What is a psychological personality characteristic
Psychological characteristics are a set of components of the personality structure that determine the individual’s orientation, character traits and style of activity. Psychological characteristics are based on stable human properties: type of nervous system, temperament, nationality, abilities, qualities of mind.
The psychological characteristics of a person undergo some changes in the process of ontogenetic development, family upbringing and systematic education. Individual elements of psychological characteristics are formed only as a result of the development of character and the development of stable interests of the individual. Family education and schooling are being replaced by self-development and self-education of a person. Starting from adolescence, people consciously form their psychological portrait.
The main components of psychological characteristics are: resilience, unity and activity. On their basis, a person’s value orientations, worldview, style of activity and communication are formed. The dynamic properties of a person allow him to master social roles, achieve his goals, and maintain his socio-psychological status.
The characteristics of a person’s abilities determine his individuality.
Rules for conducting psychological and pedagogical examination
There are fairly clear rules for drawing up a student’s characteristics. One of the fundamental requirements for conducting psychological and pedagogical characterization is objectivity . It is equally important to carefully analyze the factors influencing a child’s development as a whole, taking into account the characteristics of the student. The child should be treated as delicately as possible, minimizing any coercion or pressure on him. Only in this case can a psychological and pedagogical characterization of a student or student be as objective and useful as possible.
The student's characteristics are written by the class teacher and signed by the school director. When writing a psychological profile of a child, you may need the help of a school psychologist, testing and diagnostic results.
Psychological structure of personality
In psychology, the personality structure includes its main characteristics:
- Biological features. These include: the type of nervous system and its properties, the relationship between the processes of excitation and inhibition in it, and the performance of the brain.
- Individual typological qualities. This block is determined by the characteristics of family upbringing and the type of parent-child relationships.
- Character traits that appear in the process of socialization of an individual. The determining factors for the formation of this element of the personal structure are the child’s socio-psychological status in the group of peers, the level of development of his communication skills, and stress resistance.
- Human life experience. It is often understood as an individual’s adaptive abilities, flexibility, ability to analyze one’s actions, and make independent decisions.
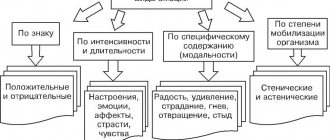
Emotions
Emotions are a mental reaction to any events. An emotional reaction is always subjective and has nothing to do with objective facts. Emotions are associated with the individual needs of the individual, as well as beliefs and experiences.
By type, emotions can be positive or negative. The first includes joy, passion, enthusiasm, faith, optimism, hope, satisfaction. The second - boredom, irritation, disappointment, anxiety, despondency, fear, sadness, excitement.
Basic psychological characteristics of personality
A general idea of a communication partner is made up of the basic psychological characteristics of his personality.
Interests and inclinations
Among all the psychological characteristics, when drawing up a personality portrait, experts first of all highlight the interests and inclinations of the individual. It is under the influence of a person’s interests that his attitude to reality is formed. The inclinations of the individual form the basis of the orientation and worldview of the individual, which explain certain behavioral reactions.
Interest, being a source of curiosity, directs our attention to certain things. Tendencies push a person towards certain types of activities. In an effort to learn something new, a person is driven by interest. When he begins voluntary practical activity, which is based on creativity, his actions are determined by his inclinations.
There are different approaches to classifying interests:
- An individual's interest can be passive or active. With passive interest, a person needs a mentor who will guide and correct his actions: recommend popular scientific literature, suggest ways to perform activities. With active interest, a person independently engages in one activity or another, reads relevant literature, and tries different work techniques. In the process of active interest, an individual’s individual style of activity is formed.
- According to their orientation, interests are classified into spiritual, social, political, and economic.
- Based on the number of people showing interest, interests can be divided into individual, public and group.
The origin of a person’s interests and inclinations is based on his needs.
If a person strives to satisfy only physiological needs, life seems uninteresting and monotonous to him. Deep interest in a certain type of activity and stable inclinations fill a person’s life with meaning and stimulate his self-development.
A person may have broad interests and be inclined towards different types of activities - in this case they speak of broad erudition and multidirectional development. Also, a person may have a pronounced interest in a particular area of activity - in this case they speak of a deep, sustainable interest of the individual. If, at the same time, a person’s interests and inclinations are subordinate to his life goal and do not interfere with conscientious work, their presence is regarded as a positive socio-psychological characteristic.
An example of the above can be a hobby. If doing what you love does not interfere with work and does not crowd out communication with friends from a person’s life, then it undoubtedly characterizes the individual in a positive way.
