Stroke is an acute disease that is accompanied by the death of brain cells due to acute cerebrovascular accident. It manifests itself with general cerebral and local symptoms. The development of a stroke is possible in two scenarios: either after 24 hours from the onset of the disease, its symptoms persist, or death occurs.
Diagnostic examination for developing stroke includes:
- clarification of complaints and history of the disease;
- neurological examination;
- blood tests (determining the level of enzymes and blood glucose, the state of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems).
- Dopplerography - study of blood flow in the vessels of the neck and brain;
- computed tomography helps distinguish between ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is more informative in cases of developing stroke;
- magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography are non-invasive methods for assessing the carotid and cerebral arteries;
- an electrocardiogram allows you to assess the condition of the heart muscle;
- Echocardiography (EchoCG) is a research method with which doctors at the Yusupov Hospital identify blood clots in the cavities of the heart, which allows them to assess the risk of developing a recurrent stroke.
Make an appointment
Types of brain strokes
The most common ischemic stroke (infarction) of the brain - 85% of cases, hemorrhagic stroke occurs in 15% of cases. Strokes can be caused by several reasons:
- formation of thromboembolism in heart diseases;
- acute circulatory disorders in the cervical and large cerebral arteries;
- disturbance of blood circulation in the small arteries of the brain during the acute course of the process.
Classification of strokes
Strokes are classified according to the causes of circulatory disorders and the duration of neurological symptoms. At the Yusupov Hospital, the patient will undergo a diagnostic examination, which will allow the type of stroke and the area of brain damage to be very quickly and accurately determined. When a patient is admitted to the clinic, a number of studies are carried out as prescribed by the doctor:
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging;
- CT – computed tomography;
- Doppler ultrasound;
- cerebral angiography.
Classification of ischemic stroke (infarction) of the brain:
- hemorheological blockage of cerebral vessels. This condition develops with increased blood clotting and platelet aggregation;
- embolic stroke. Occurs in 20% of cases of ischemic stroke, develops when an artery is blocked by emboli (intravascular substrates) that enter small vessels from larger blood vessels;
- atherothrombotic stroke. Found in 50% of patients with ischemic stroke. A blood clot forms at the site of the atherosclerotic plaque, leading to blockage of the vessel;
- lacunar stroke. Arterial hypertension leads to the development of atherosclerosis, which causes narrowing of small arteries and reduced blood flow to areas of the brain. Occurs in 25% of cases;
- hemodynamic stroke. The pathological condition is caused by a sharp narrowing of a large vessel in the brain due to a drop in blood pressure during heart failure. Blood flow to a part of the brain stops, and an ischemic stroke develops.
Classification of hemorrhagic strokes:
- an outpouring of blood when a vessel ruptures in the brain tissue - parenchymal hemorrhage;
- formation of hematoma in the ventricles of the brain - intraventricular hemorrhage;
- hemorrhage into the cavity between the pia mater and the arachnoid membrane is called subarachnoid;
- Epidural, subdural and mixed forms of hemorrhages are quite rare.
Classification according to the duration of neurological symptoms:
- minor stroke – symptoms manifest from one day to three weeks. Recovery from one day to three weeks;
- transient ischemic attack - symptoms last for about a day, recovery within a day;
- Completed ischemic stroke – symptoms of the disease have been observed for more than three weeks, recovery does not occur for more than three weeks.
Preventive actions
Prevention refers to a set of measures aimed at preventing the development of brain strokes, their relapses, and subsequent complications. Necessary:
- Conduct courses of treatment in a timely manner for existing chronic pathologies.
- If you experience frequent pain in the heart area, be sure to check with a cardiologist.
- Monitor blood pressure.
- Eat properly.
- To refuse from bad habits
Stroke is one of the most dangerous diseases, often resulting in lifelong disability and even death. A timely, competent response to the first symptoms of the disease, an accurate assessment of the patient’s condition, as well as correctly prescribed treatment will facilitate recovery and improve the prognosis.
