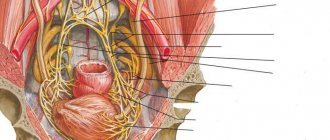
A child living a social life goes to school, communicates with friends, attends various events and crowded places. Consequently, there are plenty of reasons to experience both positive and negative emotions. Teenagers can also experience stress. How to protect your child from it? Psychologists advise playing. Simple and effective games will help relieve nervous tension in a child, get rid of anxiety and teach him to express emotions. Therefore, parents should know what to do if their teenager is stressed and how to protect him.
What where When?
“These are tics, or in other words, obsessive states,” explains child psychiatrist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation Vladislav Braginsky .
They occur in children 5-11 years old. Boys suffer from them 4 times more often than girls. And almost every tenth child is susceptible to tics, in general, a frequent attack.
Tics never disturb a child during sleep. But they intensify from excitement, excitement... In a familiar environment, they are less noticeable and have a smoothed-out character. Tics do not affect intellectual abilities in any way; a person can suffer from them in childhood, but he can think well and grow into an academician in adulthood.
This disorder is caused by different reasons, so the prognosis and treatment for tics are also different.
Psychiatrists divide them into two main types:
● neurotic (according to the new international classification – transient, transient); ● and neurosis-like (chronic).
Symptoms of crisis in a 7 year old child
During this period, even the most calm and obedient baby can turn into a real domestic tyrant, capricious and irritable. Features of the manifestation of the 7-year-old crisis most often consist in the fact that the child:
- does not fulfill requests, does not listen;
- capricious, stubborn;
- expresses protest, dissatisfaction, clowns around and is rude;
- does not accept criticism, gives extremely negative reactions to comments;
- tries to appear more mature, strives to communicate with older children, avoids younger ones;
- deliberately acts contrary to adults;
- devalues what previously seemed important to him;
- subject to mood swings.
To diagnose a 7-year-old crisis, it is necessary that the child clearly exhibits at least four to five signs. Otherwise, we are not talking about a crisis period, but about a local conflict situation.
Tick with fright
Let's say your perfectly healthy, calm child was frightened by a strange dog that rushed at him in the yard, or by a strict teacher who scolded him in front of the whole class, and now his eye twitches, or a cheek muscle, or he makes such movements with his neck as if freed from a tight collar. This is a neurotic tic. Despite the scary name, neurotic tics are a simple option. It arises from external trauma - fear, stress, tension - and is treated by a doctor in a couple of weeks, or at most in a couple of months. After treatment it disappears without a trace.
What is required from parents in this case?
● Take the child to the doctor. ● Create a calm environment at home. ● Do not burden the unfortunate person with intensive classes in mathematics, foreign languages, computer science... ● If the tics are caused by school conflicts, talk to the teacher so that he is not too strict. But obsessive states of this type are not very common, they make up only 10% of all tics.
Peculiarities of the child's psyche at 2-4 years old
When a baby turns 2 years old, he can no longer be perceived by his parents simply as a child. This is already a personality that actively declares itself. The baby demands, shows ambition and character. Everything he sees around him. It is taken to heart by him and is deposited as an imprint on his psycho-emotional development. He imitates his parents in everything and learns about the world through play.
It is at the age of 2-4 years that a child develops a social position. If parents push their child away when he needs help or attention, he will simply become withdrawn and not want to communicate with peers.
At this age, the “3-year-old crisis” begins to actively manifest itself in children, when he wants to show independence in everything. This is how the baby proves that he is an independent adult. Parents need to react to this correctly - not to scold, not to punish, but to show exceptional calm and support. Even if something breaks in the process of learning about the child’s world, this is normal. If you allow him all this, then he will grow up to be a full-fledged, liberated and inquisitive person.
Reason and reason
Another thing is the strange cough that my son once developed. Here you may not even guess that it is teak. Such neurosis-like, chronic obsessive states are the majority, according to Vladislav Braginsky, among tics they occupy 85-90%. Their reason is the weakness of the child’s nervous system. It occurs when the mother has a difficult pregnancy, or because of problems during childbirth (for example, the baby had asphyxia - oxygen starvation, or the labor was prolonged, with stimulation, or had to be performed by a caesarean section, or forceps were used...), or due to illnesses of the baby himself in the first months of life - illnesses also change the reactivity of the nervous system.
On such “prepared” soil, any reason: be it a cold or fatigue from an overwhelming academic load, can cause a neurosis-like tic.
It often begins with a real event: for example, a child has a stye, which is constantly felt and interferes, causing the child to blink frequently. Then the stye goes away, and blinking turns into an obsessive, uncontrollable action. Or my son, for example, had bronchitis. Two months have passed since the illness, all blood tests are good, but the cough drags on and on.
