Nicotine molecules bind to acetylcholine receptors, temporarily increasing their activity. This explains the feeling of mild euphoria, increased performance and a surge of energy after smoking a cigarette. But after half an hour the activity of the receptors drops. A person begins to feel the need for an additional dose of nicotine, since there are no natural substitutes for this substance in the body. If you do not smoke again, nervousness and anxiety appear.
How does smoking affect the brain?
Several years ago in Germany, as part of the fight against smoking, they organized an action: how smoking affects the brain.
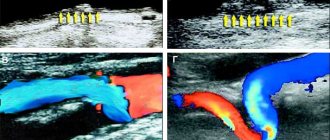
One of the exhibits of the action are posters with photographs of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain of a smoker and a non-smoker. You didn't have to be a doctor to see the difference. The feeling that the smoker simply has nothing in his skull! The action was quickly curtailed, and do you know why? Disputes began about the objectivity of the data provided. It doesn't take a visionary to suggest that large cigarette distribution concerns were involved.
Properties of nicotine
What is nicotine? It is an alkaloid - an organic heterocyclic substance consisting of carbon, nitrogen and hydrogen atoms. The group of compounds owes its name to its slightly alkaline chemical properties. Most alkaloids have an effect on the nervous system, among those. What people hear most are caffeine, cocaine, morphine.
According to its physical and organoleptic properties, nicotine is a bitter oily liquid. At certain temperatures it easily mixes with water, their densities are almost the same - about 1 g/cm3.
Nicotine dissolves well in environments with low polarity. This causes its rapid absorption through the skin and the blood-brain barrier. At high pH values, it easily penetrates through mucous membranes.
Where is nicotine found? The alkaloid is isolated from the shoots of plants of the nightshade family (tobacco, tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes). The concentration in tobacco is maximum – up to 14%. Nicotine is synthesized in plant roots, transported and accumulated in leaves. In the human body and warm-blooded animals, the compound breaks down to form safe metabolites.
The effect of smoking on cerebral vessels
Unfortunately, there is no organ in the human body that is not exposed to the harmful habit of smoking.
- Smoking changes the composition of the blood;
- Disrupts metabolism in the body;
- Affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- Causes diseases of the lungs, stomach, eyes, genitourinary system, liver.
The brain is also at great risk . Memory deterioration, the appearance of persistent headaches, depressive states, various kinds of neuroses and neurasthenia, insomnia are common symptoms of a smoker.
Studies have shown that to complete a task that takes an average of about eight hours, after smoking a pack of cigarettes it takes at least two more hours.
But people smoke in the belief that smoking will help them concentrate better and do their work better and better. Smoking in order to cheer up and improve concentration is a very common phenomenon and is nothing more than a myth and self-deception.
The risk of stroke for a smoker is many times higher than for a non-smoker. Why?
What is a stroke?
Stroke is a brain disorder caused by impaired blood circulation in the blood vessels of the brain. Stroke is divided into ischemic, hemorrhagic and mixed.
An ischemic stroke occurs when a blood vessel is blocked by a thrombus (a collection of cells or an abnormal blood clot). Smoking significantly speeds up the process of blood clot formation. These blood clots can remain attached to the vascular wall for a long time and continue to be overgrown with other cells, which leads to its enlargement. In the future, during physical activity, this blood clot can break off and begin to “travel” through the blood vessels, and here the further outcome will depend on where this blood clot ends up.
If it enters one of the arteries supplying a certain area of the brain, then this artery is immediately blocked and oxygen stops flowing to this area of the brain - an ischemic stroke develops. It should be added that this part of the brain has died and cannot be restored, which means that if a person manages to survive, he will be left with a large neurological deficit.
Smokers often experience thrombosis of cerebral vessels, which is the most common cause of strokes as such.
The second most common cause of strokes in smokers is severe damage to the arteries, as a consequence of the influence of smoking on the blood vessels of the brain. Due to damage to the arteries of the brain, they rupture and blood flows into the brain, thus forming a hemorrhagic stroke.