Periods of stroke
Among the huge number of neurological diseases, stroke is the most important problem. Hemorrhage in the brain leads to disruption of intracranial circulation, neuronal necrosis and disruption of vital body functions.
In ischemic stroke, a number of processes are observed that together lead to the death of neurons. Cell destruction occurs against the background of cerebral edema. At the same time, the brain increases in volume and intracranial pressure increases.
Due to cell swelling, displacement of the temporal lobe is observed, as well as infringement of the midbrain.
Compression of the medulla oblongata may also occur due to wedging of the cerebellar tonsils into the foramen magnum. This process quite often leads to death. Therefore, early hospitalization of the patient is extremely important.
When the first signs of an ischemic stroke appear, medical assistance should be provided within the first three hours, otherwise the prognosis is disappointing.
There are several periods of ischemic stroke:
- acute;
- spicy;
- early recovery period of stroke;
- late recovery;
- stage of residual effects.
The most acute period
In the first three hours, it is possible to restore blood flow and eliminate or reduce neuronal death through the use of thrombolytics. It is also possible to administer drugs into the stroke area itself, which helps prevent the development of complications.
Then doctors take measures to restore pressure, carry out rehydration, dehydration and oxygen therapy.
During the most acute period of a stroke (from 4 to 5 hours after the attack), the patient should be under the close supervision of a doctor in a hospital setting.
Acute period
The period up to 14 days after the attack is considered acute. The patient continues to undergo treatment in a specialized department of the hospital. He is undergoing drug therapy aimed at:
- reduction of cerebral edema;
- maintaining normal blood viscosity and coagulability;
- maintaining normal functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- relapse prevention;
- maintaining normal blood pressure.
Early recovery period
The early recovery period is considered to be the period from 2 to 6 months after a stroke. At this stage, complex treatment is carried out:
- the patient takes medications according to an individual treatment regimen;
- in case of speech impairment, a speech therapist works with the patient;
- various manipulations are prescribed to restore sensitivity of the limbs and other parts of the body (massages, baths, acupuncture and others);
- physical therapy – the method helps strengthen ligaments and muscles.
Late recovery period
The late recovery period is the time six months after the stroke. At this stage, the results of treatment and rehabilitation measures taken during the early recovery period are already visible.
The patient's finger sensitivity is restored and motor skills improve. It is extremely important not to stop the complex of procedures. Rehabilitation after a stroke is a long and labor-intensive process.
Period of residual effects
The time from one to two years after a stroke is considered the residual period. At this stage, it is important to follow all doctor’s instructions and take measures to prevent a recurrent stroke.
Rehabilitation specialists and neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital create a treatment and rehabilitation program individually for each patient, which allows achieving high results in recovery after a stroke.
Expert opinion
Author: Vladimir Vladimirovich Zakharov
Neurologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Memory Disorders
According to statistics provided by WHO, stroke ranks third in prevalence among all neurological diseases. Doctors note an annual increase in incidence. In Russia, 400 thousand new cases of stroke are registered every year. More than 30% of them are fatal. Acute cerebrovascular accident is not a disease characteristic of older people. The disease can be diagnosed in 5-year-old children. A distinctive feature of old age is considered to be a greater number of factors predisposing to the development of stroke.
At the Yusupov Hospital, diagnosis of cerebrovascular accidents is carried out using modern medical equipment. CT and MRI make it possible to assess the size of the pathological lesion, its location, and the type of stroke. Treatment is developed individually for each patient. The drugs used meet quality and safety standards. If necessary, surgical intervention is performed. During the rehabilitation period, each patient is prescribed a course of physiotherapy and a complex of physical therapy. Experienced massage therapists work the muscles, helping to restore lost functions.
