Brain heart attack and stroke are dangerous and insidious diseases. In the modern world, about one billion people suffer from high blood pressure. Hypertension causes the development of cardiovascular diseases, strokes and cerebral infarctions. Patients often ask the doctor the question: “What is the difference between a heart attack and a stroke, if in both cases there is a violation of cerebral circulation? What measures should be taken?
Heart attack and stroke, differences
A heart attack develops due to vascular thrombosis. The formation of blood clots in the vessels leads to blockage, the flow of blood into the tissues of the organ is disrupted, and necrosis develops, leading to the destruction of the affected tissues. A heart attack can affect not only the brain, but also the heart, liver and intestines.
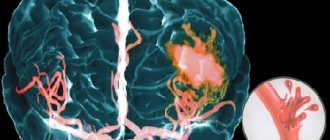
A stroke occurs due to a circulatory disorder, characterized by bleeding in the brain; in most cases, the functions of the affected area are taken over by other parts of the brain. A stroke can occur in the form of ischemic cerebral infarction or hemorrhagic cerebral stroke. Hemorrhagic stroke differs from ischemic cerebral infarction in the following manifestations:
- With a hemorrhagic stroke, a vessel wall ruptures or blood leaks through the vessel walls. Blood begins to flow into the brain tissue - a cerebral hemorrhage occurs.
- An ischemic stroke, or cerebral infarction, develops when blood vessels are blocked or there is insufficient blood flow to the brain, and the affected area of the brain dies.
At the Yusupov Hospital, doctors with extensive experience diagnose, treat and rehabilitate neurological patients. The clinic is located in Moscow on Nagornaya Street. The neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital accepts patients in any condition, even the most severe. The Neurology Clinic treats:
- hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes;
- multiple sclerosis;
- epilepsy;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- Parkinson's disease;
- consequences of traumatic brain injuries;
- diseases of the nervous system.
What does heart rate depend on and how to measure it correctly
The heart of a healthy person works like a clock, but, unlike the movement of the second hand, the frequency of its contractions either slows down or speeds up. This is influenced by many factors:
- physical exercise;
- Body temperature;
- stress, intense joy, excitement;
- dehydration;
- drinking drinks that contain alcohol and caffeine;
- smoking;
- taking certain medications.
So how do you know what your “real” heart rate is?
To do this, you need to measure it at rest, and before doing so, do not take alcohol, caffeine, take any medications, or smoke. The best time is immediately after waking up, while you are still in bed. It is most convenient to feel the pulse on the radial artery. Place your thumb on the inside of your wrist and your index finger on the outside of your wrist, under your thumb. To accurately determine your pulse, you need to use a stopwatch. You may come across recommendations that require taking measurements for 15 or 30 seconds, and then multiplying by four or two, respectively. But it’s better to spend a minute - it will be more accurate.
It is also important to remember that each person’s heart rate is individual, and it is also influenced by body size and age. Also, heart rates tend to be low in well-trained athletes.
Symptoms of diseases
Ischemic stroke is characterized by dizziness, dark vision, numbness in the limbs - a feeling of numbness appears in the arm or leg, in some cases symptoms appear on one half of the body. The patient's speech becomes incoherent or he cannot speak at all for some time. The face and lips may become distorted - facial paralysis develops. This occurs due to damage to a part of the brain and its failure to perform its functions. With timely assistance, functionality is restored - healthy areas of the brain begin to be responsible for speech, muscle function and other functions.
Hemorrhagic stroke is characterized by an acute course of the disease, the appearance of the following symptoms:
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity;
- loss of consciousness;
- photophobia;
- tinnitus;
- headache;
- vomiting, severe nausea;
- redness of the face and body;
- unsteady gait;
- convulsions;
- paralysis of one side of the face;
- paralysis of one side of the body;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- the patient speaks poorly, gets confused in words;
- coma.
It is very important to provide first aid for a brain stroke as early as possible. The patient is admitted to the hospital, diagnostics are carried out, seizures are eliminated, brain swelling is relieved, and the patient’s condition is stabilized. On the basis of the Yusupov Hospital there is a hospital, an intensive care unit, and a rehabilitation unit for patients after serious illnesses. If necessary, resuscitation measures will be carried out at the Yusupov Hospital and the seriously ill patient will be cared for.
Stroke: sudden symptoms
A stroke can also develop with abnormal development of cerebral vessels, with uncontrolled arterial hypertension, with atherosclerotic damage to the arteries supplying the brain.
