Stroke, or acute cerebrovascular accident, remains one of the leading causes of death. Practice shows that in 60% of cases the lesion is localized in the left brain structures, which control the activity of the right half of the body, where paralysis occurs. Just a few minutes of stopping blood flow is enough to kill millions of neurons and create a dead zone in the nervous tissue. The pathological process involves the pathways of CNS signals to systems and organs on the right.
Kinds
Neurology defines two types of stroke with paralysis of the right side:
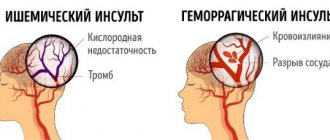
- Ischemic stroke. Occurs due to blockage of cerebral vessels by atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots. In the area of circulatory arrest, a focus of brain tissue necrosis occurs. The severity of subsequent paralysis and the ability of the central nervous system to compensate for lost functions depend on its location and size. The disease most often threatens hypertensive patients, diabetics, smokers and anyone with high cholesterol, thrombophlebitis, blood thickening, or problems with heart rhythm. Attacks of tachycardia or atrial fibrillation can provoke the formation of blood clots in the heart cavity, which enter the brain vessels with the blood flow. This type of stroke develops over 2-3 days or longer, so it has specific diagnostic features.
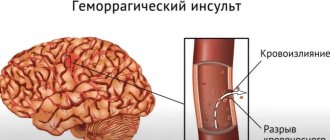
- Hemorrhagic stroke. It is characterized by a rupture of the vascular wall and a breakthrough of blood into the brain tissue, which dies from ischemia. It is provoked by a hypertensive crisis, specific aggregate states of the blood, diseases that cause pathological changes in the structure of blood vessels. Hemorrhagic stroke develops rapidly, quickly causing a coma in the patient. This diagnosis entails the most severe consequences.
The practice of neurology shows that strokes with paralysis of the right side are easier and the consequences are eliminated faster. This is explained by the fact that ischemic stroke more clearly manifests the onset of the disease with characteristic signs.
Make an appointment
Types of paralysis on the right side
According to the nature and localization of vascular accidents, the types and subtypes of paralysis are classified:
- Central paralysis. It develops when the areas of the brain and spinal cord responsible for the function of movement and the state of the neuromuscular complex are damaged. Characterized by specific spastic reactions. With the central form of paralysis, all muscles are affected, which are in constant tension, and when calm they show clonus - rhythmic twitching, mainly in the area of the knees and feet. In many areas, diagnostic reflexes are absent or weakened.
- Peripheral paralysis. With this type of stroke, a decrease or absence of neurological reflexes develops. The tone in the muscles is not determined, they atrophy, decrease in mass, patients lose the ability to move, self-care and generally do any activity. The main task is to restore the conduction pathways of impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the neuromuscular system. By the nature of the pathological symptoms and the areas of their location, it is possible to determine which segments of the central nervous system are out of order.
What causes aphasia during a stroke?
In the human brain there are several interconnected centers responsible for oral speech: for its understanding, reproduction, analysis of complex speech structures, and the ability to construct correct sentences. All of them are interconnected by nerve fibers and are located mainly in the central part of the brain, as well as in the temporal and parietal lobes. Some of these speech centers are symmetrical in both hemispheres (that is, they are duplicated in each of them), but there are also areas that right-handers have only in the left hemisphere, and left-handers have in the right.
When a stroke occurs, part of the brain dies. If death occurs in one of the speech centers, or the nerve endings connecting these zones are damaged, aphasia develops. Thus, aphasia is a violation of the understanding or reproduction of already formed oral speech, sometimes up to its complete absence. If the disorder concerns written speech, then such a neurological syndrome will already have a different name (alexia, agraphia).
Causes
The main cause of right-sided paralysis is strokes, chronic and then acute disturbances of blood supply in the structures of the left hemisphere.
A stroke is not a disease that happens suddenly. Its causes accumulate over years, decades, so that when a critical point is reached, one day the scenario of a “vascular catastrophe” unfolds. This leads to:
- Physical inactivity;
- Diet with a predominance of animal fats and proteins;
- Metabolism, carbohydrate and cholesterol status disorders;
- Limited or inadequate sleep;
- Abuse of tobacco, alcohol, drugs;
- Chronic or severe one-time stress.
Eliminating at least half of these causes will allow stroke to be removed from the list of major diseases that most often suffer in our time.
Expert opinion
Author: Ekaterina Dmitrievna Abramova
Neurologist, director of the chronic pain clinic
According to the Federal State Statistics Service, stroke ranks second in the structure of mortality. This is a dangerous neurological disease, the incidence of which is increasing every year. Statistics show that acute cerebrovascular accident occurs in every third person per 1000 population. Stroke in 60% of cases leads to disability. Due to severe complications, 10% of patients completely lose the ability to self-care. The appearance of persistent paralysis is associated with extensive brain damage.
A stroke requires immediate diagnosis and correct treatment. At the Yusupov Hospital, examinations are carried out using the latest medical equipment: CT, MRI. Thanks to them, it is possible to accurately determine the location of the pathological focus. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital develop an individual treatment and rehabilitation plan for each patient. The drugs are selected in accordance with the latest European recommendations for the treatment of strokes. Conservative treatment can be supplemented with surgical intervention if indicated. In addition, to speed up recovery, physiotherapy and a course of physical therapy are prescribed.
There are four main types of post-stroke speech disorders
Damage to the language center in the dominant hemisphere - Broca's area - leads to the fact that patients lose the ability to convey their thoughts using coherent and grammatically correct language structures. Conversely, pathological changes in Wernicke's area (sensory center) lead to problems in receptivity to language. Such patients have difficulty understanding spoken or written language. They often use correct grammatical structures, but their statements may not make sense. The most severe form of aphasia (global or total) occurs in patients with extensive damage to several areas of the brain responsible for understanding and language. The mildest form of aphasia—amnestic—leads to difficulty working with vocabulary.
How do these types of aphasia manifest themselves in practice?
