- Figurative memory
- Visual memory
- Auditory memory
- Motor memory
- Verbal-logical memory
- Emotional memory Functions of emotional memory
- Features of random memory
Human memory is, in fact, an interconnected process consisting of three components: input of information (memorization), its retention (storage) and, finally, reproduction. Their relationship is expressed in the fact that the preservation of information depends on how memorization is organized, and the quality of reproduction depends on it.
This circumstance should be taken into account when deciding for yourself the problem of how to improve soldering for an adult. Based on the nature of mental activity, they distinguish between figurative, verbal-logical, motor and emotional memory.
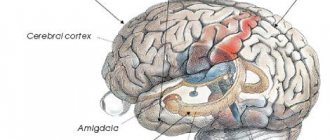
Figurative memory
Figurative memory is a repository of sounds, smells, and visual ideas. Visual-figurative memory stores material in the form of visual, auditory and other images. Therefore, several separate types of figurative memory are distinguished, such as auditory (try to remember the purring of a kitten or the crackling of brushes in a fire), visual figurative memory (the face of a loved one or a favorite vase - remember?), olfactory (the smell of a familiar perfume or just freshly cut grass), tactile (the touch of a warm hand or the pain of an injection), taste (the sourness of a slice of lemon or the sweetness of a banana). Visual-figurative memory is especially important in creative activity.
Our brain prefers to perceive the world by processing information in both hemispheres: the right one perceives the image, and the left one selects words for it. By developing figurative memory, we fill the gap caused by the lack of images: in the modern world there is a lot of information, but the bulk of it does not involve the right hemisphere in its work, an imbalance arises, as a result of which it is increasingly difficult for us to remember, maintain attention, and concentrate. The development of figurative memory helps to engage the right hemisphere, using the imagination. By imagining, we remember easily. Having understood the material, we create an image that consolidates understanding and gain knowledge.
There are visual, auditory, motor-auditory memory, visual-motor-auditory memory. These are the types of so-called sensory memory that play the most important role in learning. Knowing what type of memory predominates in a student, you can take a differentiated approach to the process of his learning, achieving better memorization results. The teacher must ensure that as many senses as possible participate in the process of learning the material. At one time, the famous teacher K.D. drew attention to this. Ushinsky.
Violations
Disorders include underdevelopment of long-term memory, when a person simply does not know how to correctly encode and reproduce information, and complete amnesia, which is characterized primarily by damage to the hippocampus. If in the first situation everything can be corrected through constant training, then in the second the forecasts most often remain unpredictable.
Causes
Physiological:
- asthenia;
- liver intoxication;
- damage to the central nervous system and brain: head injury, post-stroke condition;
- intellectual disorder, schizophrenia;
- chronic alcohol or drug intoxication.
Mental:
- overwork;
- neuroses;
- constant stress;
- excessive emotional and mental stress;
- depression;
- psychotrauma;
- dysthymia: constant bad mood.
Household:
- poor nutrition;
- lack of sleep;
- excessive physical and intellectual stress;
- improper planning of the day, lack of routine.
Symptoms
- Difficulties with conscious memorization: poems, dates, exam material learned by heart are poorly retained in memory and are reproduced with errors;
- inability to remember events from the distant or near past, memory lapses;
- confusion, violation of cause-and-effect relationships;
- forgetfulness in basic everyday situations: didn’t make a report, didn’t come to a meeting, didn’t buy bread for home;
- social maladjustment;
- decreased mental capacity and performance;
- inattention, inability to focus and concentrate;
- confusion.
If violations of short-term memory lead primarily to everyday problems (when you don’t remember what you did 5 minutes ago), then the consequences of damage to long-term memory affect almost all areas of life. At work, this leads to poor performance of one’s duties, and in the family – to the breakdown of personal relationships. The person turns out to be socially maladapted. Even if his DVP is simply poorly developed, he will not be successful compared to other students (students, employees), not to mention various forms of amnesia.
For more information about what causes memory impairments, how they manifest themselves and how to get rid of them, read our separate article.
Visual memory
Visual memory is associated with the storage and reproduction of visual images. Visual figurative memory involves the use of a visual analyzer to process information. For many people, visual figurative memory represents the main type of memorization.
The development of visual memory is especially important for artists, but we all use it widely. By developing imagination, we also help the development of visual memory, because what we imagine is easier for us to remember and reproduce.
Diagnostics
To find out how well a person's long-term memory is developed, various test methods are used.
