Make an appointment by phone: +7 (343) 355-56-57
+7
- About the disease
- Cost of services
- Sign up
- About the disease
- Prices
- Sign up
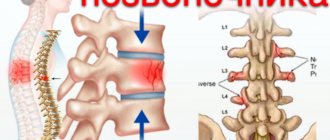
Cervical osteochondrosis is a disease in which the nutrition of the tissue of the intervertebral joints and discs of the neck occurs or their gradual destruction occurs.
Intervertebral discs lose their elasticity and can become deformed or destroyed. In this case, the cartilage tissue compresses the nerve endings, swelling and atrophy of muscles and tissues occur.
Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis can manifest itself:
•
headache;
•
dizziness with changes in the movement of objects, the nature of movement;
•
loss of consciousness;
•
impaired visual perception, loss of sound;
•
feeling of numbness of the scalp and limbs;
•
violation of movement coordination.
The main causes of the development of osteochondrosis
Causes:
- spinal deformity (scoliosis, kyphosis, lordosis), trauma;
- incorrect posture, forced posture due to professional activities;
- passive lifestyle;
- lack of physical exercise, physical inactivity;
- lack of calcium, phosphorus, zinc, manganese, vitamin D;
- genetic predisposition;
- replacement of cartilage tissue with bone tissue;
- obesity;
- autoimmune diseases (Bechterew's disease);
- stress;
- injuries.
Osteochondrosis? Feeling dizzy? They will help you at the Yusupov Hospital!
To treat osteochondrosis, the Yusupov Hospital uses modern methods of therapy. The Yusupov Hospital employs qualified doctors who have extensive experience in successfully treating this pathology. The patient receives advice from a neurologist, traumatologist, rehabilitation specialist, reflexologist and other specialists who will be necessary to carry out differential diagnosis and make the correct diagnosis. The decision on the choice of therapy is made jointly by doctors. This allows you to choose the most effective treatment that will eliminate pain, eliminate dizziness and improve the patient’s well-being. It is almost impossible to completely cure osteochondrosis. However, after treatment at the Yusupov Hospital, patients experience stable remission and are no longer bothered by unpleasant symptoms. Additionally, you can undergo regular preventive examinations, which will help identify the progression of the pathological process at an early stage and exclude relapse of the disease.
To treat osteochondrosis, the Yusupov Hospital uses an integrated approach, which will include drug therapy, physiotherapy, reflexology, massage, and physical therapy. Medicines are selected based on the patient's symptoms, as well as his general health. The presence of somatic diseases, in particular cardiological and gastroenterological diseases, is taken into account, which is necessary to prescribe safe therapy. Physiotherapy is carried out by experienced doctors who use modern effective techniques to restore the functions of the spine and improve metabolic processes in it. Gymnastics classes take place under the guidance of professional exercise therapy instructors.
The duration of the course of therapy will depend on the degree of damage to the spine, the severity of dizziness and other symptoms. The duration of treatment is determined by the attending physician based on the body's response to the therapy. After completing the main course of treatment, the patient receives recommendations from doctors and can continue rehabilitation at home. If necessary, you can always use the help of specialists from the Yusupov Hospital at any time of the day.
To make an appointment with doctors, get information about the work of the rehabilitation clinic, exercise therapy department, and clarify other information, you can call the Yusupov Hospital.
Clinical picture
The patient has a feeling that he is losing coordination in space, he notes nausea and vomiting, decreased visual acuity, hearing loss, and possible tinnitus.
Discomfort and pain appear in the cervical spine during physical activity. As the cartilage tissue grows, the pain intensifies, stiffness, crunching and headache appear. As the disease progresses, the pain increases and becomes constant, sensitivity in the cervical region decreases, snoring, nasal congestion, and a feeling of numbness in the face and hands may occur.