You can meet people whose interests and hobbies change quickly. Such people are keen, but not passionate. They are attracted to something new, bright, unusual. For example, they may enroll in a historical fencing class, but quit training after receiving the first injury. Their inclinations are due to natural impressionability. Having tried themselves in a new type of activity, they lose interest in it. Such qualities as inconstancy and impulsiveness will certainly find a place in their psychological portrait. It is very difficult for them to achieve success in any type of activity.
Abilities and giftedness
Ability is a person's biological predisposition to science, sports, or the arts.
Abilities as a psychological characteristic of a person determine the success of a person in performing certain actions. An example of an ability that influences a person’s psychological characteristics is observation. As a rule, teachers, writers, and drivers have this property.
In almost every type of professional activity, to successfully perform their job duties, a person needs the following abilities:
- visual memory;
- spatial thinking and imagination;
- concentration of attention.
When compiling a psychological profile, experts rely on the following types of abilities:
- Intellectual abilities. They provide rapid perception of information, its processing, storage in memory for a long time, as well as the ability of a person to apply existing theoretical knowledge in practice.
- Mathematical abilities. They explain man's inclination towards exact sciences. High development of mathematical abilities is often associated with good logical thinking. These mental properties are essential for accountants, programmers, physicists, mathematicians and economists.
- Technical ability. This group of abilities is needed by people involved in the design and development of innovative mechanisms.
- Creative skills. This type of ability is based on the inherent human imagination and ability to express fantasy.
- Communication skills. With their help, a person easily finds a common language with representatives of any social groups, shows empathy, and wins over them. Journalists, psychologists, politicians, and teachers use communication skills in their professional activities.
- Physical abilities. This group of abilities provides a person with sporting success.
- Literary ability. They explain the writing talent and poetic skills of people.
- Musical abilities. These include a sense of rhythm, a harmonic and melodic ear, and the ability to independently compose original melodies.
Abilities develop in the process of a person mastering practical activities. The basis for the development of abilities is inclinations. If nature has awarded a person with many inclinations, then they speak of talent, which allows him to be successful in various fields of science and art.
A synonymous concept for giftedness is talent, which determines a person’s ability to solve problems in a non-standard way. Talent is not a biological characteristic of a person. It grows out of a person’s interest in a certain activity and manifests itself in the process of performing this activity.
However, without specially organized systematic training, a naturally gifted person will not be able to become successful. In the learning process, the totality of natural inclinations determines the strength of knowledge acquisition and the rapid formation of skills and abilities.
It is impossible to equate a person’s talent and mastery in a particular activity, since giftedness represents a high level of development of natural inclinations, and mastery is the result of conscious work, which is based on the totality of theoretical knowledge, individual skills and abilities of a person.
The pace of development of abilities depends on the presence of giftedness, but learning is decisive in this process. If a person becomes a master of his craft, this means that a new level of development of abilities opens up for him.
It is important to understand that the lack of natural inclinations on the path to mastery in a particular type of activity can be successfully compensated for by such psychological characteristics of a person as: determination, perseverance, hard work, responsibility. These personality traits create the prerequisites for mastering almost any type of activity, provided there is a strong interest in it.
Thus, success in a particular activity can be explained by a variety of human abilities. The lack of some abilities is compensated by the high development of others. This means that the path to a dream is open to everyone. If a person is prepared for difficulties in the process of climbing a mountain, success will certainly await him at the end of the journey.
Every person has abilities. There is no point in comparing your own achievements with the achievements of other people. For the development of society, different talents are needed, which cannot belong to one person. When choosing a life path and profession, you should listen to yourself. After all, work that fully meets the interests and inclinations of an individual brings her not only material rewards, but also pleasure.
Temperament
Temperament is an innate psychological characteristic of a person. Classic patterns of temperament are:
- Sanguine. This is a cheerful person whose feelings quickly replace one another, as they are superficial. The main features of his psychological characteristics are: optimism, carelessness, initiative, multidirectional interests. He is fussy, his movements are fast and precise. The nervous system of a sanguine person is too mobile.
- Choleric. The main psychological characteristics of such a person are: explosive temper, hot temper, excitability, aggressiveness. He reacts vividly to events. His movements and speech are sharp, impetuous, and the pace of work is high. Choleric people lack a balance between the processes of excitation and inhibition in the nervous system.
- Phlegmatic person. This is a slow person who does not tend to demonstrate his experiences. His movements are smooth, his gait is measured. The main features of his psychological characteristics are calmness, prudence, and balance. The nervous system of a phlegmatic person is inactive.
- Melancholic. Such a person is distinguished by impressionability, vulnerability and touchiness. A melancholic person keeps his experiences to himself. Very often, melancholic people demonstrate high development of creative abilities.
“Pure” examples of temperament are rare in everyday life. Most often, the dominant type of temperament is complemented by some traits of another. For example: a phlegmatic person with a melancholic dominant, a choleric person with a sanguine dominant. The psychological characteristics of a person in this case will depend on the situation and circumstances.