Damage to the language center in the dominant hemisphere - Broca's area - leads to the fact that patients lose the ability to convey their thoughts using coherent and grammatically correct language structures. Conversely, pathological changes in Wernicke's area (sensory center) lead to problems in receptivity to language. These patients have difficulty understanding spoken or written language. They often use correct grammatical structures, but their statements may not make sense. The most severe form of aphasia (global or total) occurs in patients with extensive damage to several areas of the brain responsible for understanding and language. The mildest form of aphasia—amnestic—leads to difficulty working with vocabulary.
How do these types of aphasia manifest themselves in practice?
- Motor aphasia. You know what you want to say, but you can’t find (remember, use and pronounce) the right words.
- Sensory aphasia. You hear someone speak or see printed text, but cannot understand the meaning of the words.
- Amnestic aphasia. You find it difficult to select and use the correct words to refer to certain people, objects, places or events.
- Global aphasia. You cannot speak, write, read and do not understand what is being said to you.
Symptoms
The signs of the onset of an illness are beyond doubt; not only doctors, but also ordinary people should know them in order to help their loved ones, acquaintances, or just a person on the street who has become ill in time. You should call the emergency room immediately if you experience the following symptoms:
- Sudden loss of speech (or when it becomes slurred);
- Inability to move an arm or leg;
- Inability to smile (the right side of the mouth sags);
- drooping eyelid;
- State of stupefaction, spatial and temporal disorientation, the patient complains of “mess in the head”;
- Severe headache with vomiting, dizziness;
- The extended right leg turns the foot inward;
- The right arm is bent and pressed towards the body.
Post-stroke speech dysfunction
Speech plays one of the most important roles in human life. Certain areas of the cerebral cortex are responsible for the speech apparatus. Damages to brain structures, which include acute circulatory disorders, lead to serious disorders. A person who has had a stroke:
- puts words in the wrong order;
- cannot remember the names of objects;
- does not understand the people who approached him;
- cannot pronounce some sounds;
- loses the ability to express his thoughts clearly.
Speech impairment is long-term, but can be corrected. There are also cases when speech is restored gradually on its own. Unfortunately, this happens extremely rarely, and the patient cannot do without rehabilitation under the supervision of doctors and relatives.
Why is speech function impaired?
A person's inability to speak clearly after a stroke is called aphasia. This condition is the result of:
- rupture of neural connections;
- severe disruption of neuronal nutrition;
- hematoma pressure on nerve tissue.
Based on the complexity of the lesion, it is possible to predict how quickly the patient will recover speech after a stroke. The extent of the lesion also plays a key role: the larger it is, the more complex the aphasia. In addition, the main criteria affecting the restoration of articulation include:
- affected area;
- timeliness of treatment;
- quality of rehabilitation measures.
Types of speech disorders
When a blood vessel ruptures in the brain, speech functions are first affected. With hemorrhage, various articulation disorders appear. In addition to aphasia, there are other types of speech dysfunction:
- dysarthria;
- dyspraxia.
How to restore speech abilities after a stroke
One of the main roles in the process of acquiring lost speech abilities is played by early access to a doctor. Help for the patient should be provided in the first hours after a stroke. It is also important to establish which aspects of speech have been damaged. The specialist must conduct diagnostic tests on the basis of which he makes a conclusion.
Rehabilitation methods for improving speech after cerebral hemorrhage are presented:
- taking certain medications;
- exercises to restore pronunciation;
- speech therapy;
- additional measures: surgery, physiotherapy, massage.
The success of rehabilitation also depends on the general environment in which the patient lives. He needs a peaceful atmosphere, away from noise and harsh sounds. Stress and worry will only slow down your recovery.
How to recognize aphasia
Aphasia after a stroke can be recognized by various symptoms, the combination of which makes it possible to distinguish several types of this syndrome.
So, we can talk about sensory aphasia (Wernicke) if the patient has:
- misunderstanding of spoken speech;
- misunderstanding of allegories, sayings, proverbs;
- complaints that everyone around them began to speak as if “in a foreign language”;
- forgetting the initial part of a long sentence of the interlocutor, loss of understanding of long speech structures, which encourages the patient to ask questions about words that have slipped from memory.
At the same time, the patient can formulate his own proposal. And although it will be laconic, without descriptive phrases, there will be meaning in it.
If mnestic aphasia , an elderly person:
- can retain in memory only a few words from a listened phrase;
- having started to speak, he forgets what he wanted to say;
- speaks slowly, choosing his words carefully;
- replaces some words with others that do not fit the meaning.
This is acoustic-mnestic aphasia. There is also an optical-mnestic type of syndrome, then:
- a person can read the headlines in books or newspapers, but the meaning of the text itself is lost;
- It is difficult for him not only to describe what he sees (in the world around him or in the image), but also to name objects.
There is also amnestic aphasia , which develops with a stroke of the parietotemporal lobe. In this case, a person forgets what individual objects are called, but remembers what they are needed for. Such a patient, instead of “pen,” may say “thing that is used to write,” and the like.
Semantic aphasia is not immediately noticeable . In this case, a person who has suffered a stroke is thrown into a stupor by long sentences describing logical actions and spatial relationships.
All of these types of syndrome - Wernicke's aphasia, mnestic, semantic and amnestic types - are united under the general name " sensory aphasia ", when a person after a stroke has difficulty understanding speech. Often the patient himself does not understand what he is saying.
The second main type of disease is motor aphasia . In this case, the person, on the contrary, perfectly understands the addressed speech, but cannot reproduce it, from which he suffers greatly morally. Motor aphasia is divided into 3 types:
- Afferent motor aphasia . In this case, the patient confuses similar voiceless and voiced consonants and rearranges sounds in words.
- Dynamic aphasia . The patient understands the addressed speech and tries to answer, but the words in his sentence are so out of place that the whole phrase loses its meaning. A person hears and understands this, but cannot correct it, which is why he suffers.
- Broca's aphasia . It occurs in people who, due to a stroke, have lost an area of the brain near the frontal lobe of the left hemisphere (Broca's center is located there, which is responsible for the coordination of movements through which speech is reproduced). This is characterized by a change in communication style: a person speaks in separate words, pauses between them, and even between individual syllables, as it is difficult for him to switch from one syllable to a completely different one. Such a person begins to write and read with gross errors. He may repeat the same syllable all the time, name words that have opposite meanings, and speak unintelligibly.
