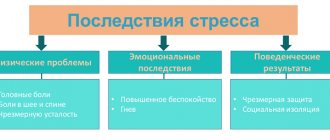
Stress can be destructive to our health. The consequences of frequent experiences affect the functioning of all organs and systems.
For example, the skin may become dry and pale, with a yellow tint. The risk of cardiovascular disease also increases significantly. Cystitis, incontinence and much more can occur due to nervousness. And most importantly, stress accelerates the aging process - both external and internal.
Therefore, it is important for modern people to know the signs of stress in order to prevent its consequences or eliminate them as early as possible.
Signs of stress
According to statistics, in Russia women are more susceptible to stress due to their increased emotionality and sensitivity. In 2021, people of all professions experienced strong negative experiences, but especially teachers, entrepreneurs and, of course, doctors.
This year has been difficult for many, so the number of people with chronic stress has increased many times over. At the same time, people began to consider their depressed state as the norm. But even in the most difficult times, it is important not to let the situation get worse and fight back the disease.
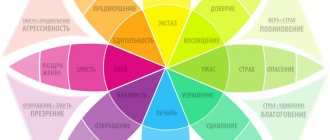
Stress changes the entire body, so you should pay attention to different symptoms.
Behavioral signs of stress:
- conflict;
- aggressiveness;
- irritability;
- loss of interest in life, friends, appearance;
- decreased self-esteem;
- suspicion;
- frequent attacks of anger and feelings of helplessness.
Lifestyle changes:
- sleep disturbance;
- the emergence of bad habits;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased performance.
Intellectual traits:
- poor concentration;
- excessive distractibility;
- decrease in attention.
Changes in thinking:
- decreased creativity and memory;
- violation of logic;
- common spelling errors.
Physiological signs:
- frequent headaches;
- cardiopalmus;
- decreased immunity;
- sudden weight loss or, conversely, rapid weight gain;
- deterioration of organ function.
call me back
How does stress affect the body?
Severe or prolonged stress may well cause the development of diseases.
In this case, the most weakened systems of the body suffer, so the consequences vary from person to person. Against the background of a stressful state, the following may develop :
- bronchial asthma due to constant tension of the muscles involved in the respiratory system;
- hypertension, heart and vascular diseases due to constantly high blood pressure and rapid heartbeat;
- peptic ulcer;
- neurotic and depressive disorders;
- damage to the gastric mucosa due to increased production of gastric juice;
- diabetes – due to the liver releasing an additional portion of glucose and increasing its concentration in the blood;
- gynecological problems up to infertility.
It is impossible to predict exactly what problems stress will provoke. Moreover, they can appear individually or in groups, or all at once, in a complex.
Types of stress
Conventionally, two types of stress can be distinguished.
- Eustress is “good” stress that does not harm a person. Without it, we would always feel calm, at ease and would not want to achieve anything. We feel eustress when we need to get out of our comfort zone and change something in our life. A simple example: you have undertaken to create a large-scale project that requires a lot of time, effort, intellectual and physical expenditure. It’s difficult for you, you’re nervous, but at the same time you feel that in the end you’ll get a pleasant feeling of pride in yourself, you’ll be praised, and all your efforts will not be in vain. Thus, eustress motivates us not to give up and move forward despite difficulties.
- Distress is harmful and occurs when stress reaches a large scale: it lasts for a long time and has several foci of occurrence. For example, when a person has to cope with several difficult and unpleasant tasks at once: a change of environment, joining the army, lack of sleep, financial losses.
Distress has an extremely negative impact on the human psyche and physiology. He stops being happy, receiving positive emotions and is constantly dissatisfied with his life. Signs of distress include sudden changes in mood, physical weakness, poor performance, and the emergence of negative thoughts.
Types of distress
- Emotional. It is associated with a person experiencing a very strong emotional state (both positive and negative). For example, the birth of a child, a promotion at work, a new trip, or, conversely, a breakup, the death of a loved one.
