Intracranial neoplasms of a benign or malignant nature are called brain tumors. They can affect not only tissues, but also nerves, blood vessels, membranes, and endocrine structures. Depending on the location of the lesion, different symptoms appear. To make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a neurologist and an ophthalmologist, as well as undergo a number of tests, including MRI of the brain and MR angiography. For treatment, surgery is most often used, which is supplemented with radiation or radiotherapy.
Stages
Over the past year, more than 34 thousand cases of brain tumors have been identified in our country. Moreover, the disease is “getting younger.” Increasingly, pathology is diagnosed in young people, men and women who have not reached the “middle age” criterion. Brain tumors often develop in pregnant women during long periods of pregnancy. In this case, it is extremely difficult to provide quality treatment. In addition, the tumor grows very quickly.
The reason for this is in the symptoms. When a person complains of fatigue, depression and loss of concentration, he is advised to rest instead of being advised to get an MRI.
Depending on the nature of the tumor, the rate of development of the disease varies. Benign neoplasms develop more slowly, but are often practically asymptomatic in the early stages. Malignant ones are more aggressive and develop faster.
For benign ones, there are several stages of development:
- Initiation. The disease can only be detected at this stage by luck. At this moment, a DNA shift occurs in the brain cells, they change under the influence of certain factors.
- Promotion. At this moment, active reproduction of mutated brain cells occurs. However, the disease may not manifest itself even at this moment.
- Progression . The mutated cells begin active growth and the neoplasm fills the free intracranial space, compressing neighboring organs and tissues.
At the last stage, the tumor itself does not lead to serious symptoms, but compression of organs and tissues can lead to convulsions, disorientation, speech delays and other obvious symptoms.
At the last stage of development, the doctor can easily diagnose brain cancer without even using special equipment.
Malignant neoplasms are characterized by rapid division and growth of the tumor with possible metastases to various, even the most distant organs. The immune system does not have time to recognize the “enemy”, as a result of which the disease invades new organs and tissues, becoming inoperable and difficult to treat. This often happens in a short time.
There are several types of benign pathologies:
- Glioma. Characterized by frequent hemorrhages.
- Neuroma. Formed from elements of the nervous system. Symptoms of the disease include redness on the skin and pain in the area of the formed tumor.
- Neuroma. It is represented by numerous nodules in the spinal cord.
- Paraganglioma . A congenital form of a benign tumor. May provoke the appearance of metastases. Manifested by headaches, tachycardia and increased blood pressure.
- Cyst. A large cavity filled with fluid that can appear in various organs and tissues, including the brain. The danger of the pathology lies in its rapid growth.
- Meningioma. The most common form of benign tumor. However, it often turns into a malignant form and provokes the appearance of metastases. According to statistics, women suffer from the pathology more often than men; the disease develops especially quickly in women carrying a child.
- Schwannoma. It disrupts the functions of the middle ear and upsets the human vestibular apparatus. Symptoms include headache with nausea and vomiting, as well as complete or partial hearing loss.
- Craniopharyngioma. Characterized by slow tumor growth and the appearance of cysts. Symptoms include diabetes insipidus, dry skin, obesity, dwarfism or infertility.
- Pituitary adenoma. The tumor compresses the organs of the brain, most often in the area of the optic nerves. This leads to loss of peripheral vision, as well as a feeling of double vision. Men with this disease experience impotence, and women have menstrual irregularities and infertility.
There are fewer types of malignant tumors. They come down to the three most common types: gliomas, sarcomas and teratomas. Sarcoma is formed from connective tissue and is characterized by rapid growth and frequent relapses. Teratomas are formed from gonocytes, and gliomas are characterized by neuroectodermal origin.
A consultation with a doctor and a series of tests will help determine what type of tumor is located in the brain and its danger to the entire body. Although the intracranial space is so vulnerable and has numerous vessels, nerve endings and other organs, even a benign tumor will be quite dangerous to the patient’s health.
Anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain, grade 2
Treatment at this stage has a positive prognosis. The disease is determined by the following signs:
- The presence of severe malaise, nausea and vomiting;
- Intensive weight loss accompanied by decreased appetite;
- Fatigue;
- Increased fatigue;
- Decreased level of performance;
- Asthenic syndrome.
This stage is not considered too difficult. Treatment of anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain is based on tumor removal. To do this, a number of diagnostic measures are carried out. An ophthalmologist, neurologist, neurosurgeon and oncologist take part in the treatment process. To fully understand the picture, MRI and CT are performed, and these procedures are recommended to be carried out with a contrast agent. A biopsy and puncture is performed, hearing, vision, and vestibular examinations are carried out.
Removal of the astrocytoma provokes an improvement in the general condition. Most often, the process of surgical implementation and drug treatment is carried out. Removal is prescribed by a doctor only if there are no contraindications and if this operation is possible. Since the ability to perform an operation also depends on the location.
Symptoms of the disease
In the early stages, it is almost impossible to detect a brain tumor. The fact is that the main symptoms are very similar to other pathologies, which complicates diagnostic measures.
Most often observed:
- nausea, unlike poisoning or rotavirus disease, relief does not occur after the stomach is emptied;
- severe pain in the head, in an upright position, but without movement, the person feels relief, but the spasm worsens if he begins to move;
- epileptic seizures or convulsions;
- memory weakens and concentration decreases.
Such symptoms are rarely taken seriously, and in the meantime, it is much easier to cure a tumor in the head in the early stages of the disease. All of the listed symptoms will indicate the disease if they are present simultaneously in the patient. At the second stage, when the tumor grows and the meninges are excited, cerebral changes appear. These include:
- the sensitivity of the skin is lost in certain areas of the body;
- sudden dizziness accompanies the patient;
- muscle tissue weakens on one or both sides of the body;
- severe fatigue and drowsiness become a constant companion of a person;
- there is double vision in the eyes.
At this stage of a brain tumor, treatment may still be effective. However, therapeutic procedures are more difficult and longer than in the early stages of the pathology. At the same time, the risk of relapse increases significantly.
The symptoms of the second stage of a brain tumor are similar to several diseases - epilepsy, hypotension or neuropathy. Therefore, you should not panic and make terrible diagnoses in advance. It is necessary to visit a specialized doctor and undergo appropriate examinations. Any of the listed conditions requires doctor's supervision and timely treatment.
Important!
If you suspect something is wrong, contact your doctor immediately. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, you will be prescribed a course of chemotherapy. It is recommended to take the course in trusted clinics. They provide high-quality diagnostics and also use the latest treatment technologies.
Causes of tumors
At the moment, medical science does not fully understand the reliable causes of the formation of cancer. Doctors name factors that increase the risk of tumor formation. An important role is played by the age and gender of a person. Some types of cancer, such as meningiomas, are more often diagnosed in women over 45-50 years of age. This is due to the characteristics of the female endocrine system and hormonal levels. For example, during pregnancy, some neoplasms progress more intensively. Brain tumors in men, as a rule, have a more severe course and complex prognosis, because in this case the tumors are highly malignant.
Other provoking factors include:
- adverse environmental impacts: radiation, hazardous industries, living in contaminated areas, etc.;
- constant contact with toxic elements;
- infection with viruses that can contribute to the development of cancer;
- genetic characteristics (the presence of certain genes in the human genome that increase the risk of developing a brain tumor);
- head injuries of various nature and origin;
- treatment with drugs, for example, hormones, chemotherapy;
- bad habits;
- consumption of low-quality food saturated with carcinogenic elements.
These factors can influence the formation of diseases both separately (for example, heredity) and in combination.
Signs of a Brain Tumor
Signs of a brain tumor may indicate a particular neoplasm, depending on its location and size. They can be identified in the early stages if you carefully take care of your health. More often observed:
- Numbness or loss of sensation in certain areas of the body.