The speech of a patient with motor aphasia is very short, consisting almost entirely of nouns and verbs, between which the person pauses. He may repeat one syllable (for example, “la”) or sound (for example, moo), trying to convey meaning into it using intonation. During a conversation, such a person often cries, as he suffers from the fact that he is unable to convey his thoughts.
The diagnosis of motor aphasia should be made by a neurologist, since in everyday life it can be difficult to distinguish this particular syndrome from the one called dysarthria. Dysarthria occurs when the centers of the brain are damaged, which carry commands to the muscles involved in the formation of speech (movement of the tongue, lips, vocal cords). Patients with dysarthria understand spoken speech and form sentences correctly. But due to changes in their voice timbre and the inability to pronounce individual sounds, their speech becomes unintelligible. If this is accompanied by breathing difficulties, this forces the sick elderly person to speak in short sentences. Descriptions, adjectives, and adverbs do not disappear from speech.
The third “large” type of aphasia, along with the sensory and motor type, is total aphasia . It is characterized by a violation of both understanding and speech reproduction. This condition can be suspected by the following symptoms:
- in response to addressed speech, looks at the speaker without understanding. If you simplify the sentence, replace the words with simpler, more primitive ones, he may fulfill the request, but still cannot answer clearly;
- such a person who has suffered a stroke is unable to clearly formulate a request;
- misses several words in a sentence at once. The remaining words are the simplest. There are no literary expressions: hyperbole, comparisons, complex adverbial phrases in the speech. In severe cases, even adjectives and adverbs disappear from phrases: the sentence consists of only nouns.
Treatment
Thanks to the efforts of healthcare organizers, the system of stroke treatment in Russia has undergone positive changes. It has become the norm to transport patients with suspected cerebral circulatory disorders to an intensive care bed or neurosurgeon's table within three hours.
Treatment for stroke, when the right side is paralyzed, begins in the intensive care unit, where patients are hospitalized urgently. The treatment regimen provides for the normalization of blood circulation in the brain, restoration of respiratory and swallowing functions, and elimination of the threat of convulsive phenomena.
The treatment regimen for hemorrhagic stroke with paralysis of the right side is somewhat different. In this case, drugs that eliminate thromboembolism come to the fore. If treatment is started on time, the blood clot is destroyed and impaired blood flow is restored. Thanks to modern medications, it is often possible to completely avoid the consequences of a stroke.
The patient's condition requires normalization of homeostasis, a decrease in the degree of permeability of the vascular walls and the formation of plasmin. In some cases, blood clots from brain vessels are removed surgically in neurosurgery departments.
Lifestyle
Stroke is a disease in which a person must start life in new conditions. Most people find it difficult to accept their condition, so deep depression is as dangerous a complication as the physical manifestations. Already in the first stages of recovery, much attention is paid to this aspect.
The scientific, material and technical base of the Yusupov Hospital allows patients to undergo rehabilitation procedures using modern equipment that meets European standards.
Aphasia. Lost speech after a stroke or injury.
Speech with aphasia takes a long time to recover - this can take up to two to three years of rehabilitation procedures. Motor or sensory aphasia is a systemic speech disorder that contributes to the development of affective, mental states, aggression, emotional lability and depression in the person suffering from aphasia. To eliminate speech impairment, it is always better to involve various specialists - speech therapist, psychologist, neuropsychologist, rehabilitation specialist. When correcting aphasia, restorative treatment should begin as early as possible, when the patient’s condition allows for various types of procedures to begin. World experience shows that rehabilitation begun in the first three months after stopping the process that caused speech impairment provides the highest percentage of recovery and socialization of the patient.
Rehabilitation (from the Late Latin rehabilitatio - restoration) is a set of medical, pedagogical, professional measures aimed at restoring or compensating for impaired body functions and the working capacity of sick and disabled people. The goal of rehabilitation of persons with health problems is to ensure their ability to implement the lifestyle of normally developing people. It follows from this that persons with health problems are integrated into the social environment. Adaptive rehabilitation is closely related to the problem of adaptation (Latin adaptio - adaptation) of the entire recovery system (rehabilitation) to ensure motor activity and restore speech of people with aphasia, which should be considered one of the current problems. One of the main tasks of adaptive rehabilitation is the restoration of lost functions and systems of the body, maintaining a person’s natural desire to return to society, his physical and spiritual status. The concept of adaptive rehabilitation reveals such an opportunity to help achieve the optimal level of development of lost functions of the human body in accordance with its potential capabilities.
To implement this process it is necessary to comply
the following conditions:
- creating conditions to meet the rehabilitation needs of each person based on adjusting the pedagogical process to the patient’s needs;
- providing the patient with real opportunities for self-affirmation, where his abilities are revealed to the maximum extent, and focusing on the reserve capabilities of the body;
- formation in the hospital and at home of an emotional field of relationships that ensure respect for the patient’s personality at the levels of communication between the patient and the doctor, instructor, teacher, relative, and other patient;
- ensuring a high level of continuous rehabilitation process in accordance with the individual characteristics of each patient and the relationship of all rehabilitation means used.
Organizing home rehabilitation is a rather complex process that requires discipline, responsibility and perseverance in overcoming all the difficulties on the way to restoring the affected organs and systems of the body of a person who has suffered a stroke (brain injury or brain surgery) and has a speech disorder. When organizing rehabilitation at home, you can focus on the following options for its application:
— home visits by a rehabilitation specialist, physical therapy instructor, neurologist, psychologist, speech therapist and other rehabilitation treatment specialists;
— training in rehabilitation techniques for family, friends, and relatives;
- basic assistance from a nurse;
— combined organization of work of a specialist and relatives during home rehabilitation;
— the use of advisory assistance from various rehabilitation specialists;
— use of information media: computer assistance, specialized literature, methodological and teaching aids;
— distance learning (by a speech therapist) for the patient and his relatives in speech restoration techniques.
