Confusion is a pathological condition expressed in impaired ability to navigate in time and space, failures in short-term memory and decreased attention. It is caused by a disorder of brain activity and can be a sign of both somatic and mental illnesses. Stupefaction is sometimes a consequence of acute intoxication (drug, alcohol, drugs), dehydration, hypothermia or heat stroke, severe physical fatigue, shock as a result of stress.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of confusion is disorientation in time and surrounding space, the patient’s inability to remember previous events, confusion, impaired attention, inadequate emotionality, slowness of reaction and perception.
Stupidity associated with acute intoxication is characterized by a decrease in the activity of mental processes, tremors, a decrease in body temperature, and eye symptoms (nystagmus, constriction or dilation of the pupils).
When alcohol is withdrawn against the background of chronic alcoholism, a severe form of clouding of consciousness sometimes occurs - delirium delirium (insanity). This is an acute psychosis in which the patient becomes extremely restless and aggressive, and experiences hallucinations. Delirium is accompanied by chills and a sharp increase in temperature, sweating, and convulsions.
Confusion may be a symptom of a closed traumatic brain injury, in which case other signs of injury may include pallor, nausea and/or vomiting, slow reaction, drowsiness, headache, convulsions, incoordination, and brief loss of consciousness. Symptoms of intracranial bleeding are impaired respiratory function, increased blood pressure, and bradycardia.
In acute cerebrovascular accidents not associated with trauma, confusion also sometimes occurs. The patient may be excited or, conversely, inhibited, characterized by disturbances in speech and perception (usually visual and auditory), asymmetrical impairment of coordination of movements and facial expressions.
But with encephalitis, stupefaction is not a profiling specific syndrome; to clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to check for the presence of other symptoms. Associated symptoms of inflammation of brain tissue are headache, photophobia, and acute fever. It is also necessary to take into account that neurological disorders may not appear immediately.
The clouding of consciousness in Alzheimer's disease is chronic with periodic exacerbations. Long before the manifestation of a severe form of impairment of consciousness, cognitive impairment, persistent apathy, and memory impairment occur. Subsequently, speech and motor function disorders occur.
In epilepsy, confusion is periodic and occurs only against the background of severe convulsive attacks.
Periodic or constant confusion of consciousness with preservation of motor functions and without somatic symptoms such as changes in body temperature and blood pressure is characteristic of mental disorders.
Affective insanity
MDP (manic depressive psychosis) refers to a group of mental disorders that manifest themselves in a pronounced form of affective disorders. Sometimes there is an alternation of depressive symptoms and mania, and mixed symptoms may form. To date, experts have not compiled a specific list of reasons that cause the occurrence of MDP in people.
The diagnosis is made on the basis of a collected medical history, therapeutic conversations and tests, as well as interviews with close family members. Based on the results obtained, individual drug treatment is selected.
Manic depressive psychosis in women
In practice, the development of MDP occurs predominantly in women, since they are more prone to emotional manifestations than men. In addition, due to the production of certain female hormones, the body becomes more susceptible to stressful situations.
According to statistics, the number of cases of MDP development in women is 2-3 times higher than in men. Speaking about world statistics, this disease accounts for about 10-15%. With pronounced clinical syndromes, the following aspects can be distinguished:
- Excessive suspiciousness
- Increased anxiety for no good reason
- Stressful situations
- Physiological ailments, including infectious types.
It is important to note that MDP is characterized by the following manifestations:
- Joy, a state of euphoria manifests itself in an inadequate form
- Unproductive type of thinking, impaired intellectual activity
- Inappropriate behavior, expressed in motor agitation, mobility, excessive activity.
With the initial development of manic-depressive psychosis, the disease appears as increased activity. A person can move actively and take initiative in solving many things. Excessive optimism prevails, and “Napoleonic” plans are often made. As it progresses, problems with sleep and appetite begin to arise.
