Everyone in their circle of friends has a person who constantly complains about their health: they have a stabbing pain, they are sick, or they simply don’t feel well. But no matter how many times he goes to doctors, no one finds a specific reason for this condition. He’s pretending, we think. But don't rush to conclusions. These symptoms may be a sign of a somatoform nervous system disorder. It does not have an organic background, but leads to a mental imbalance of the individual.
Why does the disorder develop?
Somatoform disorder is a disease of a psychological nature in which the symptoms of damage to internal organs are functional, not organic.
Such dysfunction is detected in 0.5% of the world's population, and it affects mainly women. The reason lies, first of all, in the psychological state of a person.
The first group of factors influencing the occurrence of the syndrome is heredity and character traits. For example, people with asthenoneurotic and hysterical types of character are more likely to develop it. They are characterized by hypersensitivity, timid or demonstrative behavior. Such people are characterized by rapid nervous exhaustion; as a rule, they are pessimistic.
The second group is psychogenic traumatic external influences. These include acute stress factors, when a powerful psychological blow at once leads to a disorder of nervous activity. This could be the loss of a loved one, a decrease in social status, or a situation of severe fear.
Chronic stress occurs as a result of systematic mental and physical overstrain, lack of positive emotions, unmet needs and excessive demands on oneself.
It is worth noting that somatoform disorder very often develops in people who are emotionally stingy, hide their feelings, and do not know how to express them. And since emotions need a way out in any case, they find it in this unique way. A similar state can accompany members of religious families, where an atmosphere of strict morality reigns.
Other factors that provoke the disorder include complicated pregnancy, trauma, infections, and some somatic diseases.
Teenagers
The All-Russian medical examination of children (2002) allowed us to draw the following conclusions. In the system of somatic diseases of adolescents from 15 to 17 years old, changes are observed: diseases of the endocrine system, neoplasms progress, infectious and parasitic diseases, and pathologies in the genitourinary system are observed. Somatic health is clearly suffering.
It is special in adolescents, and it is determined by two fundamental processes that occur during the transition period. The latter is characterized by a pubertal restructuring of the regulatory structure, which ensures physical, sexual and psychosexual development, on the one hand, and enters the final stage of psychosocial development, on the other.
Signs of illness
Symptoms of somatoform disorder are quite varied and manifest themselves in malfunctions of almost all body systems.
| System | Symptoms |
| Cardiovascular | Arrhythmias, sharp increases and decreases in blood pressure, pain and discomfort in the heart area. |
| Respiratory | Hyperventilation syndrome: shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air, dizziness. |
| Digestive | Irritable bowel syndrome: bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea. Digestive disorders: poor appetite, nausea, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, feeling of a lump in the throat |
| urinary system | Frequent urination, pain when passing urine. |
| Genital area | Decreased libido, inability to achieve orgasm. Vaginismus in women; in men – weak erection, impaired ejaculation. |
| Other symptoms | Increased sweating of the palms and feet, chills, hyperthermia. |
As a rule, several symptoms associated with different systems occur simultaneously.
There are the following types of this disorder:
- hypochondriacal;
- somatized;
- somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system (SDVNS);
- chronic somatoform pain disorder;
- undifferentiated somatoform disorder.
Patients with somatoform dysfunction are distinguished by several features. This includes a peculiar, emotional or overly specific narrative about one’s condition. For example, a man comes to a cardiologist with pain and discomfort in his heart. But at the same time, he speaks not only about their character, but also about the fact that they cause him a lot of inconvenience. Such attacks occur at work, at the moment when he is supposed to make a report on his achievements. As a result, he cannot concentrate, paying all attention to his heart.
The reason here is this aspect: perhaps the man is psychologically not ready to talk about his work (for example, due to his failures), and the heart is assigned to the extreme. And it is precisely this that reacts to this stressor in order to divert attention from it.
Other distinguishing features are:
- exaggeration of pathological sensations;
- denial of the role of psychological factors in their development;
- increased irritability towards others.