Restoring speech in people suffering from aphasia is one of the most significant tasks that needs to be solved in the near future. This category of people is treated by a speech therapist, as well as a speech therapist-aphasiologist. Restoring speech during aphasia in the first three months significantly increases the chances of its recovery. There are developed methods for working with aphasia. The methodological program of rehabilitation work is individual for each patient and depends on the characteristics of his speech disorder, personality, interests, needs, etc.
Basic principles in working with people with aphasia:
- in case of any form of speech disorder, it is necessary to work with a speech therapist as early as possible;
— work must begin with overcoming disorders of understanding of addressed speech, and if this aspect is preserved, then with the restoration of the semantic structure of speech, a violation of which occurs in almost all forms of aphasia;
— work should be carried out on all aspects of speech, taking into account the specifics of the violation of each speech function in different forms of aphasia;
- it is necessary to include reading and writing in the recovery period or work on their restoration if they are as grossly impaired as speech;
— everyone who surrounds the patient should be involved in the restoration work: relatives, acquaintances, neighbors, medical staff, having previously consulted them.
Classes are held at least two to three times a week, and preferably daily for several months. The work is carried out in two modes: with a speech therapist and independently. If help is not provided by a speech therapist in the first weeks, speech disorders become permanent.
The main efforts in restoring speech function in speechless patients - with aphasia - are aimed at disinhibiting speech. This is carried out on the basis of past speech stereotypes, in order to obtain at least some sounds and words. To disinhibit speech, material is selected that is of great importance in terms of semantic and emotional content. They take simple speech images that easily come to life in memory and set the language in motion as if automatically. This could be counting to ten, days of the week, months, etc. Automated speech sequences, emotional words, everyday expressions, and exclamations contribute to speech disinhibition. Sometimes such expressions “open the way” for other words, and speech begins to recover. First, the patient repeats the words together with the teacher, then repeats after him, and then speaks independently. A good remedy would be proverbs, sayings where it is necessary to finish words, singing familiar songs, reciting familiar poems.
The greatest difficulty in the rehabilitation of patients with aphasia is the group of patients in whom impressive speech disorders dominate. In this case, the severity of the course and the difficulties of recovery are due to the fact that patients are not able to recognize the presence of a speech defect. Auditory control of perceived speech is impaired, so a positive prognosis for recovery is difficult. The work begins not with individual sounds, but with words. At the moment the patient examines the object and the written word, the teacher pronounces this word out loud several times. The sound being practiced is pronounced with exaggeration of sound and articulation. Having learned to distinguish sounds, patients, as a rule, begin to understand those words that they did not understand before. In addition, the word is combined with the subject. Thus, the restoration of phonemic hearing provides the basis for restoring speech understanding in general.
When working with patients who have a severe degree of severity, bordering on total, the task of recovery techniques is to stimulate the compensatory capabilities of the subdominant (hemisphere opposite to the dominant (in right-handed people the left hemisphere is dominant)) hemisphere. At this stage, restoration of mental function in its previous form is impossible; restructuring is necessary to radically change its psychophysiological structure. There is a certain pattern of restoration of function in patients after they have suffered a cerebral infarction. Near the focus of brain damage, zones of plasticity ( capable of recovery ) and secondary replacement of lost functions are formed, while similar zones of hypermetabolism are formed in symmetrical areas of the opposite hemisphere of the brain. A number of scientists believe that a favorable prognosis for the restoration of speech thinking in patients with aphasia directly depends on whether the right hemisphere is able to temporarily take over the function of the left hemisphere in the initial stages. Therefore, at the first stage of recovery, patients with acoustic-gnostic aphasia are offered the technique of global text reading, and with acoustic-mnestic aphasia, work on normalizing visual-object gnosis is offered. So, for example, the patient must look at the half-drawn object pictures and name them. With patients with semantic aphasia, work is carried out to restore visual-spatial perception and overcome acalculia. At the next stage, when working with patients with moderate severity, the activity of the depressed dominant hemisphere (the hemisphere that has suffered) is stimulated. At the same time, the methods take into account the need for further participation of the subdominant hemisphere to increase the effectiveness of recovery. In patients with acoustic-gnostic aphasia, phonemic perception and semantics of speech are restored by introducing the word into context. To expand the volume of auditory-speech memory, patients with acoustic-mnestic aphasia are asked to remember addresses and telephone numbers. With patients with semantic aphasia, work is carried out to restore the deep meaning of a word using the interpretation of proverbs. At the third, final stage, when restoring a mild degree of severity of speech disorders in each individual case, not only the lesion site is taken into account, but also its connections with other, more complex in organization parts of the cerebral cortex, which are the tertiary parts of the second functional block (in acoustic syndromes). -gnostic and acoustic-mnestic aphasia) and prefrontal coranterior parts of the brain, corresponding to the tertiary fields of the third functional block (with semantic aphasia syndrome). This is reflected in the following types of tasks: for acoustic-gnostic aphasia, it is proposed to solve crossword puzzles, as well as explain logical-grammatical phrases; with acoustic-mnestic - retell texts and explain the figurative meanings of words; with semantics - to identify logical and stylistic errors made in the text. Due to the systemic nature of aphasic disorders, work is carried out on all aspects of speech, taking into account the specifics of the violation of each speech function. Practice shows that the same form of aphasia manifests itself differently in different people depending on their educational and cultural level, knowledge of languages, and personality traits. Often, different patients experience seemingly identical speech symptoms at first glance. But, as experience shows, the mechanisms of these symptoms differ from each other. In such cases, despite the similarity of speech disorders, various methods of speech therapy rehabilitation work should be used.
Speech restoration in aphasia is more successful the earlier correctional work is started.
The prognosis for the restoration of speech function in aphasia is determined by the location and size of the affected area, the degree of speech disorders, the start date of rehabilitation training, the age and general health of the patient.
Speech therapy work for aphasia is a long and labor-intensive process that requires the cooperation of a neurologist, neuropsychologist, speech therapist, patient and his immediate environment, and speech restoration should not take place empirically, but skillfully, at a serious professional level.
