Brain tumor is a broad concept that implies a number of diseases, the common feature of which is the appearance of tumors localized in the cranial area. These neoplasms can develop directly in the brain tissue, in its membranes, as well as in the cranial bones and blood vessels.
Tumors can be primary or secondary. In the first case, the tumor forms in the cranial cavity. In the second, metastases appear in the cranial cavity, and the primary cancer focus is located in a different place.
Tumors are also divided into benign and malignant, single and multiple. Single implies the presence of only one neoplasm, multiple – two or more.
Characteristic symptoms
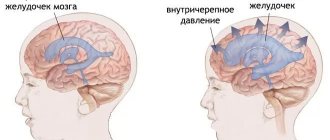
The tumor grows inside the skull and begins to compress the brain. As a result, not only those departments that are in close proximity to the outbreak suffer, but also those that are located at a distance. The larger the tumor, the higher the intracranial pressure, and the higher the likelihood of cerebral edema. All this leads to a number of symptoms:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- blurred vision;
- decrease in the functions of the nervous system, which gradually leads to loss of coordination of movement, deafness, deterioration in the functioning of taste and olfactory receptors;
- numbness of the face;
- paresis of facial muscles;
- problems with swallowing;
- abnormal movement of the eyeballs;
- paralysis;
- speech problems;
- mental and intellectual disorders;
- visual and auditory hallucinations;
- epilepsy;
- convulsions;
- hormonal disorders.
How patients react
People react differently to emotionally difficult news and events. However, in the 60s of the last century, psychiatrist Kübler-Ross found general patterns of psychological reactions that arise in most people and in 1969 proposed her theory. Initially, the Kübler-Ross model of grief was used to describe the emotional state of dying people and those who have lost a loved one, but it has also been used in other areas, including oncology and even in career psychology. The five stages of grief apply not only to the patient, but also to his loved ones:
- Denial is a person’s first reaction to hearing a diagnosis. This is a defense mechanism that the psyche turns on in response to difficult news. The person doesn’t even believe that he might have cancer; it seems to him that something was mixed up in the laboratory, that the doctor made a mistake with the diagnosis or took another person’s medical history.
- Anger. When the patient returns to “real” life, he reacts to the news with anger. The question most often asked is: “Why me?” Believers, as a rule, blame God for illness and are angry that he did not protect him. A person blames others for his illness and complains about life’s injustice. At this stage it is important to release and process anger. The sooner a person releases anger, the sooner it will go away.
- Deal. The patient seems to be conducting internal negotiations with the disease: “If I am cured, I will do charity work,” “If remission occurs, I will never smoke again.” Believers try to make a deal with God, for example, “If my husband is cured, I will become a better wife, I will do everything for him.” With these trades, the patient or loved one is trying to reassure himself, this gives him a short-term feeling of carelessness.
- Depression. It occurs when the patient begins to fully realize that he has cancer. As a rule, people have a feeling of inner emptiness, guilt for events in the past and a feeling of hopelessness. Some people experience apathy - the desire to do anything disappears, because many believe that any activity is already meaningless. At this stage, a person prepares for loss in the future.
- Adoption. The patient resigns himself to the state of affairs and accepts the situation as it is, without trying to bargain, blame or get angry. He agrees with reality. Basically, a person spends time alone, thinks a lot about the value of life and calmly perceives the outcome of the disease, even if it is fatal.
“When faced with a cancer diagnosis, most people initially react with shock and disbelief, followed by anxiety, anger and depression. An acute reaction to stress usually weakens after a few weeks, when they gradually come to terms with the disease, Nikita Prilepsky shares his experience. — Such patients can benefit from a friendly discussion of the current situation with the doctor and emotional support from family members and close friends. Depending on the stage, even suicidal thoughts may arise, so it can be extremely difficult to predict the clear behavior of each patient.”
“The response to the disease depends on stereotypes about oncology, past experience of interaction with medical institutions and doctors, as well as on whether there is a family history of oncology,” says Dmitry Olkin, head of the oncology department at GMS. — The reaction may vary depending on the stage of acceptance of the diagnosis and prognosis: shock, denial, aggression, depression, acceptance. Much depends on the personality type: in one patient anxiety and suspicion predominate, in another - aggression, denial and negativism.”
Signs of grief typically include crying and tearfulness, headaches, sleep disturbances, feelings of meaninglessness, withdrawal, erratic behavior, anxiety, restlessness and malaise. At this time, the patient questions all his ideological beliefs, including religious ones, if he is a believer.
Treatment of brain tumors
There are three main approaches to treating the disease:
- operation;
- chemotherapy;
- radiation therapy or radiosurgery.
Surgery is used mainly in cases where the tumor is isolated from other tissues, and during the operation the risk of damage to them is minimal.
The tumor can be removed completely or partially. Palliative surgery can also be performed to alleviate the patient’s condition.
Surgery is contraindicated in cases where:
- the tumor has grown into the surrounding tissue;
- metastases are present in large numbers;
- decompensation on the part of various systems and organs is clearly expressed;
- the patient is severely exhausted.
Chemotherapy aims to destroy cancer cells. The method can be used independently, as well as in conjunction with surgery. Special drugs (cytostatics) are administered intramuscularly, intraarterially, intravenously, interstitially (directly into the cavity from which the tumor was removed), intrathecally.
Radiation therapy is the exposure of cancer cells to radioactive substances. The treatment is suitable for different types of tumors, both malignant and benign, and in cases where surgery is not possible. This technique can also be used after surgery, when tumors have grown into nearby tissues.
There are also radiosurgery techniques that also belong to radiation therapy. These are Gamma Knife and Cyber Knife. In both cases, radioactive radiation is administered, which affects cancer cells and does not affect healthy tissue.
Important to remember
- Cancer patients often experience depression, anxiety, sleep disturbances, and irritability. In remission, they may experience post-traumatic stress disorder, substance abuse, and suicidal behavior.
- Most people react to a cancer diagnosis according to the Kübler-Ross model: they deny the disease, get angry, bargain, experience depression and eventually come to terms with their condition.
- Depression may reduce the likelihood of a positive outcome with treatment. At the same time, studies indicate that patients without depression have a higher chance of recovery
- Patients often become depressed and anxious due to misinformation about their illness and lack of psychological help. The task of a psychiatrist and medical psychologist is to balance the emotional background and correct the mental status with the help of medications, psychotherapy and psychological training.
Recovery after brain tumor removal
Surgery to remove a brain tumor is a very serious intervention. Even if it is carried out professionally and without consequences after it, it is very important to carry out proper recovery in order to fully recover without the risk of relapse.
After surgery there are a number of prohibitions:
- do not drink alcohol;
- you cannot fly on an airplane for at least 3 months;
- you can’t go to the bathhouse;
- During the year you should not engage in active sports, you should replace them with regular walks;
- Sun exposure and tanning are contraindicated.
It is very important to start neurorehabilitation as early as possible in order to recover as quickly as possible and avoid disability.
Restoration concerns, first of all, the patient’s previously lost functions and his return to normal life. It is not always possible to return to a completely pre-painful state; in this case, you need to try to adapt the patient to the current situation, teach him to care for himself independently.
Rehabilitation is carried out by surgeons, chemotherapists, psychologists, radiologists, physiotherapists, doctors and exercise therapy instructors, as well as junior medical staff. Only an integrated approach from all groups of specialists can ensure a high-quality rehabilitation process.
The patient is helped by:
- adapt to the consequences of surgery and a new lifestyle;
- restore lost functions;
- learn self-care skills.
The program is individually developed for each patient. Short-term and long-term goals are set for him. When short-term goals are achieved, new ones are set. And so gradually, step by step, the main goal is achieved. The process is divided into small stages so that doctors can assess the dynamics, and the patient feels the joy of achievement and receives motivation for further action.
While the patient is undergoing the process of neurorehabilitation, his relatives also need help, since the patient’s serious condition often leads to a state of depression for his entire family. In order for family members to have the strength to support their relative, they also need help.
What are the causes?
Experts do not have a clear answer to this question. The risk group for the formation of benign and malignant tumors most often includes people aged 40 to 70 years. There are several provoking factors:
- history of traumatic brain injury;
- the influence of sex hormones, due to which the problem occurs 3 times more often in women than in men;
- genetic predisposition;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- direct contact with a radiation source.
Rehabilitation programs and recovery periods
To talk about timing, you need to have an idea of the complexity of the initial condition, surgical intervention and its results. If the process is launched on time and goes well, it usually takes about 3-6 months.
Among the most popular methods:
- physiotherapy. It is aimed at symptomatic treatment, helps relieve swelling and pain;
- massage. Prescribed for paresis of the limbs. Improves blood supply, ensures the outflow of blood and lymph, increases neuromuscular conductivity and sensitivity;
- Exercise therapy. Restores lost functions, forms reflex connections, eliminates vestibular disorders.
All rehabilitation measures are carried out by specialists. But the motivation of the patient himself, his desire to work and get results is very important.
Diagnostics
The initial examination involves an oral interview and a physical examination. The doctor assesses the patient’s general condition, determines the nature of clinical manifestations, their duration and intensity, evaluates coordination, reflexes, psycho-emotional state, and so on. Next, the patient will have to undergo a thorough diagnosis, which may include the following types of studies:
- general blood and urine tests;
- blood chemistry;
- Ultrasound (echoencephalography);
- angiography - X-ray contrast study of the condition of the blood vessels of the head;
- examination of eye function and level of vision;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging – obtaining high-precision layer-by-layer images, which allows you to identify all the nuances of the disease and determine the method of tumor removal;
- magnetic resonance spectroscopy – study of the functioning of pathogenic tissues at the biochemical level;
- positron emission tomography (PET) of the head shows the characteristics of metabolic processes in the painful focus, which makes it possible to talk about the rate of development of the disease;
- biopsy - tissue collection for histological examination; in this case, the material is obtained after tumor removal.
Also of great diagnostic importance is the study of cerebral fluid, in which pathological cells are located. The stereotactic biopsy method is the most informative in terms of determining the type of carcinogenesis and its characteristics.
Make an appointment
Onko is located in Moscow, in the Central Administrative District (CAO), next to several metro stations: Novoslobodskaya, Tverskaya, Chekhovskaya, Belorusskaya and Mayakovskaya. You can contact us at any time, because we work seven days a week and even on holidays. To make an appointment with a doctor, select one of the following options:
- call +7 (495) 775-73-60;
- through an online form on the website;
- order a call back.
Three and a half thousand years before the discovery of glioma
Watch
Now it’s stupid to guess which approach will hit the jackpot. We need to develop all areas. The creation of glioma biobanks, as well as the creation of glioma cell culture banks, is very helpful in research. Also important are bioinformatics approaches that can find patterns by analyzing large amounts of information about tumors. Technologies are developing quickly, we just need to continue the massive attack on the monster in the brain from all sides.
He's not immortal.
Galina Pavlova, Doctor of Biological Sciences, Professor of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Head of the Laboratory of Neurogenetics and Developmental Genetics of the Institute of Gene Biology of the Russian Academy of Sciences