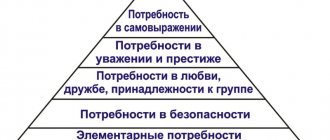
Dilts' logical levels model or neurological levels technique is a concept that helps understand the meaning of human actions at different levels.
The Dilts Pyramid explores a specific task/goal through a gradual progression from the level of everyday life to the level where a person fully comprehends his mission and purpose.
Further in the opposite direction, from top to bottom, where a new semantic understanding and value is introduced to each underlying layer.
Enriching your path with meaning allows you to introduce new guidelines and new personal values. A person enriches his stock of options for action at the lower level of the pyramid. A person sees new ways to realize the identified meaning, reacts through the prism of opportunities and emerging new ideas.
Dilts Pyramid and NLP
The Dilts Pyramid in NLP (Neuro Linguistic Programming) is an effective tool to:
- Organize thinking, collect information, communicate.
- Understand what drives people or makes them run away from solving problems.
When communicating or interviewing in the background, you can run in your mind the decomposition of the interlocutor’s answers into these logical levels.
When using a pyramid, we clearly and structuredly understand what exactly motivates a person. Let's look at the model from bottom to top, how it works in self-analysis.
Level 1. Environment: what do I have?
When a person is engaged in a certain work, he interacts with the environment : people, places, material things, etc.
Level 2 Behavior: What am I doing?
Actions or inactions , the results that an observer sees, hears and feels when a person participates in a particular movement.
Level 3: Opportunities: How do I choose?
A person is determined by what he is capable of: this is an independent expansion of innate abilities and skills. This is the effective use of skills and acquired skills to solve life issues. This is the internal behavior of the individual.
Level 4. Beliefs, values: what do I believe in?
Belief in the possible and the impossible , what is good for a person and what is bad.
What does he attach importance to, what is of greatest value, and does he feel motivated by these reasons? Personal values support or hinder behavior in guiding behavior and determining life path.
Level 5. Personality: Who am I?
Personal self-esteem , self-awareness, a person’s awareness of his place and role in the world. May include identification with work, religion, marital status, etc. This is the interpretation of events from the point of view of one's self-esteem.
Level 6. Mission: why am I living?
The Dilts pyramid is crowned by a level that implies a person’s awareness of his mission : where he is going, with what people, what contribution he is going to make to the world. What does he live for, what is a powerful incentive to overcome difficulties and obstacles that arise in the process of life.
The importance of physically recording tasks
In many coaching sessions, the Dilts Pyramid is the most important because it is used more frequently. What is typical is that one important and mandatory condition must be observed - all goals, including processing of results for each specific level, are recorded in writing. There is a completely natural and logical explanation for this:
- When writing a text, many essential points are learned more easily. As a result, it is easier to find a solution to a problem or a way out of the current situation. Perhaps this is why all students write notes during lessons - for better assimilation of incoming information.
- Writing text leads to the emergence of new nerve impulses that enter the brain. This contributes to a more precise formulation of the problem, which allows you to quickly find the right solution.
- In the process of writing a goal, it acquires visual outlines, which happens involuntarily. If an individual imagines himself in the place of a person with an already solved problem, then he acquires a significant incentive to action.
- As the task is recorded on paper, the vision of the situation sometimes changes. But if you have a factual description of the problem before your eyes, then it is possible to easily make the appropriate adjustments.
To understand all the features, you should immediately move from theory to practice, that is, devote time to answering the questions asked. Based on the degree of responsibility for such work and honesty with oneself, everything will begin to become clearer on its own. To do this, keep a piece of paper with a pen (pencil) or a voice recorder nearby.
Why is the Dilts pyramid needed?
The idea behind logical layers is that if a problem is detected at the pyramid level, you can determine where the failure occurred in order to correct the situation in accordance with the characteristics of the level.
Developing skills in using the Dilts Model will develop accuracy and depth of communication with and understanding of others.
Logical layers show the structure for understanding what is happening in each area of the relationship: the individual, family, organization, team, children, partnership.
The pyramid helps to recognize how the different layers are connected and interact. This makes it possible:
- Ask and check the relevance of information.
- Keep track of a large amount of information in a structured way. When discussing an issue, keeping track can be done on a piece of paper or in your head.
- Recognize the layers of the pyramid where the problem manifests itself.
- Determine the appropriate level at which corrective decisions can be made.
A number of additional questions
Giving answers to the key questions of each level, the Dilts pyramid allows you to objectively assess the picture of everything that is happening. However, everything is seen only in a general light; in order to clearly see the essence of what is happening and find the right solution to the existing problems, you should use the help of a number of additional questions:
- After I achieve my goal, what will others do? Will it please them or will it?
- In what direction should the personal perception of others change after achieving the goals?
- Will the result be fruitful for my colleagues and loved ones?
- If I achieve my goal, will my mission change?
- Can I do some simple things towards my goal within 48 hours?
- How will my loved ones react to my intentions? Will they be able to make appropriate adjustments if necessary?
Something similar is covered in many additional coaching classes.
How to use the Dilts pyramid to set goals
Part I: Carrying the target state through neurological levels (NE)
- A short discussion is held to set goals that meet the criteria: positive, specific, environmentally friendly, resourced, meaningful.
- When performing the exercise, hold the “frame”: “Assume that you have already achieved your goal...” Go through all NEs with this “frame”.
You need to start from the bottom level - the environment (people, objects, space). Climb up step by step. Using a spatial anchor, and perhaps with symbols and terms, reinforce the vision of achieving the goal.
When a lack of resources is detected at one or two levels, move to a higher level. Look for missing resources on it or plan to move to a higher layer a little later.
Practical questions at different levels of the problem pyramid:
- Environment:
- Where and with whom are you?
- What do you see and hear?