Right side massage
Recovery after a stroke with paralysis of the right side with the help of massage begins on the 20th day of illness. This is an average date; the severity of the patient’s condition, age, concomitant diseases, etc. are taken into account.
The first massage sessions begin with gentle stroking of the limbs, back and neck muscles. The intensity of the effect increases from session to session, the massage therapist’s actions are aimed at restoring normal blood circulation and sensitivity in the affected part of the body.
Speech, reading and writing disorders after stroke. How can the patient’s family and friends help him?
Authors:
Kadykov Albert Serafimovich – Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Neurological Department of the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Scientific Center of Neurology”, Moscow.
Chernikova Lyudmila Aleksandrovna - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor.
Shakhparonova Natalya Vladimirovna - Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Leading Researcher of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "Scientific Center of Neurology", Moscow.
Aphasia, which occurs in almost a third of patients who have suffered a stroke, is a kind of thinking disorder in which the ability to correctly operate with words is impaired. In some cases, the patient cannot form a phrase or remember the right word, in others he ceases to understand the speech of others. However, as a rule, in patients with aphasia, intelligence, imaginative thinking, visual memory, vision, and hearing are completely preserved, based on which a speech restoration specialist works.
In addition to aphasia, patients who have suffered a stroke also have another type of speech disorder - dysarthria, which is characterized by a violation of the correct pronunciation of sounds and words. Unlike patients with aphasia, those with dysarthria have preserved “inner speech” (speech to oneself), understanding the speech of others, reading and writing.
Restoration of movements and speech does not always occur in parallel. The process of speech restoration sometimes occurs somewhat slower than the restoration of movements, and can last a year or two, and in some cases three or even more years. And here the role of the family is invaluable, especially since speech therapy services are available in only a few cities in the country. Relatives, having received the necessary consultation from a speech therapist or a doctor familiar with the problem of speech therapy training, can greatly help the patient in restoring speech and functions closely related to speech such as reading and writing. Various speech correction aids can help with this.
Speech restoration classes are recommended to begin in the first 1-2 weeks after a stroke. It is at this time that the greatest effectiveness of remedial training is observed. Relatives and friends of the patient need to know that intelligence, as a rule, does not suffer in cases of speech impairment, and a patient with aphasia cannot be treated as half-crazed or as an unreasonable child. Even with severe speech impairments, not only logical thinking and an adequate reaction to the environment, but also creative abilities are preserved. Thus, the famous Russian composer Alfred Schnittke, suffering in the last years of his life from speech disorders as a result of repeated strokes, continued to compose beautiful music.
Motor aphasia
Motor aphasia develops with damage to the posterior frontal parts of the left hemisphere (the so-called Broca's speech area). The motor speech center located in this area regulates not only the choice of sounds, syllables and words in the process of speech utterance, but also the choice of prepositions, endings of nouns and verbs, i.e. organizes the syntactic design of a sentence. When this area is affected, the patient gets stuck on a word or syllable and repeats it several times, or has difficulty moving on to the next word, resulting in long pauses in speech. In the most severe cases, speech is completely absent or the patient is able to repeat only individual words. It is important to encourage patients with a disorder of their own speech, which is mainly found in motor aphasia, to make their own statements, to build a conversation with them in the form of a conversation, a dialogue, and to more often ask some question when doing housework. At the dinner table, watching TV. The patient himself, especially at first, when answering, should not rush, trying to pronounce the word or phrase clearly and slowly.
Sometimes classes conducted with the sick relatives are limited only to exercises in naming and repeating individual objects, as a rule, nouns in the nominative case. And in the future, as speech is restored, they may develop the so-called. “telegraph style” when such a patient, instead of the phrase “Take the plate with ham out of the refrigerator,” says “Fridge, plate, ham.”
To avoid this, you must immediately strive to form a speech that, at least at first, consists of short phrases like “hello,” “I’m thirsty,” “give me some bread,” “let’s go for a walk.”
“Disinhibition” techniques play a major role in restoring one’s own speech. Disinhibition of speech function is possible due to the involvement of preserved speech automatisms: ordinal counting to ten, the names of the days of the week and months of the year, couplets of favorite songs and stanzas of familiar poems.
As speech is restored in classes with the patient, they move on to repeating relatively simple phrases, the topic of which is suggested by the latest events of the day: “Today there was a doctor. I am feeling better. Now I will have lunch. Give me some medicine."
As the patient’s speech improves, they move from dialogue to restoring a monologue—the patient’s own speech utterance, and this restoration is carried out in several stages:
— Retelling a text told by a speech therapist or read by a patient (initially very simple, later more complex);
— Story based on the picture;
- A story on a given topic: “in the store”, “in the pharmacy”, “in the theatre”, biographies of writers, scientists, public figures known to the patient;
- A story about your own life, about your day;
— Collective (in the family, speech therapy group) discussion of a topic.
At a certain stage of speech restoration, it makes sense to use a tape recorder. The patient listens to the text spoken by him, finds the mistakes made, repeats it and listens to the recording again.
Sensory aphasia
In the posterior parts of the temporal lobe of the left hemisphere of the brain there is a center for understanding the speech of others (Wernicke's center), which takes part in the auditory perception of specific speech sounds (phonemes) and carries out auditory-verbal memory. When Wernicke's area is damaged, a disturbance in understanding the speech of others occurs, which is based on a violation of phonemic hearing and auditory-verbal memory.
Speech understanding has three main components:
- Understanding the meaning of the word;
— Understanding the meaning of the sentence;
— Understanding the meaning of the target utterance.
Accordingly, the restoration of speech understanding also goes through three stages: from understanding the meaning of a word to understanding a sentence, and then the statement as a whole. Guessing understanding is of great importance when the patient does not understand the statement as a whole, but from individual words that he understands and from the situation he can guess what the interlocutor wants to say. This sometimes misleads relatives, who mistakenly believe that the patient understands everything well.
The most destructive thing for speech restoration is the so-called “speech isolation” of the patient, when he is left to his own devices, they talk to him little, he is not invited to participate in a general conversation or to discuss domestic problems.
