Coma is a serious state of the body bordering between life and death, which can occur as a result of acute cerebral circulatory disorders, inflammation, head injuries, hepatitis, diabetes and poisoning. This condition is characterized by loss of consciousness, a sharp decline in reflex activity and reactions to external stimuli (up to their loss), disturbances in the process of breathing, thermoregulation, vascular tone, as well as a slowdown or increase in heart rate. In fact, this is not an independent disease, but depending on its form and the reason that provoked it, it has a classification. At the same time, coma is not a type of disorder whose duration and consequences can be predicted with confidence, and, therefore, recovery after a coma cannot be called simple.
Main symptoms and signs of coma
The process of coma development can be either almost instantaneous or gradual. This can be a time period from several minutes to several days. Symptoms of comatose states may vary depending on the underlying disease. A very important point is the timely recognition of the condition preceding the onset of coma. In some cases, in addition to loss of consciousness, symptoms include changes in the color of the skin, the presence of unusual odors in the air exhaled by the patient, a decrease or increase in body temperature, as well as pressure. X-ray, laboratory and instrumental examinations make it possible to clarify the diagnosed coma.
Vegetative state: how I was a vegetable
I don't remember how I came out of the coma. I remember only a few moments: how I was in intensive care and how they sent me down for rehabilitation. What helped me move from being a vegetable to being a human? I'll tell you in order.
When my mother found out that I had crashed, she found money somewhere, bought a ticket and came the next day, when they had already brought me from Vyselok. She was shocked: I was in a coma with severe injuries, and the doctors could not console her. They say: “We can’t say anything. Whether he will live or not is unknown.”
The mother cries and takes pills, prays... The grandmother called and said: “You can’t help with this! Pull yourself together and think about how you can help him.”
After this, the mother insisted and began to come for 15–20 minutes every day. She was allowed to come in, but only for a short time. After a month and a half, I came out of the coma. The mother came and was told that there was no threat to life, but there was no positive dynamics either. I entered an elementary (vegetative) state, that is, I was a vegetable, looked at one point and did not pay attention to anyone. I was connected to a ventilator, the impacted lungs did not open, enteral nutrition, a catheter, stents were sewn to my neck, since the veins in my arms could no longer be found (they did stenting). The doctors did not see any prospects in me and wanted to discharge me to the hospital at my place of residence - with a tracheostomy, with food in my nose, connected to various devices. If they had sent me, I definitely wouldn’t be in this state now.
For the transfer, an intensive care unit was needed and to free up space in the intensive care unit of another hospital. But my mother managed to persuade me to leave me for a month. From a large intensive care unit, where there are 15 people in bed, all of them heavy, and the instruments beeping every minute, like in scary movies, I was transferred to a three-bed ward. And there, finally, my mother was allowed to come twice a day for 30–40 minutes.
Mom started massaging me: using oriental massagers, a roller, and needles, she massaged my feet, fingers, hands, and sensitive places. The skin on my feet was peeling off from the antibiotics. I behaved restlessly, I did not sleep since I came out of the coma, since the light was not turned off. In the three-bed ward, I began to experience tachycardia and high blood pressure.
I was in a stable and serious condition: I lay and always looked straight ahead, rarely blinking. My mother stood above me, talked and at times thought that I was looking at her, then she turned her head away, and I continued to look at the same point.
On one of these days, she saw that I was lying, excuse me, having emptied. Mom started swearing because this was not the first time. Then she was allowed to wash me, and she saw a large bedsore on my tailbone. It appeared because the bed was at a slight angle, they constantly lifted me up and I rolled down. The bedsore could not be healed for more than two months.
I think this painful moment, together with the massage, gave impetus to positive dynamics. When I started moving my right arm and leg and pulled the tube out of my nose (nutrition), thank God, they didn’t put it back. Mom just came, the doctor allowed her to try to give me something to drink from a syringe, and I began to swallow - drop by drop, but I swallowed.
A day later, my mother brought me juice for the children and also gave me 10–20 g from a syringe, then more. That is, the swallowing and taste buds worked. During these days I began to move on the bed more and more intensely.
Consequences and complications of coma
In fact, it is not the coma itself that leaves the consequences, but the painful state of the body that resulted from it. The severity of the consequences depends on the degree of coma. They can be so serious that a person simply loses the ability to exist without medical equipment and outside help. There may be another situation when the patient successfully recovers, restoring all body functions to the maximum extent possible. One of the most common consequences of coma is impairment of memory (to the point of amnesia), attention, and everyday skills (inability to eat independently, carry out usual hygiene procedures, etc.). In addition, prolonged lying down causes the development of bedsores. If you have suffered a coma, rehabilitation can greatly help the body cope with its consequences.