Dizziness caused by pathology of the cervical spine
Dizziness and otoneurological symptoms are described in various types of pathology in the neck: traumatic injuries of the neck and spinal cord [4, 5, 10], cervical osteochondrosis [2], occlusion of the vertebral artery (VA) [1, 3, 12] and strokes caused by VA injuries [1, 11, 13, 15], VA dissection, in connection with neck movement or manipulation of the cervical spine [6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14].
The identification of vertebrogenic dizziness is due to the prevalence of the pathology among young people, the severity of the disease, the variety of symptoms, and the occurrence of strokes during manipulation of the neck.
A distinctive feature of vertebrogenic dizziness is an acute onset associated with a certain position of the head (bending forward, throwing back, sharply turning to the side, etc.), often in the morning, after sleep. Dizziness, which occurs as a result of a change in the position of the head, can be caused by both irritation of the inner ear and the central vestibular structures of the brain (trunk, cerebellum). Compression of the arteries develops with osteophytes and lateral disc herniations in uncovertebral areas, anterior exostoses of the articular processes, as well as with subluxation.
The anatomical and topographical features of the VA include the location of most of its extracranial part in the spinal canal, where it is displaced and compressed by osteophytes or articular processes in various degenerative diseases, in particular osteochondrosis (Fig. 1).
An otoneurological examination of the patient allows for accurate topical diagnosis, as well as differential diagnosis from peripheral dizziness caused by other diseases: Meniere's disease, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo, vestibular neuronitis.
Barre (1926), who first drew attention to the connection between otoneurological symptoms and pathology in the neck, described them under the name “posterior cervical sympathetic syndrome,” pointing out the importance of the connection between the head and neck through the sympathetic nervous system.
It has been shown that an in-depth study of the VA, taking into account not only the diameter and characteristics of the blood flow, but also using functional tests, allows us to identify points important for the differential diagnosis between hemodynamically significant and insignificant extravasal compression of the VA.
The damaging effect of extravasal compression factors is directed primarily at its nerve plexus. Irritation of the spinal nerve, increasing the tone of the VA, can reduce the velocity of volumetric blood flow in it by 30% of the initial value, by 40% in the branches of the main artery, in particular the inner ear [1].
Thus, the functional state of the spinal nerve and structural changes in the VA are the basis for the development of blood flow insufficiency in the vertebrobasilar system (VBS) at the extra- and intracranial level. As various authors emphasize, cochleovestibular syndrome can develop with circulatory insufficiency in the VBS, both in the area of the inner ear and in the area of the vestibular nuclei and pathways of the brain stem and cerebellum.
In addition to disturbances in the blood supply to the VBS, impaired proprioceptive nerve impulses from the structures of the neck also play a role in the pathogenesis of vertebrogenic dizziness. Movements in the joints of the cervical vertebrae and discs altered by osteochondrosis and spondyloarthrosis, as well as the resulting tonic muscle tension, contribute to the development of inadequate afferent impulses and incorrect assessment by the vestibular system of information about the position of the head, which causes a feeling of dizziness and imbalance.
The purpose of the work carried out at the Scientific Center for Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences was to identify clinical features and otoneurological symptoms in patients with vertebrogenic dizziness against the background of pathological changes in the cervical spine, as well as to compare vestibular disorders with structural changes in the vertebral column, blood pressure level, and the condition of the internal jugular veins.
We examined 115 patients with acute and chronic circulatory failure in the VBS, including 47 patients with degenerative-dystrophic changes in the cervical spine, of which 33 had degenerative changes (osteochondrosis), 9 had craniovertebral pathology, Kimmerli’s anomaly, in 4 patients there was an anomaly in the entry of the VA into the canal at the level of C4, and spinal canal stenosis in one patient. The age of the patients ranged from 28 to 74 years.
The main diseases against which vestibular disorders developed were arterial hypertension (AH) in combination with atherosclerosis, vegetative-vascular dystonia, and osteochondrosis.
