Anesthesiologist-resuscitator
Smirnov
Igor Valerievich
18 years of experience
Leading anesthesiologist-resuscitator of the highest category, member of the European Society of Anaesthesiology
Make an appointment
Coma is a life-threatening pathology of consciousness caused by damage to brain tissue. The patient completely loses contact with the outside world. Coma can occur due to metabolic (intoxication with metabolic products or chemicals), organic (deformation of brain areas) reasons.
The key symptom is an unconscious state, the patient’s pupils do not react even to strong stimuli. To diagnose pathology, CT, MRI, and laboratory tests of blood plasma are used. Therapy is aimed at combating the cause of the coma.
Symptoms and signs of coma in adults
As already noted, the main symptoms of coma are the absence of any mental activity of the patient. Other symptoms of coma depend on the cause that caused damage to the brain structures.
- Body temperature indicators. Coma, which is caused by overheating, is accompanied by elevated body temperature (up to 43 degrees) and dry skin. Intoxication with alcoholic beverages and sedatives is associated with hypothermia (temperature up to 34 degrees).
- Inhalation/exhalation frequency. Slow breathing is a sign of a hypothyroid type coma (lack of thyroid hormones). Deep breathing is common in patients with pneumonia, brain cancer, and kidney failure.
- Blood pressure, heartbeat. A decrease in the number of heart contractions indicates that the person has fallen into a coma due to an acute disease of the heart muscle. Arterial hypertension is observed in patients who have become comatose due to a stroke. Low blood pressure indicates a diabetic coma, intoxication with sedatives, or a heart attack.
- Color of the skin. The skin turns cherry color if a person is poisoned by carbon monoxide. Blue ends of the fingers indicate a reduced concentration of oxygen in the blood plasma. Pale skin is typical for patients who have lost a lot of blood.
- Contact with the environment. With a mild coma, the patient can make different sounds, which suggests a favorable prognosis. As the coma worsens, the ability to make sounds disappears.
Are you experiencing coma symptoms?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Artificial coma - what is it?
An artificial coma is a specific state of the body, also called drug-induced sleep, into which the patient is immersed with the help of special medications. A medically induced coma is different from a typical coma and is more like the deep sleep of anesthesia.
When a patient is placed into a medically induced coma, special drugs are used to temporarily slow down the patient's vital functions. Artificial coma is used in the treatment of serious illnesses to reduce the risk of death of the patient.
When a patient is put into an artificial coma, the work of the subcortical parts of the brain is inhibited, reflexes and pain sensitivity are suppressed, the breathing and heart rate decreases, body temperature decreases and muscles relax.
The patient is put into an artificial coma by administering barbiturates, benzodiazepines, ketamine, and propofol. Subsequently, to maintain an induced coma, the patient is administered doses of drugs that support medicinal sleep.
The patient's condition is constantly monitored by specialists (blood gas composition, electrolyte levels, acid-base balance, biochemical blood parameters are monitored).
For reference. It should be noted that the procedure for introducing a patient into an induced coma and further removing it from it is an extremely complex procedure. Therefore, in practice, drug-induced coma is rarely used, only for health reasons, when the potential benefits justify the possible risks associated with the procedure.
Causes
Why do they fall into a coma? The main causes of this condition in adults:
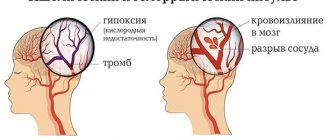
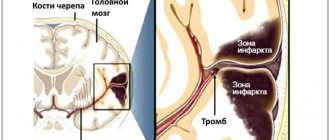
- organic factors (stroke, gunshot wound, bruise, bleeding into the brain);
- internal chemical compounds. They are metabolic products that appear due to organ diseases;
- external chemical compounds. Poisoning of the central nervous system can occur due to an overdose of drugs, sedatives, or neurotropics.
The reasons listed above explain how people fall into a coma. Particularly worth highlighting is a factor that combines signs of organic and chemical causes. This is an increase in pressure inside the skull. A similar pathology is observed with head injuries and neoplasms in the nervous system.
Artificial coma - what for?
Induction into an artificial coma is carried out in severe pathologies, when placing the patient on medication is the only way to prevent the development of irreversible changes in organs and tissues.
For reference. Artificial coma can be used to speed up the patient’s recovery after a serious illness or injury, restore damaged nerve tissue, slow down or prevent the development of necrotic processes in tissues against the background of severe hypoxia.
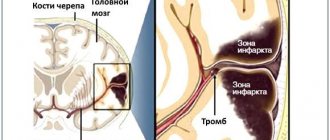
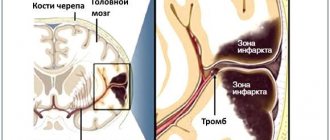
For example, an induced coma helps slow blood circulation and metabolic processes in brain tissue, and therefore can prevent the development of a necrotic lesion and progressive cerebral edema during a major stroke .