Factors influencing the somatic condition
Any disturbances in the human body can be caused by:
- Psychological factors, mental disorders that affect how a somatic disease develops and proceeds.
- Mental disorders as a personality reaction to somatic illness.
- A mental disorder that results from physiological changes in somatic illnesses.
- Somatic manifestations obscure mental disorders (masked depression, hysteria).
- Psychosomatic diseases.
It is important to note the following. With various somatic diseases - severe, life-threatening - neurotic disorders are especially acute. For example, a stroke or heart attack, oncology or HIV infection, or illnesses leading to a defect in appearance can provoke depression. It is important for the relatives of such a person to pay attention to this in a timely manner and try to help him. You may need to see a psychologist or psychotherapist.
Hypochondriacal dysfunction
Hypochondriacal disorder is characterized by a person's extreme concern about his or her health. He is sure that he is developing a severe, sometimes fatal disease. But their types may vary from case to case. One time the patient thinks that he has cancer, another time it is a severe heart pathology, etc.
The degree of sensation also changes. Either it seems to the individual that he is on the verge of death, then the manifestations become quite bearable.
It has been established that about 14% of patients visiting doctors of various specialties suffer from hypochondria. Most often it occurs in childhood and adolescence, as well as in mature people.
Basically, the patient is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- from the cardiovascular system - pain in the heart, disruptions in its functioning. The patient's conclusion is heart defects, heart attack;
- from the digestive system - abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation. Conclusion – stomach and intestinal cancer;
- on the part of the excretory system – fear of uncontrolled urination, and therefore patients even limit leaving the house. Pain in the lower abdomen.
Important criteria for recognizing pathology are the presence of senestopathies and mood disorders.
Senestopathies are manifested by unusual and painful tactile sensations. This may be itching and burning, a feeling of cold, compression and constriction, pulsation of blood in the vessels, twisting, displacement and other similar phenomena.
Mood disorders manifest themselves in increased anxiety, sadness, melancholy, and a feeling of hopelessness. Patients focus only on themselves, and do not hear others at all. At the same time, they believe that no one needs them, everyone has abandoned them.
Such people systematically seek help from doctors. And if a specific disease is not found, they insist on re-examination.
The following nuances will help determine pathology:
- constant belief that a person has a serious illness, often with other concomitant illnesses. And even numerous normal examination results cannot convince them;
- lack of trust in doctors, despite their regular visits;
- the activity of such a patient is not aimed at alleviating the condition, but at confirming the presence of a progressive pathology;
- constant concentration on your illness;
- independent diagnosis.
As hypochondria worsens, it can develop into a paranoid state or hypochondriacal depression.
The diagnosis of hypochondriacal disorder is made when schizophrenia and schizotypal disorders, bipolar affective disorder are excluded.
Hypochondriacs are often found among famous people. Actor and director Woody Allen is one of them. One day, his illness saved him from food poisoning. The entire crew ate pizza, which only he refused due to concerns about his health. As a result, everyone except him developed an eating disorder.
What suffers most often?
In this large system, we can identify the basis - a disorder of the endocrine system, pathologies of the central nervous system and the fact of dysplasia (muscle weakness). In this case, it would be reasonable to correct the underlying pathologies rather than treat differentially the disorders.
When analyzing the health status of an individual teenager, it is important to identify and assess the interdependence of different components of health (somatic, reproductive, mental, social components). In this case, prevention and treatment will be optimal and effective. In this case, a “convex” example would be the diagnosis of anorexia nervosa. A symptom such as cessation of menstruation may be a reason to contact a specialist.
Somatization and chronic somatoform pain disorder
Somatized dysfunction, in addition to organ manifestations, causes a decrease in the functioning of analyzers: vision, hearing, touch, smell. Coordination of movements is impaired: patients become clumsy and have an unsteady gait. Movement disorders manifest themselves in the form of paresis and paralysis.
