Drinking alcohol in large quantities not only leads to the development of persistent addiction, but also provokes the destruction of brain cells. The longer a person drinks, the more his nervous system suffers, and his mental abilities are significantly reduced. If treatment is not started, alcoholism leads to complete personality degradation.
- Read in the article:
- How alcohol affects brain function: mechanism of action
- How many brain cells does 100 grams of vodka kill?
- How does the brain die from alcohol?
- The effect of alcohol on the nervous system
- Stages of brain damage by alcohol
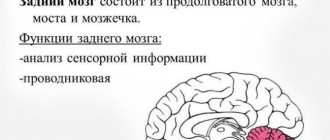
- Cerebellum and alcohol
- How does alcohol affect the brain?
- The brain of a drinker: photo
- The effect of alcohol on the blood vessels of the brain
- How long does it take for the brain to recover after alcohol?
- Causes of cerebral edema from alcohol
- Why do alcoholics have strokes?
- Effect of alcohol on memory
- How does wine affect blood and blood vessels?
- Detoxification of the body from alcohol in
Treatment prices:
| Sign up for a free and anonymous consultation with a narcologist | 0 ₽ |
| Initial consultation with a narcologist | for free |
| Consultation with a psychologist in person or Skype | 3 000 ₽ |
| Psychiatrist consultation | 5 000 ₽ |
| Psychodiagnostics / pathological diagnostics | 7 500 ₽ |
| Narcopsychotherapy | 50 000 ₽ |
| Consultation with a psychologist and selection of a treatment and rehabilitation program for an addict | for free |
| Intervention session | 12 000 ₽ |
| Social rehabilitation of alcohol addicts | for free |
| Outpatient rehabilitation in Moscow | 33 000 ₽ |
| Standard rehabilitation program | 40 000 ₽ |
| Intensive rehabilitation program | 80 000 ₽ |
| Premium rehabilitation program | 120 000 ₽ |
| Medical and social rehabilitation (21 days) | 150 000 ₽ |
| Rehabilitation Spain, Bulgaria | 200 000 ₽ |
| VIP rehabilitation program | 350 000 ₽ |
| Online addiction rehabilitation course | 28 000 ₽ |
| Rehabilitation of age-related alcohol addicts | 50 000 ₽ |
| Rehabilitation of drug addicts | 60 000 ₽ |
| Adolescent social-psychological-pedagogical rehabilitation | 70 000 ₽ |
| Psychotherapy | 5 000 ₽ |
| Family psychotherapy | 6 000 ₽ |
| Support groups for loved ones of addicts | for free |
| Webinars for relatives of addicts | for free |
| School for codependents | 3 000 ₽ |
| Transfer support | negotiable |
| Motivation for treatment | 6 000 ₽ |
| Escort to the clinic | 6 000 ₽ |
| Testing (urine/blood/hair) | specify |
Expand
Still have questions? Call us!
8
Free consultation and appointment
Where to go for help?
To help patients with alcoholism, as well as other types of drug addiction, there are specialized institutions in our country - drug treatment clinics. Each dispensary serves a specific area. People living in the area can go there on their own or with the referral of other specialists. They and their relatives will be provided with:
- advisory assistance
- examination
- treatment
Doctors working in dispensaries conduct examinations of patients, medicinal treatment and psychotherapy, and bring patients out of a hangover. Physiotherapeutic procedures are widely used.
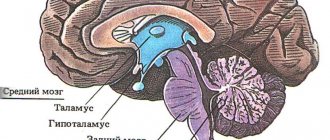
How alcohol affects brain function: mechanism of action
In severe alcohol addiction, ethanol, which is part of alcohol-containing drinks, has a destructive effect on the functioning of the brain and all organs. Drinking even a small amount of alcohol leads to muscle relaxation and causes a feeling of euphoria. The distribution mechanism of ethanol is such that its highest concentration occurs in the brain tissues, and not in the circulatory system. Therefore, it is the brain that suffers the most.
When drinking alcohol, the functioning of neurons is suppressed. This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Concentration decreases.
- Memory is impaired.
- Brain abilities decrease.
When a person begins to drink systematically, neurons stop performing their direct functions, and this leads to irreversible consequences.
Our phone numbers:
What is alcohol?
Alcohol is a depressant, that is, a substance that slows down all processes in the body. Small doses of alcohol give a feeling of relaxation and self-confidence. In large doses, it slows down the reaction and negatively affects, for example, the eye and coordination. Driving while not sober is extremely dangerous. A person in a state of severe intoxication experiences nausea, dizziness, and may lose consciousness, then on top of everything else there is the danger of choking on his own vomit.
The degree of intoxication may depend in part on the strength of the drink, that is, on the concentration of alcohol in it. The strongest drinks are whiskey, vodka, followed by various wines, and finally, BEER. In addition, the size of the drinker matters. In general, larger people are more resistant to the effects of alcohol than smaller people.
Alcohol abuse can lead to obesity, because alcohol contains calories, although it is not nutritious at all, to ulcers, cirrhosis of the liver, as well as to diseases of the brain, kidneys and muscles, including the heart.