- What smells do you smell?
- What flavors do you smell?
- Behavior:
- What are you doing in this place?
- What are others doing?
- Abilities (skills):
- How do you do what you do?
- How do you feel about the people here?
- What special skills do you have?
- Beliefs and values:
- What are some of the important things you believe in?
- Why do you do what you do?
- What are your thoughts about yourself, the people around you, your work?
- Individuality (identity):
- Your understanding of yourself, your image?
- Who do you consider yourself to be, what is your essence and role?
- Affiliation:
- Are there people or groups here that you belong to?
- What is your mission in all of this?
- Can you express in words the meaning of your actions?
Move on to the next stage.
Your subconscious mind will reveal important information in the form of an idea, symbol, feeling or picture. It is your subconscious that has worked for you and for your goal. Take it all in and take a short break.
Part II: Gathering Resources
- Go back and remember all the ideas and resources you found along the way. Feel what each layer is rich in, what knowledge and experience it is strengthened with.
- When something is not enough at a level, go to a higher stage and take resources from there . Go back and evaluate the changes that have occurred with the resources you have taken.
- Go to the “environment” level and remember your goal. Feel whether your goal has become richer compared to the initial one.
Part III: Completion
- Go through all the stages again at your own pace. Take at least a little time for this step.
- Go through all the levels in reverse order from top to bottom - quickly, without thinking. Walk through, return to the starting position and see how much richer the target has become.
- Indicate when the first step towards the goal will be taken?
A Brief History of Dilts Logic Levels
The version of neurological layers above is based on the original technique developed by Robert Dilts and Todd Epstein.
Robert Dilts developed the Neurological Levels of Change technique, inspired by the work of Gregory Bateson and the philosopher Bertrand Russell. In Bateson's book, Steps to an Ecology of Mind, the idea is that learning occurs at different stages. According to Bateson's idea, the source of a person's difficulties is specified and he finds resources to solve his problem.
Bateson's concept was that learning occurs at different levels, and Dilts' model directly reflects this. Changing things at a higher level inevitably leads to changes in things at lower levels . Changing things at a lower level can, but does not necessarily, affect higher levels.
Bateson layers (and Dilts layers in brackets):
- Learning context (environment).
- Learn (behavior).
- Learn to learn (ability and competence).
- Belief that education is vital (beliefs and values).
- Becoming a disciple (identity).
- Assist others with your learning (goal).
What is the need
Why do we need some kind of Dilts pyramid model and its logical levels, you ask? There are difficult situations in every person's life. Perhaps these are problems at work or in relationships, an unsatisfactory standard of living, or social circle. There are hundreds of options. And that's okay. The Dilts Pyramid will help in all these cases:
- It will give you the opportunity to realize that something needs to be changed in life. It will also show which areas need adjustment.
- Allows you to rank problems by complexity and importance. Their solution starts from the bottom level. Thanks to this, a person sees in which direction he needs to move. This is similar to how moving up the career ladder occurs.
Dilts's pyramid of logical levels is applicable in almost all areas of life. This is a career, financial condition, personal growth, building personal relationships and in a team.
Examples of beliefs at the levels of the Dilts pyramid
| Level | Causes | Meaning | Limitation |
| Environment | I didn't go to university. | I have no specialty - poor initial prospects. | Nothing bright shines in my life. |
| Behavior | I can’t find a job or start my own business after failure. | I look gloomy, and they don’t want to take me into the team. | You can't take risks, you have to stick to the old. |
| Capabilities | I can't write because I always had twins at school. | If one person can do something, others can learn it too. | You can't learn anything without practice. |
| Beliefs and values | Honesty is sacred to me because I myself was constantly lied to by my parents. | Equality in relationships means true partnership. | Trust is impossible without openness. |
| Identity | I'm a failure because no one ever supported me. | Unemployed people are a burden on society. | As a recipient of benefits, I am at the bottom of society. |
| Affiliation | She believes in God because that is what she has learned. | To believe means to be in harmony with yourself and the world. | Without faith, you might as well kill yourself. |
Situation
Let's say your problem is this: I am not valued or respected for my work at work. How to disassemble it according to the Dilts pyramid?
- Environment. Here you ask yourself the question: “Who exactly should value me?” Bosses.
- Behavior. “What should I do to be appreciated? What should management do to make me feel like I’m valued?” For example, your answer is: “I should show good work results, and my superiors should praise and encourage me.”
- Capabilities. “What qualities and skills should I demonstrate in order for my superiors to value me?” For example, determination, creativity and responsibility.
- Values. “Why is it so important for me to be valued by my superiors?” Your answer could be: “So that I understand that I am a valuable employee, without whom the company will work worse.”
- Identity. “Who should I be to be valued by my superiors?” For example: “A person who is needed.”
- Mission. We reach the most difficult and sometimes painful question: “Why do I need this?” And here you need to make a lot of effort to get to the truth. Maybe you will discover memories that you would prefer to forget long ago or something that will cause you negative emotions. For example, your answer: “Because this way I can prove to myself and my parents that I can succeed.”
We finally got to the bottom of the truth. The problem of disrespect from superiors lies at the “value” level, while its solution lies at the “mission” level. It turns out that you want to be respected by your superiors in order to prove to your family that you are worth a lot and can achieve anything. Perhaps it’s not worth saying that the management has nothing to do with it?
This way you can understand any of your problems and draw conclusions on how to solve them. At what level are your problems and desires?
Don’t forget to tell your friends and acquaintances on the invme service about the Dilts pyramid. Maybe this will help them cope with difficult situations. If you have problems not in self-identification, but in family relationships, then the pyramid will also help you. Not the Dilts pyramid, but the Karpman triangle
. Read the article about him, and perhaps you will answer many questions for yourself.