To stimulate understanding of the speech of others, conversations are used, mainly on simple topics. They ask the patient if he wants to eat, drink, go for a walk, sleep, ask him to pass some object (without pointing a finger at it), or perform some action (stand up, sit down, take a fork, turn on the TV, etc.). d.).
If the patient finds it difficult to perform an action or show an object, it is necessary to prompt him and ask him again. After mastering simple operations, the range of objects and actions expands.
In order for a patient with sensory aphasia to realize his speech defect, he is asked to copy down a few simple words or solve simple arithmetic parameters. The patient must be delicately shown his mistakes. Since his understanding of speech is impaired, he has to communicate with him using facial expressions and gestures. If the patient ignores the gestures and facial expressions of the interlocutor, you can highlight his mistakes with a red pencil. To restore understanding of speech, pictures depicting various objects, animals, body parts, with captions are used. It is convenient to use pictures from children's lotto. The patient is asked to lay out captions for the subject pictures, indicating their words, written on separate small strips of paper. When the patient learns to cope with this task, they are offered to copy these signatures and read them out loud.
Restoring reading and writing
In parallel with speech communication and classes to restore oral speech, patients must be taught reading and writing, because restoration of these functions will significantly contribute to the restoration of speech. If there is no hope of restoring writing with the right hand, the patient should be taught to write with the left. It is better to start learning writing than typing on a typewriter/computer, because... Writing in cursive is closely related to the function of speech. In the future, with satisfactory restoration of cursive writing skills, you can begin learning to type on a typewriter/computer, especially in cases where the patient already knew them before illness. It is better to start reading with printed words; the patient should try to write written assignments in block letters at first and only later switch to capital letters written legibly and clearly. From the first days, even before the reading function is fully restored, the patient should be allowed to look through newspapers and magazines that he used to read before the illness, because even in patients with impaired analytical reading functions, the ability to guess reading is often retained.
To conduct classes to restore speech, reading, and writing, various aids are required:
— Subject and plot pictures (they can be cut out from children’s books and magazines);
— Split alphabet, primer;
— Books to read; at first these are books for younger children: fairy tales, stories, for example L.N. Tolstoy, Russian language textbooks for foreigners.
Classes to restore speech if the patient is in good general condition are held for 30-60 minutes 1-3 times a day. However, many patients cannot concentrate their attention for long. With prolonged mental stress, they experience headaches, dizziness, and increased blood pressure. In these cases, classes should be carried out for 10-15-20 minutes, but their number during the day should be increased to 5-7 times. However, in an effort to conduct rehabilitation exercises more often, there is no need to apply psychological pressure when the patient feels unwell or is not in the mood; you should not interrupt if he wants to say something, but it doesn’t come out well.
Fighting bedsores
Bedsores are a dangerous enemy of bedridden patients who have to remain in bed for long periods of time. Bedsores appear in areas that are subject to the greatest pressure - the tailbone, shoulder blades, buttocks, legs, forearms.
Bedsores in advanced stages require surgical treatment. There are cases when a patient was saved in intensive care, but then, due to poor care, he died from sepsis that developed from banal bedsores. Nursing after a stroke is exactly the case when an experienced and conscientious nurse is just as important as a doctor. And sometimes it’s even more important.
How long does it take for speech to be restored?
Rehabilitation of speech functions usually begins a week after the rupture of a blood vessel in the brain, provided that the patient’s condition is stable. However, there are situations when the patient is not able to start exercising even after a month. One way or another, rehabilitation therapy should begin no later than two months later. Otherwise, it will be much more difficult to regain lost abilities.
It is very difficult to give an accurate forecast regarding the time of speech recovery after a stroke. Rehabilitation is a step-by-step process with a clear sequence. The duration of each stage varies and is individual for each patient. On average, the maximum improvement in speech abilities is observed in the first six months after the illness. The entire recovery period lasts from three to five years.
How to treat aphasia
As everyone is taught from childhood, “nerve cells do not regenerate.” In fact, this is not entirely true: even in very old people, new connections can be formed between living neurons - “bridges” along which information will flow from the nerve cell on one side from the source of the stroke to the neuron on the other side. But for this you need:
- daily activities that will use areas of the brain located next to the dead zone;
- sufficient blood supply to the brain, especially in the affected area;
- providing the brain with the necessary amount of oxygen;
- elimination of additional chaotic impulses that arise in the brain during stress and prevent the flow of impulses from being directed to the area near the site of dead cells. Stress in aphasia is caused by the fact that a person understands his inability to convey his thoughts to others.
Aphasia after a stroke is also treated according to these principles. It needs to be started as early as possible - as soon as the swelling of the brain is stopped, which is manifested by depression of consciousness (from drowsiness to coma), convulsions, and hallucinations.
Therapy should be:
- started as early as possible;
- carried out daily, to the extent that the patient can handle;
- is aimed at correcting not only oral, but also written speech, if such a syndrome occurs in your relative.
In some cases, aphasia after a stroke can resolve on its own, but this is extremely rare, so you should not count on such an outcome. Basically, treatment of this syndrome is a long and painstaking process, requiring great dedication from relatives.
Let's look at each type of therapy in detail.
Drug treatment
It is prescribed by a neurologist at the hospital where the stroke patient is located, and begins as early as possible. Drug therapy includes drugs that improve the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the brain, strengthen nerve connections in it, and optimize metabolism in it. This:
See also:
- Ischemic cerebral stroke: symptoms, prognosis, treatment
- Dementia stages and disease prognosis: challenges and solutions along the disease trajectory
- Microstroke: first signs and symptoms, consequences, treatment
- "Cerebrolysin" ("Semax");
- "Gliatilin" ("Holitilin", "Cereton");
- "Somazina" ("Ceraxon");
- succinic acid preparations “Cytoflavin”, “Reamberin”, “Mexidol”;
- B-group vitamins: Neuromidin, Milgamma.
These drugs are used in combination, according to the scheme that is practiced by this medical institution. Initially, they are administered intravenously and intramuscularly for 1-3 weeks. Next, they switch to the tablet form of these medications.