The brain of a person who regularly drinks alcohol in large doses constantly struggles with its depressive effects. If such a person stops drinking, his brain, by inertia, continues its compensatory activity, which is why he becomes excited, nervous, fussy, his hands tremble, and this continues until he drinks more. Here is a typical example of alcohol addiction.
Scientific studies and statistics show that people who drink alcohol in light or moderate doses have lower premature mortality than non-drinkers and heavy drinkers. Various theories have been put forward to explain this phenomenon: some believe that alcohol causes the body to produce substances known as high-density lipoproteins, which prevent cholesterol from depositing in the arteries. Others believe that the heart is protected by substances found in certain varieties of red wines that inhibit oxidative processes. The well-known relaxing effect of alcohol also helps with stress.
It would be bad if these facts prompted someone to take a drink for the first time or increase their alcohol consumption. Drinking destroys the brain, liver, digestive tract and stomach. Liver cirrhosis and pancreatic cancer are diseases of drinkers. Obesity and hypertension, as well as heart disease, are the result of heavy drinking.
The level of alcohol concentration in the blood depends on a number of factors.
- If you eat fatty foods, then intoxication will not be as quick.
- The high content of animal and vegetable fats slows down the absorption of alcohol and the digestion of the food itself.
- The fuller the stomach, the longer it will take for alcohol to reach the circulatory system.
- The thicker your body fat, the slower alcohol is digested and absorbed into the blood.
- Body weight: the heavier you are, the lesser the effects of alcohol on you.
- Your reaction to drinking 80 mg of alcohol may be completely different than someone else's. Typically, young people and women are more susceptible to alcohol.
The ability to consume alcohol and the effect it has on different people varies; however, it is believed that a safe dose (from a health point of view) is somewhere around 5 liters of BEER of medium strength or 10 large glasses of wine per week for men and 2/ 3 of this dose for women, provided, of course, that this amount will be lost evenly over the course of a week, and not in 1-2 times. If you can, try not to drink on an empty stomach.
One of the surest ways to avoid a hangover is to not drink on an empty stomach. Some argue that drinking a glass of milk before drinking alcohol slows down its absorption in the body. Following this advice, drink in moderation and dilute alcoholic drinks.
Alcoholism – what is it?
Alcoholism is the regular, compulsive consumption of large amounts of alcohol over a long period of time. It is the most serious form of drug addiction in modern times, affecting between 1 and 5% of the population in most countries. An alcoholic drinks compulsively in response to a psychological or physical dependence on alcohol.
Anyone can become an alcoholic. However, studies have shown that for children of alcoholics, the risk of becoming alcohol dependent is 4-6 times higher than for children of non-alcoholics.
The study of alcohol consumption among young people in Russia is largely based on the experience of similar studies abroad, which in the late 19th and early 20th centuries were widely carried out in Western Europe and North America and were conducted in a variety of directions:
- The prevalence and patterns of alcohol consumption among students were studied.
- The effect of alcohol on children's and adolescents' bodies was studied.
- The relationship between academic performance and alcohol consumption was determined.
- Anti-alcohol education programs were developed and tested.
A significant place among the studies of this period was occupied by works illustrating the prevalence and nature of drinking customs, when children were given alcoholic beverages for:
- “health promotion”
- "appetite"
- “improved growth”
- “to relieve teething”
- “warming up”
- “satisfy hunger”
- "calm"
The strong belief in the strengthening effect of alcohol that existed in the 19th and at the turn of the 20th centuries often resulted in the direct alcoholization of the child.
It is estimated that two thirds of alcoholics are men. Case studies of alcoholism show that alcoholism is often part of the overall picture of depressive illness. Many alcoholics suffer from childhood emotional problems, often related to the loss, absence, or inadequacy of one or both parents.
Six stages of alcoholism
Casual drunkenness can lead to alcoholism: because the drinker begins to turn to alcohol to relieve stress, or because it is so strong that the initial stages of addiction remain unnoticed.
Early alcoholism is marked by the appearance of memory lapses. Alcoholization of the younger generation is considered by most researchers as a significant indicator of the dysfunction of the microsocial environment. This determines the constant interest in studying the problem of the prevalence and nature of early alcoholism.
Early alcoholism includes exposure to intoxicating doses of alcohol before the age of 16. Early (teenage) alcoholism should be discussed when its first signs appear before the age of 18. When analyzing the alcoholism of minors, we proceeded from the methodologically important proposition that the use of alcoholic beverages by adolescents must be considered as a form of behavioral disorder. This requires a broader and deeper approach to the problem under consideration, not limited to the framework of social and clinical narcology.
Boys drink the main types of alcoholic beverages more often than girls, and as their strength increases, this difference becomes significant. Among urban schoolchildren, it is common to consume predominantly weak alcoholic drinks - beer, wine, while students in rural schools are more familiar with the tastes of strong alcoholic drinks. In the 1920s and 1920s, one could find fairly widespread use of moonshine by schoolchildren: 1.0–32.0% among boys and 0.9–12% among girls. The frequency of vodka consumption increased with age.