Method No. 1. Memorizing words that are logically unrelated to each other
The bottom line. The subjects are given 2 lists of words (for children 6-12 years old one will be enough), which are logically unrelated to each other. Each of them is numbered.
Recommended Material:
Task options:
- Lists can be read aloud (without allowing subjects to write them down). If the words are read out, this must be done 2-3 times for adults and 4-5 times for children 6-12 years old.
- They can be written on the board.
- They can be distributed on separate pieces of paper to each subject.
Exercise:
- Listen/read the lists of words carefully and try to remember them.
- After listening/reading multiple times, try to reproduce it on paper. Preferably in the same order.
- Next, you need to be distracted by some other activity.
- After half an hour, the lists are read/listened to one more time and played again.
- The same thing is done twice more - the next day and a week later. The words are read/listened to again, but only once.
The results of all 4 tests are calculated using the following formula:
C (DVP coefficient) = B (number of correctly reproduced words): A (total number of words) x 100.
Next, the arithmetic mean of all 4 tests is found and based on the resulting result, conclusions are drawn:
Method No. 2. Memorizing text with semantic connections
The essence of the technique is almost the same. Only the text is not read aloud, but is distributed to each subject. At the same time, attention is drawn to the fact that the main thoughts are highlighted in bold, which must then be reproduced. That is, it is not necessary to memorize the sentences themselves and the entire text.
This technique is used to diagnose DVP in adolescents (13-17 years old) and adults.
Card with text:
You need to reproduce the main ideas of the text immediately after reading, then after half an hour, the next day and a week later. The results of all 4 tests are calculated using the formula:
C (DVP coefficient) = B (number of correctly reproduced thoughts): A (total number of highlights in the text) x 100.
Next, the arithmetic mean of all 4 tests is found and, based on the resulting result, conclusions are drawn according to the table above.
In case of serious impairments of long-term memory, laboratory diagnostic methods (EEG, CT, MRI, ultrasound) are performed.
Motor memory
Motor memory retains everything related to motor activity. It’s as if the arms and legs themselves “remember” what to do.
Motor memory helps us remember movements and then reproduce them. Thanks to her, we learn dances, work with instruments, ride a bike, etc.
The development of motor memory is promoted not only by the refinement of movements, accuracy, and dexterity. Without it, it is simply impossible to achieve success in any business, no matter what we undertake. It underlies the skills of walking, riding, writing, and all work and practical skills. If we did not have this memory, we would be forced to learn to repeat this or that action. The more familiar the conditions, the more accurate and precise the movements, the better the result.
Usually one type of memory predominates, but there are also mixed and combined ones. Thus, motor-auditory memory and visual-motor-auditory memory belong to combined types of memory.
Medical supplies
The use of medications or dietary supplements does not lead to any negative consequences. However, when choosing products, it is important to take into account the person’s age, possible side effects, contraindications, as well as their effectiveness. To do this, just study the instructions and read reviews on the Internet. Additionally, it is recommended to consult a doctor, which is especially important for people with chronic diseases. What should you take to improve your memory?
Over-the-counter
Glycine has become the most popular drug for eliminating inattention and strengthening memory in Russia. The drug is inexpensive and quite effective. Its main advantage is not only the effect on memory, but also the reduction of stress. It is enough to take Glycine 1 tablet 3 times a day.
What other drugs can you pay attention to:
- Vitrum Memory;
- Undevit;
- Bilobil;
- Intellan;
- Aminalon.
All of them have a positive effect on memory quality. These tools are especially effective for schoolchildren, students, and anyone whose work requires interaction with large amounts of information.
Prescription
You can get them only after consulting a doctor. All of them are dispensed from the pharmacy strictly according to a prescription. Such medications easily eliminate inattention, relieve forgetfulness, and also have a special effect on the body if necessary. Piracetam has gained great popularity, as it reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, while simultaneously strengthening memory and eliminating circulatory disorders in the brain. Also known in our country is Cavinton, which improves the condition after a stroke and other brain diseases. Additionally you can consider:
- Phezam;
- Nootropil;
- Phenotropil;
- Encephabol;
- Picamilon;
- Cerebrolysin;
- Noofen.
For prescription drugs, the list of possible side effects and contraindications is much wider, which must be taken into account.
Taking medications or dietary supplements alone is not enough to develop memory. They should be used exclusively as an additional method in combination with others.
