As women age, the likelihood of having a stroke increases significantly. So, if in women over 60 years of age the incidence rate is 2-3%, then at the age of 75 to 80 this percentage increases to 11%. At this age, both men and women are equally at risk of stroke. Due to age-related disorders in brain tissue, cerebral infarctions and spontaneous hemorrhages develop more often. At this age, symptoms are not as pronounced as at a younger age. Symptoms may be flickering or wave-like. The lesions may be small and therefore may go unnoticed. Accordingly, prolonged treatment time will not give the expected positive effect.
It is known that during a stroke, brain cells (neurons) die. The more neurons died, the worse the consequences of the disease. Diagnosis is also complicated by the fact that it is very difficult to obtain a clinical picture in an elderly patient. Therefore, doctors use instrumental diagnostic methods - CT and MRI. Computer diagnostics will help to accurately determine the location of the lesion, its size, and whether there were other undetected microstrokes and in what quantity.
Types of stroke
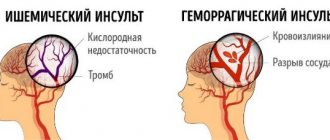
Clinicians distinguish two types of stroke: hemorrhagic and ischemic. The ischemic type accounts for more than 80% of all cases of the disease. It occurs due to narrowing or blockage of blood arteries, which impedes the flow of oxygen to the brain. Typically, this type of stroke occurs after age 60.
Hemorrhagic occurs when blood vessels rupture as a result of high blood pressure and bleeding in the brain. In this case, the prognosis for recovery is unfavorable and the survival rate is quite low.
It is also worth highlighting transient ischemic attack (ministroke). An acute transient circulatory disorder lasts from 5 to 10 minutes, but if this is not given due importance, the consequences can be quite serious.
Limbic system
{banner_banstat9}
The key symptom of damage to subcortical structures (in particular the cerebellum) is a violation of orientation in space.
The patient loses understanding of the spatial structure and her position in it. A painful manifestation. If during dizziness the sense of place is formally preserved, in this case it is also lost.
At the same time, there may be a loss of the ability to learn, absorb new information and use it.
Pre-stroke, transient ischemia of the limbic system is rare: 3-5% of the total number of cases.
Signs of a stroke
Most often, cerebrovascular accident occurs suddenly. Symptoms include:
- Increased blood pressure.
- Strong headache.
- Dizziness.
- Loss of balance.
- Noise in ears.
- Visual impairment (loss of fields).
- Numbness of the facial muscles and limbs.
- Articulation impairment.
In addition, older women may have atypical symptoms: hiccups, fever, attacks of fear.
A stroke can develop from several hours to days. You can understand that changes in blood circulation are occurring by the occurrence of tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), attacks of fear, decreased attention, and loss of orientation.
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to seek emergency medical help. Taking timely measures will help stop cell death and avoid serious complications.
Brain stem
With ischemia, life- and health-threatening manifestations develop. Like stopping breathing, cardiac activity. This is the only case when a pre-stroke in a woman can lead to death even without the death of cerebral tissue.
Additionally, it is possible to develop elevated body temperature. Thermoregulation is disrupted, the readings fluctuate, from 35 to 38 degrees Celsius or more.
The sign is also considered threatening and requires urgent correction in a hospital setting. The patient is constantly monitored for timely resuscitation.
Stroke in older women
According to statistical studies, stroke occurs in 1.5-2% of the population every year, while timely medical care is provided only in 50% of cases. It is for this reason that this pathology often causes disability and death.
As a rule, women are susceptible to stroke after 60 years of age, while in men this risk occurs much earlier - after 40 years of age. This is largely due to hormonal disorders that occur in the body of women during menopause. Smoking, alcohol, long-term use of hormonal drugs, and blood clotting disorders also contribute to the development of stroke in women.
Women suffer the pathology more severely than men and only a small percentage of patients return to a normal lifestyle. The reason for this is untimely provision of medical care.
Patterns of development of the pre-stroke state
Primary signs of a pre-stroke condition in elderly women may be nonspecific. May appear:
- frequent headaches;
- nausea;
- malfunction of the sense organs.