Almost all socio-hygienic and clinical-social studies of youth alcoholism used the survey method in various modifications - from correspondence questionnaires to telephone interviews and clinical interviews.
It is most difficult to compare data on the prevalence and frequency of alcohol consumption among young people, since authors not only from different countries, but even from the same country in the same historical period used qualitatively different methods for identifying users and non-users. alcohol, different age classifications, etc.
Despite the diversity of criteria for identifying alcohol abusers and alcoholics in adolescence, data from various authors still allows us to judge that their number is quite large. Analysis of the materials shows that over the past 100 years, regardless of the level of consumption and abuse of alcoholic beverages, the prevalence of alcoholism itself among young people remains at a fairly stable level, not exceeding 5% of patients under 20 years of age and 8-10% of patients under 25 years of age. This fact is of fundamental importance, as it indicates the dynamics of the emergence and development of early forms of alcoholism in the holistic structure of alcohol morbidity. Drinking on the sly and an urgent need for the first drink indicate a growing addiction. The drinker feels guilty, but cannot discuss his problem with others.
Basic alcoholism - the drinker cannot stop until he reaches the stage of poisoning. He encourages himself with self-justifications and pompous promises, but all his promises and intentions remain unfulfilled. He begins to avoid family and friends and neglect food, past interests, work and money. Physical deterioration of health occurs. Resistance to alcohol decreases.
Chronic alcoholism is characterized by further moral decline, irrational thinking, vague fears, fantasies and psychopathic behavior. Physical damage is mounting. The drinker no longer has an alibi, and he can no longer take steps to get out of the current situation. A person can reach this stage in 5-25 years.
Treatment is usually carried out through special programs for alcoholics. Psychologically, the desire to get help is revived in the alcoholic, and he begins to think more rationally. Ideally, he also develops hope, moral responsibility, external interests, self-esteem, and satisfaction with abstinence from alcohol.
The final stage of alcoholism occurs if the alcoholic refuses treatment or breaks down again after treatment. Irreversible mental and physical damage usually ends in death.
If you write all this briefly, this is what you get:
- Domestic drunkenness
- Early alcoholism
- Basic alcoholism
- Chronic alcoholism
- Cure
- The final stage of alcoholism
What determines the degree of intoxication of a person?
The effect of alcohol on behavior depends on the amount of alcohol that reaches the brain through the blood. This “blood alcohol level” is determined by several other factors besides how much you drink.
The size of the liver determines the rate of oxidation and elimination of alcohol.
The weight of the person himself determines the amount of blood in the body, since the volume of blood is proportional to it. The larger the person, the more the blood is diluted by the alcohol consumed and the more it is needed to have the same effect.
The speed and manner of alcohol consumption are also important. The slower a person drinks a certain amount of alcohol, the weaker its effects.
Drinking alcohol on an empty stomach has a stronger and faster effect than drinking it during or after a meal. Food acts as a buffer during absorption.
The process of intoxication.
When drinking alcohol, the transmission of impulses in the nervous system slows down. The highest levels of the brain are the first to be affected - inhibitions, excitement and anxiety disappear, giving way to a feeling of contentment and euphoria. As the lower levels of the brain are affected, coordination, vision and speech deteriorate. Small blood vessels in the skin dilate. Heat is radiated and the person becomes hot. This means that the blood has diverted away from the internal organs of the body, where the blood vessels have already narrowed due to the effects of alcohol on the nervous system. Therefore, the temperature of the internal organs drops at the same time. A possible increase in sexual desire is associated with the suppression of ordinary prohibitions. As blood alcohol levels rise, physical sexual performance becomes increasingly impaired. Eventually the toxic effects of alcohol cause nausea and possibly vomiting.
Hangover
A hangover is bad... And now in more detail:
A hangover is physical discomfort after consuming excessive amounts of alcohol. Symptoms may include headache, upset stomach, thirst, dizziness and irritability. A hangover occurs as a result of three processes. Firstly, the gastric mucosa is irritated by excess alcohol, and the functioning of the stomach is impaired. Secondly, cell dehydration occurs if the amount of alcohol consumed exceeds the liver's capacity, resulting in alcohol remaining in the blood for a long time. Thirdly, the level of alcohol has a “shock” effect on the nervous system, from which it takes time to recover.
The best way to avoid a hangover is not to drink too much (or better yet, not to drink at all). But the likelihood of a hangover is reduced if alcohol is mixed with a snack (Havka): the intake and absorption of alcohol is extended over a longer period of time, and food serves as a barrier. Non-alcoholic drinks taken at the same time or after will dilute the alcohol. The ill effects are also usually reduced if alcohol is consumed in a relaxed environment and smoking is kept to a minimum.