Symptoms and signs of manic-depressive psychosis in women
The complexity of the disease is characterized by the onset of a depressive form, which manifests itself in the following:
- Depressed mood
- Thinking starts to slow down
- Motor activity begins to decrease. Sometimes a person may remain in bed for several days.
If the disease does not respond to timely treatment, semantic, auditory or visual hallucinations may occur, accompanied by delusions. Bradypsychia is accompanied not only by a negative emotional background, but also by physiological disorders, expressed in loss of sleep and appetite, a tendency to violence may occur, interest in the opposite sex usually fades, and the number of sexual contacts decreases sharply.
Manic depressive psychosis in men
Despite the fact that statistics show the development of MDP in men is much less common, gender is rarely considered a determining factor. Often the disease develops in suspicious and melancholic individuals. It is generally accepted that the final formation of the disease occurs at the age of 25-30 years, and the primary inclinations appear in adolescence.
MDP is often formed in men due to two reasons:
- Hereditary factor
- Features of the central nervous system.
There is also a second category of physiological reasons:
- Previous head injuries
- Pathological work of the thyroid gland
- Hormonal imbalances
- Oncological formations
- Taking illegal medications or drugs
- Insufficient production of serotonin (the hormone of joy).
In addition, MDP often develops in men as a protective function in response to a negative experience or event (family breakdown, loss of a loved one). Some men throw themselves into work or begin to lead a wild life with promiscuous relationships.
Symptoms and signs of manic depressive psychosis in men
Symptoms resulting from MDP are usually divided into 2 categories:
- Inherent in manic behavior
- With the development of depressive disorder.
As for women, the symptoms of the first category are expressed in the following manifestations:
- Overly optimistic attitude. Occurs as a result of an inadequate assessment of one’s own capabilities; often a person sets unrealistically high goals for himself
- Manifestation of rapid gestures. The speech process is too fast, so other members of society cannot always understand what a person is saying. In addition, speech is accompanied by gestures
- Inadequate self-confidence. If a person is criticized from the outside, this can lead to a scandal; he is skeptical about the advice of relatives and friends
- Excessive risk. An inadequate assessment of one's own capabilities can sometimes commit robbery and risk one's life unreasonably.
The second category includes a number of depressive manifestations: loss of interest in life, a prevailing pessimistic mood, low self-esteem, some men strive to lead a hermit lifestyle, since the number of contacts with other people is reduced, unreasonable irritability appears, no activity brings positive emotions. Also, a person often refuses to eat and cannot sleep fully.
Manic depressive psychosis in children
In practice, MDP develops much less frequently in children than in adults. As a rule, manic depressive psychosis can often be diagnosed after the age of 10 years. In addition, the disease is more clear and formalized. However, experts were able to describe the signs and symptoms of MDP, characteristic of a younger age of 3-4 years.
The child’s body in childhood is not yet fully formed, including the functioning of the psyche. Therefore, the disease often involves excessive activity. Boys are often rude to girls. A depressive state may also occur, which is not at all typical for children. Sadness is often expressed, manifested in boredom. Sometimes it is replaced by uncontrollable fear.
However, it is rare for a child to begin to blame himself for everything that happens in the world around him, unlike an adult. Another distinctive feature is that the disease is not so deep-rooted, melancholy does not occur.
Another feature of the course of MDP in childhood is the emergence of a mixed state. At the same time, agitation and melancholy develop in the child. The baby may seek to cause serious physical harm to himself, and tearfulness increases. In some situations, unfortunately, suicide attempts due to a reduced instinct of self-preservation end in death.
Diagnostics
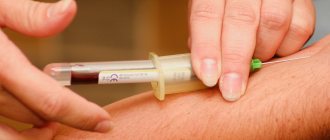
Making a diagnosis for confusion is aimed at establishing the cause that caused it. The difficulty is that the patient, as a rule, is not able to provide a medical history. A general and biochemical examination of the patient’s blood and urine makes it possible to determine the presence of acute infection or intoxication. MRI is indicated to detect organic changes in the structure of the brain and circulatory disorders of its tissues. An EEG may show changes consistent with epilepsy.