The main manifestations are speech impairment, sudden facial asymmetry, weakness or decreased sensitivity in the limbs. The main symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident are associated with the development of acute ischemia of the part of the brain that is responsible for certain functions of the human body.
Article on the topic
Stroke and methods of its treatment. What you need to know about anticoagulants
In young patients, an acute ischemic attack in the brain or myocardium is malignant, often leading to disability and even death. This is due to the fact that with age, the number of small vessels supplying blood to the myocardium and brain increases. During the acute period, “bypass” small vessels begin to function, which help to nourish and replenish oxygen deficiency, saving the affected organ from total death. Young people do not have such “donors”.
It is worth paying special attention to a person’s subjective feelings. Signs of a stroke are associated with dysfunction of the muscles of the head and body. This means that if a person has an unnatural smile - with a distortion in the corners of the lips due to the impossibility of normal muscle contraction, he cannot raise his arms normally, and his handshake is weak, there are problems with speech, it is worth showing him to the doctor as soon as possible. It must be remembered that in case of a stroke, assistance should be provided in the next couple of hours.
Article on the topic
One step before a stroke. How to recognize the symptoms of the disease in time
Causes of heart attack and stroke
Causes of development of ischemic cerebral infarction:
- increased blood viscosity;
- blood clots;
- decreased cerebral blood flow due to diseases of the heart, vascular system, and blood;
- age;
- physical inactivity;
- bad habits;
- pathology of the vertebral and carotid arteries.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke increase gradually. Over time, a cyst forms at the site of the area affected by ischemic cerebral infarction.
The main causes of hemorrhagic stroke:
- high blood pressure (hypertension);
- microangiopathy (pathological condition of the vessels responsible for metabolism).
Diagnosis of stroke
Diagnosis of a stroke is quite complex, because to identify the cause and assess brain damage, and therefore the consequences of a stroke, the doctor will need a large amount of data.
To visualize the condition of the brain vessels, CT or MRI can be used, depending on the situation. A fairly informative study on the state of blood flow will be angiography - an X-ray examination using a contrast agent injected into the vessels.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe blood and urine tests; test for glucose and cholesterol levels; conduct an ultrasound examination.
Course of the disease
Cerebral infarction most often occurs in older people. Before an ischemic cerebral infarction, patients do not always complain of surges in blood pressure or any pronounced symptoms of trouble in the functioning of the blood vessels of the brain. Ischemic cerebral infarction occurs in people with normal blood pressure after nervous stress or heavy physical activity. Depending on the volume of the affected area and its location, brain function is restored. If the affected area is large and vital centers are affected, the patient may lose speech, and the consequences in the form of paralysis, tremors and other disorders of the nervous system will last a lifetime. Most often, the prognosis after an ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction) is favorable - patients recover within a few weeks, can live a long life, work, and take full care of themselves.
Hemorrhagic stroke is acute; about 70% of patients receive surgical treatment - low-traumatic puncture operations are performed to remove brain hematomas. The severity of the patient's condition depends on the location of the hemorrhage and the degree of vascular damage.
Highly qualified medical staff provide effective treatment and good care for patients after heart attack and stroke. Rehabilitation of patients takes place using high-quality European equipment - patients are helped to restore social skills with the help of exercise machines and special equipment, blood circulation in tissues is improved with the help of massage, psychologists and speech therapists work with patients after a stroke. For seriously ill patients after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, the Yusupov Hospital operates a rehabilitation department. You can make an appointment with a neurologist by phone.
First aid
Both pathologies are extremely serious. If a pain attack behind the sternum of a squeezing or squeezing nature persists or increases, accompanied by weakness, cold sweat, severe shortness of breath, or if speech disturbances or impaired motor function occur, it is necessary to call an ambulance as quickly as possible. In this situation, delay is like death. The sooner specialized qualified care is started, the higher the survival rate.
The gold standard in the treatment of acute coronary pathology is emergency surgery aimed at restoring blood flow in the shortest possible time. Currently, all large hospitals are equipped with appropriate equipment.
To prevent a heart attack or stroke, you must adhere to several rules: do not smoke, walk 10,000 steps per day, adhere to a balanced diet, maintain a drinking regime (1–1.5 liters of clean still water per day), do not abuse alcohol, control your weight and, accordingly, , waist circumference (for men no more than 94 cm, for women no more than 80 cm), monitor blood pressure levels, check blood glucose and cholesterol levels. You are also required to undergo an annual medical examination. If you already have cardiac pathology, take prescribed medications regularly. If your health suddenly deteriorates, you should immediately call an ambulance.