The stomach is soothed by a fresh lining: milk, raw eggs or just a good breakfast! Only then can you take aspirin or other painkillers to relieve your headache. The risk of stomach irritation from pain medications is much greater when the stomach is empty. It is known that citrus juices, honey and vitamin C contain an “anti-hangover factor”. Fizzy drinks can have a soothing effect on the stomach. Liquids of any kind will help restore the fluid content of dehydrated cells. Coffee and tea are used to clear your head (caffeine stimulates the nervous system), and sugar will provide you with energy; but both caffeine and sugar can make a person's condition worse after their immediate effects wear off. In the same way, alcohol is also taken as a temporary relief, which (in moderation) encourages a withered nervous system and seems to disperse unpleasant sensations. But this is only a reprieve: the initial hangover and the hangover from a new dose of alcohol are still waiting for you!
The effect of alcohol on the body
Blood. Alcohol inhibits the production of platelets, as well as white and red blood cells. Result: anemia, infections, bleeding
Brain . Alcohol slows down blood circulation in the vessels of the brain, leading to constant oxygen starvation of its cells, resulting in weakening of memory and slow mental degradation (or simply dullness). Early sclerotic changes develop in the vessels, and the risk of cerebral hemorrhage increases. Alcohol destroys the connections between the nerve cells of the brain, developing in them the need for alcohol and alcohol dependence. Destruction of brain cells and degeneration of the nervous system sometimes lead to pneumonia, heart and kidney failure, or organic psychosis. Delirium tremens is a condition accompanied by extreme agitation, mental insanity, restlessness, fever, trembling, fast and irregular pulse and hallucinations, which often occurs when drinking large quantities of alcohol after several days of abstinence.
Heart. Alcohol abuse causes increased blood cholesterol levels, persistent hypertension and myocardial dystrophy. Cardiovascular failure puts the patient on the brink of the grave. Alcoholic myopathy: muscle degeneration resulting from alcoholism. The reasons for this are lack of use of muscles, poor diet and alcohol damage to the nervous system. Alcoholic cardiomyopathy affects the heart muscle.
Intestines. The constant effect of alcohol on the wall of the small intestine leads to a change in the structure of cells, and they lose the ability to fully absorb nutrients and mineral components, which ends in the depletion of the alcoholic’s body.
Diseases associated with poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency , such as scurvy, pellagra and beriberi, caused by neglecting food for the sake of drinking. Persistent inflammation of the stomach and later intestines with an increased risk of ulcers.
Liver. Considering that 95% of all alcohol entering the body is neutralized in the liver, it is clear that this organ suffers the most from alcohol: an inflammatory process occurs (hepatitis), and then scarring (cirrhosis). The liver ceases to perform its function of disinfecting toxic metabolic products, producing blood proteins and other important functions, which leads to the inevitable death of the patient. Cirrhosis is an insidious disease: it slowly creeps up on a person, and then strikes, and immediately leads to death. Ten percent of chronic alcoholics have cirrhosis of the liver, and 75% of people with cirrhosis are or have been alcoholics. Until cirrhosis develops sufficiently, there are almost no symptoms, then the alcoholic begins to complain of a general deterioration in health, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and digestive problems. The cause of the disease is the toxic effects of alcohol.
Pancreas. Patients suffering from alcoholism are 10 times more likely to develop diabetes than non-drinkers: alcohol destroys the pancreas, the organ that produces insulin, and profoundly distorts metabolism.
Leather. A drinking person almost always looks older than his age: his skin very soon loses its elasticity and ages prematurely.
Stomach . Alcohol suppresses the production of mucin, which performs a protective function in relation to the gastric mucosa, which leads to the occurrence of peptic ulcers.
A characteristic manifestation of alcohol poisoning is repeated vomiting. Even a single consumption of small doses of alcoholic beverages is accompanied in adolescents by pronounced manifestations of intoxication, especially in the nervous system. The most severe poisonings are observed in persons with a complicated medical history, against the background of organic cerebral insufficiency or concomitant somatic pathology.
It is much less clear to describe the nature of the influence of alcohol on the psyche of a teenager. In general, the clinical picture of severe intoxication in a teenager in most cases looks like this: short-term excitement is then replaced by general depression, stupor, increasing drowsiness, lethargy, slow incoherent speech, and loss of orientation.
If we turn to subjective data, to survey data, then despite their incorrectness (usually those who have recently become acquainted with alcohol and those who have some experience of alcoholism are simultaneously interviewed; it is not always checked whether the child being interviewed correctly understood the researcher’s question and etc.) it can be stated that in subjective experiences, especially at the very beginning of acquaintance with alcohol, negative or indifferent sensations play a predominant role. Of the 605 schoolchildren aged 6-16 years surveyed, while drinking alcohol, 41.1% had unpleasant and severe somatopsychic sensations, 35.6% had an indifferent state, 23% had a pleasant state, and 61.2% had a headache after drinking. %, nausea – in 8.4%, vomiting – in 14.8%, depressed state in 3.6%, weakness in 12.4% of respondents. When asked about how they felt when they were drunk, the following answers were received from schoolchildren:
- mood lifting – 47.8%
- indifferent state – 18.4%
- low mood – 6.1%
- physical illness – 27.6%
When drinking alcohol for the first time, 53% of teenagers felt disgust. Over time, with an increase in the “experience” of drinking alcohol, the objective picture, however, changes dramatically. More than 90% of the adolescents surveyed with two years or more “experience” of drinking believed that intoxication is accompanied by a feeling of a surge of energy, a feeling of contentment, comfort, and an increase in mood, that is, those attributes of a mental state that ordinary consciousness often attributes to the action begin to appear in their statements. alcohol.