Coma
Coma is a lack of consciousness resulting from injury, infection, or serious illness. Coma is not an independent disease; it is a severe complication of the central nervous system. Cases in which coma :
- swelling of the brain (usually due to traumatic brain injury)
- brain tumor
- stroke
- aneurysm rupture
- liver or kidney failure
- complication of diabetes
- low blood pressure
- major blood loss
- infection or poisoning
- burn
- severe complications of cardiac diseases
- alcohol intoxication
If a catastrophe occurs with a person’s condition, his level of consciousness changes. There are several degrees of depression of consciousness. At the everyday level, this change in consciousness can be compared to sleep. But not the sleep of healthy people, but sleep due to the condition of the brain as a result of injury, infection or serious illness.
Stupefaction: the affected person is just trying to sleep and he is at least a little accessible to speech contact, does not answer immediately, in monosyllables and tries to close his eyes.
Stupor : a person who is sick and lying with his eyes closed can still be awakened by touch.
In these conditions, patients can be transported to the nearest hospital by local medical transport.
Coma : the person cannot be woken up due to the severity of the condition.
There are degrees of coma depth:
Coma 1st degree (moderate or superficial coma). The patient retains independent natural movements of the limbs, defensive reactions are active and there is still facial expression.
Coma 2nd degree (deep coma). The injured person may have independent limb movements, but they are not natural, there are no protective movements, and spontaneous breathing is not regular.
In these stages of coma, patients can be transported to local hospitals or specialized medical centers only by resuscitation teams in intensive care vehicles.
Coma 3rd degree (atonic coma) The patient has no movements, even pathological ones, spontaneous breathing fades away, hemodynamics are not stable, the pupils become wide. Without medical care in intensive care, this stage of coma extremely quickly ends in the death of the patient.
If your loved one falls into a Coma, then this is a critical condition, with the need to provide first aid for a coma (you need to turn the person on his stomach or side, remove mucus and stomach contents from the mouth) and immediately call a doctor.
Hospital, coma, intensive care unit - these are frightening words for any person, especially if an accident happened to someone you love. But at this moment, not only a person’s health, but also a person’s life depends on your actions. Therefore, do not hesitate and do not allow panic to take over you. Call an Ambulance for hospitalization at the nearest hospital, and then contact a resuscitation consultant at “Special Medical Care” for transfer to a specialized medical center. Treatment and rehabilitation of a patient after a coma should be carried out under the supervision of a qualified specialist.
Remember that the lack of timely diagnosis and specialized treatment can lead to future disability or death!
It is hospitalization in specialized medical centers that makes it possible to correctly diagnose, stabilize and improve the condition of a patient in a coma, and avoid or overcome complications of a coma. All this reduces the mortality and disability of the patient in a coma.
The main condition for a favorable prognosis in a comatose state is the patient’s ability to be in these specialized medical centers without deterioration and on time. This is precisely where interaction between the patient’s relatives and our company’s doctors is necessary. We can help at any stage: advice by phone (listed at the beginning of the site), consultation in the department where the patient is in a coma, as well as organize transportation and hospitalization to specialized medical centers in Moscow.
Call us and we can help your sick relatives!
Rehabilitation after a coma
There is a position according to which timely and high-quality treatment can significantly help the body cope with this condition. Initially, to maintain vital functions, the patient is provided with the ability to breathe and function of the cardiovascular system. Next, all the necessary studies are carried out aimed at identifying the disease - the cause of the development of coma. It is the research results that determine further treatment, prescription and use of medications. When a patient comes out of a coma, treatment of the underlying disease not only does not stop, but complications are also prevented. In the future, rehabilitation measures are prescribed.
Treatment methods
At home, in order to remove alcohol from the stomach, which has not yet been absorbed into the blood, they induce vomiting. If the person is conscious, a high concentration of activated carbon should be given to drink.
Ammonia will help bring a person to consciousness. If this does not happen, the help of specialists is required.
In the hospital, the human body is cleansed of alcohol by gastric lavage. Then he is given drips with glucose, ascorbic acid and vitamins. They help remove ethanol from the body faster.
The doctor can prescribe drugs for the treatment of alcoholic coma (atropine, caffeine, cordiamine) and antibiotics to stop the running negative processes in the patient’s body.
Recovery after a coma
Rehabilitation after a coma becomes extremely important: a set of measures that can help you get closer to or return to your previous way of life. Everything is subject to calculation - from the load level to the program itself. The Clinical Brain Institute has been successfully dealing with these problems for quite a long time. We are ready to offer effective rehabilitation programs developed with special care, which are selected individually for each patient. Our specialists, being professionals in their field, are also very responsive and attentive people, which is something that patients so often lack!