Ischemic stroke: symptoms, consequences, treatment - MEDSI
Table of contents
- Forms of ischemic stroke
- Causes of ischemic stroke
- Main symptoms
- Diagnosis of stroke
- Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
- Nutrition after stroke
- Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
- Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
- Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
Ischemic stroke
is a condition that occurs against the background of damage to brain tissue due to impaired blood circulation in its vessels and is accompanied by various neurological signs. As a result of its appearance, the functioning of parts of the brain is disrupted (depending on the focus of the disease).
Of the three existing types of strokes, ischemic stroke is the most common, occurring in 80% of cases. The other 20% are subarachnoid hemorrhage and hemorrhagic stroke.
Stroke has especially dangerous consequences: impaired cognitive and neurological functions, paralysis, problems with oral and written speech, etc.
Forms of ischemic stroke
There are several classifications of stroke: by reason of occurrence, by the degree of damage to brain tissue and by severity.
- Reasons for appearance:
- Lacunar – the syndrome affects a tissue area up to 15 mm in size and is accompanied by a small number of neurological symptoms
- Thromboembolic - occurs due to blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus
- Hemodynamic - in this case, vascular spasm is prolonged, and brain cells stop receiving the necessary nutrients
- Transient attack - the lesion is small, and neurological signs quickly disappear
- Small – brain functions are restored within 21 days
- Progressive - its neurological signs do not appear immediately and accumulate over time; after treatment, some of these symptoms may persist
- Extensive - signs of its appearance are recorded for a long time, including after treatment
- Mild – symptoms are mild and disappear within a few days
- Medium – signs appear, but are not accompanied by a disorder of consciousness
- Severe – in this case consciousness is depressed and brain tissue is severely damaged
Causes of ischemic stroke
The causes of stroke include diseases and dysfunctions of the body such as:
- Hypertension
- Cardiac ischemia
- Arrhythmia
- Bleeding disorder
- Various diseases of the vascular system
- Pathologies of blood vessels of the neck and head
- Migraine
- Kidney diseases
- Diabetes
- Atherosclerosis
- Obesity
- Thrombophlebitis
The following people are also at risk:
- Heavy and frequent smokers
- Experiencing constant psycho-emotional overload
- Those who have suffered blood loss
- Suffering from chronic headaches
- Excessive alcohol drinkers
- Regular overeaters
Given the above factors, men and women over 50 years of age are especially at risk of ischemic stroke.
Main symptoms
Signs of ischemic stroke consist of general signs characteristic of all types of stroke and symptoms that reflect the nature and location of damage to brain tissue.
- General symptoms:
- Fever
- Vomiting and nausea
- Loss of consciousness
- Headache
- Problems with orientation in space
- Inability to move limbs or move incorrectly
- Dizziness
- Speech difficulties - problems with reading, speaking, understanding what is said, writing, counting
- Visual dysfunction – sudden deterioration, double vision
- Swallowing dysfunction
- Inability to perform simple everyday activities (comb your hair, etc.)
- The occurrence of amnesia and other serious memory impairments
- If the left hemisphere is affected, paralysis may also occur
- With damage to the temporal lobe - depression, impairment of cognitive and logical functions
Diagnosis of stroke
A qualified neurologist can determine the presence of a stroke quite quickly. But in order to prescribe the most effective treatment, he needs to identify both the localization of the lesion and the causes of its appearance, concomitant diseases. For this, the following diagnostic procedures and equipment are used:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and magnetic resonance angiography
- Doppler ultrasound of cerebral vessels
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Cerebral angiography using contrast agent
- Blood biochemistry for sugar and cholesterol
- ECHO-KG
- Electroencephalogram
- ECG
- Coagulogram (blood clotting test)
Ischemic cerebral stroke - treatment
Since this phenomenon disrupts brain function, ischemic stroke requires treatment that will be complex and long-term. Otherwise, swelling, thromboembolism and other negative consequences may occur.