- Physiological. Directly affects body tissues. It can be caused by climatic (cold, heat, thunderstorm), chemical (deficiency or increased oxygen content in the air) or physical factors (overexertion, injury). These triggers do not go unnoticed. Even after everything has returned to normal, a person experiences apathy, overwork, and constant fatigue for some time.
- Chronic. This is a long-term adaptive reaction of the body to negative influences from the environment. It is the most dangerous type of stress. It can arise from overwork at work, as a result of family quarrels, etc. The consequences can be a change in the size of the brain, its structure and work in general. Leads to various types of diseases (neurosis, heart disease, vascular disease).
- Nervous. Characterized by excessive stress emotionally and physically. A person cannot control his emotions and behaves aggressively and hot-tempered.
1. Weight loss, systemic disorders due to pathological intensive weight loss
Weight loss
during normal physical activity, it is most often associated with a deterioration in appetite. A decrease in the need for food is accompanied by many diseases.
It is known that an increase in body temperature reduces appetite due to the fact that digestive enzymes are able to “work” only in a narrow temperature range (up to 37 degrees). Refusal to eat in this case is not dangerous, since the body has enough internal resources for the acute period, and bed rest reduces energy consumption. However, some serious diseases (oncological, tuberculosis, gastrointestinal ulcers, endocrine disorders, severe depression) can lead to real exhaustion, even with adequate nutrition. Sometimes it is prolonged and significant weight loss that indicates an illness that does not manifest itself in any way at an early stage.
Pathologically intense weight loss leads to systemic disorders:
- sudden mood swings;
- sleep disorders;
- muscle weakness;
- dizziness;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- menstrual irregularities;
- tachycardia.
These phenomena may be a consequence of lack of nutrition, since simultaneously with the consumption of fat reserves, other organs and tissues are also depleted. Only with adequate physical activity is it possible to lose fat while simultaneously increasing muscle mass and improving the functional state of internal organs.
If sudden weight loss occurs against the background of a normal lifestyle, then this is a blow to the entire body.
A number of accompanying changes and conditions may indicate certain causes of weight loss. It is worth paying attention to them and not putting off going to a doctor of the appropriate specialty.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Stages of stress
- 1. Anxiety. A person is scared, a signal is sent to the hypothalamus - there is an active production of adrenaline, cortisol, norepinephrine. As a result, the pulse and breathing increase.
- 2. Adaptation. The body is trying to bounce back and normalize its functions. If it doesn’t work out, then it goes to the third stage.
- 3. Exhaustion. The body does not have the strength to fight on its own, so nervous breakdowns, depression, and other diseases develop and manifest themselves. A specialist should be involved in getting out of this state.
What is depression?
When doctors talk about depression, they are talking about a condition called major depression. Patients with major depression experience the following symptoms all day long, almost every day for at least 2 weeks in a row.
If you have depression, you may also have headaches, pain in other parts of your body, or problems with digestion or sex life. An older person with depression may have difficulty understanding simple messages or requests made to them.
Symptoms of depression:
- lack of interest in activities that were previously enjoyable.
- Feeling sad or empty.
- Tearfulness, causeless crying.
- A feeling of inhibition or, conversely, a feeling of restlessness and the inability to sit in one place.
- Feelings of worthlessness or guilt.
- Rapid weight gain or loss.
- Thoughts about death or suicide.
- Difficulty thinking, remembering, or concentrating on current activities.
- Difficulty making everyday decisions.
- Trouble sleeping, especially in the early morning hours or feeling sleepy throughout the day.
- Constant feeling of fatigue.
- Feelings of emotional numbness, sometimes to the point of being completely unable to cry.
Chemistry of stress
The body's response to stress is controlled by the hypothalamus and adrenal glands. When detecting a stressful situation, the body releases certain hormones. Adrenaline and norepinephrine are produced in the adrenal glands at the first sign of danger. It increases during anxiety and shock, causing the heart rate to increase and the pupils to dilate.
Norepinephrine is released in any shock situations. Its action is associated with an increase in blood pressure.