Diseases or simply PSYCHOSIS
Delirium tremens usually occurs against the background of a hangover, with a sudden cessation of drinking or during a period of abstinence, in cases of the addition of somatic diseases, injuries (especially fractures). The initial symptoms of psychosis are worsening night sleep, the appearance of vegetative symptoms and tremors, as well as the general liveliness of the patient, noted in his movements, speech, facial expressions and especially mood. Over a short period of time, one can notice a variety of shades of mood, while during the period of a hangover the mood is monotonous, characterized by depression and anxiety. Unusual changes in mood and general liveliness intensify in the evening and at night, while during the day these disorders decrease sharply and may even disappear completely, which allows the patient to carry out his professional duties. As the symptoms of psychosis increase, complete insomnia appears, against which visual illusions first arise, and then various hallucinations and delusions.
Delirium tremens is characterized by a predominance of true visual hallucinations. They are characterized by a multiplicity of images and mobility. Most often these are insects (bugs, cockroaches, beetles, flies) and small animals (cats, rats, mice). Less often, patients see large animals and people, in some cases having a fantastic appearance. Visions of snakes, devils, as well as deceased relatives, the so-called wandering dead, are very typical. In some cases, visual illusions and hallucinations are single, in others they are multiple and scene-like, i.e. the patient sees complex pictures. Often there are auditory, tactile, olfactory hallucinations, sensations of disturbance of the body position in space. The mood of patients is extremely changeable. In it, within a short time, one can note fear, complacency, bewilderment, surprise, and despair. Patients usually move continuously, their facial expressions are expressive. Motor reactions correspond to the prevailing hallucinations and affect at the moment - with fear and frightening visions, the patient hides, defends himself, is excited; during periods of complacency - passive.
Patients are characterized by extreme distractibility to external events; everything around them attracts their attention. Delirium in alcoholic delirium is fragmentary and reflects hallucinatory disorders. In terms of content, this is most often delirium of persecution. Patients are usually falsely oriented in place (while in the hospital, they say that they are at home, in a restaurant, at work), but are oriented in their own personality. Alcoholic delirium is characterized by periodic temporary disappearance of a significant part of mental disorders, the so-called lucid - light - intervals, as well as a naturally pronounced increase in symptoms of psychosis in the evening and at night.
Delirium tremens is constantly accompanied by a variety of somatic disorders - trembling, sudden sweating, hyperemia of the skin, especially the face. The temperature is most often low-grade. The pulse is increased. Protein often appears in the urine; in the blood - increased bilirubin content, a shift in the leukocyte formula to the left, acceleration of ROE. The course of the disease is usually short-term. Even without treatment, symptoms of psychosis disappear within 3–5 days. Less commonly, the disease drags on for 1–1.5 weeks. Recovery is more often observed in the form of a crisis - after deep sleep. Sometimes recovery is gradual, worsening in the evening and at night and improving during the day. Signs indicating an unfavorable prognosis for delirium tremens are the development of symptoms of occupational and delirium delirium, high fever, and collapsed states.
Alcoholic hallucination develops either during a hangover or at the height of binge drinking. The main disorder is abundant auditory hallucinations combined with delusions of persecution. Verbal auditory hallucinations predominate, and the patient usually hears words “uttered” by a large number of people - a “chorus of voices,” as patients often define it. Most often, the “voices” talk among themselves about the patient, less often they are addressed to the patient himself. The content of verbal hallucinations is threats, accusing discussions of the patient’s past actions, cynical abuse, insults. Often hallucinations are mocking and teasing in nature. The voices either intensify to a scream or weaken to a whisper. Delusional ideas in content are closely related to auditory hallucinations - the so-called. hallucinatory delusion. They are fragmentary and unsystematic. The predominant affect is intense anxiety and fear. At the beginning of psychosis, patients are motorically excited, but soon some retardation appears or very orderly behavior is observed, masking the psychosis. The latter creates a false and dangerous idea of improvement. As a rule, symptoms of psychosis intensify in the evening and at night. Somatic disorders, usual for hangover syndrome, are constant. The duration of alcoholic hallucinosis is from 2-3 days to several weeks; in rare cases, the disease drags on for up to several months.
Alcohol depression always appears against the background of a hangover syndrome. Characterized by a depressed-anxious mood, ideas of self-deprecation, tearfulness, as well as individual ideas of relationship and persecution. Duration – from several days to 1–2 weeks. It is in a state of alcoholic depression that alcoholics most often commit suicide.