Similar symptoms can appear with the progression of many diseases, including hypertensive crisis, a drop in sugar levels, and others.
However, despite the nonspecificity of the symptoms, it is still possible to recognize a pre-stroke condition. There are several factors that allow you to determine pathology at an early stage:
- The pre-stroke state was preceded by a long period. It is clear that transient ischemia cannot develop suddenly over a few days or hours. There is always an initial stage from which signs are taken into account. This stage usually takes 14-21 days, but in some patients it can last longer.
- The general condition worsens. In women, pre-stroke is much more severe than in men and often ends in necrosis.
- The manifestations are more pronounced. This factor is directly related to the previous one.
- The likelihood of an emergency occurring is much higher. Most often it is characterized by tissue death.
How to recognize a stroke
You can determine the development of a stroke by doing the following:
- Try to quickly repeat the phrase.
- Smile widely (if a stroke develops, the immobility of part of the face will be noticeable).
- Raise your arms up (if cerebral circulation is impaired, this will not be possible).
- Ask the person to show their tongue (in the case of a stroke, its tip will be deviated towards the brain lesion).
If the patient cannot pass this test, you must immediately call an ambulance, and during this time provide first aid:
- Lay the patient down, raising his head above body level.
- Provide air flow (open a window, balcony).
- Free yourself from tight clothing (unfasten your bra, belt, belt, tie, etc.).
- When vomiting, turn your head to the side.
- Measure blood pressure, pulse, record all readings.
When signs of a stroke appear, it is important to behave calmly and reassure the person, since excessive emotionality contributes to increased blood pressure.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Frontal lobe of the brain
Responsible for mental activity, the ability to make logical constructs, synthesis of new information from existing data, behavior, muscle tone and some other functions.
- Infantilism. The patient relapses into childhood. Primary reflexes, such as grasping and sucking, return. Behavior is inappropriate for age; this is a temporary phenomenon. Recovery after the end of the pre-stroke state is spontaneous. The intervention of doctors contributes to rapid correction.
- Thinking disorders. By type of productivity decline. The patient is unable to solve basic logical problems. Inferences are impossible, judgments do not have an adequate basis. Formally, intelligence is preserved. But the woman is unable to use the resources because the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted.
- Unsteadiness of gait. The victim cannot walk in a straight line. This is due not so much to a violation of orientation in space, but to insufficient muscle tone, a partial loss of control over the muscles.
- Behavioral disorders. The woman becomes inappropriately cheerful, whiny, and aggressive. Accented personality traits are sharpened. Therefore, the pattern (model) of the disorder is determined by the individual properties of a particular person. His character.
- Paralysis, paresis. On the one hand, opposite to the localization of the lesion. The upper and lower limbs and face are affected. The notorious distortion of facial muscles occurs, which is inherent in a classic stroke.
- Epileptic seizures. Total or large with loss of consciousness and tonic-clonic convulsions. They cover all muscle groups and the body as a whole. It is necessary to distinguish the pathological process from classic true epilepsy. This can be done both due to accompanying symptoms, clinical picture, and based on the results of instrumental diagnostics.
Lack of smell on one side. A specific sign of damage to the frontal lobes. When subcortical structures and the limbic system are involved in ischemia, the absence of odor perception is complete.
Rehabilitation
Elderly people who have suffered a stroke must undergo a long course of rehabilitation. This period is very important, since rehabilitation will help minimize the consequences of circulatory disorders and significantly improve your overall condition.
The list of actions to restore the patient includes both physical and psychological assistance. A person must feel important and supported; only in this case will he be able to overcome the psychological discomfort associated with the partial loss of cognitive functions.
Even if the patient’s motor function is normal, it is necessary to purchase an orthopedic mattress. When a disruption in activity does occur and a person has limited physical capabilities, it is necessary to regularly change his position (to avoid bedsores).
Often, a person who has suffered a stroke is prescribed medications to normalize blood circulation. They must be taken strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the attending physician. If signs of apathy or aggression appear, the help of a psychologist, and in some cases a psychiatrist, is necessary.