Cortisol levels rise during extreme situations or physical activity. In small doses it does not affect the body. But long-term exposure to this hormone causes damage to the brain, literally shrinking it in size. High amounts of cortisol cause a loss of synaptic connections between neurons and a shrinkage of the prefrontal cortex, which regulates concentration, decision-making, judgment and social interaction.
Prolactin especially affects women whose target organ is the mammary glands. In a situation of severe stress, the release of this hormone begins, as a result of which metabolic problems begin.
Corticoliberin activates the center of fear and anxiety, causes anorexia, and increases blood pressure.
Sign up for a consultation
Hormones and vitamins
In addition to mental ones, there are also “material” reasons that force you to eat or not eat. One of the main ones is hormonal imbalance in the body. During very strong sudden stress, a large dose of adrenaline is immediately released into the bloodstream - it suppresses appetite. But constant, exhausting stress causes the adrenal glands to increase the release of another hormone - cortisol. By the way, it can be measured using a simple saliva test. The more it is, the stronger a person’s desire to eat heavily.
Stress Prevention
Of course, stress is an integral part of life. But we can learn to manage it and prevent its devastating effects on our health.
For this, it is important to practice prevention. For example:
- Include foods rich in beneficial microelements in your diet. For example, magnesium plays an important role - one of the main helpers in the fight against stress; it reduces cortisol levels. Magnesium is found in nuts (peanuts, almonds, hazelnuts), sesame seeds, seeds, seaweed, dark chocolate and buckwheat.
- Limit your alcohol consumption. It exacerbates the effects of chronic stress and leads to depression.
- Limit caffeine consumption after 15-00. Especially with high levels of cortisol, the stress hormone.
- Contact a psychologist. If you are worried about any fears or emotional experiences, then a consultation with a specialist who will help you understand yourself and guide you on the right path will be very effective.
- Limit the flow of information from the Internet. And it is highly advisable to stop comparing your life with ideal pictures from social networks.
- Normalize sleep. It is important that it lasts 7-8 hours.
- Exercise. It helps increase activity and concentration, improves overall cognitive function.
- Don't burden yourself with many complex tasks. Good time management is the key to preventing stress.
- Try meditation practices. Relaxation techniques provide the opportunity to step back, become aware of what is happening, and choose how to respond to stress.
The most important thing is to monitor your feelings and emotions and not put them in a “distant box.”
3.Diagnosis of diseases
There are many other, less common and obvious, but no less dangerous reasons for weight loss. You should control your weight and not leave its sharp fluctuations unattended. If your weight change is not due to diet, increased activity, or other controllable factors, you should definitely consult a physician. Necessary weight loss testing may include:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- analysis of thyroid hormones;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- analysis of stool and blood for parasites;
- fluorography.
Further medical care depends on the diagnostic results. The effectiveness of treatment can be increased by: immunomodulatory therapy, vitamins, help from a psychologist, exercise therapy, a high-calorie diet and physiotherapy.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Treatment of stress
Do not delay making an appointment with a specialist if you feel that you cannot cope with stress on your own. Based on the patient's complaints, a treatment plan is prescribed.
An approximate treatment regimen looks like this:
- Therapeutic practice with a psychologist. At the moment, there are many psychological techniques that will help you cope with stress and return to normal life. The specialist will choose the one you need based on the patient’s condition and personal characteristics.
- Collection of analyses. Since stress can affect many organs, it is important to identify the problem early.
- Drug therapy. If the stress is not prolonged, then mild sedatives are prescribed that will reduce anxiety and anxiety. In more severe cases, patients are recommended to take tranquilizers and antidepressants.
- Relaxation. Healthy relaxation techniques include breathing techniques, massage and yoga.
How to solve the psychological problem of excess weight
It is necessary to treat obesity, which is psychosomatic, together with a psychologist. But first you need to make sure that the problem has a psychological cause and is not associated with endocrine disorders or other diseases. To do this, an examination is carried out by a therapist and an endocrinologist.