Why should you contact the New Method clinic?
We provide services for the diagnosis and treatment of alcoholism and its consequences. The clinic has all the necessary equipment to help a person in a coma. We make house calls or provide home assistance.
reasons to contact us :
- A staff of experienced specialists (narcologists, resuscitators, psychiatrists);
- Using only proven and high-quality drugs;
- Guarantee of complete anonymity;
- Versatile comprehensive treatment;
- Reasonable prices;
- Psychological support for patients.
If a coma appears as a result of chronic alcoholism, you can undergo treatment in a hospital (stay for up to 8 months). We provide a lifetime guarantee against relapse. We do not forcefully treat. Psychologists and psychiatrists use psychological influence techniques to gently convince the patient that it is time to take the path of recovery.
We also work with relatives, helping to restore lost social connections, find a job or return to school. At all stages of treatment, our patients receive legal support .
You can call a doctor to your home if your friend or relative is in a coma . We will deliver him to the clinic ourselves. The doctor arrives at your home within 40 minutes.
Private sobering-up station
From 3200 ₽/day
Alcohol rehabilitation
From 3200 ₽/day
Coding by injection
From 5500 ₽
Anonymous withdrawal from binge drinking
From 3100 ₽/dropper
Anonymous treatment of alcoholism
From 2200 ₽
Drug treatment
From 40,000 ₽/month
Detoxification at home
From 3100 ₽/dropper
Causes
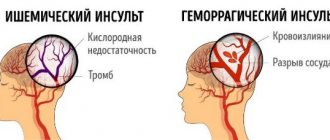
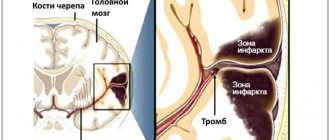
Post-stroke cerebral coma is a common complication of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke of the brain. This condition occurs when a major brain accident disrupts the normal functioning of the central nervous activity.
The following conditions can trigger ischemic stroke:
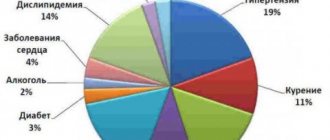
- Atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. When intravascular proliferation of an atherosclerotic plaque occurs, a blockage of the lumen of this vessel is observed, leading to disruption of the nutrition of a separate area of the brain;
- Hemodynamic disorders. With constant lability of blood pressure and organic disorders in the vessels of the brain, a violation of the nutrition of soft tissues occurs;
- Cardioembolic disorders. In this case, the blockage of blood vessels in the brain is caused by blood clots brought in from the heart valves or heart chambers. Conditions such as myocardial infarction and arrhythmia can provoke blood clot detachment.
The following factors contribute to the development of so-called coma and hemorrhagic stroke:
- Presence of vascular aneurysms;
- External damage to large vessels;
- Defect in the development of the blood vessel wall.
Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke is a more severe and life-threatening condition. This condition is associated with cerebral hemorrhage. Brain hemorrhage is difficult to deal with. Coma after a hemorrhagic stroke is more difficult to tolerate.
Classification
It should be noted that a brainstem stroke results in almost instantaneous death. Only in rare cases is it possible to save the patient’s life with such a diagnosis. At the same time, there is no likelihood of returning to a full life.
The brain stem is the center of all body systems and is directly connected to the spinal cord. It serves as a link between the commands of the brain centers and the nerves of the body: it is thanks to it that we are able to move, breathe, swallow, see, hear, and so on. The brain stem also regulates the circulatory system, thermoregulation, and heartbeat. That is why damage to it during a stroke most often leads to death.
Based on their origin, primary and secondary hemorrhagic stroke are distinguished:
| Primary | provoked by a hypertensive crisis or thinning of the walls of arteries and veins due to prolonged stress on them (for example, due to high blood pressure, physical and nervous overload, etc.) |
| Secondary | provoked by the rupture of an aneurysm, hemangioma and other vascular deformations and anomalies (malformations), congenital or formed in the process of life. |
Depending on the localization zone, I distinguish the following types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Subarachnoid - hemorrhage into the space between the hard, soft and arachnoid membranes of the brain;
- Hemorrhage on the periphery of the brain or in the thickness of its tissue;
- Venticular hemorrhage - localized in the lateral ventricles;
- Combined type: occurs with extensive hemorrhage affecting several areas of the brain.