- A patient in acute condition is sent to the ward or intensive care unit
- First of all, medical personnel restore the functioning of the respiratory and circulatory systems
- If necessary, surgery may be performed to remove the blood clot.
- Medicines can also be used to liquefy the clot.
- In general, in the process of treating a patient, the following types of drugs are used: anticoagulants, blood thinners, vasoactive drugs, antiplatelet agents, angioprotectors, neurotrophics, antioxidants
Remember, all medications must be prescribed by a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous!
Nutrition after stroke
If the patient is diagnosed with ischemic stroke, treatment should not be limited to hospital stay. An important part of the fight against the consequences of a stroke is proper nutrition and rehabilitation measures.
It is necessary to include in the diet such products as:
- Porridge
- Lean fish, meat and seafood (boiled)
- Vegetables (cabbage, spinach, beets, etc.)
- Berries (blueberries, cranberries, etc.)
- Fruits
- Dairy
- Vegetable oil
The following should be strictly avoided:
- Fried
- Smoked
- Fat
- Dishes with a lot of spices
- Flour products
It is also necessary to reduce the amount of salt in food.
It is important to remember that after a stroke you need to get rid of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol).
Rehabilitation measures after a stroke
Since a stroke can lead to many negative consequences (impaired speech skills, memory, cognitive functions, paralysis), it is better to undergo rehabilitation procedures in a specialized institution (sanatorium). To restore a number of functions, you need to contact professionals:
- Speech therapist – for restoration of speech and graphic skills
- Physical therapy specialist – to improve coordination and motor function
- Specialist in physiotherapeutic procedures (electrical stimulation, reflexology, etc.) - to accelerate the regeneration of nerve tissue and improve blood supply
- Neurologists and psychologists – to eliminate cognitive and emotional disorders, restore memory
Prevention and prognosis of ischemic cerebral stroke
If concomitant diseases or other risk factors persist, ischemic stroke may recur. Therefore it is necessary:
- Regularly undergo preventive examinations of the circulatory system and heart
- Treat hypertension and other concomitant diseases in a timely manner
- Contact a doctor immediately if you feel unwell
- Adhere to a healthy lifestyle and proper nutrition
According to statistics, the occurrence of a stroke ends in death in the first weeks in 25% of cases, in 50% of cases the patient lives after a stroke for about 5 years, the remaining 25% can live at least 10 years.
Advantages of carrying out the procedure at MEDSI
- A full range of services for the management of patients with stroke: from stabilizing the patient to prescribing rehabilitation procedures and therapy
- MEDSI specialists are candidates of medical sciences, have high qualification categories and have extensive experience working with stroke patients
- Experienced surgeons of a specialized department perform precise operations on blood vessels through mini-accesses using the latest expert-level equipment
- All studies and procedures are in one place
- MEDSI doctors provide follow-up care for patients who have suffered a stroke, including at home
- At the first signs of a stroke in you or your relatives, call 8 (495) 7-800-500
Causes and consequences of stroke
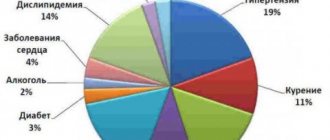
The following causes of stroke are known:
- age. People at risk for stroke include older people, especially those who have high blood pressure, lead a sedentary lifestyle, are overweight, or smoke or drink heavily. Currently, stroke is increasingly developing in young people;
- floor. In most age groups, stroke is more common in men than in women. However, it is more severe and more often fatal in women. This is due to the use of contraceptives, hormonal imbalance and emotional imbalance in women;
- family history. In most cases, the closest relatives of patients suffering from stroke have suffered acute cerebrovascular accident;
- smoking. Individuals who smoke more than 20 cigarettes per day have a 2-fold increased risk of stroke;
- nutrition. The predominance of saturated fats, light carbohydrates and excess amounts of table salt in the diet contributes to an increase in blood pressure, which is the main factor in hemorrhagic stroke;
- insufficient physical activity. Lack of regular exercise increases the risk of obesity and increases poor circulation, which contributes to the development of stroke.
