types of waves. However, for a specific type of activity or behavior, the brain is able to initially produce waves of one group.
Essentially, the waves of brain activity are like the waves of a lake. When strong winds blow, large waves appear far out in the lake (high amplitude, low frequency). And when we throw a pebble into the lake, small waves appear very close to the place of disturbance (low amplitude, high frequency). An interesting relationship is that as the frequency increases, the amplitude decreases. Figure 3 shows the relationship between the types of behavior associated with the predominance of one frequency group.
BRAIN WAVES AND HUMAN HEALTH
A healthy brain performs many important mental functions simultaneously, producing a large number of waves of brain activity of different frequencies that reflect these functions. In today's stressful lifestyle, we often exhibit increased beta activity. To overcome this negativity, many are looking for ways to produce alpha waves - a peaceful existence, relaxation. When we increase our alpha and theta (including mu) activity through constructive processes - meditation, exercise, audio visual stimulation (AVS), we achieve changes in the state of consciousness or "alpha activity". It is important that we learn to produce alpha waves on a daily basis through meditation or ABC. However, many find that it is easier to achieve alpha activity through the use of destructive means such as drugs or alcohol. Also, the constant, uncontrolled, abnormal presence of low-frequency alpha or theta activity is the cause of fatigue or painful conditions associated with insomnia, depression, attention disorders, premenstrual syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome. The most important aspect linking brain waves to human health is the ability to change these states according to the demands of the situation.
Therapeutic effect
Brain wave therapy continues to be studied. According to already available data:
- Alpha rhythms help reduce anxiety, tension and restlessness, and improve memory. It accelerates blood supply to the brain structures, increasing the saturation of the body with oxygen and beneficial microelements. Facilitates the recovery period after illness. Reduces the negative impact of traumatic situations. Determines the release of the neurotransmitter serotonin, increasing its level in the body.
- Beta stimulation helps improve learning, communication skills and perseverance in patients. In addition, such exposure helps reduce fatigue.
- The effect of gamma rhythms has proven itself to be effective in enhancing the speed of information processing and stimulating short-term memory. These frequencies have also been found to have a beneficial effect on the brain in chronic migraine. In approximately half of the subjects, the frequency and intensity of attacks decreases.
- Stimulation of the δ rhythm helps reduce stress levels and relieve attacks of chronic pain, including cephalgia.
- Exposure to θ waves can enhance creativity, improve memory, control over the emotional sphere, and enhance intuition. It helps reduce anxiety and stress, strengthen the immune system, and enhance long-term memory, since the rhythm of theta waves is characteristic of the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for storing information and memories.
Delta waves
The delta waves of the human brain are recorded at the lowest frequency. They can operate in a rhythm from 0.1 to 4 hertz. When neurons begin to emit such waves, people are in a state of trance or dreamless sleep. The rhythm can be compared to a light symphony
This type of waves is associated with a person’s involvement in some process when everything else does not interest him. It is believed that every child under one year of age constantly experiences a predominance of delta waves in the head. They help to navigate in space and time, make one anticipate various dangers, increase intuition, and develop instincts. As a rule, the presence of developed delta waves is observed in people engaged in research into human psychology and feelings, i.e. from psychotherapists.
If you notice the work of such waves, they will immediately complete their activity.
This is the type of waves that allows you to establish a connection with the unconscious. To do this, you will need to overestimate the degree of their activity. When activated, a person’s consciousness turns off and is distracted from the outside world, and with good training, one will be able to independently and consciously enter a state of trance. However, even with weak delta waves, a person may have problems concentrating on any task. To do this, you will need to weaken their effect by showing maximum activity.
Some people have a large amplitude of delta waves. They have very developed intuition. They can literally think a minute or second before an event that it will happen. This often happens to them, for example, before meeting an acquaintance or shortly before receiving a call on their mobile phone. They can also sense other people. This manifests itself both emotionally and physically. An excess of waves leads to problems. They manifest themselves psychologically. Waves of excessive brain activity of this frequency lead to the fact that a person receives too much information at an unconscious level. Also, people often feel guilty for someone else’s pain, which they suddenly begin to feel.
Clairvoyants and healers actively use the power of delta waves when receiving the necessary information.
Alpha wave stimulation
There are several ways to stimulate the body’s wave activity:
- Breathing exercises that allow you to maintain deep breathing saturate the brain cells with oxygen. Systematic breathing exercises promote the generation of alpha waves.