The child understands that tics are unusual and painful movements. He is often embarrassed by them, tries to restrain himself in public, but this causes him to experience enormous internal tension, which tires him terribly. Attempts to control tics end up making them worse.
Neurosis-like tics are difficult to treat and take a long time. They may appear, then disappear for a month or six months, then return again even without a visible push, for example, obeying seasonal fluctuations. The time of exacerbation of tics is spring and autumn.
“Will these twitches, blinks, and coughs really haunt us all our lives?” - Parents usually ask the doctor. No, they will not do. Tics are extremely rare in teenagers. And those violent adults we see on the streets or in the subway are suffering from the consequences of other illnesses or head injuries.
Peculiarities of the child's psyche per year
The child’s psyche is an important component of the child’s overall health. All parents should pay due attention to it in order to raise a person with a normal perception of the world, character and ambitions.
As the results of studies of the child’s psyche show, it begins to form in him even when he develops in the womb. This process is influenced solely by the lifestyle of the expectant mother, as well as genetics. The baby is born with his own character and begins to show it from the first days. At first, the child’s behavior is determined only by his reflexes, which are developed gradually as he grows:
- In the first few days he has only one reflex - sucking. With characteristic movements of his lips, he shows his mother that he is hungry.
- He develops sensory reflexes much faster than motor ones. First, he begins to see, hear, tactilely feel, and only then learns to control his movements.
- When the newborn period ends (this usually happens at 2 months of a child’s life), he already knows where his mom and dad are. The “revival” reflex actively manifests itself.
- During the period of a child’s life up to one year, his psyche is most strongly influenced by his parents, who must respond correctly to his needs. The baby repeats everything after them, imitates them. It is very important for him to have the attention of his relatives at this stage of his life so that he grows and develops fully.
- Closer to a year, the baby is already trying to say something, because he has well-developed connections between the objects that he most often sees and holds in his hands, and their names.
How to treat
Although medicine claims that tics are not for life, the child must be treated, which means it must be shown to a doctor: a psychiatrist or neuropsychiatrist, psychotherapist.
Firstly, to make sure that your case is just a weakness of the nervous system, and not symptoms of serious mental illness. The doctor can judge this by examining what other disorders the tic is observed in. For example, neurosis-like tics are combined with fatigue, irritability, tearfulness, mood swings, poor sleep...
It is necessary to exclude a rare type of obsessive states in which tics become more complex over the years.
Secondly, when the diagnosis becomes clear, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
To begin with, these could be physiotherapy: pine baths (they work very well for 5-6 year old children), soothing tea, electrosleep, electrophoresis with bromine... All this relaxes the nervous system. Massage of the collar area is useful - it improves blood supply to the brain. It’s good to drink warm milk with honey at night - it also calms you down. Much can be achieved with such simple means.
For tics, psychotherapy or psychocorrection is useful. This includes hypnosis, for older children - auto-training - the ability to use self-hypnosis to help yourself relax, and special breathing exercises for relaxation - the doctor will teach the child all this.
And in addition to treatment with words, medications are needed: vitamins, drugs that improve the nutrition of the brain, its metabolism, sedatives.
We can advise parents:
● Create a calm environment at home. ● Make sure that a child with a weak nervous system gets enough sleep. ● He needs a gentle regime and proper rest on weekends. ● Take special care of his nervous system after illness: even a minor cold makes it vulnerable for another two weeks. ● And don't discuss his tics. The more you talk about them, the worse the child gets. He already understands that something is wrong with him, and is waiting for help from you.
Proper nutrition is the basis of central nervous system health
For proper functioning of the central nervous system, vitamins are required, which must be ingested with food. A person needs vitamins A, B, C, D, amino acids, trace elements, minerals. But proper nutrition is not limited to just this - a balanced diet is required:
- more greenery;
- sufficient calorie content;
- vegetables and fruits, natural juices;
- the right ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
The state of the nervous system is positively influenced by foods such as river and sea fish, lean meat, fermented milk products, nuts, vegetables and fruits, and grain crops. The menu should have enough phosphorus, calcium, iron and potassium.
Post-Covid syndrome?
The entire diverse set of consequences in people who have survived a new coronavirus infection has already been called “post-COVID-19 syndrome.” Among its symptoms are mental disorders that are already well known to us: “fog in the head,” disorientation in space, panic attacks and cognitive disorders. However, some researchers say that mental problems in Covid survivors are not unique consequences of the new disease, but complications that cause any severe infectious disease.