- drug use. Drugs, especially methamphetamine and cocaine, are a major factor in the development of stroke in young people. Anabolic steroids, which athletes often take, also increase the likelihood of stroke.
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels. People suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system, especially those accompanied by cardiac arrhythmias, and peripheral vascular pathology are at increased risk of developing stroke;
- a stroke increases the risk of acute cerebrovascular accident by 10 times;
- Arterial hypertension is the cause of 70% of strokes. Patients with hypertension have a 10 times higher risk of stroke than people with normal blood pressure.
- high cholesterol levels increase the risk of developing atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries and impaired blood flow through the cerebral vessels;
- Coronary heart disease increases the risk of stroke. Anti-clotting drugs, which are used to treat cardiovascular diseases, dissolve blood clots but also increase the risk of hemorrhagic stroke.
- Atrial fibrillation is a major risk factor for stroke associated with heart rhythm disturbances. 2-4% of patients with atrial fibrillation without warning signs of cerebral bleeding develop a stroke.
The consequences of a stroke are impaired motor, speech, visual, cognitive function, and sensitivity disorders. They are prevented at the Yusupov Hospital by a team of specialists, which includes neurologists, cardiologists, speech therapists, psychotherapists, and rehabilitation specialists.
Seizures after stroke
Some consequences of a stroke can be treated and restored with adequate medical care. These consequences include seizures that occur in women and men after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke.
The development of convulsive syndrome is caused by the death of brain neurons and the formation of a focus of necrosis. The body's response to this process is the activation of other neurons to restore blood circulation and stop the pathological process. Necrotic tissue is replaced by a cavity filled with fluid; when a cyst forms, a person does not feel discomfort. However, when neurons are irritated by the cyst, seizures can occur.
After a stroke, seizures can manifest in patients in the form of:
- numbness of one or both limbs at the same time, feeling of a wooden leg or arm;
- contractions of the muscles of the face and neck, resulting in a “mask-like face”, tilting of the head to one side or asymmetry of the face on one side;
- contractions of the facial muscles against the background of numbness of the limbs.
Some patients experience mild tremors after a stroke, while other patients experience short-term cramps throughout the body.
Temperature values
What does the temperature reading after a stroke indicate? It characterizes the degree of brain damage and reflects the dynamics of the victim’s recovery.
Based on the fluctuations of this criterion, it is customary to distinguish several values:
- Moderate hyperthermia – the level does not exceed subfebrile values (up to 37.50 C). May be a variant of the norm. The optimal value after a stroke is considered to be 37.20 C, but a deviation of 1 degree is not critical.
- If the readings increase above 38 degrees, further examination is necessary to determine the cause.
- A low temperature of up to 36.0 °C during an ischemic attack is a positive characteristic.
Based on the marks on the thermometer, you can predict the outcome of the disease. The higher they are, the less likely a person is to recover from a stroke. The temperature does not change immediately after the stroke is stopped, however, the later it rises, the worse the prognosis for the patient.
Complications of hyperthermia
Changes caused by high temperature during a stroke:
- acceleration of metabolism due to oxygen deficiency,
- necrosis of the inflammation focus,
- blood flow disturbance,
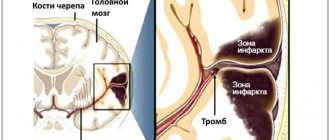
- expansion of the cerebral infarction zone during ischemia,
- focal changes in the structure of matter.
Without a rapid decrease in numbers, post-stroke pathologies develop, which can lead to a person’s disability or result in his death.
Violations during the rehabilitation period
The rise in temperature even after an impact is life-threatening. It does not matter whether the person suffered an ischemic or hemorrhagic type of stroke. Research by specialists shows that when hyperthermia occurs within a month, there is an increase in mortality. Factors contributing to the increase in indicators:
- the presence of an infectious process,
- insufficient patient care,
- bedsores,
- tracheostomy,
- diseases of the lower respiratory tract.