They describe failures in the functioning of internal organs colorfully and with charm. For example, my head hurts, as if a hoop was put on it and was gradually being squeezed. Or your stomach is swollen like a balloon.
Unlike a hypochondriac, who expresses anxiety about his health, such a patient responds more rudely and persistently. He is convinced that he is sick. And if the doctor tries to hint at the psychogenic nature of the disorder, he screams and is indignant, rejecting what was said, and demands additional examination. This patient is constantly dissatisfied and complains.
The course of the disease is chronic, with wide variability of symptoms that persist for 2 years or more.
Often, a person, due to his anxiety and aggressiveness, experiences social maladjustment and family conflicts.
A pain disorder is distinguished by the presence of severe, debilitating pain that occurs for no reason. Usually it has a clear localization - the stomach, the heart. The pain characteristics do not change, there are no other symptoms.
During somatoform dysfunction, an undifferentiated disorder is also distinguished. With it, a person suffers all the typical symptoms of the disease, but it is not possible to classify them into any known group.
Adults
Mature people react more adequately to illness. But older people become hypochondriacs and more often suffer from phobias and depression. They listen to their feelings and become scrupulous in matters of health. But this doesn't always happen. It all depends on the individual characteristics of the individual.
We looked at somatic health. It is necessary to carefully monitor him, visit doctors in a timely manner and undergo a comprehensive examination.
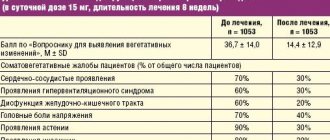
Somatoform dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system
The syndrome develops when there is a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which controls the functioning of internal organs, blood vessels, and is responsible for the course of physiological processes and the mobilization of the body as a whole.
The ANS consists of 2 sections: parasympathetic and sympathetic.
The sympathetic nervous system increases the heart rate, constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure. Increases sweating and slows down intestinal motility. It relaxes the bladder, dilates the bronchi and pupil. Sympathy speeds up metabolism and activates the body as a whole.
The parasympathetic system has the opposite effect. But, despite the opposition of departments, normal well-being of a person is ensured by their coordinated work. Any malfunctions in the functioning of both systems cause various pathological sensations and syndromes, in particular, somatoform dysfunction.
There are 3 types of disorders:
- with a predominance of sympathy;
- with a predominance of parasympathetics;
- mixed.
According to the flow, stable and paroxysmal, with vascular and other types of crisis are distinguished.
Pathology can be primary, that is, it develops on its own, or secondary, after previous illnesses. Its symptoms manifest themselves under the influence of a psychotraumatic factor.
Such patients are characterized, first of all, by the appearance of vegetative signs: severe sweating, tremors of the limbs, paleness and redness of the skin.
Another group of signs expresses the dysfunction of internal organs under the control of the ANS:
- cough, shortness of breath, laryngeal spasm;
- tachycardia, arrhythmia, blood pressure changes. Heart pain does not have a clear localization and can be of various types. It happens that they are accompanied by a feeling of anxiety or fear. They are worse at rest, but go away during physical activity. Lasts from a few minutes to several days. Heart symptoms are so believable that they sometimes confuse even specialists;
- abdominal pain, bloating, difficulty swallowing; “bear disease” - diarrhea under the influence of stress;
- difficulty urinating, urinary incontinence;
- headaches, fatigue, poor sleep.
The complaints are numerous, but lack specifics. They signal a disruption in the functioning of several organs at once.
Patients are concerned about their condition, but still not to the same extent as hypochondriacs. They strive to find a way out of the situation and receive adequate treatment.
Diseases of adolescents in structural characteristics
What diseases are most often of a somatic nature?
- Diseases that have a nosological form are common to age groups (let’s take anemia and pneumonia as examples).
- Diseases characteristic of puberty (for example, a disorder of bilirubin metabolism called Gilbert's syndrome, osteochondropathy, hypothalamic syndrome during puberty, enlarged thyroid gland).
- Characteristic of the developmental phase in life are “behavioral diseases” (increased trauma, STDs or diseases transmitted as a result of unprotected sex, use of alcohol, drugs, etc.).