So, back in 2021, an article appeared in the authoritative medical journal The Lancet, which analyzed 72 studies of the consequences of epidemics - the predecessors of COVID-19 - SARS-1 and MERS viruses. Mental disorders in those who recovered from these infections turned out to be identical: confusion, depressed mood, anxiety, memory impairment, insomnia and even delirium. Thus, we can draw a preliminary conclusion: the COVID-19 virus does not necessarily have any unique properties that affect the psyche.
Photo © Pixabay
Every modern teacher, who often in practice has to deal with students experiencing “hard times” (certain unfavorable living conditions) or a state of acute grief that occurs after a significant loss, and every parent needs to learn to identify the presence of symptoms of a stressful state in children and master a set of special techniques and technologies for working with such children.
Stress accompanies a person throughout his life
The famous Hans Selye, a Canadian biologist and physician, the creator of the doctrine of stress, said: “Complete freedom from stress means death.” He did not consider stress to be harmful, but viewed it as a reaction that helps the body survive.
Hans Selye divided stress into eustress and distress. Eustress is characterized by a positive effect on human activity. Distress (“distress”, English - grief, need, suffering, malaise, exhaustion), on the contrary, produces destructive effects in the human body. Distress can also increase a person’s adaptive capabilities, but still inhibits his development and leads to exhaustion of strength.
Psychological stress is a state of increased emotional tension. It occurs in a person as a result of intellectual and emotional overload.
Stress leads to various changes in the body, personality and its relationships with the outside world.
Different stressors, activating hormonal systems, lead to different types of diseases. In medicine, a distinction is made between active stress and passive stress. With active stress, symptoms of heart failure are more often observed; with passive stress, diseases associated with malfunctions in the immune system are observed.
A person’s adaptive capabilities are quite large, so many minor deviations that arise in the body’s activity under the influence of stressful situations are easily reversible.
But in situations of prolonged nervous tension, diseases such as hypertension, heart failure, diabetes, stomach ulcers, etc. can develop. Negative conditions arise when the load exceeds a person’s resistance to adverse effects. A little stress does not have a destructive effect on a person’s health and often mobilizes his reserve and creative capabilities, promoting somatic, mental and personal development.
What situations cause stress in a child?
– Any significant but natural changes in the child’s life. For example, entering kindergarten or school, the appearance of a younger brother or sister, moving, changing schools, divorce or remarriage of parents. Of course, different children may perceive the same situation differently.
– Crisis situations (violence committed against a child or in front of his eyes, entering a military conflict zone, acts of terrorism, a natural disaster that deprived a family of a home or property, an accident, illness or loss of a loved one, etc.). It is important to remember: for a child, a psychologically traumatic situation can be an event that is insignificant from the point of view of an adult - for example, the death of a beloved hamster.
– Ordinary life situations associated with the unknown, or separation from family, or pain. For example, the first trip to summer camp, a visit to the dentist or prescribed medical procedures (injections, gastric probing, etc.), examination in the hospital, upcoming surgery. Joyful events can also serve as a source of stress. For example, an upcoming date or visiting guests.
– Intense mental and emotional stress: school overload, tests, examinations, tests, situations of constant rivalry, competition with other children, information overload (television, Internet).
– Unfavorable situation in the family (quarrels between parents, broken relationships between the child himself and his parents or other family members), tense relationships with classmates, conflicts with teachers.
An adult sooner or later develops his own ways of responding to conflicts, his own ways of dealing with mental stress. The child has not yet developed such protection against stress.
Main signs of stress in children
1. The child’s mood often changes or he has a persistent negative mood.
2. The child's sleep becomes poor, he has difficulty falling asleep and sleeps very restlessly.
3. The child gets tired quickly after a load that was very easy for him just recently.
4. The child becomes touchy for no reason, can easily cry over an insignificant reason or, conversely, becomes too aggressive.
5. The child shows signs of an uncomfortable psychological state: he is absent-minded, forgetful, restless, he lacks confidence in himself and his abilities.
6. In a child, a state of psychological stress can manifest itself in previously unobserved antics and stubbornness, fear of contacts, and desire for loneliness. He stops participating in the games of his peers and has difficulty maintaining discipline.
7. Sometimes a child constantly chews or sucks something that has not been noticed before. Or he has a persistent loss of appetite.
8. Signs of a stressful state in a child also include previously unobserved coughing, trembling hands, shaking the head, twitching of the shoulders, playing with the genitals, night and even daytime urinary incontinence.
9. Some children under prolonged stress begin to lose weight, look exhausted, or, on the contrary, they experience symptoms of obesity.