The mechanism of development of nicotine addiction
Usually, addiction to tobacco begins in adolescence and is mistaken for some kind of self-indulgence.
However, this bad habit very quickly develops into addiction. First, of course, psychological, since for any smoker the process of smoking becomes a method of communication with other people, a means of distraction, concentration, etc. Most addicted people associate smoking with different situations - be it a break at work, waking up with a cup of coffee and a cigarette, waiting for transport, meeting and relaxing with friends, excitement before various events. Smoking becomes a powerful ritual, formed over the years, which can be very, very difficult to destroy (I’ll immediately explain that this is self-deception and self-hypnosis; it’s just as easy to walk 5 circles around the house), and then into the physical. In people, the self-defense function does not work, which should warn us from everything that can harm, because, subjectively, there is no direct and quick negative effect on the body. And even more so, no one immediately thinks about the effect of nicotine on the brain. However, it is very large. The formation of physical dependence on tobacco occurs with the participation of the central nervous system. The main substance that transmits impulses between the nuclei and cells of the central nervous system is the neurotransmitter dopamine. If a lot of dopamine is released, a person experiences pleasure, and when the amount of dopamine drops, he experiences withdrawal symptoms. After 7-10 seconds of smoking, nicotine enters the brain. After initial consumption, nicotine increases dopamine transmission, giving a pleasant sensation and causing addiction. Regular smoking changes the dopamine transmission complex, nicotine becomes part of this complex, that is, without this substance, dopamine transmission will not be normal. There is a strong craving for smoking, or nicotine addiction.
Effects of smoking on the brain
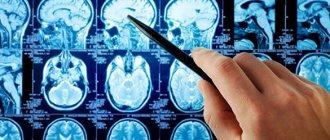
This is what a stroke looks like on a tomogram
Interesting facts: The effect of smoking on the brain occurs within ten seconds after the first puff. Smoking is recognized by the World Health Organization as a psychiatric disease. Smoking is the leading cause of brain cancer.
The most vulnerable, complexly organized and demanding system of the body is the nervous system. A person spends approximately a quarter of all energy received on brain function. This takes into account the constant stress on the muscles, liver, kidneys, stomach work and the continuous work of the heart. In addition, unlike the same muscles, the brain almost does not accumulate nutrients, but immediately processes them. Therefore, glucose remains the best food for the brain: it is processed very quickly, although it burns out quickly. These features make the brain uniquely sensitive to nicotine and other poisons from tobacco products.
The effect of smoking on the brain is not noticeable, at least at first, because the harmful effects of this poison, at least at first, are successfully compensated by the restorative properties of the body itself. However, over time, the difference in well-being becomes more noticeable, and the risk of certain diseases increases.
Smoking is nothing more than the effect of poison on the body; you will neither get used to it nor benefit from it over time. Over time, the condition only gets worse. This is especially true for three systems:
- respiratory, since first of all smoke affects the lungs, and the lion's share of pathogenic substances settles there;
- cardiovascular, since toxic substances are absorbed into the blood and affect blood vessels before penetrating other organs;
- nervous, because this system is the most receptive and closely related to the bloodstream.
Many people forget that the brain must be continuously supplied with blood, more abundantly and more intensely than most other internal organs.
Nicotine itself, according to scientists, is a nerve poison. In small doses, it, while remaining a dangerous and toxic substance, increases excitability. But this does not mean that nicotine can be regarded as a stimulant. Its impact disrupts the natural rhythms of many organs.
The surge of strength that comes immediately after smoking is due to the fact that first the vessels supplying blood to the brain dilate. But the reverse process occurs very quickly.
According to scientific data, smoking provokes special brain cells that process dead or infected cells to attack healthy ones. In addition, this habit, especially after a certain time, affects the composition of the blood itself, and this affects the immediate functions of this fluid, namely its ability to carry oxygen. Not only does blood enter the brain in insufficient quantities, but its quality also deteriorates.