Despite the temperature deviation from the norm, the patient may not complain of health, there is no pain. A characteristic symptom of the complication is the low effect of taking antipyretics.
The longer the temperature remains outside the normal range, the greater the pressure on tissues and the higher the likelihood of complications.
.
Consequences of rising temperatures
Against the background of increased oxidative reactions in tissues, their need for oxygen simultaneously increases. Without restoration of normal blood supply, hypoxia quickly sets in. In the absence of adequate therapy, the rehabilitation process slows down, the patient may fall into a coma or die.
Temperature after stroke
Temperature during a stroke is an indicator of cerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke. With an ischemic stroke, the temperature in most cases is slightly lowered; with a hemorrhagic stroke, the temperature rises.
Timely medical care reduces the risk of developing severe complications. After a stroke, it is difficult to deal with high fever - antipyretics can aggravate the condition of a patient with a hemorrhagic stroke, and in the case of an ischemic stroke cause hemorrhagic transformation.
Temperature after stroke: causes and treatment
Temperature during a stroke is a very important indicator of the patient’s condition. It is most often used to determine the degree of brain damage in a patient. Temperature readings up to 38 degrees are considered to be the maximum permissible.
Stroke studies have shown that the majority of stroke patients had a normal mean temperature upon admission to the clinic. In patients with extensive strokes, the temperature began to rise after a few hours (4-6) to 40 degrees. In patients with moderate strokes, the temperature rose to 40 degrees 12 hours after the stroke. A mild stroke most often occurs without fever or with a slight rise in temperature.
Complications after a stroke
After a stroke, fever often occurs due to the following complications:
- the damage occurred over a large area of the brain;
- swelling of brain tissue has developed;
- during a stroke, the thermoregulation center in the brain was damaged;
- complication after a stroke – pneumonia;
- an allergic reaction to medications developed.
In cases where the cause of the increase in temperature is its central genesis, doctors perform craniocerebral hypothermia. The brain is cooled through the outer covering of the head using special equipment. This method increases the brain's resistance to oxygen starvation, reduces the risk of developing cerebral edema, relieves existing edema, and reduces tissue temperature.
Care after ischemic stroke
The patient should be in a bright, well-ventilated room, protected from extraneous noise, in which wet cleaning should be carried out regularly, at least 1-2 times a day.
The room should be ventilated several times a day so that the patient is not in a draft, and the average air temperature in the room is maintained at + 18-22 degrees.
Beds with sagging metal mesh cannot be used. It should be tightly stretched and covered with a dense mattress, for example foam rubber - the most hygienic and comfortable.
The caregiver is recommended to keep a diary in which to record indicators characterizing the patient: blood pressure, pulse, body temperature (it must be measured at least 3 times a day), the amount of fluid consumed (drinks, liquid dishes, fluid administered by infusion), the amount of excreted urine, frequency of bowel movements.
It is necessary to monitor the regularity of following the doctor's prescriptions.
To prevent congestion in the lungs, bedridden patients should do breathing exercises several times a day. The simplest type of breathing exercise is inflating a balloon.
In order to prevent bedsores, every 2-3 hours it is necessary to turn the patient over in bed, while performing a light massage of the skin on the back and sides of the chest, buttocks (stroking, rubbing). Special inflatable rings are placed under areas of the body where the risk of developing pressure sores is highest (heels, elbows, shoulder blades, buttocks, back of the head).
It is necessary to monitor the cleanliness of the patient's skin: regularly wash the patient's body with towels soaked in a weak soap solution, then wipe the skin dry. In some cases, camphor alcohol is used to cleanse the patient's skin.
After each meal, you need to clean your mouth of food debris.