All patients underwent a complete classical otoneurological examination, including the study of spontaneous and experimental vestibular reactions (rotational and caloric tests) and hearing. The auditory analyzer study was carried out using audiometry and auditory evoked potentials.
Structural changes in the great arteries of the head (MAG) and hemodynamic parameters of blood flow through the VA and internal carotid artery (ICA) were studied using duplex ultrasound scanning of the MAG (MAG DS) with functional tests, in some cases during spiral computed tomography (SCT), magnetic resonance angiography.
Diagnostics
Patients who complain of dizziness are required to undergo a diagnosis of the condition of the cervical spine and blood vessels. But initially, the doctor will collect a complete history and find out what symptoms still bother the patient, the conditions for the onset of dizziness, the duration and severity of the attacks, etc. After this, an examination is carried out, during which the doctor will determine the presence or absence of nystagmus, and will conduct tests to determine the degree of stability of the patient , unsteadiness of gait, ability to maintain balance, etc. Patients will also be asked to undergo a series of neurological tests to assess the nature of neurological disorders or confirm their absence.
The data obtained allows us to assume the presence of vertebrogenic, i.e., associated with pathologies of the spine, dizziness and determine the degree of existing disorders. To confirm the diagnosis, identify the stage of osteochondrosis, the level of damage, and assess the quality of blood flow in the vertebrobasilar system, instrumental research methods are prescribed:
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head.
The most informative diagnostic methods from the point of view of diagnosing degenerative changes in intervertebral discs is magnetic resonance imaging or MRI. It allows you to detect the slightest deviations from the norm and, in most cases, determine what exactly caused the dizziness, and therefore select the optimal treatment tactics.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures pursue a number of goals:
- Localization of the inflammatory process;
- Relieving muscle spasm;
- Pain relief;
- Launch of regenerative processes;
- Increasing general and local immunity;
- Restoring the normal position of nerve fibers, eliminating compression and pinching.
Most often, the following procedures are prescribed for cervical osteochondrosis:
- Shock wave therapy. Using a special device, the acoustic wave is directed directly to the cartilage tissue of the spine that has been damaged. As a result, metabolic processes are launched, salt and calcium deposits are destroyed, which interfere with the normal movement of joints and vertebrae. The procedure is characterized by a cumulative effect, often the first results become noticeable only 2-3 months after the start of treatment.
- Acupuncture. Acupuncture is often used to treat and prevent cervical osteochondrosis. It is important that the procedure is performed only by a qualified doctor, otherwise you may not only experience a lack of effect, but also a worsening of the current condition. The essence of the procedure is that special needles are installed on biologically active points, forcing the body to start metabolic processes and stimulate the production of natural painkillers.
- Massage. The main goal is to reduce pain and improve blood circulation in the damaged area of the cervical spine. With proper massage, the muscles acquire the lost tone, and as a result, it is possible to eliminate the risk of relapse of osteochondrosis in the future. When attending the first massage sessions, the patient encounters severe pain; it is important not to stop treatment due to pain, but to go through all the procedures prescribed by the doctor.
Surgery
It is mainly prescribed in advanced stages of the disease, when the use of medications and visits to physiotherapeutic procedures does not bring any results. The indication for surgical intervention is catastrophic narrowing of the spinal canal.
Modern surgical techniques allow the patient to be discharged from the hospital within 3-5 days and begin outpatient treatment of the symptoms of cervicothoracic osteochondrosis. Over the next three months, the patient undergoes rehabilitation.
Physiotherapy
A correctly chosen set of exercises for osteochondrosis can not only improve the patient’s general condition, but also speed up the process of treating the disease. There are several effective exercises:
- Turns and tilts the head in different directions. The exercise is performed in a sitting position, it is important not to jerk, all movements should be smooth with a gradual increase in the number of repetitions and the amplitude of the inclination.
- Tilt the head to the sides with resistance. Body position - sitting at the table, one elbow stands on the table, while the palm presses on the temple. Tilt your head towards your hand, creating slight resistance.
