Glioblastoma of the brain is a type of malignant neoplasm characterized by a high degree of aggressiveness. A tumor in the brain is characterized by rapid and aggressive growth. Early signs are usually absent, but as carcinogenesis progresses, a corresponding clinical picture appears. The main type of treatment is surgical removal of the pathological focus, supported by radio and chemotherapy. Glioblastoma is prone to frequent recurrence, so the prognosis is negative.
What is glioblastoma of the brain
Glioblastoma can develop from cells in the brain or spinal cord. The tumor begins with neuroglial cells that perform auxiliary functions. They support the vital activity and functioning of neurons. The neoplasm belongs to the highest (fourth) degree of malignancy; it can often form from gliomas (astrocytomas) of the third degree of malignancy. In any case, the tumor behaves extremely aggressively, grows quickly, invades neighboring tissues, has no clearly defined boundaries, and recurs quickly and often, which will significantly complicate the treatment of glioblastoma. The metastatic process is poorly developed.
Note. This type of brain cancer most often occurs in men between 40 and 65 years of age. It has not yet been possible to understand why this happens.
Glioblastomas account for approximately 20% of the total number of all primary intracerebral tumors, but despite this, the disease is diagnosed quite rarely: up to 3 cases per hundred thousand people. Without adequate treatment, death occurs within a few months because the pathological tissue grows rapidly and attacks healthy structures. Most often, glioblastomas form in the temporal or frontal zone of the brain. The general name refers to the following forms of the disease:
- giant cell glioblastoma;
- glioblastoma multiforme;
- gliosarcoma.
The most common form is glioblastoma multiforme. This species is extremely aggressive, because many vessels are formed in the neoplasm, and they early undergo necrosis.
Glioblastomas are the most aggressive tumors of the glioma group. Below is a generally accepted classification according to the degree of malignancy:
- First degree of malignancy, for example, astrocytoma. These are benign tumors, have no signs of cancer, do not metastasize, are characterized by slow growth and almost never degenerate into cancer.
- Second degree of malignancy, for example, diffuse astrocytoma. In this case, gliomas are classified as low-grade, i.e., benign formations. Atypia is observed in the cells - one of the signs of malignancy. These formations can become malignant and progress to the following stages.
- The third degree of malignancy (anaplastic astrocytoma) has all the signs of cancer, except for necrosis; the tumor is poorly differentiated, grows and invades other tissues. Easily progresses to an aggressive type of cancer of the 4th degree.
- The fourth degree of malignancy (glioblastoma) is the most aggressive type of cancer. There are all the signs of malignancy, treatment is difficult, the patient’s life is at risk.
Causes
As is the case with other types of cancer, it has not yet been possible to understand the exact reasons for the formation of malignant tumors that form in the head. Formations can be primary (from dividing, growing or degenerating neuroglial cells) or secondary. In the latter case, carcinogenesis in the brain tissue begins with metastatic cells. Provoking factors are:
- lower grade brain tumors, such as astrocytomas;
- poor environment, employment in hazardous enterprises, compounds containing lead are especially harmful;
- exposure to ionizing sources;
- genetic factors;
- head and upper spine injuries;
- as consequences of alcohol abuse (the role of smoking in this case has not been established);
- malaria (possibly malaria mosquitoes carry a virus that causes cancer);
- neurofibromatosis;
- defeat by oncogenic viruses.
Note. In the presence of astrocytomas in the brain, in approximately every tenth patient they are modified into glioblastomas.
Classification
According to the mechanism of development, they are distinguished:
- Primary glioblastoma arising on unchanged tissue.
- Secondary headache developing from an astrocytoma of a lesser degree of malignancy. This form is more common in young people.
According to histological type, they are distinguished:
- Giant cell.
- Glioblastoma multiforme is the most common and most malignant neoplasm.
- Gliosarcoma.
The tumor can be located in any part of the brain, but most often it is localized in the white matter of the frontal and temporal regions, often growing into the corpus callosum and into the opposite hemisphere.