Alcoholic epilepsy is symptomatic and associated with toxicosis. Seizures most often occur at the height of intoxication during a hangover or during alcoholic delirium. As a rule, epileptiform seizures are observed. Minor seizures, twilight stupefactions, and auras do not occur in alcoholic epilepsy. With the cessation of alcohol abuse, seizures disappear.
Alcoholic paranoid is an alcoholic psychosis, the main symptom of which is delusion. Occurs in a state of hangover syndrome and at the height of binge drinking. The content of delusional ideas is limited to persecution or jealousy (ideas of adultery). In the first case, patients believe that there is a group of people who want to rob or kill them. They see confirmation of their thoughts in the gestures, actions and words of others. Characterized by confusion, intense anxiety, often giving way to fear. The actions of patients are impulsive - they jump off vehicles while moving, suddenly run away, turn to government authorities for help, and sometimes attack imaginary enemies. In some cases, delirium is accompanied by mild verbal illusions and hallucinations, and individual delirious symptoms that occur in the evening and at night. The course of this form of paranoid is usually short-term - from several days to several weeks. Occasionally, psychosis lasts for months.
Alcoholic encephalopathies are alcoholic psychoses that develop in connection with metabolic disorders, primarily of vitamins B and PP. Alcoholic encephalopathy occurs as a result of many years of alcoholism, accompanied by chronic gastritis or enteritis and, as a consequence of the latter, impaired absorption in the intestine. Alcoholic encephalopathies develop mainly in those individuals who drink a lot but eat very little. Most often, alcoholic encephalopathies occur in the spring and early summer months. They are conventionally divided into acute and chronic. There are no sharp transitions between them. The most common form of acute alcoholic encephalopathy is Gaye-Wernicke encephalopathy. The onset is most often gradual, lasting 2–3 months, rarely longer. Increasing asthenia appears, in which weakness and exhaustion, combined with memory disorders, predominate. Appetite decreases and then completely disappears, night sleep is disrupted, diarrhea and vomiting, headaches and dizziness, loss of balance, and polyneuritis develop somewhat less frequently. Subsequently, the full picture of the disease develops. Emerging psychoses most often represent erased and undeveloped delirious pictures, less often – anxiety-delusional states. A few days later - two to three weeks after the onset of psychotic disorders - the mental state begins to be determined by either symptoms of apathetic stupor or stupor, turning into a coma. Without treatment, the disease most often ends in death. Neurological disorders are constant and great. Autonomic symptoms usually include heart rhythm disturbances, fever of central origin, breathing problems, and sphincter weakness. You can constantly observe an increase in muscle tone. Sharply increased sensitivity to pain, e.g. for injections. Various hyperkinesis are common. The appearance of paralysis of the extraocular muscles, photophobia, and nystagmus usually indicates the highest phase of the disease. It is always possible to identify polyneuritis phenomena varying in intensity and localization. The general physical condition of patients is characterized by progressive weight loss up to severe cachexia. The skin is pale or dark brown in color.
Chronic forms of alcoholic encephalopathy include Korsakoff psychosis and alcoholic pseudoparalysis. In some cases, they develop gradually, over a number of months, and then the nature of the onset corresponds to Gaye-Vorik encephalopathy, in others - acutely, after alcoholic psychoses, usually after delirium tremens.
Korsakov psychosis is manifested by memory impairments: the patient does not remember anything from current events or remembers little; Retrograde amnesia and false memories are noted - confabulations regarding everyday events. The latter can be expressed to varying degrees, sometimes absent. Patients are lethargic, passive, and show no interest in their surroundings. Speech and motor reactions are impoverished. Of the neurological disorders, the most common phenomena are polyneuritis of varying intensity. The disease lasts for months, sometimes years. Improvements are possible when you stop drinking. Alcoholic pseudoparalysis is characterized by dementia with pronounced changes in memory, loss of acquired knowledge and skills, profound impairments in judgment, and loss of awareness of the disease and criticism. The background of the mood is determined by carelessness and, in some cases, ideas of greatness. Sometimes memory disorders predominate in combination with confabulations. The course is similar to Korsakov psychosis.
Treatment of alcoholic psychoses. Patients with alcoholic psychosis must be urgently admitted to a special hospital. Some patients with hangover syndrome are also subject to hospitalization in cases where mental disorders, especially mood changes, are intense. Treatment of alcoholic psychosis in the hospital should be comprehensive - the use of multivitamins (B1, C, PP), cardiac and hypnotics with hypoglycemic and comatose doses of insulin or psychotronic (aminazine, haloperidol) drugs. The only effective treatment for alcoholic, especially acute, encephalonitis is therapy with large doses of vitamins: B1 - up to 600 mg, C - up to 1000 mg, PP - up to 300-400 mg per day for 2-4 weeks.
Alcohol poisoning.
People who abuse alcohol sometimes fall into a state of stupor, leading to coma. In extremely severe cases, breathing may stop.
However, do not assume that a person who appears intoxicated has necessarily consumed alcohol. Similar symptoms are observed in other conditions (head injuries, stroke and diabetes, as well as overdose of certain drugs).
First aid.