Be sure to monitor the condition of the skin in natural folds (perineal area, groin and armpits, in women - under the mammary glands), as well as in fat folds. Areas of skin redness (maceration) should be treated with a gauze swab moistened with a pink solution of potassium permanganate or camphor alcohol.
If bedsores appear, you should consult a doctor about the rules of their treatment.
Signs and symptoms after a stroke
The symptoms of a stroke largely depend on the cause of the disease. The first signs of a stroke are the following symptoms:
- sudden numbness or weakness in an arm or leg on one side of the body;
- confusion;
- Strong headache;
- speech disorder;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dizziness;
- loss of balance or coordination.
The speed at which symptoms of an ischemic stroke appear may indicate its origin: if an acute cerebrovascular accident is caused by an embolism, the disease is sudden. Headache and seizures may develop within seconds of arterial thromboembolism.
In patients with the consequences of a stroke, there are three main types of disorders:
- damage, defect. The following damages after a stroke are distinguished: motor, cognitive, emotional-volitional, speech, visual, sensory, sexual and pelvic disorders;
- impaired ability. Expressed in impairment of walking and self-care;
- impairment of social functioning. It is expressed in the restriction of the implementation of the social role that was the norm for the patient before the illness.
Symptoms after a stroke go away if doctors begin rehabilitation measures in a timely manner. When a patient is admitted to the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, a team consisting of the following specialists is included in the rehabilitation process:
- neurologists;
- therapists;
- kinesitherapy specialists;
- aphasiologists;
- massage therapists;
- physiotherapists;
- acupuncturists;
- psychologists;
- biofeedback specialists.
Muscle pain due to stroke
Muscle pain after a stroke, which should be treated immediately, occurs in most patients. Muscle soreness can interfere with the body's recovery. Post-stroke pain can be strategic or thalamic. Strategic pain occurs in the area of the brain that controls sensations, particularly pain, and is caused by spasms. Thalamic pain appears after a stroke in one side of the body several months after the circulatory disorder.
The occurrence of pain after a stroke can be associated with various factors. Neurologists and rehabilitation specialists advise patients to follow recommendations that will prevent the onset of this condition. Measures to prevent muscle pain after a stroke:
- do not take hot baths;
- prefer clothes made from natural materials, do not wear light clothes;
- be in a comfortable position and avoid tightly grouping the body;
- do not put pressure on the affected side;
- use special devices for paralyzed and weakened limbs;
- fix the paralyzed arm while sitting so that the pain localized in the shoulder does not get worse;
- When moving, support from another person is desirable.
If you have pain in the legs after a stroke, it is important to trust treatment to qualified neurologists and rehabilitation specialists.
First aid
Measures to reduce the temperature depend on the cause that caused it and are determined by the doctor. For this purpose, it is necessary to undergo a diagnostic examination.
It is not allowed to engage in treatment without the supervision of a doctor. Before contacting a medical facility, you can use antipyretic drugs. Under no circumstances should antibiotics or hormonal drugs be taken orally.
Before giving the patient medicine, you need to make sure that his swallowing function is not impaired.
If the temperature does not return to normal after taking medications, it is reduced in a hospital setting. To do this, the patient is injected with lytic mixtures by drip. If immediate hospitalization is not possible, you should avoid overheating and wipe the neck, elbows, and popliteal fossae with cool water.
Carefully! Some anti-inflammatory drugs help thin the blood. Taking them may cause bleeding.
Features of stroke in older people
Age is one of the significant factors in the development of acute vascular pathologies of the brain that impair blood circulation. Diseases of the blood vessels in older people are much more severe than in young people. This is due to physiological changes in the body, and in particular in the central nervous system, such as:
- reduction in brain volume and weight;
- thinning of the leptomeningeal membranes;
- senile neuronal atrophy;
- degenerative changes in white matter;
- decreased functional activity of neurons;
- neuronal death caused by electrolyte imbalance;
- reduction of the blood-brain barrier;
- pathological changes in the cerebral ventricles.