- Listening to stereo sounds with alpha waves is a technique accessible to everyone.
- Yoga and meditation are powerful activators of the α rhythm.
- Hot baths can help you relax and switch to alpha wave production mode.
Pathological deviations
Disturbances in brain wave activity are observed when:
- Oligophrenia. With it, the total activity of alpha rhythms is abnormally increased.
- Epilepsy, which causes disturbances in the frequency and amplitude of wave activity. This is associated with the development of direct or interhemispheric asymmetry in the hemispheres of the brain.
- Hypertension, weakening the frequency of alpha rhythms and increasing beta activity. Circulatory and cardiovascular system disorders always affect brain wave activity. A similar picture can be observed with beta-lactamase activity of bacteria.
- Paranoid schizophrenia, in which the brain generates an increased number of beta rhythms.
- Cysts and inflammatory processes of the corpus callosum. They cause severe asymmetry between the hemispheres, reaching 30%.
- The pathological picture can occur with traumatic brain injuries, congenital or acquired dementia, and delayed psychomotor development in children.
To evaluate alpha rhythms, it is necessary to undergo an EEG from time to time. You can find out the addresses of clinics that perform this diagnostic procedure on the website.
How does information enter the brain?
All information from the body reaches the brain through the spinal cord
.
It resembles a thick telephone cable with a large number of wires inside. If the spinal cord is damaged, a person cannot move or feel what is happening to his body. Also, commands are given to the body through the spinal cord. But information from the eyes and ears goes directly to the brain
, bypassing the spinal cord.
This is why completely paralyzed people can see and hear without problems. Information from the spinal cord is processed in gray matter
, located on the surface of the cerebral hemispheres.
White matter
is called the “conducting system”, which consists of axons.
Disadvantages of the method
Excessive wave stimulation can cause negative reactions in the body. So, with an excess of alpha activity, a decrease in concentration develops, the formation of attention deficit, depression, and a decrease in visual clarity. A person begins to need daytime sleep and gets tired faster. In addition, under the influence of alpha waves, suggestibility increases.
The downside of beta wave stimulation is increased anxiety, overexcitement and the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder. There are signs of stress and paranoia. Also, under the influence of such stimulation, muscle tension increases and insomnia occurs. The effect on the cerebellar amygdala and hypothalamus provokes an increase in blood pressure.
When exposed to theta waves, you can develop concentration disorders, depression, hyperactivity, or, conversely, apathy. Under the influence of such stimulation, drowsiness, indifference to life, and increased suggestibility occur.
Therefore, before resorting to any methods of stimulating brain wave activity, it is better to consult with specialists.
Beta waves
Another type is beta brain waves. They are recorded in the range from 14 to 30 vibrations per second. Such fast waves are normal and are activated when a person is involved in the world around him. They are also actively emitted when excited, stressed or anxious. In order for them to begin to dominate, it is enough to start a conversation with any person. All the attention of people with dominant beta waves is directed to the environment.
Beta activity in the human brain is associated with increased blood pressure and a sharp increase in metabolism. Its rhythm is similar to drumming. If the brain rarely functions in the beta rhythm, then the person will experience frequent depression, lack of normal concentration, and very poor memory.
The dominance of such waves is considered a state close to stress, regardless of the nature of a person’s emotions.
You can develop beta rhythms through normal active life. Any communication, physical activity, manifestation of a social position, stress, fears - all this contributes to their increase. You can reduce their activity by simply relaxing and giving up negative thoughts.
There are three types of beta waves. They are separated for a more accurate characterization of several intervals, because The frequency range is quite large, and the sensations may be different. The following types are distinguished:
- Low (13-16 hertz). When the activity of brain neurons begins to emit impulses at this pace, weak involvement in the world around us begins to appear. This activates the left hemisphere of the brain. The person loses the feeling of relaxation, but there is still no excitement. With regular training of this frequency, the skill of managing concentration and attention will appear.
- Medium (16-18 hertz). At such frequencies, the right hemisphere of the brain is connected to work. An awareness of one’s “I” and surrounding things appears. People start to feel a little excited and involved in the world. When performing training, intellectual abilities and concentration will develop.
- High (18-30 hertz). Such waves are compared to driving fast in a sports car. The sensations are similar to those when a lot of adrenaline is released. Strong excitement and interest in the world around us and everything that happens appears.
The work of the brain in such a rhythm causes two sensations. On the one hand, a person is active and shows interest in the world around him. On the other hand, he is under a lot of stress.