Putting a patient into an artificial coma is used for:
- high risk of developing cerebral edema due to trauma, heart attack, stroke, extensive cranial hematomas of non-traumatic injury, brain tumors ;
- extensive burn damage;
- severe life-threatening intoxications;
- intractable seizures and status epilepticus;
- severe alcohol withdrawal syndrome;
- acute psychosis;
- asphyxia of newborns (severe hypoxia of newborns);
- rabies (medically induced coma is used as part of the experimental treatment of rabies; putting the patient into medicated sleep helps prevent the development of severe life-threatening brain damage).
Also, artificial coma is used when performing complex long-term operations on the heart and brain, with combined severe injuries with intense pain (if the patient requires several reconstructive operations, between which there is no point in restoring his consciousness).
What is the benefit
An artificial coma after surgery can be used for restorative purposes.
Most often, coma after surgery is used in the recovery period after extensive neurosurgical operations to provide a neuroprotective effect.
Putting the patient into an induced coma can reduce the risk of severe injuries in patients with prolonged convulsions. With cerebral edema, medicated sleep allows you to slow down metabolic processes in tissues, promotes narrowing of intracranial vessels, normalizes intracranial pressure and allows you to quickly stop the progression of edema.
For reference. Medically induced coma after major surgical interventions can significantly reduce the risk of life-threatening complications and speed up the rehabilitation period.
In case of extensive strokes, putting the patient into an artificial coma helps restore damaged nerve cells, improve the functioning of the central nervous system after general resuscitation, and also prevents the development of necrosis of brain tissue.
If the patient has severe traumatic head injuries, a medically induced coma prevents the development of intracranial hemorrhage.
Introducing medicated sleep to newborns who have suffered severe intrauterine asphyxia allows normalizing metabolic processes in tissues, as well as restoring the functioning of the central nervous system.
When to see a doctor
If a person falls into a coma, you should immediately consult a doctor. There can be no exceptions here. First of all, the patient will need the help of a resuscitator who will try to quickly remove the patient from the pathological condition. If resuscitation measures have no effect, treatment of the patient must be started.
Which specialist will treat the patient depends on the cause that caused the disturbance in the state of consciousness. You can seek qualified medical help at our clinic. We have specialists who understand how to work with people who have fallen into a coma. The choice of a doctor who will treat coma in the Central Administrative District depends on the cause that led to the development of the pathology.
How long does an induced coma last?
The duration of drug-induced sleep is different for each patient and depends on the initial severity of his condition and diagnosis. Since the likelihood of complications directly depends on the duration of the induced coma, doctors try to reduce its duration as much as possible.
In most cases, the patient is put into medicated sleep for several hours or days. Less commonly, a medically induced coma can last up to several months.
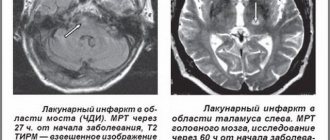
Diagnosis of coma in adults
To diagnose coma 1, 2, 3 degrees in the center of Moscow, the following methods are used.
CT. One of the most informative methods of radiation diagnostics. The advantages of this procedure include the following:
- fast scanning;
- it is possible to obtain thinly sliced images (up to 0.1 cm) without increasing the radiation dose to the patient;
- increased resolution, which allows you to obtain clear images of internal organs.
MRI. A modern diagnostic method through which the doctor can obtain images of sections of soft tissues and organs in different planes.
Blood analysis. Performed to determine the concentration of hormones in the blood plasma.
Recommendations for relatives of patients
A person emerging from a coma requires increased attention.
To avoid the recurrence of apoplexy, the following recommendations must be observed:
- inspire hope for recovery;
- create a favorable psychological climate and comfortable environment;
- motivate for daily exercise and praise for success;
- master manual massage skills.
Only love, care and attention can work miracles. Love and take care of yourself and your loved ones, and a favorable prognosis will not be long in coming.
- Nutrition for stroke and diabetes: what can a diabetic eat?
Myths and dangerous misconceptions in the treatment of coma in adults
Based on Hollywood films, people might have the idea that a first-degree coma is a kind of vacation, a break from the outside world. In the movies, the patient after a coma looks fresh and rested. However, in reality this is not the case. Many patients never fully recover after emerging from a comatose state. It is not uncommon for a person to remain disabled and bedridden for the rest of his life. For this reason, the family of a person who has fallen into a coma needs to prepare for long-term care for their loved one and provide him with moral support.