Verbal-logical memory
The verbal-logical type of memory stores information in the form of verbal concepts and numbers. It is responsible for meaning, logic, interaction between elements of verbal information . In the learning process, both figurative and verbal-logical memory are widely used. Figurative memory is inextricably linked with imagination and is in demand in many areas of human life.
We use the verbal-logical type of memory all the time. When we study new material, it is mainly she who works. The development of all other types of memory in a person also depends on the development of verbal-logical memory: it relies on them and plays a leading role in the assimilation of new knowledge.
It is very important to develop the verbal and logical memory of younger schoolchildren, because, as practice shows, if a child does not master the techniques of mental activity and learn to study (forgive the tautology) in the lower grades, then he will fail in the middle and high grades, falling behind in his studies.
The development of verbal and logical memory helps to improve erudition and increase education. The peculiarity of verbal-logical memory is that thoughts do not exist without the participation of language, without words, and neither does their reproduction. We always work with thoughts expressed in words, hence the name - verbal-logical memory.
Human memory in psychology
Human memory has always been the object of close attention of scientists. Initially this concept was philosophical. Later it began to be classified as psychology. Today, memory mechanisms are studied by such sciences as physiology, biology, and mathematics. Research by scientists gives rise to various theories and hypotheses.
Thanks to different types of memory, a person recognizes the faces of relatives and friends, studies and works, plays sports, and drives a car. Without the ability to remember and retain necessary information, any activity would be impossible, even to satisfy basic needs. It is impossible to overestimate the role of memory in human life.
Its most important property, volume, shows capabilities that have large individual differences. The degree of memory development depends on a number of external and internal factors:
- genetic characteristics;
- state of mental and physical health;
- lifestyle and characteristics;
- upbringing and education.
In psychology, there are many types of memory, each of which is of great importance for the development of human abilities.
Emotional memory
Emotional memory contains all memories of experienced emotions and feelings. A feature of emotional memory is its brightness even after many years after the emotional outburst received. Usually, supported by an emotional impulse, it stores information for a long time and firmly. This may be due to the fact that, under the influence of strong emotions, adrenal hormones are included in the memorization mechanism, which are not involved in normal memorization.
Sometimes primary emotions are replaced by secondary ones, sometimes opposite ones, and then we overestimate our attitude towards events that once took place.
The development of the emotional type of memory helps to increase a person’s intellectual potential. Both success and comfortable emotional state in the family and society depend on the development of emotional memory. Works of art, wildlife, and fiction stimulate the development of imaginative thinking, which also contributes to the development of emotional memory.
Functions of emotional memory:
- Accumulation and reproduction of emotional experience associated with the event that caused the emotion.
- Formation of emotional intelligence.
- Influence on the development of personality and its creative abilities.
Through memory for emotional states, we make decisions about our next steps, we have the opportunity to learn from our mistakes and repeat successful experiences. The functions of emotional memory make its contribution to the formation of personality very significant.
Thanks to the emotional type of memory, we know how to suffer, rejoice, and sympathize. Once experienced feelings hold us back from something, encourage us to do something. Emotions are involved in the mechanism that motivates us to action. It is not thinking, but emotions that charge us with energy.
Study methods
To study a person’s ability to remember and process information, they use:
- Collection of information - studying the biography of the subject, observation, conducting experiments and tests, studying the results of activities.
- Analytical biochemistry. Conducted based on the results of clinical studies.
- Electrophysiology. Brain activity is recorded using magnetic resonance imaging.
- Pharmacology. The effects of various stimulant drugs on brain activity are being studied.
- Clinical psychophysiology. The subject's behavior is observed in a clinical laboratory setting.
If necessary, it is possible to study not only human memory. Scientists conduct experiments on mammals, plants and even microorganisms.
Long-term, short-term and working memory
Based on the time it takes to store information, we distinguish between instant, short-term, operational and long-term memory. Short-term memory is capable of storing information for a very short time, about 40 seconds, and its volume is small, it is 7 plus or minus 2 units of information. This volume can be increased by combining information into blocks.
Most of the information from short-term memory is then erased, and less goes into the so-called working memory. This is facilitated by some factors, such as the emotionality of the presentation, brightness, surprise, unusualness of the material, repeated repetition, and importance for a particular person. Information is stored in RAM for up to a day (maximum), then the less important part is erased, and the more important part goes into long-term memory. Here, information is stored throughout life, and for this the body uses special nucleic acids and memory proteins.