Temporal lobe
The work of this area ensures normal memory, internal speech and mental activity, and hearing in general.
- Epileptic seizures. As is the case with those with lesions of the frontal lobes, they develop suddenly. But they last less time. Otherwise, it is not possible to notice the difference without instrumental techniques. The difference is in the localization of the pathological impulse.
- Lack of hearing. The so-called cortical deafness. The patient completely loses the ability to navigate sounds. This is a temporary phenomenon; treatment as such does not make sense.
- Lack of speech perception. Formally, there is a noise stimulus, but it is impossible to evaluate the logic of the statements, the meaning of them, and even recognize the words.
- Verbal hallucinations of the mental type. So-called pseudohallucinations in outdated terminology. The proverbial voices in my head. Associated with disruption of Wernicke's area.
It is responsible for the production of inner speech. As a result of the anomaly, the signal moves to Broca's center.
He, in turn, identifies external stimuli and perceives them as such, as outside speech. A paradoxical reaction arises.
- Memory impairments of various types. Amnesia, failures. The feeling of a repetition of something that once happened (déjà vu).
Prevention
The following preventive measures will help prevent a stroke:
- Annual medical examination (cholesterol control, blood glucose levels).
- Regular blood pressure monitoring.
- Quitting alcohol and smoking.
- Sleep at least 7 hours.
- Daily walking.
- Proper nutrition (the diet should include a lot of protein, vegetables, fruits).
- Active lifestyle (exercise, yoga, swimming).
Stroke is a disease that leads to disability. To avoid it, you need to be careful about your health and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Risk factors
- Severe arterial hypertension. This also includes persistently high blood pressure. Pathologies are observed in 70% of elderly people. Over the course of a year, 3–4 hypertensive crises occur, which after 80 years of age often provoke a stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation (another name is atrial fibrillation). It is a heart rhythm disorder that causes uneven blood flow and blood clots in the heart. When blood clots enter the brain, they cause a stroke.
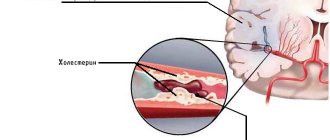
- Increased blood cholesterol levels. In older people, lipid metabolism is disrupted, as a result of which excess cholesterol begins to settle on the walls of blood vessels. Over time, blood flow becomes more difficult and, in severe cases, stops completely.
- Obesity in combination with the metabolic syndrome characteristic of the elderly (metabolic disorders, production of vital hormones and other processes). Increases the load on the heart.
- Myocardial infarction. Heart failure in people over 85 years of age. They are signs of the development of atherosclerotic processes that affect all vessels, including cerebral ones.
- Floor. There is a predisposition in females up to 80 years of age, and in males after 82 years of age.
- Alcoholism and smoking. They worsen the condition of the cardiovascular system and provoke obesity.
- Uncontrolled use of medications that affect blood circulation and the functioning of the heart muscle. For example, taking estrogen-containing contraceptives by women who smoke and have hypertension increases the risk of stroke.
- Diabetes.
- Sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity. Provokes slow blood circulation and obesity.
- Constant stress, increased mental stress, nervous exhaustion. Contraindicated for older people who have already had a stroke before.
Important! The presence of two or more factors in an elderly person increases the risk of a fatal stroke.
Also at risk are older people who have:
- congenital defects in the structure of the myocardium and valve apparatus;
- chronic diseases that provoke an increase in blood pressure, but are not pathologies;
- acquired defects of the cardiac folds, leading to disruption of blood flow;
- narrowing of the paired artery;
- damage to the cranial bones and soft tissues of the head;
- IHD;
- inflammatory process in the arterial vessels of the legs;
- holding your breath during sleep;
- inflammatory process of an autoimmune nature of the walls of blood vessels;
- muscle and joint diseases affecting the cardiovascular system.
The causes of a spinal stroke can be:
- injuries, surgeries and other physical impacts;
- atherosclerotic pathological processes;
- embolism.