Bipolar manic depressive psychosis
It is characterized by a sharp change in the emotional background, where episodes of joy contrast sharply with depression or apathy. Therefore, this disease is classified as an affective mental disorder.
The development of the diagnosis can occur at any age, but most often it affects the younger generation aged 20-30 years. The bipolar type of disorder is much less common, and the probability of the disease ranges from 0.4-1.6%.
The symptoms of bipolar manic depressive psychosis can be divided into three categories:
- Signs characteristic of mania: an excessive feeling of happiness, speech that is too fast, due to which it is impossible to understand what the person is saying, increased impulsiveness and constant anxiety, inadequate assessment of one’s own strengths and capabilities.
- Depressive symptoms: sadness, loneliness, melancholy, pessimistic mood persist for a long time, thinking and speech slow down, reluctance to lead an active lifestyle, isolation, sometimes suicidal tendencies develop
- Psychosomatic: the emergence of delusional ideas (thinking is characterized by unrealistic images), hallucinations. Often the manifestations are similar to those of schizophrenia.
However, it is worth noting that, unlike schizophrenia, these manifestations are not sustainable.
Treatment
Since confusion is only a syndrome of general pathological conditions of the body, treatment is aimed at relieving the underlying disease. In case of acute intoxication, measures are taken aimed at removing toxic substances from the body and maintaining breathing and cardiac activity.
For cerebrovascular accidents associated with trauma or stroke, surgery may be indicated. Prescribed drugs that improve blood circulation in the brain tissue.
Treatment of encephalitis is based on antiviral therapy and prevention of cerebral edema with corticosteroids and diuretics.
For epilepsy, maintenance therapy with anticonvulsants is carried out to prevent seizures. In Alzheimer's disease, drug therapy for cognitive impairment is possible, but the disease is incurable.
If confusion is caused by post-traumatic shock or mental disorders, drugs are prescribed that help stabilize the patient’s psycho-emotional state - antidepressants, antipsychotics and tranquilizers.
The reception is conducted by specialists
Tagirov Akram Karamovich
neurologist, reflexologist
Phases of manic-depressive psychosis
It is customary to distinguish several phases of MDP:
- Depressed. As a rule, it is characterized by disappointment in the people around him and in himself, a person can often freeze in the same position, a premonition appears that is not justified by any events, the person does not hope that any positive changes await him in the future, constant violations in techniques food and sleep
- Manic. It assumes the opposite dynamics, which manifests itself in unreasonable positive energy, self-confidence and an unrealistic assessment of one’s own strengths, skills and abilities, and excessive initiative.
As a rule, the disease develops gradually and does not involve sudden changes. However, if symptoms persist for a long time, it is advisable to consult a specialist for advice, diagnosis and treatment.
Causes
The development of the disease can be influenced by a number of factors, which are divided into 4 subgroups:
- Diseases of the nervous system that are organic in nature;
- Psychogenic factors: anxiety and stress (chronic), fears, neuroses, hysteria, neurasthenia;
- Lack of magnesium, calcium and other metabolic disorders, as well as intoxication;
- Various diseases: hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes and others.
Psychogenic factors are the most common. It has been proven that hyperventilation syndrome very often overcomes people who, in childhood and adolescence, had to periodically observe respiratory disorders. There are a lot of examples: suffocation of drowning people, asthma, and so on.
Hyperventilation syndrome from a neurological point of view is a kind of failure of the “inhale-exhale” program. The alternation of inhalation and exhalation becomes unstable, resulting in excessive oxygen supply to the lungs. This process starts from the brain stem, where excessive excitability of the respiratory center occurs. All this leads to increased acidity and a decrease in the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood, and mineral imbalance occurs. Changes occurring in the body cause the symptoms of this disease.