Peripheral hemorrhage is much less dangerous than intracerebral hemorrhage, which inevitably provokes the formation of hematomas, edema and subsequent death of brain tissue. Hematomas are also distinguished by location:
- Lobar - the hematoma is localized within one lobe of the brain, without going beyond the cerebral cortex.
- Medial - hemorrhage damages the thalamus.
- Lateral – damage to the subcortical nuclei localized in the white matter of the hemispheres (fence, amygdala, caudate, lenticular nuclei).
- Mixed - hematomas affecting several areas of the brain at once are most common.
Life with a clean slate
Until now, only one case is known in which a patient, after a long coma, managed to return to a full life. On June 12, 1984 Terry Wallace from Arkansas, having drunk a lot, went for a ride with a friend. The car fell off a cliff. The friend died, Wallace fell into a coma. A month later he entered a vegetative state, in which he remained for almost 20 years. In 2003, he unexpectedly uttered two words: “Pepsi-Cola” and “mom.” After conducting an MRI study, scientists discovered that the incredible had happened: the brain repaired itself, growing new structures to replace the damaged ones. Over 20 years of immobility, all of Wallace's muscles atrophied and he lost the simplest self-care skills. He also did not remember anything about the accident or the events of the past years. In fact, he had to start life from scratch. However, the example of this man still gives hope to those who continue to fight for the return of their loved ones to normal life.
Locked brain. Do people in a coma hear everything, think and can communicate? More details
Mikhail Piradov, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Director of the Scientific Center for Neurology:
- From the point of view of pathophysiology, any coma ends no later than 4 weeks after its onset (if the patient does not die). Possible options for exiting a coma: transition to consciousness, a vegetative state (the patient opens his eyes, breathes independently, the sleep-wake cycle is restored, there is no consciousness), a state of minimal consciousness. A vegetative state is considered permanent if it lasts (according to various criteria) from 3-6 months to a year. In my long practice, I have not seen a single patient who emerged from a vegetative state without loss. The prognosis for each individual patient depends on many factors, the main of which are the nature and nature of the injuries received. The most favorable prognosis is usually for patients with metabolic (eg, diabetic) coma. If resuscitation care was provided competently and in a timely manner, such patients recover from coma quickly enough and often without any losses. However, there have always been, are and will be patients with severe brain damage, who are very difficult to help even with the highest level of resuscitation and rehabilitation. The worst prognosis is for comas caused by vascular origin (after a stroke).
For family and friends
In addition to feature films, there are many stories, oral and written, about how relatives refused to believe in the hopelessness of a loved one and were rewarded with his subsequent awakening and restoration. Here you need to keep in mind that, as a rule, in such stories there is no documentary data about what exactly doctors understood by the word “hopeless” and whether all 9 signs of brain death were recorded and recorded.
As for recovery after a long coma, in cases of famous people followed by numerous fans, we observe a very slow and far from complete recovery. Miracles did not happen, sadly, neither with Michael Schumacher, nor with Nikolai Karachentsov, who received excellent medical care and care.
For loved ones, however, the very fact that a loved one is alive, provides the opportunity for care and at least limited contact, is often a joy. Here is the story told by a woman who fought for 19 years to restore her son, who was injured in an accident and spent 4 months in a coma. Nathan, 36, remains severely disabled, but his mother is happy that they are together.
And one more inspiring fact for the relatives of patients in a coma.
In January 2015, the journal Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repaire published data from a study of American doctors demonstrating the fact that comatose patients recovered faster and better than other patients in the same condition if they listened to recordings of their family members' stories. about the events of family history known to them. These were the voices of parents, brothers and sisters, whom the patients listened to through headphones. Using magnetic resonance imaging while listening to the recordings, the scientists were able to track increased neural activity in the areas of the patient's brain responsible for language and long-term memory, and after 6 weeks of such stimulation, the patients began to respond better to other external stimuli.
Here are recommendations for relatives and friends of a patient in a coma, posted on the UK Department of Health website:
- When visiting a patient, tell him who you are; Try to be positive in conversations.
- Talk about how your day went, as if the patient understood you.
- Keep in mind that everything you say in the presence of the patient may be heard by him.
- Show him your love and support, even if just by sitting next to him and holding his hand.
- Let him listen to his favorite music through headphones.
Of course, conversations between relatives and patients are not a miracle cure for a complete cure, however, contrary to the fair criticism of Dr. Vidzhdiks, the “Talk to Her” recipe turns out to be effective. And if art proclaims the limitlessness of a person’s ability to awaken another person, dear and loved, to life, then science recognizes our limitations, and nevertheless confirms that feelings and relationships can become the bridge through which our loved ones are able to return to us.