Symptoms
Clinical signs at an early stage are usually latent. As the disease progresses, characteristic symptoms appear. The initial signs are weak, but they intensify with the growth of pathological tissue. Negative manifestations can be general (wide-brain - provoked by increased intracranial pressure and intoxication of the body) and local, which depend on the location of cancer formation in the brain.
General signs of glioblastoma:
- headache, dizziness, often the pain intensifies while lying down and is not relieved by simple analgesics;
- nausea and vomiting, which do not depend on food intake; the patient does not feel better after vomiting;
- loss of appetite, decrease in body weight;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- decreased brain activity: memory and attention suffer, difficulty concentrating;
- the psycho-emotional state changes: the person becomes nervous, aggressive, depression and apathy are possible.
Local (focal) neurotic signs can manifest themselves in disruption of the visual, speech and auditory analyzers, impaired sense of smell, coordination, balance, convulsions, paresis, paralysis of limbs or body parts, and epileptic seizures are possible.
Diagnostics
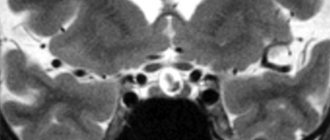
The success and consequences of treatment for brain cancer largely depend on at what stage of carcinogenesis the tumor is detected. The earlier glioblastoma is detected, the better the treatment. Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging using contrast remains the gold standard in head examination. Recently, PET – positron emission tomography – has been widely used. The most accurate diagnosis and all its features can be determined by cytohistological analysis of the selected material (biopsy). These are the main diagnostic measures; in addition to them, the following can be carried out:
- ultrasound diagnostics;
- angiography of head vessels;
- molecular tests;
- immunohistochemical tests;
- histological typing;
- genetic analysis of genes.
Stages
There are several stages of cancer development:
- Stage I. Pathological cells are located at the site of formation, do not grow into neighboring tissues, and growth is still relatively slow. The clinic is absent or weakly expressed.
- Stage II. The tissue grows, which leads to an increase in its size, and growth into neighboring tissues is observed. General cerebral signs appear, there may be convulsions and mild seizures of the epileptic type.
- Stage III. The tumor is actively growing, spreading into neighboring tissues, and the first regional metastases begin to form. Clinical signs are quite pronounced. The quality of life is deteriorating.
- Stage IV. The cancer grows and spreads quickly, and the clinical manifestations are very strong. The metastatic process intensifies. Palliative treatment is indicated. Removal of glioblastoma of the brain is not performed at this stage; the life prognosis is extremely negative.
Anastasia Zavorotnyuk and her illness: latest news
Rumors about Anastasia Zavorotnyuk’s illness have been circulating since August. It turned out that the actress was diagnosed with a malignant brain tumor about a year ago. She underwent radiation and chemotherapy in a Polish clinic, but to no avail.
By the end of August, Zavorotnyuk was transported to one of the Moscow hospitals, media reported. On September 13, it became known that the actress was sent to intensive care in critical condition. The tumor gave multiple metastases, which led to cerebral edema. Doctors decided to put the actress into a medically induced coma and connected her to a ventilator. Zavorotnyuk developed pneumonia and multiple organ failure - her internal organs began to fail.
The actress’s relatives forbade her director Stas Hristov to officially comment on Zavorotnyuk’s condition. But rumors still leak through colleagues. Producer of the group “Tender May” Andrei Razin said that the actress had only a few days left to live. Pop singer Philip Kirkorov supported the people's artist on Instagram and thereby confirmed her illness. Actor Stanislav Sadalsky showed a message in which Zavorotnyuk thanks him for his support.
Photo: instagram / a_zavorotnyuk
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain
Treatment of glioblastoma is selected individually, depending on the stage of carcinogenesis and the general condition of the patient. How long they live after removal of glioblastoma will directly depend on how far into the disease the surgery to remove the tumor was performed. In the initial stages, when the tumor is still small, it is possible to remove glioblastoma using new methods. These endoscopic techniques are minimally invasive and allow excision of the affected tissue without craniotomy. Microsurgery is performed using intraoperative fluorescent navigation. Before surgery, the patient is injected with a solution that stains the neoplasia tissue, which allows better visualization of the tumor. In this case, the removal of glioblastoma of the brain takes place with minimal trauma, the consequences of the surgical intervention quickly heal, which reduces the rehabilitation time.