In addition to these medications, the patient is administered those medications that his condition requires. Therefore, if aphasia after a stroke is complemented by other, more life-threatening disorders, the complex of treatment for the speech disorder itself is “cut down” - to reduce the drug load on the internal organs.
Physiotherapy
To treat aphasia after a stroke, physiotherapeutic procedures are performed to improve cerebral circulation. This:
- acupuncture;
- electromyostimulation (exposure to current pulses) of the muscles involved in articulation;
- exposure of the cerebral cortex to a magnetic field.
Classes with a speech therapist
A special speech therapist, an aphasiologist, deals with the relief of aphasia after a stroke. Typically, these specialists work in the same medical institution that treats stroke, but in some cases, relatives have to find such a specialist on their own.
Classes with an aphasiologist should begin in the neurological department, a week after the patient is transferred from the intensive care ward. This doctor trains an older person who has had a stroke for 5-7 minutes at first, gradually increasing the training time to 15 minutes. It works like this:
- Build a dialogue with the patient.
- Seek understanding.
- Practice reading.
- Recall writing skills.
Before starting classes with a patient with sensory aphasia, if he does not understand his condition, he is asked to write a word (usually he writes a set of letters), then read it. They communicate with him through facial expressions and gestures. On a piece of paper with a set of letters, underline with a pencil or pen.
The aphasiologist must show the relatives the exercises he performs with the patient so that they can repeat them in the evening.
Examples of exercises:
- Bloating of the cheeks.
- Licking the tongue alternately between the upper and lower lips.
- Stretching your lips with a tube, after which you need to hold them in this position for 5 seconds, then relax.
- Tongue movements: to the tip of the nose - to the chin.
- Attempts to form a tube in front of a mirror.
- Move the lower jaw forward and upward to grab the upper lip with your teeth. Then do the same with the lower jaw.
- With your mouth closed, you need to try to reach the tongue with your tongue.
- Clicking the tongue against the roof of the mouth.
- Image of kisses.
- Pronunciation of simple familiar words.
With an aphasiologist, they learn a phrase or word with which to start communication, “remember” counting from 1 to 10 and in reverse order.
Melodic intonation therapy is effective in the treatment of aphasia: while singing, articulation improves and self-confidence appears. They begin singing with a familiar song, supporting the patient in every possible way, even if he could not utter a single intelligible sound.
For sensory aphasia, training with cards with pictures on them helps. You can use special computer programs (for example, a program for speech therapists by Ryabtsun) or applications on your phone. The aphasiologist asks the patient to explain what he wants to say using pictures. Also, if a person confuses letters in words, he asks to show where, for example, “barrel” is depicted and where “kidney” is depicted.
If speech is slightly affected, or at later stages of treatment, they resort to dictations and reading aloud. For treatment, it is also important to pronounce tongue twisters, especially those sounds that the patient cannot pronounce.
After each successfully completed task, the patient is praised.
In addition to exercises and dictations, a speech therapist-aphasiologist performs speech therapy massage. To do this, he carefully massages different areas of the tongue, lips, cheeks, and palate using a spatula or spoon. The purpose of the massage is to restore muscle tone in these areas in order to improve speech.
Sessions with a psychotherapist
Patients with aphasia after a stroke, especially its motor variety (when they understand speech, but cannot reproduce it), are distinguished by tearfulness and depressed mood. To prevent them from developing depression, they need sessions with a psychotherapist. This specialist will assess the mental state of your relative and, based on this, prescribe the appropriate type of psychotherapy, which can be supplemented with the necessary medication support.
In most cases, the psychotherapist conducts classes not only with the patient himself, but also with his relatives. He explains how they need to build a line of behavior towards the patient, how to communicate with him, how to react to his tears or attacks of anger.
Alternative Treatments
At the moment, for the treatment of severe forms of aphasia that are not amenable to standard therapy, the following can be used:
- Introducing stem cells into the blood - those human cells that can turn into any other cells in the body. It is assumed that stem cells, sensing “signals” from the stroke-damaged brain, are sent there and replace (at least partially) the dead areas of nervous tissue. As a result, the volume of dead brain tissue decreases, and further sessions with a speech therapist have a better chance of restoring speech.
- An operation called extra-intracranial anastomosis. It consists of creating an artificial connection between an artery lying outside the cranial cavity (temporal artery) and the middle cerebral artery, which supplies the brain. The operation has not yet received widespread use and is aimed at improving blood supply to the brain.
What to do at home
After discharge, relatives will need to continue the therapy started in the hospital:
- taking medications in tablets;
- exercises for the speech apparatus: prescribed by a doctor or those listed above;
- speaking tongue twisters;
- if necessary, sessions with a psychologist and psychotherapist.
You need to treat the patient politely, try not to focus on the fact that his speech is incomprehensible, repeat that this is a temporary difficulty and with joint efforts you will cope with this disease. Speak clearly, clearly, but not as loudly as with a mentally retarded or unintelligent baby. Try to touch only on topics that will inspire him with optimism.
Don't isolate an elderly relative. On the contrary, try to gather around him many relatives and friends who will communicate with him and among themselves, so that he can hear their speech. If the speech impairment is severe, then it is better to ask him questions in such a way that he can answer negatively or affirmatively.
The patient can watch programs and videos, but no more than 2 hours a day. This is explained by the fact that you cannot overload certain areas of the brain that has not yet fully recovered, so as not to cause a deterioration in the condition. The programs, films or videos you watch must be positive.
Complications
Neurologists have to deal with numerous complications of the physical and psychological state of a stroke, which include:
- Gross disturbances of mental, cognitive, speech activity;
- Perceptual inhibition;
- Inflammatory phenomena of the bronchopulmonary, genitourinary system due to congestion in an immobilized patient;
- Depressive states with suicidal statements.
These manifestations require the closest attention and active therapy from specialists in various fields.
The Yusupov Hospital has a full range of rehabilitation equipment, including innovative ones, and a staff of highly qualified specialists who are proficient in modern techniques and types of massage and physical therapy. Their efforts, led by the country's best neurologists, are helping people recover from stroke paralysis.