Heart attack
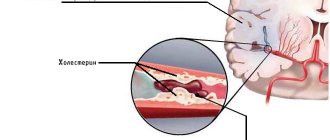
It is a circulatory problem that occurs when arteries become blocked and the normal flow of oxygen through the blood to the chambers of the heart is prevented. The attack occurs when the coronary arteries, which are responsible for transporting blood to the heart, become smaller due to the accumulation of fatty substances, calcium and protein in them.
Over time, these deposits form a plaque that hardens on the outside. This can lead to rupture, causing blood clots to form around them. When these blood clots block the coronary arteries completely, blood cannot reach the heart, which ends up starving for oxygen. When this happens, the muscle cells in the heart begin to die and can become damaged, which is what constitutes a heart attack.
Symptoms of cardiac arrest
In more than half of cases, cardiac arrest occurs without symptoms, as a “sudden event.” However, some patients experience a range of symptoms in anticipation of the problem. These include:
- Rapid heartbeat or extreme heartbeat.
- Feelings of dizziness and disorientation.
- Loss of breath and chest pain.
Although these indicators can predict cardiac arrest, most people will be alerted to it by the most severe symptoms, such as sudden weakness or loss of consciousness. In most cases, it is therefore very difficult to distinguish a stroke from a heart attack in advance.
Case from practice
A patient was admitted to the hospital with complaints of weakness, severe chest pain and heaviness in the head.
At the same time, dizziness, shortness of breath, blue discoloration of the nasolabial triangle, high blood pressure, and increased pulse rate were noted. The ECG revealed signs of acute myocardial ischemia in the posterior basal parts of the heart. When taking an EEG, no abnormalities were found; there were no pathological symptoms from the nervous system. A blood test showed an increase in myoglobin, troponin, ALS and AST, and low-density cholesterol levels. Diagnosis: Acute macrofocal myocardial infarction. Hypertension II degree.
Treatment was carried out (oxygen therapy, intravenous nitrates in a dropper, Heparin, beta blockers, diuretics, sedatives). After 3 weeks of intensive therapy, the condition improved, the cardiogram showed positive dynamics, and scar formation was noted. He was discharged under the supervision of a cardiologist at his place of residence. Secondary prevention of the disease is recommended, constant intake of Aspirin, Nitroglycerin when pain occurs, Bisoprolol, Atorvastatin for life, a diet with limited fatty foods.
Heart Attack Symptoms
Symptoms that indicate a heart attack may come and go, but the condition may also worsen over time. They are also likely to be more acute during physical activity.
- Chest pain: Also known as angina. Sufferers often describe a feeling of heaviness or tightness in the chest. This feeling often comes and goes and can easily be confused with indigestion.
- Pain and numbness in other areas of the body: Feelings of pain or discomfort in the arms, neck, or jaw are common indicators of cardiovascular disease. The left side of the body is more likely to experience more pain than the right side.
- Unexplained difficulty breathing, hoarseness, and extreme weakness.
- Fast or irregular pulse or heartbeat.
- Dizziness, nausea and vomiting.
- Intense and often unexplained feelings of anxiety.
What is more dangerous for humans?
The likelihood of complications and death is high in both cases. But the incidence and survival rate depend on gender. Infarction with damage to the heart muscle in middle age is more common in men; after 50 years, this difference smooths out.
The fact is that in a young woman, a high level of estrogen protects her from the development of atherosclerosis, and during menopause, hormonal levels change. The mortality rate due to myocardial necrosis remains higher in the stronger sex. Stroke occurs less frequently in women, but in them it is more likely to be fatal.
It makes no sense to talk about what is more dangerous: a stroke or a heart attack. The prognosis and outcome of each of these diseases depends on many factors:
- age and gender;
- degree of irreversible damage to organ tissue;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- speed and accuracy of emergency care.
The probability of death of the patient in the first hours of acute vascular pathology is the same in both cases. But in this sense, my colleagues and I consider a heart attack to be more dangerous. Myocardial necrosis develops very quickly, and doctors simply do not have time to get to the patient. However, after a stroke, it takes much longer to recover and more often leads to severe disability: the prognosis for quality of life is less favorable.