Severity
There are 5 degrees of coma after a stroke of varying severity:
- Precoma – moderate confusion, stupor. The victim looks drowsy, reacts inhibited to external stimuli, or, on the contrary, is overly active.
- 1st degree – severe deafness. The patient reacts very slowly to strong external stimuli, including pain. Can perform simple actions (rolling around in bed, drinking), respond with a meaningless set of words/individual sounds, muscle tone is weak.
- 2nd degree – loss of consciousness (stupor), basic reflexes are preserved (reaction of the pupils to light, closing of the eye when touching the cornea). When approaching the patient, there is no reaction, his rare movements are chaotic. Pain reflexes are suppressed. The nature of breathing changes: it becomes intermittent, shallow, and irregular. Possible involuntary urination and bowel movements. Trembling of individual muscles and twisting of limbs are observed.
- 3rd degree – loss of consciousness, absence of pain response, some basic reflexes. Involuntary urination, defecation. Muscle tone is reduced. The pulse is palpable poorly, breathing is irregular and weak, body temperature is reduced.
- 4th degree (extraordinary) – absence of any reflexes. Agonal breathing, palpitations, ends in death.
- Stroke prevention: how and with what to protect yourself from a dangerous disease?
Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at prompt treatment of diseases that can lead to a coma. If a person has suffered a stroke, he needs to periodically visit a doctor so that he monitors the condition of the patient’s body and can detect signs of coma in time.
You also need to stop drinking alcohol and drugs. People suffering from alcoholism and drug addiction are at risk. They are unable to control the amount of ethyl alcohol and drugs they take, so they risk getting an overdose and falling into a coma.
It is extremely important to monitor your health. You cannot ignore the recommendations of doctors and other specialists. A proper daily routine, sleep and eating patterns, giving up bad habits are just the minimum of what every person should remember.
If there are any contraindications to playing serious sports, then all of them should be abandoned. Physical activity is allowed, but it is important to maintain its degree. In some cases, only light exercises in gymnastics, fitness and any other sport where the load is minimal are allowed.
Any deviation from the general rules (especially for those people who are at risk) can lead to undesirable consequences. It is important not only to remember this, but also to follow all recommendations.
If you have any questions or do not know whether excessive loads are allowed for you, it is better to seek advice from relevant specialists. If necessary, they will carry out a series of diagnostic measures and, based on the results obtained, will give you a conclusion.
Prevention is the best measure in the fight against any pathology, regardless of its type and severity. And the health of each person is in his own hands. Doctors and other specialists can only guide you along the right path.
Why is an induced coma dangerous?
The most common complications of an induced coma are bedsores. In order to avoid their development, the patient’s relatives and medical personnel must periodically change the position in which the patient is, give him a gentle massage, and carefully monitor skin hygiene.
Attention. Due to muscle relaxation, lack of consciousness and impaired swallowing, an induced coma can be complicated by severe aspiration pneumonia associated with the reflux of gastric contents into the lungs.
It is also possible to develop:
- laryngeal stenosis and pulmonary edema (against the background of constant mechanical ventilation (artificial ventilation));
- acute cardiovascular failure;
- collapse;
- renal failure;
- infectious and inflammatory processes in internal organs;
- sepsis.
After the patient is brought out of a medically induced coma, there may be a temporary decrease in memory, impaired speech and motor activity, and lethargy.
The duration of the rehabilitation period in this case will depend on the duration of the induced coma and the severity of the resulting disorders.
For reference. It should be noted that during the first year after drug-induced sleep, approximately every 10 patient manages to return to normal life. In other cases, the period of complete recovery takes a longer period of time.
How to call a resuscitator
If you decide to go to our clinic in the center of Moscow for medical help, dial the ambulance number -. A team of our specialists will arrive at the address you specified to transport the patient to a medical facility and provide him with first aid.
All our specialists are highly qualified and have extensive medical experience. All diagnostic measures are carried out promptly. This is also due to the availability of modern equipment. Our doctors choose the most optimal treatment method, taking into account the characteristics of the disease and the patient’s body.
Our clinic is located at the address: Moscow, Central Administrative District, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, building 10. The nearest metro station is Mayakovskaya (5 min walk).
Remember that if a person falls into a coma, he requires emergency assistance from specialists. The slightest delay can lead to the death of the patient.
Types of newborn asphyxia
Classification is carried out according to several criteria. First of all, depending on the time of development of the pathological condition, the following are distinguished:
- primary, or intrauterine asphyxia - develops directly in the womb;
- secondary, or extrauterine asphyxia – occurs in the first hours of the baby’s life.
In turn, primary asphyxia is also divided into two subtypes:
- antenatal, or chronic - develops even before the onset of labor;
- intrapartum, or acute - occurs during the period of uterine dilation and fetal birth.