Sometimes the impetus for successful weight loss is the conclusion of a diagnostician, which indicates serious wear and tear on internal organs. Often, grade 2-3 obesity is accompanied by fatty hepatosis (obesity and impaired liver function), an increased risk of atherosclerosis, impaired glucose tolerance and a tendency to surges in blood pressure at a young age.
To treat psychosomatics, it is important to find an experienced psychologist who will help you find the causes of overeating and teach you how to control your desires. This process takes a lot of time and consists of several stages, during which the psychologist will suggest performing certain exercises:
- The identification of subpersonalities, one of which seeks to overeat, and the second – to control. Psychology usually recommends giving them names and setting up a dialogue, during which you can determine the reasons why a woman overeats, how one side controls this process, and the other interferes.
- Search for motivation, or the benefits of excess weight. A woman may blame obesity for the misfortunes that happen to her. But subconsciously she often justifies herself, looking for benefits in this situation. Thanks to this exercise, she can identify her needs, which are satisfied with the help of excess weight, and find another way to satisfy them.
- At the third stage, the psychologist suggests answering questions about excess weight, dividing the answers into columns with pros and cons. Once she is convinced that the disadvantages of obesity are greater, a woman can set herself up for drastic weight loss.
Sometimes emotional problems or experiences are so significant that they require medication correction. The doctor may prescribe herbal sedatives that will not cause harm and will help maintain mental balance. These can be valerian tablets, motherwort tincture, Novopassit or Persen. These medications do not disrupt carbohydrate metabolism, unlike antidepressants.
In addition to finding the reason for eating high-calorie foods, with the help of psychology you can try to give it up if you build the right motivation. Psychological techniques work well when the same portion of food is crushed into small pieces. They visually look more voluminous than one large piece of meat or other dish. It helps to replace standard plates for meals with small ones that visually increase the amount of food.
For psychosomatic causes of excess weight, positive emotions are needed that will displace unpleasant experiences and help overcome stress. For reinforcement you can use:
- creativity - drawing, singing, playing musical instruments, dancing - any areas that will help get rid of negativity or switch to good emotions;
- sports – if obesity has not reached a severe stage, when physical activity worsens your well-being, you can remember your previous hobbies or find new ones. These can be team sports, martial arts or any other types of activity;
- hobby - helps you not to eat high-calorie foods, but to take your mind off troubles and switch your attention to activities that bring pleasure.
The results of losing weight for psychosomatic reasons need to be recorded so that the woman sees changes for the better. But weighing should not be daily, because... body weight may fluctuate. It’s better to step on the scale once a week to confirm positive changes.
Diagnosis and treatment of stress at Expert Clinics
Expert Clinics is a European-level clinic in Moscow, which fundamentally and comprehensively deals with the diagnosis and treatment of stress, as well as its consequences.
First of all, you should make an appointment. Next, based on the patient’s complaints, a treatment plan is prescribed.
It is important to understand that stress is not cured with one or two visits to the doctor. Recovery occurs in stages. It is important that this path becomes conscious for you. And correct and timely diagnosis of stress will be an important step towards a happy life.