Interestingly, in the slow-wave sleep phase, logical information processing occurs, and in the fast sleep phase, selected information is transferred to long-term memory. You can read more about these processes and the development of long-term memory, as well as the development of short-term memory, in our blog.
General classification
There are a large number of classifications of memory in domestic and foreign psychology. If you need to study this material in detail, you should look at the works of P. P. Blonsky, R. S. Nemov, F. N. Shemyakin, D. O. Hebb and other specialists.
There are only the main types; psychology identifies the following:
In fact, in addition to the main types of memory, descriptions of others can be found in the works of psychologists. For example, the classification according to the nature of mental activity sometimes also includes:
- sensory - visual, when fixation occurs at the moment of blinking;
- eidetic - combined, when visual impressions (which form its basis) are reinforced by others (auditory, gustatory, tactile), which allows subsequently to reproduce an unusually vivid image;
- social - preservation of socially significant information accumulated by previous generations;
- spatial - visual, allowing you to navigate the area well, remembering the features of the route.
The classification by duration is expanded by such a type as ultra-short-term memory (another name is the sensory register) - retaining information for several seconds. Includes iconic (for fixing visual material, lasts less than a second) and echoic (for acoustic, lasts 2 seconds).
Some psychologists classify types of memory into a separate group based on the type of organization of memorization:
- episodic - storage of specific information limited to a certain period (about a concert, for example);
- procedural (automatic) - a way of performing an action without taking into account its content, through skills brought to automaticity (driving skill).
Within each typology, several more species are distinguished. Psychologists are actively engaged in their classification to this day, constantly expanding and improving it.
Involuntary memory and voluntary memory
According to the degree of volitional regulation, a distinction is made between voluntary and involuntary memory.
Involuntary memory is a process that occurs effortlessly, “on its own,” involuntarily. But, as a rule, imprinting in this case is associated with strong emotions, causing, for example, surprise and interest. Material learned using involuntary memory is imprinted better than using voluntary memory, because involuntarily we remember what is in the center of attention, what is interesting, what will definitely be useful, and especially if mental work was associated with it. But it is precisely this information that the brain prefers to send to long-term memory storage.
The development of involuntary memory in preschoolers is associated with their involvement in active interaction with objects, with learning to understand their importance and the ability to divide them into groups. Expanding a child's interests also contributes to the development of involuntary memory.
Voluntary memory is a process in which a person makes volitional efforts to achieve memorization. In this case, when “you don’t want to, but you have to,” we use “tricks”: mnemonics, concentration, motivation; We stimulate and reward ourselves for efforts and successes.
The development of voluntary memory plays a huge role in learning, allowing younger schoolchildren to master the curriculum and promoting general intellectual development, including the ability to think logically and draw conclusions, which is so necessary for high school students. You can read about exercises for developing voluntary memory here:
According to the method of learning, there are two types of voluntary memory: mechanical and semantic.
- When memorizing material by rote learning, without using analysis and transformations, we are talking about the use of mechanical memory.
- When remembering the meaning, and not the form of information, when the material is connected with what is already available and structured, we talk about the use of semantic memory.
But, no matter what type of voluntary memory we use, the result of memorization depends on whether we are able to provide strong, long-term attention to the subject of memorization.
We can say that voluntary memory has features that reflect its specificity.
Random Memory Features:
- Having the intention to retain information in memory.
- Making a certain effort to remember information.
- Using mnemonic devices or other memorization techniques.
- Organized repetition for better memorization.
Memory is one of the most important cognitive functions of the brain, necessary for a full life and human development, and it can and should be trained.
You can train your memory using special memory development exercises. In a fun form of game for this purpose, you can practice on educational brain simulators online.
We wish you success in self-development!
What types of memory can be developed
Throughout his life, a person uses different types of memory. In the left and right hemispheres, acquired various knowledge is deposited like “bricks”. To extract the necessary information sometimes requires considerable effort. With the help of forgetting, the nervous system is unloaded; this is considered a normal process.
Bad memory and good memory sometimes mean completely different things. For some, it is important to remember everyday trifles, for others, people and events, and others are interested in the amount of information before an exam or an important presentation. Therefore, it is important to know what kind of memory needs to be developed to solve problems. Conventionally, it is customary to distinguish between two types:
- Natural memory. It is as it is, and is inherent in nature itself. Everyone uses it without exception.