If the victim is unconscious but still breathing, remove anything obstructing breathing (pieces of snacks, breakfast) from the mouth and pharynx with your finger, do not try to induce vomiting. Place the victim in the resuscitation position, free the neck and waist from tight clothing, and ensure that the airway remains patent.
If the victim does not regain consciousness, call an ambulance.
Conclusion
Alcoholism is a serious disease that in some cases develops over many years. So it’s better not to drink a lot and often! And if you drink, then drink BEER!!! :)
Dentist Lisitsina E.E.
How many brain cells does 100 grams of vodka kill?
When consumed, alcohol immediately enters the bloodstream and reaches the brain within 5 minutes. The first effect of euphoria occurs due to the release of endorphins, so the person begins to feel happy and sociable. Alcohol does not kill brain cells, but it does have short- and long-term effects on them. If you drink 100 grams of vodka, 8,000 nerve cells will be damaged.
The effect of alcohol on the nervous system
Alcoholic drinks affect the functioning of the central nervous system in two ways:
- Penetrates nerve cells and affects receptors and ion channels.
- Activates the functioning of certain brain receptors.
When drinking alcohol, the nervous system is in an excited state. Ethanol stimulates the release of dopamine, which increases activity and gives a person a feeling of euphoria. After resources are depleted, the opposite effect occurs - weakness, depression, and poor health appear.
Stages of brain damage by alcohol
Alcohol destroys neural connections, due to which there are more and more receiving receptors, and it is more difficult to activate them each time. Brain damage develops in stages and has three stages:
- First . There is a constant desire to drink, the craving for alcohol becomes systematic.
- Average . After drinking alcohol, a severe hangover begins and a strong psychological need for alcohol-containing drinks develops. Diseases of the internal organs begin to develop.
- Heavy . The person degrades, alcoholism becomes chronic.
Literature:
- Sytinsky, I.A. Alcohol and the brain. - Baku: Society "Knowledge" of the AzSSR, 1981. - 38 p.
- Etin G. M. Alcohol and the brain: lecture notes. - M.: Center of the Scientific Research Institute of Health Education of the USSR Ministry of Health, 1967. - 23 p.
- Popova E. N. Brain, alcohol and offspring. - Kazan: Kazan University Publishing House, 1994. - 147 p.
- Popova E. N. Ultrastructure of the brain, alcohol and offspring. - M.: Scientific world, 2010. - 155 p.
Need some advice?
OR CALL A DOCTOR
CALL!
+7
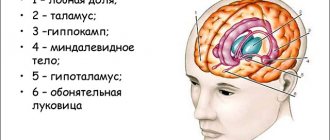
How does alcohol affect the brain?
The human brain is a complex neural structure, all areas of which are closely interconnected. All of them are responsible for the coordination of movements, for the transmission of information, and for the functioning of internal organs. The normal functioning of brain cells allows people to express their thoughts and feelings, communicate, and remember information.
Regardless of what a person drinks - beer, vodka or cognac, ethyl alcohol enters the body. The harmful substance instantly affects all areas of the brain, leading to the following changes:
- The level of thinking decreases.
- Lost control over movements.
- Drowsiness appears.
- Consciousness becomes cloudy.
- Speech is confused.
Regular drinking causes the addict to become lethargic, develop insomnia, and experience frequent outbursts of aggression. There are frequent cases of the development of mental disorders.
You keep getting drunk...
You drink further, and at this stage your tongue most likely begins to slur. The memory shuts down because the glutamate receptors are blocked, and you start repeating and repeating and repeating.
In addition, you probably begin to find many things funny, including the very things that you persistently repeat, due to the activation of the serotonin system and the GABA system. Alcohol suppresses the brain centers that control coordination of movements, and your legs can no longer support you.
When dopamine levels rise and self-control fails, you are tempted to engage in conflict. You also start doing some stupid things: you light up a cigarette even though you quit a long time ago, you drive drunk, you start racing shopping carts - simply because you are not able to think straight. Getting drunk seriously impairs your brain's performance, an effect that can be compared to a computer virus.
Continuing to drink, you are moving towards complete anesthesia, towards blackout. By the way, medical anesthesia also affects the glutamate and GABA systems. Before the invention of modern anesthetics, sailors facing amputation were drugged with alcohol until they were unconscious before the operation. And there is a reason for this: alcohol reduces pain sensitivity, and at the same time turns off memory. Anesthetics used for minor surgery stimulate the release of GABA to put you to sleep. During major surgeries, medications are used to reduce the level of glutamate that keeps you awake and alive. This is why artificial ventilation is required in such cases - the patient can no longer breathe on his own.
The fact that alcohol affects both the GABA and glutamic acid systems (the aforementioned double whammy) is what makes it so dangerous. GABA and glutamate regulate not only the balance of sleep and wakefulness, but also all vital processes of the body. This is why people die from alcohol poisoning. If you drink enough, you'll simply stop breathing.
The effect of alcohol on the blood vessels of the brain
When alcohol enters the body, it constricts blood vessels in the brain. As a result, red blood cells moving through the circulatory system stick together and turn into blood clots. Such clots prevent oxygen from reaching the brain, causing nerve cells to die. With each new alcoholic drink consumed, a person's risk of stroke increases.