Sign up
Sweet disease from a hard life
Diabetes mellitus is a disease caused by a lack of insulin, a pancreatic hormone. Diabetes mellitus manifests itself in increased blood sugar levels (normal 3.3-5.5), the appearance of sugar in the urine, and metabolic disorders. Diabetes mellitus is classified into two types: Type I diabetes mellitus - insulin-dependent. The first type of diabetes mellitus develops when up to 90% of pancreatic cells die due to viral or autoimmune damage. As a result, insulin is not produced. Type I diabetes affects people at a young age. Type II diabetes mellitus is non-insulin dependent. The second type of diabetes mellitus develops as a result of impaired sensitivity of body tissue cells to insulin. Insulin is produced in the body, even in increased quantities, but cannot perform its functions, since the cells “do not listen to it.” Type II diabetes mellitus is hereditary. It usually affects people over 40 years of age, especially those who are prone to obesity. Symptoms and course The main symptoms of the development of diabetes mellitus are the appearance of severe thirst and an increase in the amount of urine (up to 3-5 liters per day). For diagnosis, a blood sugar test is performed. Type I diabetes develops rapidly. Its signs are sudden weight loss (up to 10-15 kg per month), weakness, fatigue, and the smell of acetone from the mouth. If treatment is not started in time, diabetic coma develops, which leads to death. In type II diabetes, the disease develops slowly. Characteristic symptoms develop gradually and can manifest themselves in the form of thirst, dry mouth, itching, and pustular skin lesions. Diabetic coma occurs extremely rarely. Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes mellitus has very serious complications. High blood sugar levels lead to the destruction of capillaries - microvessels in various organs, which disrupts their blood supply and functioning. As a result, cataracts can develop, hemorrhages occur in the retina of the eyes, and blindness occurs. Diabetes also affects the kidneys, which leads to the development of chronic renal failure and uremia. When capillaries in the vessels of the lower extremities are destroyed, trophic ulcers appear on the legs, and gangrene of the fingers and feet develops. Neuropathy may develop. Its symptoms are pain in the legs, followed by loss of skin sensation. Men develop impotence. Since patients suffering from diabetes mellitus have reduced body resistance to viral infections, genitourinary tract inflammation and tuberculosis may be associated with the disease. In diabetes mellitus, fat accumulates in the liver, resulting in fatty degeneration and cirrhosis of the liver. People with diabetes often experience a number of psychological problems. Some patients make a whole “cult” out of their illness, living in the concept: “I am a diabetic, my life is suffering.” This position not only worsens a person’s emotional state, but also complicates the treatment of the disease. Tendency to diabetes Three categories of people have a tendency to diabetes: Overweight people perceive everything that happens very sensitively, they often have mood swings. They tend to be good-natured and extroverted. But at the same time, they are self-centered, strive to attract attention to themselves and know how to manipulate other people. Sedentary people. Observations show that in the early stages of diabetes, in 80% of people, blood sugar levels can be normalized by increasing physical activity. 'Owls' are people with a disrupted circadian rhythm, those who prefer to stay awake at night. It is in the morning hours that the endocrine system puts the entire body in order. And if a person usually sleeps at this time, then over time the insulin production mechanism is disrupted. Risk factors for the development of diabetes mellitus from the position of academic medicine: abuse of refined carbohydrates; eating fatty foods; physical inactivity; overweight; daytime nap; stress; alcohol consumption. The most common factor leading to the development of diabetes mellitus is the abuse of refined carbohydrates, i.e. products containing white sugar and white flour (confectionery, baked goods). Refined carbohydrates do not provide any beneficial substances, but have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. When consuming carbohydrates, there is first a sharp rise in blood sugar, and then a sharp drop, with almost no stability in the level. Sudden jumps in sugar levels lead to the following problems: excess weight; cholelithiasis; diabetes mellitus type II; hormonal disorders; diseases of internal organs (for example, pancreatitis). Diabetes mellitus in children The development of diabetes mellitus in children is associated with a lack of love and excessive consumption of refined carbohydrates. Diabetes mellitus occurs in children when parents are constantly busy and do not pay attention to the child. Instead of love, communication and joint activities, they bribe the child with sweets. Sweets become a substitute for love. The child becomes addicted to sweets both physically and psychologically. For adults, alcohol becomes a similar substitute for love. Diet for diabetes If you have diabetes, diet is a must. Excluded from the diet: sugar; jam; syrups; confectionery and sweet bakery products; sweet cookies; grapes, dates; alcohol. Psychosomatic causes of diabetes mellitus Dr. Torsunov O.G. names two factors predisposing to the development of diabetes mellitus: depressed emotional state: resentment, apathy, mental antagonism towards other people; overwork at