Neurology Center in Moscow
Aphasia refers to the partial or complete loss of speech function. This disorder is associated with organic brain damage. May result from acute cerebrovascular accident, brain tumor or traumatic brain injury. The development and degree of aphasia depends on the location of the brain lesion.
Aphasia ranges from mild to severe forms. Total aphasia implies a complete absence of speech and its understanding. Then the transition of total aphasia to a motor or sensory form is possible.
Motor aphasia
With motor aphasia, a person understands speech addressed to him. However, he can only communicate with others using one word or sound combination. So, motor aphasia is a condition in which a person cannot speak, but can understand speech addressed to him. Motor aphasia is associated with damage to the frontal lobes of the cerebral cortex.
Sometimes the patient can still pronounce words with great difficulty (he sometimes speaks words in syllables). A person tries to avoid complex words in words, limiting himself to simple ones. The patient's speech is quite difficult to distinguish. However, in most cases the speech is understandable. With motor aphasia, speech is always meaningful - this is different from sensory aphasia. Speech is accompanied by eloquent gestures, this is how the patient helps himself to express himself.
Every year, acute cerebrovascular accident affects a large number of people. Afferent motor aphasia develops if the pathological focus is located in the parietal lobe of the brain. A characteristic feature of this disorder is confusion of sounds that are similar in pronunciation. This type of motor aphasia is also characterized by reading impairment. Motor aphasia has a better prognosis than sensory aphasia. Treatment of these types of diseases in stroke patients is carried out by highly qualified speech therapists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Sensory aphasia
Aphasia is a language disorder that affects expressive and expressive language and the ability to read and write.
Aphasia can be so severe that communication with the patient is almost impossible, or the disorder can be very mild. This can affect the ability to select words, the ability to combine words in sentences, and the ability to read. Typically, several aspects of communication are disrupted while some channels remain available for limited information exchange.
With sensory aphasia, speech understanding is impaired. A person does not understand either his own speech or someone else’s, but the ability to speak is often preserved. The condition is associated with damage to the left temporal lobe of the brain. As is correct, the patient is talkative and talks a lot. However, he does not understand himself or those around him. The patient's speech is incomprehensible. There is no meaning in the patient’s words - due to the lack of understanding of one’s own and others’ speech, there is a loss of control over speech. The patient can invent new words, change words, rearrange letters and syllables, pronounce unrelated strings of sentences and words. Since the perception of sounds is impaired, the speech of others becomes incomprehensible to the patient.
Sensory aphasia is otherwise called acoustic-gnostic. The auditory zone of the cerebral cortex is affected. This is the so-called Wernicke's area lesion. Damage occurs to the auditory analyzer - the primary auditory field.
Aphasia refers to the destruction of already established speech. This usually occurs as a result of brain damage. A person can no longer speak normally, ceases to understand other people’s speech, read and write. Neurolinguistics deals with the problem of speech impairment after brain damage. Aphasiologists and neuropsychologists are involved in the study of this problem.
Causes of aphasia
Aphasia often develops due to brain injury or stroke, especially in older people. Aphasia can also be caused by brain tumors or infections.
The most common cause of aphasia is stroke. Sometimes seriously ill patients after a stroke experience aphasia, but this is a temporary phenomenon, and then speech is restored. Less common causes of aphasia are traumatic brain injury, neuroinfection, and neurosurgical intervention.
Aphasia is characterized by difficulty remembering words. Sometimes the fluency of speech is impaired. Such patients have a limited vocabulary and speak little. There are constant hesitations in speech. Speech is distorted and incorrect. Severe situations of aphasia are manifested by the use of just one word or syllable in any communication situations. Aphasia affects adults with already formed speech skills - this is its difference from alalia.
The consequence of aphasia is problems with the perception of the surrounding world. A sick person is unable to recognize sounds, voices, or objects. The sentences are distorted and short. The patient finds it difficult to perform simple language gestures: he cannot fold his tongue into a tube, click his tongue, or put his tongue between his teeth and upper lip.
Dynamic motor aphasia is characteristic of damage to the anterior and middle parts of the inferior frontal gyrus. This is an area located next to Broca's area. There is a decrease in speech initiative. The amount of spontaneous speech decreases. With aphasia, only “remnants” of speech may remain - truncated words and syllables. This disorder is effectively treated at the Yusupov Hospital. Corrective work is carried out by highly qualified speech therapists.
Aphasia after stroke
Aphasia after a stroke is a disease that requires the help of a highly qualified speech therapist. Aphasia is a condition where a person can no longer speak coherently. Speech disorders significantly affect self-confidence and social status.
Speech restoration specialists work at the Yusupov Hospital. The clinic uses special rehabilitation methods such as therapeutic massage, physiotherapy and electrical stimulation. Restoring speech after a stroke is not a passive process. The patient must be ready to study, he must believe in himself, and be patient. In aphasia, cells in one or more of the brain's language centers die. This is a consequence of a stroke. As a result, the patient's speech becomes slurred and severely truncated. Sometimes the patient speaks in syllables or uses one word. Daily therapy should be carried out to the extent feasible for the patient.
One of the treatments for aphasia is physical therapy. After a stroke, to treat aphasia, physiotherapeutic procedures are performed that improve cerebral circulation. What are the responsibilities of a doctor who treats speech disorders after a stroke? First of all, you need daily activity that affects the areas of the brain that are located next to the dead zone.
With medication, you should try to ensure sufficient blood supply to the brain, especially in the affected area. The brain must be provided with the necessary supply of oxygen. These are the principles of treating aphasia after stroke. Therapy should be started as early as possible, immediately after cerebral edema is relieved - it manifests itself as convulsions, hallucinations, depression of consciousness (up to coma). It is necessary to start therapy as early as possible. Treatment of aphasia after stroke is one of the very important tasks of early rehabilitation of stroke patients.
Sign up for the Neurology Center:
- by phone: +7 925 191 50 55
- fill out the form: APPLICATION FOR TREATMENT
- Get advice by email [email protected]
- Clinic address: Moscow, Nagornaya st., 17 to 6
+7 (495) 506 61 01 –
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC