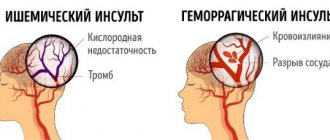
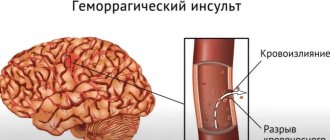
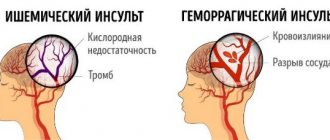
A stroke is a sudden disruption in the circulatory system of the brain, which leads to damage to various parts of the brain that lose functionality.
Along with the blood, the supply of oxygen to the brain stops. This leads to disruption of cell nutrition.
The short answer to the question of how long people live after a stroke depends on the type of brain stroke, as well as how serious the consequences are - with ischemic, mortality in the first 72 hours is no more than 15%; for hemorrhagic – no more than 35%; the most dangerous is subarachnoid hemorrhage - survival rate in the first 72 hours is about 50%. Details are below.
How to prolong and improve life after an ischemic stroke
The period after an ischemic attack is divided into five periods:
- The critical stage is the first 72 hours.
- Acute period – 25-30 days.
- The first stage of recovery is from 3 to 6 months.
- The second recovery period is 12–24 months.
- Residual processes – From 24 months or more.
Life expectancy after an ischemic stroke depends on numerous factors, from the size of the brain lesion to treatment measures.
Providing first aid also affects the outcome of recovery; a simple rule applies here: the sooner, the better. In the first year after ischemic hemorrhage, 65% of patients survive, after 5 years half survive, but after 10 years only a quarter remain alive.
Help to prolong life:
- correct lifestyle;
- diagnostics every 2 – 3 months;
- nutrition;
- restorative gymnastics.
Salt, sugar, fatty and flour foods, smoked meats and sauces should be excluded from the diet. The diet should be dominated by vegetables and fruits, a large amount of fiber and vegetarian soups. Meals should be fractional, 5 meals in small portions.
Timely diagnosis and physical therapy, which improves the quality of blood flow, will help prevent a recurrent attack.
Massage
After normalization of the patient’s vital functions, massage can be used. Typically this period takes from 5 to 7 days. After this, it is recommended to turn the patient over and gently rub the skin of the back and sacrum. A full massage is carried out after 1–1.5 months.
An integral part of rehabilitation is massage.
Like other types of treatment, massage should be done in doses. Up to three sessions of 3–5 minutes each can be performed per day. The specialist performs the procedure using the following technique:
- stroking the skin with transverse or circular movements;
- rubbing fingers;
- tapping with a fist or the edge of the palm over the entire massaged surface;
- vibrating movements, pinching;
- at the end of the procedure - stroking.
Such actions help prevent muscle tissue atrophy, improve blood circulation, and prevent bedsores.
Important! The procedure should only be performed by a specialist. Unprofessional actions can only do harm.
How can you increase your chances?
Each person is individual and their body copes with illness differently. Some stop walking and working, while others simply become less active. Anyone can recover, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and listen to your body.
The sooner you start rehabilitation, the faster your brain will recover. In the beginning, gymnastics and massage will help. The rehabilitation program includes exercise therapy and classes on robotic simulators.
Important! Stroke also affects the psyche. Often, the help of a psychiatrist is required.
Forecast
As is already known, the five-year survival prognosis is disappointing. Loss of intellectual and motor abilities after a second stroke can be lifelong. Most patients after a relapse suffer from irreversible changes and pathologies in the cerebral cortex.
After lesions, patients usually experience disability. In more than half of patients, after suffering a recurrent stroke, a coma occurs, which does not allow the doctor to give a positive prognosis about recovery from it.
Rehabilitation of patients after repeated ischemic stroke in the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital is based on traditional, latest and original methods for the recovery of patients who have suffered a stroke.
Thanks to the extensive practice and rich knowledge of the clinic’s specialists in the field of rehabilitation medicine, comprehensive rehabilitation of patients is carried out at the highest level, meeting international standards.
For optimal rehabilitation, patients are provided with comfortable conditions of stay: cozy rooms, good nutrition and attentive attitude of the staff.
Call by phone and the coordinating doctor will answer all your questions.
Make an appointment
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
Subsequent life after a stroke will depend on the type of disease, the extent of damage and the presence of additional underlying diseases. There are a number of circumstances that can both facilitate and complicate the course of the underlying disease and the process of restoration of brain cells. So, here are the key factors that have a direct impact on the healing process:
- Stroke on the right side, consequences, how long do they live after it and how is it treated?
- Damage area. It affects the patient's future life. In the case of extensive damage, the cells are damaged so severely that they can no longer be restored. Because of this, the functioning of the brain is disrupted, which leads to malfunctions of other systems and organs and even to the death of the patient.
- Consequences of a stroke. Patients suffering from paralysis, impaired speech function, sensitivity, and mental disorders are unlikely to be able to lead a normal and fulfilling life. If they manage to recover, it will be only partially. The prognosis is unfavorable because these conditions lead to bedsores, intoxication, and other complications. All these phenomena significantly reduce life expectancy.
- Age characteristics. Older people are least likely to recover from a stroke. The fact is that their cells do not have the ability to quickly renew themselves, they more often develop inflammatory processes, vascular pathologies, and repeated hemorrhages and heart attacks occur. Even if patients manage to survive the attack itself, in case of nervous strain or an attack of hypertension, there is a risk of another stroke. In addition, women have a much greater chance of recovery than men, which is due to their physiological characteristics. Therefore, the general condition of the patient also depends on age and gender.
- Prolonged immobility. When a patient recovers from a stroke, he is often unable to move due to paralysis or paresis. If you neglect to implement the rehabilitation program, the muscles gradually lose their tone and the blood supply to the internal organs deteriorates. This leads to thrombosis, tissue necrosis, and intoxication. Therefore, the condition worsens even more, inflammation, infectious processes, and cardiovascular diseases develop. Such a patient has much less time to live than a person who regularly moves, does exercises and has a positive attitude.
- Localization of the disease. Of course, the prognosis directly depends on the location of the affected areas. Ischemia can affect the tissues that supply blood to the carotid artery, the main and vertebral arteries, as well as their branches. In addition, ischemic cerebral stroke is the most dangerous condition, reducing the chances of survival. Hemorrhagic stroke most often affects the putamen (in 55% of cases), the thalamus, cerebellum, and brain stem.
No one can give an unambiguous answer to the question related to life expectancy after a stroke. This is due to the individual characteristics of each organism. However, according to statistics, about 35% of deaths occur in the first month after the disease, and 50% of patients die during the first year. In any case, you should adhere to one recommendation: lead a healthy lifestyle. It is this that will allow you to avoid complications, prolong life and make it more fulfilling.
Diet features
To restore the body and prevent various negative consequences, the patient after suffering an attack must eat properly. The diet helps saturate the body with beneficial vitamins and minerals, as well as cleanse blood vessels by removing bad cholesterol.
Proper nutrition is essential for successful rehabilitation
Healthy foods
Therapeutic nutrition is based on products that include vitamins and other components for the speedy rehabilitation of the patient. These include:
- vitamins C, B and D - help prevent recurrent strokes, found in asparagus, cashews, walnuts, sunflower seeds, wheat germ;
- Omega 3 and 6 acids are necessary for the normal functioning of the heart and blood vessels. These substances are found in sea fish, vegetable oils (soybean, olive, coconut);
- complex carbohydrates – lower cholesterol in the blood and promote the regeneration of brain cells. Such carbohydrates are found in cereals, apples, zucchini;
- folic acid – helps maintain blood pressure and prevents relapse. The substance is found in legumes;
- iron, magnesium, potassium, calcium - improve metabolic processes in the body, found in dried apricots, tomatoes, prunes, plums, citrus fruits;
- antioxidants and beta-carotene - help lower blood pressure and improve metabolic processes. There are a large number of them in apricots, cabbage, beets, cranberries, carrots, bell peppers;
- Protein is necessary for general restoration of the body and provision of vital energy. Patients after a stroke should eat lean meats - rabbit, turkey, chicken.
In addition, you must include low-fat dairy and fermented milk products, a large amount of vegetables and fruits in your menu. Last but not least is proper drinking regimen. The patient should drink at least 1.5 liters of water, green tea, and herbal infusions.
Prohibited foods
The list of prohibited products includes:
- fatty fish and meat;
- butter, margarine, whole milk, full-fat sour cream, cottage cheese;
- any types of alcohol, strong tea, coffee;
- chocolate, baked goods, baked goods made from white flour varieties;
- fast food, ice cream, egg yolk, chips, crackers;
- spicy, sour, salty, pickled, smoked dishes.
When choosing a cooking method, preference should be given to boiling, stewing, and baking. Frying, smoking and salting are unacceptable.
Diet after a stroke should not include junk food
Important! Diet helps not only to recover from a stroke, but also to improve a person’s overall well-being and prevent the development of many diseases.
How many years do people live after a stroke?
Statistics answer the question of how many years people live after a stroke. As a rule, life expectancy is about 10 years, but in severe cases, death can occur immediately after the attack. Observations of specialists showed:
- some patients (30-35%) die in the first month after the attack;
- After the first year, only half of stroke victims are alive.
In addition, how long people live after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke also depends on the number of attacks.
Repeated cerebral circulatory disorders are extremely dangerous. So, if after the first attack the life expectancy is approximately 9 years, then the secondary attack reduces it to a period of 2 to 3 years. But what is the overall picture and how long will a person live after a repeated major, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
In such circumstances, only 5-15% survive the first year after an attack, and over the next 5 years - about 42% of men and 25% of women. There are many reasons for such sad statistics, but the main thing is that the factors that led to the blow do not disappear anywhere. That is, a predisposition to blood clots, vascular damage due to atherosclerosis, hypertension and heart problems still remain in the body.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
The duration of life after an impact directly depends on such factors.
- The severity of the attack and the extent of damage to brain tissue. Sometimes the severity of the blow is excessive, which leads to death or a global reduction in the life expectancy of the victim.
- Consequences of vascular damage. A person with extensive paralysis is doomed to a lying position, which without proper care is fraught with bedsores and pneumonia.
- Immobility after an impact provokes the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities. Such blood clots, when they break off, often enter the lungs and provoke thromboembolism, which often leads to death.
- Ensuring the safety of a stroke victim. It is necessary to exclude falls caused by dizziness and weakness in the legs, since any fractures, especially the femoral neck, are quite difficult to treat in elderly patients.
- Age. This is an equally important factor, since young people are more likely to survive.
- General health.
Features of the rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after a stroke
After a vascular lesion of the brain, rehabilitation measures are mandatory, regardless of the severity of the lesions caused by the stroke. The entire recovery period can be divided into two stages: the first days after the attack within the walls of a medical institution and the rehabilitation period in special centers and at home.
Recovery stage in the first month after the attack
As a rule, doctors insist that the victim stay in a specialized department for 2 to 4 weeks. At this point, specialists of various profiles can reduce the entire therapeutic process to a specific system and further recovery. Disturbances in the blood supply to the brain lead to the formation of a focus of dead cells, and nearby cells often exhibit rather weak activity. To restore their normal activity, timely medical care is required.
It is better to remain under the supervision of specialists for some time after a stroke
First, patients are placed in the correct and comfortable position for them, and only then they begin physical therapy. Thanks to regular exercise and medication, brain cells begin to function more actively, which stimulates the restoration of damaged areas of the organ. But positive changes can only be achieved with a daily increase in loads. In the first 14 days, the victim is prescribed only a light massage with stroking and rubbing and procedures using electrical muscle stimulation. If the patient tolerated this stage well, then they begin to restore speech function.
- Life expectancy and consequences after left-sided ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation after discharge
Sometimes all the problems that arise can be eliminated in 2-4 weeks in the hospital, but if this does not happen, then the recovery stage is delayed. It is important for the victim to continue to systematically increase the load over the next two months.
The program of the therapeutic and gymnastic complex, carried out at home, is previously agreed upon with the local doctor. The neurologist develops an adaptation map, based on which all exercises and procedures must be performed. It should be noted that for older people (over the age of 70), a stroke is too severe a trauma, rehabilitation after which is almost impossible.
Healing Fitness
In addition to caring for the person and proper nutrition, many patients are prescribed special physical exercises. Physical education helps to quickly tone muscles and restore the ability to self-care.
The first exercises are for the patient to learn to sit independently, then lower his legs from the bed, and walk. These simple elements are given to most patients with great difficulty. Later, the load gradually increases. The patient performs exercises designed to work different muscle groups. Bending, swinging your arms, turning your head - all these elements help restore normal motor activity and prevent stagnation.
In rehabilitation centers, the following types of treatment are used to restore a person:
- mirror therapy;
- modeling;
- drawing;
- collecting puzzles.
Therapy based on biofeedback has good results. This method involves controlling the affected arm or leg using your imagination. This is believed to help revitalize areas of the brain damaged during a stroke.
Stroke in old age
How long do older people live after a stroke? In older people, the disease can occur for the following reasons:
- hypertension;
- kidney disease;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- diabetes;
- vascular aneurysms;
- atrial fibrillation;
- rheumatism;
- high cholesterol;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- any viral disease in severe form.
The most common cause of stroke in older people is atherosclerosis, which can provoke a large number of attacks per year, and they may go completely unnoticed by the person. If this process continues for a long time, it is impossible to survive - death occurs.
How long a person lives after a stroke in old age is a complex question. According to statistics, the forecasts are as follows:
- With extensive hemorrhage that occurred in the brain center - death.
- With atherosclerosis and hypertension, survival is possible in rare cases, and the consequences will be very severe.
- With cerebral edema, the prognosis is also poor.
- In case of relapse - death.
The average life expectancy after a stroke that occurs after age 80 is a week. It turns out that the older you are, the less likely you are not only for recovery, but also for survival in general.
Proper care for paralyzed patients
How to live after a stroke for a bedridden person? For many, paralysis becomes a death sentence, because in this state a person completely loses the ability to move and self-care. He needs the care of loved ones or a nurse.
Proper care for a person is the key to successful recovery
The person providing assistance must know a few simple rules:
- A bedridden patient should be turned over every 2 hours. This will help prevent bedsores and congestion in the lungs, leading to the development of pneumonia;
- The patient's skin should be wiped with an alcohol solution. This will prevent the development of bedsores and infection;
- the room needs to be ventilated regularly;
- if bedsores have already formed, the doctor should prescribe special medications in the form of ointments for their treatment;
- for fecal and urinary incontinence, diapers, diapers, and urinals are used;
- For patients in a coma, fluid is administered through a special tube. It should only be installed by a specialist.
In addition, the psychological aspect is important. If the paralyzed person is conscious, you need to talk to him and take an interest in his well-being. For such patients, it is necessary to understand that they are not alone and there are people who will always support them.
There is an exit
In 2002, for the first time in Russia, a specialized interdisciplinary service “STOP-Stroke” was created in the multidisciplinary clinic CELT for the effective prevention of vascular accidents. Over three years, more than 2,000 people took part in the stroke prevention program. The creation of a preventive angioneurology service became possible due to the fact that CELT has created all the necessary conditions for timely diagnosis of changes in the heart, blood or cerebral vessels that can lead to acute cerebrovascular accident. A modern laboratory quickly determines cholesterol levels, blood viscosity and blood clotting. Safe and informative ultrasound diagnostic methods provide insight into the condition of the brain vessels and allow timely detection of dangerous atherosclerotic plaques and critical narrowing of the arteries. Echocardiography and daily monitoring of ECG and blood pressure provide a complete picture of the work of the heart. When necessary, computed tomography and angiography supplement doctors’ opinions on the condition of the blood vessels and brain. All this data is needed in order to identify possible preconditions for a stroke. After all, not only high blood pressure can lead to a brain catastrophe. Often the danger lies in the properties of the blood - the tendency to form blood clots or, for example, in an increase in the level of homocysteine - an amino acid that “damages” the vascular wall and contributes to the development of atherosclerosis.
Literature
1. Mancia G. Prevention and treatment of stroke in patients with hypertension. Clin Ther. 2004; 26(5):631-48. 2. Medic V.A. Population morbidity: history, current status and study methodology. – M.: Medicine, 2003. – 512 p. 3. Gusev E.I. The problem of stroke in Russia // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after S.S. Korsakov (STROKE supplement to the journal). 2003; 9:3-7. 4. Sarti C, Rastenyte D, Cepaitis Z, Tuomilehto J. International trends in mortality from stroke, 1968 to 1994. Stroke 2000; 31:1588-601. 5. Skvortsova V.I., Chazova I.E., Stakhovskaya L.V. Secondary prevention of stroke. M.: PAGRI, 2002.-120 p. 6. Kadyrmaeva D.R. Clinical significance of a complex of environmental factors of the population of an industrial city in the spread of acute cerebrovascular accidents. Abstract of dissertation….candidate of medical sciences - 2004.-25 p. 7. Vilensky B.S. Stroke. St. Petersburg: Medical Information Agency, 1995. –288 p. 8. Kaste M. How to improve the quality of medical care for patients with stroke on a nationwide scale? Finnish experience. Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after S.S. Korsakov (STROKE supplement to the journal). 2003; 9: 65-68. 9. Yamaguchi T. Current state of the problem of acute ischemic stroke in Japan: results of a nationwide hospital study 1999-2000 // Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry named after S.S. Korsakov (STROKE supplement to the journal). 2003; 9: P. 72-74 . 10. Antonicelli R, Germano G. What is new about stroke prevention? Ital Heart J. 2003; 4(12):958-64. 11. Howard G., Howard VJ Stroke incidence, mortality, and prevalence/The prevention of stroke/edited by Philip B. Gorelick and Milton Alter. The Parthenon Publishing Group, 2002; 1:1-10. 12. ARGUS. Arterial hypertension in people of older age groups. Monograph. –M.: “Medical Information Agency”, 2002.-448 p. 13. Centers for Disease Control. Achievements in public health, 1900-1999:decline in deaths from heart disease and stroke – United States, 1900-1999. Morbid Mortal Weekly Rep. 1999; 48:649-56. 14. Straus SE, Majumdar SR, McAlister FA. New evidence for stroke prevention: clinical applications. JAMA. 2002; 18: (11): 396-8. 15. Wolf PA, D'Agostino RB, Balander AJ, Kannel WB Probability of stroke: a risk profile from the Framingham Study. Stroke. 1991; 22: 312-18. 16. US Census Bureau. Population projections program, population division, US Census Bureau, Washington, DC: 20233, 2001. 17. Howard VJ Howard G., “Nonmodifiable” risk factors for stroke: age, race, sex, and geography/The prevention of stroke/edited by Philip B. Gorelick and Milton Alter. The Parthenon Publishing Group, 2002. Ch. 2. P.-11-20. 18. Shevchenko O.P., Praskurnichy E.A. Prevalence of stroke in the population. The importance of arterial hypertension//Secondary prevention of stroke in patients with arterial hypertension. MOSES results, 2005 19. Chizhevsky A.L. The earth in the arms of the sun. - M.: Eksmo Publishing House, 2004. - 928 p. 20. Melatonin in health and pathology/Edited by F.I. Komarov, S.I. Rapoport, N.K. Malinovskaya, V.N. Anisimov. –M.: Publishing House Medpraktika-M, 2004. –308 p. 21. Hankey GJ, Warlow CP Treatment and secondary prevention of stroke: evidence, costs, and effects on individuals and populations. The Lancet. 1999; 354: 1457-63. 22. Update of American recommendations for the early management of patients with ischemic stroke. Pharmateka. 2005; 17: 66-69. 23. Plavinsky S.L. The end of heroic medicine. Medical Bulletin. 2005; 29: 4. 24. Gavrilova S.I. Pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer's disease. –M.: Pulse, 2003. –320 p. 25. Skvortsova V.I. Rescue algorithm. Medical Bulletin. 2005; 29:9-10.