- Hearing and vision loss, partial or complete.
- Confusion, significant memory impairment.
- Intelligence and self-awareness are greatly altered.
- The speech is confused.
- “Jumping” hormonal levels.
- Changes in mood in a person with a high switching speed.
- Aggressive states, increased irritability, hallucinations.
Vision problems indicate a tumor in the back of the brain, and spasms and numbness in the frontal lobes. To determine the location of the tumor and carry out quick, high-quality therapy, you need to visit a doctor and take the necessary tests. Instrumental studies and examinations on devices are also carried out to thoroughly diagnose the disease.
The latest cancer treatment methods: immunotherapy and virotherapy
After weighing the risks associated with repeated brain surgery and potential complications, the patient decided to seek advice from Professor Slavin, under whose supervision she was during this entire period. According to Professor Slavin, it was possible to achieve a reduction in the volume of the tumor mass using a conservative method, without surgery. However, it was necessary to take into account the resistance of the cancer tumor - its acquired resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Based on this, Professor Slavin recommended an alternative treatment strategy, proposing to shift the focus towards immunotherapy.
The goal of immunotherapy is not to directly destroy malignant cells, but to turn them into a target for the immune system, which is normally capable of recognizing and attacking substances foreign to the human body.
Additionally, the patient received oncolytic virotherapy. Genetically modified oncolytic viruses are harmless to humans, and at the same time they specifically infect cancer cells, causing their death. But even if a cancer cell remains viable after a viral attack, it becomes a carrier of specific viral antigens that serve as a signaling target for the immune system.
Another group of drugs, called immune checkpoint inhibitors, have been used to stimulate the natural antitumor activity of T cells.
Diagnosis of the disease
When primary symptoms or signs of a brain tumor appear, a person needs to immediately see a neurologist and ophthalmologist. To collect anamnesis, echocardiography, EEG, and focal symptoms are examined.
A brain tumor, the symptoms of which are often focused on a person’s vision, requires consultation with a specialist. The ophthalmologist checks your visual acuity by performing standard examinations. Also determines visual fields and performs ophthalmoscopy procedures. This is important for understanding the size and impact of the tumor on the visual organs and other important body functions.
If necessary, an additional consultation with a specialist otoneurologist is scheduled.
If the doctor suspects a large tumor, you will have to undergo a CT or MRI of the brain. This can be done at the clinic medart.by. Such studies help to visualize the tumor and determine its boundaries, clear location and influence on other organs and systems.
In addition to standard procedures, the doctor can prescribe a number of special studies that help determine the malignancy of the tumor, analyze metabolic abnormalities, and distinguish between multifocal tumors. Sometimes it is necessary to do a biopsy of the tumor, which will provide accurate data about the nature of the tumor.
Among the main analyzes are:
- MRI of cerebral vessels;
- functional MRI;
- MR thermography;
- MR spectroscopy;
- PET scan of the brain;
- SPECT.
Tests and diagnostic studies are prescribed exclusively by the doctor after collecting an anamnesis. Going through these procedures on your own without justification and prior consultation is unacceptable. A person can go to the doctor on his own if he believes that his symptoms are similar to those of brain cancer, but he can only visit an MRI, ultrasound or other functional diagnostic rooms with a referral from a doctor.
Diagnosis is required when relatives already have cancer in the family, and the patient also has all the signs of early-stage brain cancer. It's a good idea to get regular checkups for people who have suffered a traumatic brain injury or stroke.
First stage of treatment: surgery and chemotherapy
The final diagnosis was made after histological analysis of the removed tumor: anaplastic astrocytoma - a glioma of the third degree of malignancy, characterized by aggressive growth and rapid invasion into surrounding tissues. Because anaplastic astrocytomas cannot be completely removed, after surgery, patients usually require adjuvant (additional) treatment aimed at destroying the residual tumor. Therefore, the patient was prescribed radiation therapy, and then a long course of chemotherapy according to the protocol for the treatment of astrocytoma.