About 80% of stroke cases are diagnosed in people over 70 years of age. And, unfortunately, the prognosis for recovery is very often unfavorable. The consequences of stroke in older people are difficult to predict, since it is difficult for such patients to choose effective therapy.
Causes of stroke in older people
Among the causes of stroke in older people, etiological factors and risk factors are distinguished. The former cause the disease itself, while the latter increase the likelihood of pathology occurring. The main causes of acute disorders of blood flow in the brain include:
- arterial hypertension;
- vasculitis and angiopathy;
- improper use of drugs that affect blood clotting;
- neoplasms in the cells of nerve or connective tissues;
- changes in heart rate;
- atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries;
- hormonal imbalance, which increases the risk of blood clots.
The main risk factors for stroke in older people include:
- gender (statistically, men are more susceptible to extensive bleeding into the brain);
- presence of cardiovascular diseases;
- increased cholesterol levels in the blood;
- history of micro-strokes.
As a rule, a stroke is preceded by certain vascular and cardiac diseases. Some of them are systemic atherosclerosis and atrial fibrillation, which develop at the age of 85 years.
Systemic vascular atherosclerosis
This disease is heterogeneous plaques that form in medium and large arteries, including the brain. Elderly and senile age are the main risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis.
Frequent atrial fibrillation after 85 years
Heart rhythm disturbances that lead to an irregular heartbeat indicate the presence of atrial fibrillation. The sinus node cannot cope with the coordination of the heart rhythm, which is why the upper chambers flicker chaotically. As a result, insufficient blood enters the ventricles. The main symptoms of atrial fibrillation are:
- trembling in the chest;
- cardiopalmus;
- irregular heart rhythm;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the chest;
- dizziness;
- fatigue, drowsiness;
- increased anxiety and restlessness.
Many people live with this disease for decades. It is not a direct threat to life, but when a person reaches old age it leads to a number of complications, including stroke.
Stroke in people over 70 years of age
With age, cerebral circulation deteriorates. These disorders are explained by natural aging changes, due to which the body's compensatory reserves decrease. As a result, the walls of blood vessels become brittle, the inner lining of the arteries is affected by atherosclerotic plaques, and cases of sudden jumps in blood pressure become more frequent.
The consequences of a stroke in elderly patients (over 70 years of age) are very life-threatening and radically change it. The first episode of cerebral vessel rupture leads to coma in more than half of the cases. The recovery process after an acute cerebral circulatory disorder is difficult and lengthy.
Signs of stroke in older people
In most cases, the disease manifests itself almost immediately. Deprived of normal blood supply, brain cells die, which is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe headache;
- dizziness;
- fainting, short-term loss of consciousness;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- deterioration of speech and pronunciation (slowness, deterioration of diction, inability to reproduce sounds);
- decreased vision, darkening of the eyes, blurred and unclear images;
- confusion, absent-mindedness;
- disorientation in space.
Signs of stroke in older people have some peculiarities. A vascular accident in the brain occurs regardless of the time of day, but more often develops in the early morning or evening. In older patients, the condition often worsens gradually over several days. This is due to the fact that cerebral hemorrhage occurs quite slowly.
Clinical picture as a whole
In addition to hyperthermia, doctors include general cerebral and focal symptoms in the clinical picture of a stroke.
General cerebral symptoms
Includes the following features:
- dizziness and headache;
- noise in ears;
- urge to vomit;
- disturbances in consciousness - from slight disorientation in space and time to partial or complete loss of consciousness and immersion in a coma;
- convulsions.
Focal signs
Damage to the right hemisphere is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- paresis of the left half of the body;
- speech problems;
- conduct disorder;
- lethargy;
- memory problems.
If there is a violation in the left hemisphere, the following signs are observed:
- paresis of the right half of the body;
- problems with spatial perception;
- hot temper and aggression;
- behavioral disorders.