10. The unfavorable psycho-emotional state of the child is indicated by such signs as impaired memory functions, difficulties with imagination, poor concentration, loss of interest in everything that previously caused activity.
All of the above signs may indicate a stressful condition in a child only if they have not been observed previously. It should also be noted that not all of these signs can be expressed explicitly. But adults need to start worrying already when some of them have been noticed.
The presence of the above symptoms indicates the appearance of psychosomatic disorders, which affect both the well-being and behavior of the child. Ignoring them can lead not only to persistent problems in the child’s health, but also affect the formation of his personal qualities.
Psycho-emotional stress deprives a child of a natural state of immediate joy for his age and can lead to the development of neuroses. With neurosis, control of body functions deteriorates. Therefore, children not only become irritable and touchy, they begin to complain of frequent headaches or disorders of the digestive system, their heart rhythm may be disturbed, and an increase in blood pressure is noted.
In what cases may a child need professional help?
– if the child is unable to fully control his behavior for a long period of time (he is aggressive, unable to control his actions and expressions, quick-tempered, overly touchy, whiny, etc.);
– if he has a complete lack of expression of feelings (the child has become lethargic, indifferent to everything, has lost interest in activities that previously fascinated him, etc.);
– if the child shows persistent loss of appetite or has had insomnia for a long period of time;
– if the child has strong fears;
– if a child’s process of experiencing acute grief is too long, he cannot return to the usual course of life, or adjust to the changes that have occurred to him.
Basic means of prevention and correction of psycho-emotional stress in children
1. Adults need to learn to recognize signs of emotional distress in a child, try to hear how the child signals that he is overexerted, and not ignore unfavorable symptoms, expecting that everything will go away on its own.
2. Each child has a certain limit of physical and mental capabilities. It is imperative to study the characteristics of a particular child and protect him from unbearable loads, skillfully distributing and wisely combining them with periods of rest to recuperate.
3. It is impossible to protect a child from stressful situations. It is necessary to develop his stress resistance skills and provide him with the necessary support.
To do this, first of all, you need to teach your child not to lose an optimistic approach to life under any circumstances. “We’ll break through!”, “Every cloud has a silver lining!”, “Is this such a big problem?” - such phrases should firmly enter the child’s vocabulary and become his life credo. Humor and self-confidence are one of the best ways to prevent and relieve stress at any age and in any people.
You can teach your child to look at difficulties in life from different positions: how your favorite book or movie hero, the Sage or Superman, would react to this. The child must understand and always remember that the difficulties and problems encountered in his life are temporary and will definitely be resolved, each problem has several options for resolution, and there are always close people next to him, ready to help and support him at any time.
4. As a rule, in order to get out of a state of stress, the child tries to use up the excess of released hormones that caused irritation. To do this, some children will smash toys or dishes, others will hit someone around them, others will run, fuss, scream or listen to loud music. Sometimes children begin to chew something, often without feeling the taste of the food.
Do not pull the child back, forcing him to calm down under pain of punishment. This way of interacting with him will only cause additional stress. Find a rewarding outlet for your child's pent-up energy by using physical strength around the house, in the classroom, or outdoors. Let your child be sure to engage in active sports and often play outdoor games with other children.
5. The risk of stress is especially high in childhood if conditions for normal physical development are violated. Science has long proven the interdependence of a person’s physical and mental state. The feeling of health, physical capabilities and bodily well-being contributes to a stable sense of inner comfort.
The child needs to be provided with the most comfortable working and rest conditions: long sleep in a well-ventilated room, a properly selected diet, well-distributed physical and intellectual stress according to the individual characteristics of the child. A prerequisite for optimally favorable development of a child must be adherence to a daily routine specially designed for him.
6. Teach your child the skills of muscle relaxation, auto-relaxation techniques, breathing exercises, evoking positive visual images, etc. They can be found in popular literature. Muscle relaxation causes a decrease in emotional stress and leads to calm and restoration of breathing.
Reliable ways to relieve stress vary from person to person. For some it is physical activity, for others it is communication with nature, with like-minded people or art, someone enjoys solitude or meditates.
Help your child find his own, individual ways to get rid of excessive emotional stress.
7. In crisis situations, do not neglect qualified assistance from specialists. In St. Petersburg there are special services for helping children and adolescents, hotlines, psychological consultations and other types of assistance for children and adults.
In our Center, you and your children can be provided with highly qualified assistance in the form of psychological consultations, differential diagnostics to determine the current mental state and find the most effective ways to resolve the current situation, classes are conducted on individual or group psychocorrection of observed difficulties in children.
Teacher-psychologist of the highest qualification category Oksana Vladimirovna Gyuninen