How long does it take for the brain to recover after alcohol?
Scientists have proven that after an addict stops consuming products containing ethyl alcohol, the brain suffers for a long time. After giving up drinking, a person continues the recovery process for about six weeks. Even when alcohol is not supplied, the body cannot quickly restore cognitive abilities such as attention and memory. The duration of recovery is influenced by the following factors:
- Alcohol is a powerful diuretic, as a result of which the body loses a lot of fluid during the period of drunkenness. Dehydration occurs and the meninges shrink.
- Along with urine, nutrients such as magnesium, sodium and potassium, which are necessary for normal brain function, are washed out of the body. It takes time to make up for their deficiency.
To avoid all the negative consequences of drinking alcohol, you should stop drinking them forever. If you cannot get rid of addiction on your own, then you need to go to a drug treatment clinic.
Stages of female alcoholism
Conventionally, the development of addiction can be divided into four stages. The first can be conditionally called pre-dependence. It proceeds most easily. A woman can still easily give up drinking without drug treatment. Only sometimes she wants to drink. She has good self-control when drinking. But because of problems, he begins to drink more and more often, and then the craving for alcohol intensifies.
In the second stage, the frequency of drinking alcohol increases. I want to drink more and more often. During the feast, the patient may behave inappropriately - start scandals or have too much fun. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract make themselves felt. Memory is impaired.
The third stage is advanced alcoholism . You can already tell by the patient’s appearance that she drinks. Pathologies of internal organs develop, and nervous system disorders progress. Emotional instability appears.
The fourth stage is the most dangerous. It becomes very difficult to get out of the alcohol swamp. The patient degrades , breaks ties with relatives and friends. Her whole life consists of nothing but drinking. To overcome stage four alcoholism, you need to undergo long-term rehabilitation after coding.
Causes of cerebral edema from alcohol
The main cause of cerebral edema is severe intoxication of the body due to alcohol poisoning. The following factors can also trigger swelling:
- Manifestation of allergic reactions . Often, due to drunkenness, a severe allergy develops, which causes swelling.
- Bruises, traumatic brain injuries . People who abuse alcohol may fall or get hit by a car due to poor coordination of movements, so they have an increased risk of injury.
- Poor blood circulation in the brain or, in other words, a stroke . Weak blood vessels in the brain of an alcoholic cannot withstand the load, which leads to stroke and edema.
- Development of cardiac, hepatic or renal pathology . These important organs are primarily affected by alcoholism.
Effect of alcohol on memory
Alcoholic drinks negatively affect memory. A person may experience short-term memory lapses, as well as complete memory loss while drinking. The next day, the addict may forget absolutely everything he did, although his drinking buddies say that he was awake. Under the influence of ethanol, the memory function of the brain changes. Ethanol is a powerful toxin, and if the brain is severely intoxicated, it can change the type of synoptic transmission. Therefore, the brain simply stops working normally.
Alcohol and mental activity
Alcohol disrupts mental processes of an associative nature. This is a scientifically proven fact. As a consequence, the brain includes only the basic mental operations responsible for perception. Intellectual activity decreases.
VND centers affected by drinking are affected. It takes several weeks for them to start working fully after a one-time alcohol poisoning. With alcoholism and prolonged drinking bouts, there is no need to talk about complete recovery at all. The situation is improving very slowly. For the brain to start working stably, at least one year must pass. During this entire period, the drunkard should not drink alcohol.
Speaking about the effect of alcohol on mental activity, one cannot fail to mention that it destroys neurotransmitters. Hence the feeling of anxiety, constant mood swings, and depression. Patients lose the ability to correctly express their emotions and feelings. It is very difficult to communicate constructively with them.
Fight alcoholism competently - seek help from a narcology clinic. Don't let alcohol addiction turn you into a "close-minded Neanderthal." Value your mind and intellect. Don't let alcohol ruin your life.
How does wine affect blood and blood vessels?
Wine, consumed in small doses, can benefit the body. First of all, the drink is beneficial for blood vessels. Wine contains substances that increase the strength and elasticity of the walls of blood vessels.
- Red wine . Dry wines are the most beneficial. They contain magnesium, potassium, antioxidants and fructose. Dilates blood vessels provided you drink no more than 100 ml per day.
- White wine . Contains fewer antioxidants than red wine, but is also rich in nutrients. Reasonable consumption helps strengthen the immune system.
Still have questions? Call us!
8
Free consultation and appointment
Detoxification of the body from alcohol in
With prolonged consumption of alcohol, toxic substances formed during the breakdown of ethanol accumulate in the body. To get rid of poisons and toxins, you should detoxify your body. Specialists of the drug treatment center carry out the cleansing procedure in the hospital and at home.
Professionals use IVs, intravenous and intramuscular injections for this purpose. All medicines are certified and highly effective. Only an individual approach from specialists, drug therapy and rehabilitation will help you get rid of alcohol addiction forever.