So, temperament is a set of psychological characteristics of a person that determines a person’s general mobility, the speed at which his feelings arise and their severity, and the peculiarities of the manifestation of his emotional experiences. Each person needs to learn to subjugate his temperament - then the positive traits of his personality will come to the fore.
Character
Character is the psychological core of personality, which is formed from early childhood to adolescence. The structure of this psychological characteristic includes cognitive processes, emotionality, willpower, individual style of activity, and value orientations. Character traits determine a person’s attitude towards work. They are manifested in the motives of his activities, in the methods that he chooses to solve the assigned problems.
The psychological characteristics of a person are based on the following character traits:
- General character traits. They form the psychological type of the individual. These include: consistency, activity, integrity, honesty, discipline, courage.
- Character traits that reflect an individual’s self-attitude and self-perception. These are: modesty, self-esteem, shyness, touchiness, selfishness and egocentrism.
- Character traits that reflect an individual's attitude towards other people. This group includes: sociability, sensitivity, openness, politeness, willingness to help.
- Character traits that reflect an individual's attitude towards work. Among them: hard work, perseverance, initiative, accuracy, conscientiousness, responsibility.
Characterological features form the basis of a person’s worldview.
Knowing the characteristics of a person’s character allows us to predict his reactions. Systematic work on oneself allows a person to form his character, develop positive qualities in himself and eliminate negative ones.
How does Platonov's method work in psychology?
In fact, the described method is successfully used in the field of psychiatry and psychology. After all, before helping a person solve his problem, a specialist characterizes his personal qualities.
So, how to write a psychological portrait of a personality? Examples of this are quite varied. One of them implies, in addition to describing the type of temperament, also defining the emotional side of human character. For example, experts consider 4 types of emotions: demonstrative, pedantic, stuck, excitable.
Methodology for compiling psychological characteristics
Psychological characteristics of a person are compiled by psychologists using the following methods:
- Observation. Through specially organized observation, the psychologist receives information about the characteristics of an individual’s behavior. In psychological characteristics, observation results indirectly reflect personality characteristics.
- Psychodiagnostic methods. Using personality tests and questionnaires, the psychologist determines the client’s temperament type, his interests and inclinations, and the prevailing motives for his activity. This information is the main one in the psychological characteristics.
- Sociometry. With the help of this diagnostic tool, the psychologist receives information about the socio-psychological status of the individual in the educational or work community. Sociometry allows us to identify the characteristics of a person’s interpersonal interaction with friends and colleagues.
- Interview. If sufficient information about a person cannot be obtained through tests, the psychologist develops a series of questions that he asks the client. This method of collecting information is used to clarify facts and eliminate contradictions.
Psychological characteristics begin with the listing of a person’s personal data: indicating the last name, first name and patronymic, date of birth, place of residence, reporting information about family members and characteristics of family upbringing. The following are described:
- inclinations and interests;
- personality abilities;
- characteristics of temperament and character;
- a person's attitude towards himself;
- a person's attitude towards other people;
- a person's attitude towards work.
An example of a person's psychological characteristics
Letovaltsev Andrey Yurievich
Date 04/19/2008.
Mother: Letovaltseva Anna Gennadievna.
Father: Letovaltsev Yuri Alekseevich.
Place of residence: Novodvinsk
The child is raised in a complete family. Parents take an active part in the boy's life. For Andrey, his older brother is a role model.
The boy shows interest in exact sciences and has a high level of development of logical thinking. For two years, Andrey has been attending robotics courses and participating in city and regional competitions.
The boy's level of voluntary attention is above average. There are no signs of fatigue when performing work. The pace of work is high.
The boy has a high level of visual memory development. Auditory memory is moderately developed. The dominant channel for obtaining information is visual.
The predominant motive for activity is to avoid failure. The level of anxiety corresponds to the age norm.
In the course of solving intellectual problems, Andrey demonstrates independence and rationality. Willingly comes to the aid of his comrades. Shows interest in pair work. When working in a group, he imposes his opinion on his comrades and makes many comments. He takes criticism addressed to him painfully.
In a group of peers, the boy strives to become a leader. He is ambitious and active. Andrey tries to assert himself at the expense of other children. However, in order to become a leader, the boy lacks sensitivity and attentiveness to others. In addition, the boy has high self-esteem.
Andrey has a choleric type of temperament. The young man is emotional, assertive, and purposeful. He often has conflicts in his relationships with peers. Poor development of communication skills does not allow making concessions and finding a compromise solution to controversial situations. The boy is characterized by sudden mood changes.
There are outbreaks of aggression in behavior. It is difficult for a boy to control his emotional reactions.