All this leads to the following consequences, to combat which you will have to make an appointment with a neurologist:
- A smoker, over time and with an increased number of cigarettes smoked, suffers from a decrease in intellectual abilities. This occurs due to a decrease in the electrical activity of brain cells;
- memory deteriorates, it becomes more difficult to concentrate;
- solving certain problems requires a person to spend relatively more time. The difference is quite large - approximately 20%;
- Smoking gradually affects behavior - irritability appears, and sometimes there is a risk of nervous disorders.
Of course, smoking has a detrimental effect on the regeneration of nerve cells, so it is contraindicated for people suffering from certain neurological diseases, as well as people who have suffered injuries, such as concussion.
It is the narrowing of blood vessels that can be called the main destructive factor in the influence of this habit on blood circulation in the brain. Constriction of blood vessels leads to a lack of incoming blood, which causes oxygen starvation. As a consequence of this, the death of nerve cells occurs.
Smoking is also one of the main sources of risk for various types of stroke. Due to disruption of the circulatory system, there is a danger of blocking blood vessels in the brain. After all, due to smoking, the vessels have become narrower, so it is more difficult for blood clots to pass through their channels. There is also a risk of another type of stroke, in which the blood vessels themselves are affected. The consequence of this is extensive and often fatal hemorrhage. Stroke is one of the most common causes of death, second only to myocardial infarction among other diseases of the circulatory system.
Harm from hookah and electronic cigarettes
Many tobacco lovers, in an attempt to quit smoking, switch to electronic cigarettes (vapes), considering them completely safe for health. This is not entirely true. Such products do not emit combustion products, only vapor, but they are filled with liquid containing a certain proportion of nicotine.
This can be either a fairly high percentage or a minimal one. Any buyer can independently purchase the most suitable liquid. The presence of nicotine in such a liquid still has a slight negative effect on the body of a man or woman.
Today, nicotine-free liquids are available for sale, in which this substance is completely absent, but they contain substances such as propylene glycol and glycerin. When heated, these components have an aggressive effect on the organs of the respiratory system, disrupt the blood circulation process, and provoke an exacerbation of various diseases. It can be concluded that e-cigarettes are also harmful to health.
An alternative to conventional tobacco products is hookah, which has been the subject of controversy for many years. Fans of hookah smoking speak out about its safety:
- Hookah has a more gentle effect on passive smokers, since its vapors do not contain heavy metals and quickly and completely dissolve in the air.
- The product does not contain paper - it is its burning in a cigarette that is harmful, since it contains a large number of carcinogens.
- Before entering the respiratory system, hookah smoke is cleaned and cooled.
But besides the positive, there are also negative sides. Tobacco, which is used to smoke a hookah, contains a small proportion of nicotine, so harm to the body is still caused. In addition, since smoking occurs through inhalation, all harmful substances enter the lowermost parts of the respiratory system. Therefore, hookah cannot be called completely safe.
Smoking tobacco products, electronic cigarettes or hookahs has a detrimental effect on a person’s health and can lead to severe brain diseases. And the longer a smoker is, the higher the likelihood of pathologies such as atherosclerosis or stroke, which can lead to death.
How to restore your brain after smoking
The basis of the recovery process is to quit a bad habit. Smoking gradually kills the body; its harmful effects on the brain are too large-scale to be successfully compensated for by one or another method and make smoking harmless. You should consult a neurologist, who, after conducting all the necessary examinations, including hardware examinations, for example, MRI, will make a conclusion about the state of the brain and peripheral nervous system.
What happens after quitting smoking - stages of cleansing and restoring the body hourly and day by day!
The elasticity of blood vessels is restored on its own, and quite quickly - in just three weeks. After this period of time, a sufficient amount of blood begins to flow into the brain to fully supply it with oxygen, and therefore to function. The cells of the brain itself gradually return to normal. But atherosclerotic lesions will have to be dealt with separately with the help of a neurologist, lowering the level of cholesterol in the blood with the help of special drug therapy. The renewal of the nervous impulse system occurs within a month, during which time irritability and nicotine withdrawal will go away.