work, when a person is too strongly attached to the result of work and works too hard - either physically or intellectually. Scientists from the Psychosomatics Clinic of the University of Munich identify three main reasons for the development of diabetes: 1. Post-traumatic depression, that is, a person’s prolonged stay in a state of shock after a severe shock: the loss of a loved one, a debilitating divorce, etc. A person cannot let go of this situation, although it is already a thing of the past. 2. Chronic problems and stress in the family (for example, alcoholism or infidelity of a spouse). People have been suffering from the same problems for years, and do not dare to solve them radically. The hormonal system is very sensitive to the environment, its work depends on the emotional state of a person. A person feels a lack of love as emotional hunger, which he tries to fill with food. Against the background of emotional hunger, gluttony may occur, followed by obesity and prolonged hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar), which leads to depletion of the insular apparatus. Chronic stress in which a person lives is one of the most common causes of diabetes. To normalize blood sugar levels, a person first needs peace of mind. 3. Increased anxiety, which can manifest itself either as fear or rage. The state of the pancreas is especially negatively affected by the lack of stability and a feeling of panicky anticipation. In a state of anxiety, the body burns sugar very quickly, so a person feels the urge to eat sweets. Gradually, the habit of “healing” from negative emotions with the help of chocolate develops. A dependence on sweets appears, which results in impaired insulin production and the development of type II diabetes. Psychosomatic treatment of diabetes mellitus Treatment of diabetes mellitus is primarily psychological work. And above all, a person’s purposeful independent work on his condition. Let's list the mental states that need to be worked out in diabetes mellitus: A person wants other people to love him and pay attention to him. But at the same time he does not know how to show his love towards other people. The other side of this problem: a person considers himself unworthy, undeserving of love. Complications to the kidneys (a paired organ) indicate that a person does not know how to find agreement with other people and enters into conflict situations. Fatigue, fatigue accompanying diabetes mellitus, may indicate dissatisfaction with work (a person is busy with something other than his own business). Diabetic retinopathy, or degeneration of the blood vessels in the retina, (leading to blindness) is an indicator that a person cannot see the world with loving eyes. Psychotherapy and psychoself-regulation are necessary conditions in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. When the mental state is stabilized, somatic homeostasis (the state of the internal environment of the body) is also equalized. A sign of successful treatment is the absence of disease progression combined with an improvement in emotional state. Qualified medical care The Angarsk City Hospital No. 1 provides comprehensive treatment for diabetes mellitus: outpatient appointments are carried out in clinic No. 1 (Sewing Factory stop). You can make an appointment with an endocrinologist by calling the reception: (3955) 58-60-03 daily, from 7-30; During classes at the School of Diabetes Mellitus, patients learn the most optimal lifestyle for this disease (you can enroll in the School from an endocrinologist); specialized endocrinology beds operate in the therapeutic department of the hospital (a referral for inpatient treatment can be obtained from an endocrinologist or a local general practitioner).
Protasova Valentina Anatolyevna
Section: Healthy lifestyle
How is depression treated?
Depression is treated with medication or a special type of counseling called psychotherapy. Sometimes these methods are combined.
What about drug therapy?
Several types of medications can be used to treat depression. These drugs are called antidepressants, and they have proven themselves very well. These drugs correct the chemical imbalance in brain cells that leads to depression.
Antidepressants work differently for different people. Each of them also has its own side effects. Therefore, if one of the antidepressants is not suitable for you or is not effective enough, it is quite possible that another drug from this group will help you. Improvement may occur after 1 week of treatment with an antidepressant, but the full effect is usually achieved after 6 to 8 weeks of treatment. Side effects usually occur at the beginning of treatment, but usually go away after a few weeks.
How long should I take the medications?
The length of treatment depends on the type of depression you have. Your doctor will likely prescribe you a course of therapy lasting 4 to 6 months or more. The duration of treatment should be sufficient to reduce the risk of relapse of depression. Be sure to discuss all aspects of your drug treatment with your doctor.
How can depression be diagnosed?
If you have symptoms of depression, be sure to tell your doctor about it, this is the only way you can get effective help. Don't think your doctor can tell you're depressed based on your appearance. The sooner you seek help, the faster you will get rid of depression.
If you tell your doctor how you are feeling, he or she may ask some clarifying questions about your symptoms, your health, and your family's medical history. Your doctor may also order some tests and perform a general examination.