After completing the course of chemotherapy, the patient's condition stabilized. She was recommended to be monitored by a neuro-oncologist, during which she underwent annual follow-up MRI scans.
Forecasts
Brain cancer is characterized by cautious predictions by doctors. A positive outcome depends on the nature of the tumor, its location, size and ability to provoke the spread of metastases.
The easiest way to treat small tumors in a place accessible for surgical intervention, benign in nature and not metastasizing to other organs. Usually one course of radiation or chemotherapy is enough to rid a person of pathology.
However, most benign tumors tend to recur. In this case, repeated surgery will be required, which can lead to serious damage to the nervous system.
Malignant tumors develop rapidly and contribute to the spread of metastases. As a rule, the location is inconvenient for surgical intervention. Removing a brain tumor is impractical or even dangerous. In this case, the prognosis is in most cases unfavorable.
The age and general health of the patient are of great importance. In elderly citizens with severe concomitant pathologies, removal of the tumor through surgery is not available.
PDT is the best alternative and auxiliary option for complex restoration
Long-term studies in the Russian Federation and abroad have proven the high effectiveness of photodynamic therapy (PDT) at the time of surgery and after it. Natural or artificial concentrates are used as a photosensitizer (PS). The patented method of Dr. Borisov Selective chronophototherapy (2341307) (ICP), which is based on photodynamic therapy, is capable of activating a cascade of biochemical and cellular reactions to regulate the level of immune status indicators. A special substance is introduced into the body - chlorin E6 (a natural photosensitizer of the latest generation), which accumulates in cancer cells. A laser beam is sent to the site of accumulation, capable of synchronizing with the patient’s rhythms, which makes it possible to reduce or increase the intensity of the effect. Penetrating to the required depth, it concentrates on pathological cells, destroying them, without touching healthy ones. Over the course of several months, the tumor disintegrates.
In our clinical practice, we use highly purified E6 chlorine, chlorophyll, processed using a unique technology and having a wide spectrum of action:
- diagnostic and antitumor;
- antiviral and antibacterial;
- normalizing hormonal status;
- improving metabolism, circulation and blood properties;
- increasing immunity.
It is capable of localizing in pathological areas and being activated under the influence of the red spectrum of hardware radiation, after which it begins to release high-energy molecular oxygen. Which, in turn, is considered a powerful oxidizing agent that destroys tumors and cleanses the body of them.
Carrying out ICHFT0, which is based on PDT, when removing meningiomas of the brain and spinal cord increases the inter-relapse period and human life expectancy.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method directly depends on the nature of the disease, the location of the tumor, its size and type. The age and general condition of the patient are also taken into account. The main treatment methods include:
- Surgical intervention. Some tumors have a convenient localization and are easily separated from the tissues without damaging the surrounding organ. If the location is inconvenient, there is a brain tumor, surgery will not completely help. The surgeon cuts off part of the tumor to eliminate compression and significantly improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Radiosurgery. It refers to the types of radiation. As part of the procedure, the patient undergoes small doses of radiation from different directions, while the rays converge at the location of the tumor, destroying it. At the same time, the surrounding tissues remain unharmed.
- Radiation therapy. You can irradiate the tumor directly or the patient’s entire brain. The second option is used for relapses, when it is necessary to eliminate the risk of developing metastases in tissues.
- Chemotherapy. Drugs that have a systemic effect on the tumor and destroy it, preventing the development of metastases to organs. It helps fight symptoms, slow down the growth of tumors and reduce the risk of relapse.
- Targeted treatment. They have a targeted effect on tumor cells, killing them. Reproduction and growth are blocked. Causing cell death.
To regulate the patient's condition, constant monitoring is carried out using MRI. If the tumor does not shrink or continues to grow, the chosen method of therapy is not effective. Also, regular studies are carried out after victory over brain cancer to exclude recurrence of the pathology.