- The list of rare diseases includes hypertension.
This is how the somatic health of a child suffers during adolescence.
SDVNS in children
Often, somatoform autonomic disorder appears in children at puberty, that is, during the period of maturation. This is due to a hormonal surge and intensive growth of the body.
The following factors can provoke the process:
- heredity;
- stress;
- mental, physical stress;
- infections;
- bad habits;
- surgical interventions;
- large body weight;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- staying at the computer for a long time.
The appearance of teenagers is typical. If sympathy predominates, then the skin of such children is moist and oily, with acne. She alternately turns red and pale. A bluish tint appears. Cold, with a marbled pattern called a vascular necklace. When pressed with a finger, the skin turns pale and red dermographism is observed.
When parasympathetics dominate, the skin is dry, with pink or white dermographism. These children have an increased appetite, but they do not gain weight.
The disorder is accompanied by a sudden rise in temperature under the influence of stress. A typical occurrence is fainting.
All characteristic changes in internal organs are present.
The psycho-emotional sphere is also undergoing changes. Such a child becomes distracted and nervous. He quickly gets tired, drowsiness and apathy appear, and his memory deteriorates.
In most cases, the course of the disease is stable. But periodically panic attacks and crises occur:
- sympatho-adrenal - accompanied by tachycardia, elevated blood pressure, headaches, thirst, chills and hyperthermia. Anxiety and feelings of fear develop;
- vagoinsular – migraine-like attacks, nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdominal area. Hyperhidrosis, decreased blood pressure and fainting, slow heart rate, increased urine output, breathing disorders;
- mixed.
The attack can last up to several hours.
Assessment of physical (somatic) health
Professor Apanasenko G. A. believes that the level of somatic health can be measured by a simple, reliable and accessible method. The assessment is carried out in points. To do this, you need to determine some indicators:
- body weight;
- height;
- blood pressure;
- hand strength;
- heart rate;
- vital capacity of the lungs;
- the time it takes for the heart rate to recover after exercise.
This method helps to identify deviations from the norm in a timely manner. Somatic health is also determined by other indicators:
- experience in physical exercise;
- general endurance;
- strength endurance;
- dexterity;
- effectiveness of the immune system;
- maximum oxygen consumption;
- presence of chronic diseases.
Treatment
Different somatic disorders may be subject to separate treatment methods. For example, in case of an acute illness that is caused by stress, depression, fear, the patient may be prescribed a course of antidepressants, vitamins or other medications that affect the psyche, taking into account all existing contraindications. In addition, the patient is recommended to engage in physical therapy and normalize nutrition.
In severe cases, treatment of diseases will be carried out only in a hospital hospital in the intensive care unit and under the strict supervision of a doctor. Among medications, preference is given to those that quickly and effectively eliminate the symptoms of diseases. Along with this, psychological therapy is carried out to address the root cause of the symptoms. For severe anxiety, doctors may use tranquilizers.
Diagnosis of pathologies
In order to identify the cause of somatic symptoms, the doctor will need to conduct a number of tests, including:
- a complete collection of the patient’s medical history, including interviewing relatives and collecting previous medical histories;
- visual examination of the victim, palpation of problem areas;
- urine test;
- analysis of stool, blood from a finger or vein;
- sputum collection;
- soft tissue biopsy;
- use of functional diagnostic methods - MRI, CT, X-ray;
- surgical intervention.
Classification
In addition to the diseases listed above, experts divide somatic diseases into 3 classes:
- Conversion diseases are an expression of neurotic conflict. Vivid examples of neuropathy: hysterical paralysis, temporary blindness or deafness.
- Organic somatic diseases - the cause is a physical reaction to experience, stress, fear. Patients complain of pain in different parts of the body, which they consider the most vulnerable.
- Pathologies associated with individual personality characteristics. For example, a person’s tendency to get injured or emotional abuse due to bad habits (alcoholism, smoking, overeating).