- Shoulder lift. Raise your shoulders as high as possible and hold in this position for a while.
- Self-kneading of the back of the head and neck with your fingertips. It is important that the movements are soft and do not cause pain. You can perform self-massage in any comfortable position.
It is important not to treat cervical osteochondrosis at home without consulting a neurologist; a set of exercises must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
The vestibular system and the main features of its functioning
The vestibular system is responsible for maintaining body balance when performing all movements, both voluntary and involuntary, as well as when changing body position or posture. This is achieved due to its close relationship with other parts of the nervous system, in particular the visual, cerebellar, proprioceptive, extrapyramidal, cortical and spinal.
When the body is faced with the need to maintain balance, the nerve impulse initially originates in the peripheral receptors of the semicircular canals of the labyrinth, which are part of the inner ear. From them, through the vestibular nuclei of the brain stem, they are transmitted to other systems and turn on complex mechanisms for maintaining balance at each individual moment in time when performing a particular movement. This ensures maintaining balance when running, walking, bending, changing direction and speed, etc.
Of great importance in this mechanism is the transmission of nerve impulses from the lateral vestibular nuclei to the motor ones located in the spinal cord. This is realized through the vestibulospinal and reticulospinal tracts, as they are responsible for the degree of tonic tension of skeletal muscles. They trigger a mechanism for reducing the tone of some muscle groups, while simultaneously increasing the tone of others in accordance with the characteristics of changes in body position. This is called reciprocity or reciprocal innervation. This ensures stability and balance.
Causes of dizziness
Dizziness itself is caused by decreased blood flow to the brain. Oxygen starvation of the brain occurs, since the vertebral arteries are compressed during osteochondrosis. However, there may be other causes of headaches that you should not tolerate and try to get rid of them on your own without consulting a doctor:
- Sharp spasm of the neck muscles
- Vertebral artery syndrome
- Low mobility of the spine due to an inactive lifestyle
- Psychological factor – frequent worries due to the presence of the disease
Preventing the condition with medications
In addition to the course of taking balanced complexes of vitamins and microelements, doctors prescribe systemic chondroprotectors to patients. These are Teraflex, Dona, Arthra, Structum, Chondroxide, Alflutop, Chondrogard. The use of chondroprotectors at the initial stage of development of osteochondrosis allows for partial restoration of damaged discs. And in case of a disease of 2 or 3 degrees of severity, drugs are used to prevent its spread to healthy tissue.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
The doctor selects the appropriate treatment method for the patient depending on the stage of the disease. Most often, drug treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is used in combination with physiotherapeutic procedures. In advanced cases, surgery may be required to remove overgrown connective tissue and bone spurs.
Conservative treatment
Most often it is based on taking certain medications. Drug treatment helps reduce pain, get rid of muscle tension, and localize inflammation. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers are used.
Often, the doctor includes chondroprotectors in the prescription. This group of drugs activates the restoration of damaged tissue in the area of intervertebral discs.
These drugs are prescribed in the form of injections or tablets. Good therapeutic results are demonstrated by ointments based on NSAIDs. They are rubbed into the damaged area, relieving pain within 10-20 minutes. The main advantage of ointments is the local effect on the painful area and minimal impact on other organs.
In what case should you see a doctor?
Since constant dizziness can cause the development of a stroke of ischemic origin, you should consult a doctor at the first signs of osteochondrosis. This is pain of any severity in the back of the neck. It usually intensifies when turning or tilting the head. You should make an appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist if you experience dizziness more than 2-3 times a month, especially if they are accompanied by visual or auditory disorders.
Features of treatment during pregnancy
During pregnancy, dizziness caused by cervical osteochondrosis is eliminated mainly through physiotherapy, massage, and daily physical therapy exercises. Pharmacological drugs are also used in therapy. Vertebrologists prefer ointments, gels, and balms. The ingredients of external agents almost do not penetrate into the bloodstream and do not have a teratogenic effect.