- Artificial. It must be trained and developed throughout life.
There are people with phenomenal memory. Others can't hold anything in their head for more than a minute. Experts are confident that the ability to remember can be trained and developed, just like your own body. If you take this seriously, you can achieve significant success.
Memory Features
Important! The testing method can reveal the type of memory in any person, as well as the presence of any pathologies.
Causes of memory impairment and increased forgetfulness:
- age-related changes;
- Alzheimer's disease and some other diseases;
- lack of water in the body;
- absent-mindedness;
- bad dream.
Memory development has a positive effect on a person’s abilities. For adults, this process is more difficult, since regular training is not needed in monotonous work and everyday life.
Useful qualities to improve the memorization process:
- attentiveness and observation;
- interest in life, positive attitude;
- organization in everyday life;
- use of imaginative thinking;
- learning foreign languages;
- Reading books;
- memorizing poems and quotes;
- Mind games;
- physical exercise;
- proper nutrition;
- the ability to correctly express your memories;
- reflections before going to bed about the past day, listing tasks for the next.
If you follow the advice and recommendations of experts and know the characteristics of human memory, then its comprehensive development is possible. Developed memory is valued and helps to achieve a high position in society. This is also important for successful work in all areas.
Computer as a brain
Current processor development is largely based on process reduction. As time goes on, the effectiveness of this approach decreases. Is it possible to replace the current architecture with an architecture similar to the human brain? Of course, given the reality of the lack of knowledge about the brain, this comparison is incorrect, but let’s imagine. What are the advantages of the brain over the computer? The first thing that comes to mind is the presence of consciousness and the ability to be creative. But it’s not entirely clear what the difference is between them and their computer simulation? The problem of qualia and similar issues are best left to philosophers and concentrated on more practical aspects. It is clear that in some tasks that depend on the speed of information processing we lose. But at the same time, the brain has many advantages over modern computers:
- the brain is more energy efficient: on average it consumes 20–30 W;
- the brain copes better with recognizing images, speech, and streams of complex information;
- the brain is plastic, unlike the modular architecture of a computer: one department can perform the functions of another (if necessary);
- the work of the brain can be described as parallel, there is no need for a clock generator;
- based on existing experience, the brain is capable of predicting future events;
- The brain is incredibly learnable and adaptive.
Some advantages of the human brain over computers are quite obvious. In light of these advantages, developing brain-like systems seems like a great idea. But, as always, this approach has disadvantages:
- Absolute borrowing from nature is not always optimal:
Natural “technologies” are naturally formed under the influence of evolution. But, often, such solutions are not suitable for human tasks. For example, attempts to create an aircraft based on birds and their flight techniques were not successful.
- Do you need a computer like a brain?
First, the brain is not a perfect system. We cannot purposefully forget certain information. It is very difficult for the brain to perform several complex tasks at the same time. Second, every brain is unique. Some people are better at drawing, while others are better at math problems. Do you need a computer that can handle tasks of approximately the same complexity in different amounts of time?
- Creation of an “artificial brain”:
Let's come down from heaven to earth.
If you imagine the creation of computers with an architecture similar to the structure of the brain, then thousands of nuances will immediately appear. How to manage such a system, how to support it, create software for it, how to integrate it with other systems, what materials to make components from, and much more. Practice shows that it is better to borrow the best, but, as mentioned above, the lack of knowledge about the brain does not allow this.
Cloud servers from MacLeod are fast and secure.
Register using the link above or by clicking on the banner and receive a 10% discount on the first month of renting a server of any configuration!
Stages of information processing when memorizing
If we talk about the structure and mechanism of perception, analysis and sending for storage into memory of any information received, then this happens at the following levels.
- Sensory processing of any data. Fractions of a second are allotted for this period. Everything is remembered briefly and put aside for longer storage only if it has been analyzed as valuable.
- At the next stage, the received data is sent for storage. If they are used in the very near future and a person uses them almost immediately, then this type is called short-term. This includes, for example, orders at work that need to be completed during the current working day.
- Next comes long-term or long-term. This place is a repository for everything important that will be used over a long period of life. As a rule, this includes all acquired skills and life experience, knowledge and abilities, memories and impressions.
- RAM is similar to internal computer memory. This type is used when you need to work with small amounts of information over a long period of time. Despite its similarity with short-term, there are still certain differences between them.
- Tertiary memory refers to long-term memory. Most often used to store language arrays.
Tweet Pin It