Craniotomy (open brain surgery by opening the skull) is often performed because, as a rule, the tumor reaches a large size by the time of diagnosis, so it can only be removed by trephination or resection of the skull.
Due to the spread of the tumor, the unclearness of its boundaries and proximity to vital areas, it is not always possible to completely remove the tumor. In this case, surgery to remove glioblastoma will be considered palliative treatment. This will reduce intracranial pressure, significantly reduce negative manifestations and increase life expectancy. The consequences of surgery to remove glioblastoma will depend on how much pathological tissue is removed. The best result is when the tumor is completely removed.
Important. For this type of brain cancer, surgical treatment can reduce negative symptoms and increase life expectancy by a year or more.
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain in Russia is characterized by high standards that are not inferior to similar therapy in Western clinics. The advantage of domestic cancer centers is the lower cost of treatment and the availability of insurance programs. Treatment of glioblastoma is always complex. The operation is supplemented with radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Before surgery, these methods help stabilize tumor growth and reduce its size, and after surgery, kill or significantly weaken the remaining cancer cells.
It is important to note that in advanced stages of glioblastoma, surgery is often not possible. In this case, treatment of inoperable glioblastoma is carried out using radiotherapy (which becomes the main method of treatment) supported by the administration of cytostatic drugs. However, as practice has shown, glioblastoma cells exhibit high resistance to ionizing radiation.
To eliminate unfavorable symptoms, symptomatic treatment is prescribed:
- analgesics;
- anti-inflammatory;
- narcotic painkillers;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- sedatives;
- antinausea, antiemetic drugs and others.
Favorable factors
Although the disease is still fatal, the following factors can significantly improve the quality of life and increase the duration:
• early detection of pathology; • an increase in the size of the formation for a long time does not lead to disruption of important brain functions and the appearance of complications that are incompatible with life;
• cancer cells are sensitive to chemotherapy and radiation therapy;
• the general health of the patient allows for complex treatment, including radical removal;
• “convenient” localization of the pathological focus, allowing it to be removed without serious complications, for example, cerebellar tumors, as well as those growing towards the skull bones, are easier to remove than glioblastoma of the brain stem.
Consequences of the operation
The rehabilitation period after minimally invasive techniques is relatively easy. After craniotomy or resection, recovery is difficult. The patient is subject to careful postoperative diagnosis (in order to understand the success of treatment) and constant monitoring, since glioblastomas belong to the group of tumors that are characterized by relapses. Often patients need to learn again to adapt, talk, walk, etc., so rehabilitation specialists, psychologists, speech therapists, physiotherapists and other specialized specialists are involved in postoperative therapy. Physical overload is contraindicated. The patient must unquestioningly comply with all the doctors’ requirements.
Important. Glioblastomas are prone to relapses after surgical treatment. Their cells are low-sensitive to radiotherapy and often do not respond well to chemotherapy.
Life prognosis for glioblastoma
How long a person will live with this type of cancer is an individual question. Much depends on the type of glioblastoma, duration of the disease, quality of surgical treatment, age and general condition of the patient. Without treatment (after diagnosis), only 10% of patients will live more than 3 months. With proper therapy and successful surgery, it is possible to extend life by one and a half or two years; in 5% of cases, patients can live about five years or even longer. The most critical prognosis when diagnosing glioblastoma multiforme of the brain. In this case, even with successful surgery and adequate anticancer therapy, life expectancy rarely exceeds more than a year.
Forecast
Unfortunately, the prognosis for glioblastoma is extremely unfavorable. Five-year survival rate is no more than 10%. The average life expectancy with this diagnosis is about 8 months. Despite the rapid development of medicine, there has been no significant breakthrough in the treatment of glioblastoma in recent decades.
Any treatment for glioblastoma is considered palliative, that is, temporarily relieving the condition. Combination therapy can extend the patient's life by an average of 1-1.5 years. However, cases of stabilization of the process for a much longer time have been described.