Based on the results of psychological diagnostics, Andrey can be recommended a course of individual sessions with a psychologist aimed at correcting the emotional-volitional sphere. The boy will also benefit from group classes in the form of training to develop communication skills.
Two difficult types
Are there any difficulties when drawing up a psychological portrait of a person? An example of writing according to Platonov shows: yes, this happens. For example, there are 2 personality types: stuck and excitable. At first glance they are similar.
And some individuals are able to intertwine in character. But a professional in his field is still able to figure it out. For example, stuck-type individuals are distinguished by the fact that they are able not to demonstrate their negative emotions for a long time. “Revenge is a dish best served cold” is an expression that perfectly describes their condition. Such individuals are touchy and vindictive. First of all, they are offered programs to get rid of old grievances.
An excitable personality type manifests itself in constant dissatisfaction and irritability. These negative phenomena lead to the fact that the individual is in conflict with the outside world and himself. What leads to this condition? The psychologist carefully works with the applicant, trying to piece together all the details of life events, taking into account his temperament, genetic characteristics, social conditions and circle of acquaintances.
For a student with a low level of knowledge and performance
Nikita Kornilovsky has been studying at the State Institution “KSOSH No. 2” in Kirov since the 1st grade.
Throughout his time at school, he showed such qualities as laziness and indifference to the educational process. Does not show due attention to the proposed educational material, is distracted by extraneous activities and ignores teacher comments. He is more interested in communicating with his classmates. Passive behavior in the classroom leads to poor academic results. Doesn't complete homework assignments, but is a master at copying. Doesn't miss classes for no reason.
Shows a certain interest in humanitarian subjects, loves poetry and history.
Has the necessary work skills, but is not proactive enough to apply them. Gives greater priority to participation in class and school social events.
Loves attention from the outside, demands respect for himself and his opinion. In a conversation he may use obscene words, considering this the norm of behavior.
He has a significant level of athletic training and goes to the gym. Does not accept bad habits.
He is friendly with his peers and enjoys authority. He is not always polite with elders. Does not tolerate injustice.
Lives with his father, mother and younger brother, whom he cares for very much. Parents regularly appear at school and communicate with the class teacher. They are actively trying to improve Nikita’s knowledge level.
Nose
How to draw a portrait of a person if you don’t learn how to draw one of the most difficult details, the nose. We do this step by step.
Step 1
We draw parallel lines - this is the width of the nose.
Step 2
The two lines end with the original “capsule”. This is a widening of the nose.
Step 3
We depict the nostrils.
Step 4
Shading for a chiaroscuro effect.
Step 5
To make the shadow look natural, we even it out a little.
Sources used:
- https://studopedia.ru/11_251651_psihologicheskie-harakteristiki-lichnosti.html
- https://srazu.pro/lichnost/kachestva-lichnosti-v-psixologii.html
- https://cosmeton.ru/karera/psihologicheskij-portret-lichnosti.html
Purpose and content
Children are the most defenseless in the harsh realities of the cruel modern world. It is with the aim of protecting this category of the planet’s population that special guardianship and trusteeship bodies have been created in each state.
Their powers/official responsibilities include constant monitoring of compliance with the rights of the child in the family, on the street, in educational and other social institutions. Characteristics help to collect and classify complete information about each young child or adolescent.
The document contains maximum information about such factors as:
- social adaptation of a young/minor child;
- the level of his intellectual and mental development;
- character traits, behavioral aspects, hobbies;
- level of material support;
- general psychological comfort of the given environment where the child resides.
Only a person who spends a long time with a minor during the day can provide the above information with a high level of reliability. For example, a class teacher at a school, a circle leader, a school psychologist or a social worker who has been observing the student’s behavior for a long time.
Ears
Look at the pictures to see how to draw ears. The ear is located between the brow and nasal lines.
In the ¾ portrait the man is depicted with one ear, the other ear is “hidden”. Remember, the ear should be tilted towards the head.
Human individuality ↑
There are as many individuals as there are people, because each person is an individual.
The driving force for the development of individuality, its programming properties:
- Direction is the motivation of behavior and activity.
- Intelligence is a person’s ability to assess a situation, make a decision, and control their behavior.
- Self-awareness - this includes self-esteem (low, adequate, high) - attitude towards yourself and your actions; self-control – the ability to control one’s behavior and emotions.
There are also basic personality traits: temperament, character, abilities.
Platonov's method in society
Palatonov’s method is used in various creative shows, politics, and science. Indeed, in this activity, the psychological portrait is primarily important. It is impossible for a famous person, just like an ordinary person, to avoid such a characteristic. In this case, the scientist Platonov proposes to consider a person’s intelligence and orientation.
That is, does he have a certain talent and will he be able to realize it based on willpower? In addition, experts take into account a person’s ability to manage their emotions in a state of passion and control moods and feelings.