After treatment and victory over brain cancer, rehabilitation will be required. Most often, the tumor affects important functions that will have to be restored after quality therapy.
Typically, rehabilitation includes a number of important activities. For example, classes with a speech therapist to restore normal speech, individual lessons with a tutor, physical therapy and occupational therapy. It is also recommended to use appropriate medications to reduce the severity of symptoms and increase the effect of treatment, as well as eliminate side effects.
Clinical manifestations
Sometimes the detected disease proceeds unnoticed, then the patient is simply under the supervision of specialists and periodically undergoes magnetic resonance imaging. As the tumor grows, compression of the brain tissue occurs, and the symptoms become more pronounced. Specific signs appear:
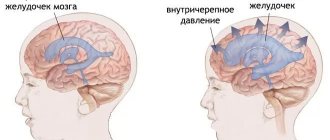
- a sharp increase in intracranial pressure;
- severe headaches;
- nausea, vomiting;
- epilepsy attacks;
- loss of visual acuity, diplopia (double vision);
- psycho-emotional disorders;
- impaired coordination of movements, paresis (weakness in the limbs).
Making a diagnosis can be difficult with multiple localization, when the formation is located in several areas and in the spinal canal. If the course of the pathology poses a real threat to the patient’s life, then the meningioma must be removed.
Prevention
Preventive measures to get rid of brain cancer include a number of measures that are aimed at eliminating the recurrence or growth of tumors in the brain.
First of all, it is necessary to exclude oncogenic effects and head injuries. They can provoke the development of tumors or cause a relapse of already cured pathologies. The patient is advised to spend more time in the fresh air, to choose a place of residence away from industrial plants and other objects hazardous to health.
Be sure to check your health regularly so that, if necessary, you can identify a cancerous tumor at an early stage of brain cancer. It is also recommended to avoid taking biogenic drugs that can provoke the growth of tumors in the brain.
Brain cancer is a dangerous pathology, most often characterized by unfavorable prognosis, since any surgical intervention in the brain can provoke serious changes in consciousness and body function. It is much easier and more effective to treat a brain tumor in the early stages of development. However, diagnosing the disease during this period is extremely difficult.
Introduction
Cancer begins when healthy cells change and begin to grow uncontrollably, forming a mass called a tumor. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor may grow but not spread to other tissues.
Head and neck cancer
Head and neck cancer is a term used to describe a number of different cancers that develop in or in the throat, larynx, nose, sinuses and mouth.
Most head and neck cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. This type of cancer begins in epithelial cells, which make up a thin layer of surface tissue. Just below the epithelium, in some areas of the head and neck, there is a layer of moist tissue called mucosa. If cancer is found only in the squamous cell layer, it is called carcinoma in situ. If the cancer has grown beyond this cell layer and into deeper tissue, it is called invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
When head and neck cancer begins in the salivary glands, the tumor is usually classified as adenocarcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, or mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
Types of head and neck cancer
There are 5 main types of head and neck cancer, each named according to the part of the body where it is found.
- Laryngeal cancer and hypopharyngeal cancer. The larynx is an integral part of the vocal apparatus. This tubular organ in the neck is used for breathing, speaking and swallowing. It is located at the top of the windpipe, or trachea. The hypopharynx (esophagus) is the lower part of the throat, surrounded by the larynx.
- Cancer of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses . The nasal cavity is the space behind the nose where air enters the throat. The paranasal sinuses are the air-filled areas surrounding the nasal cavity.
- Nasopharyngeal cancer. The nasopharynx is the air cavity at the top of the throat behind the nose.
- Cancer of the oral cavity and oropharynx . The oral cavity includes the mouth and tongue. The oropharynx includes the middle of the throat, from the tonsils to the tip of the voice box.
- Salivary gland cancer . The salivary gland produces saliva. Saliva is a fluid that is secreted in the mouth to maintain moisture and contains enzymes that break down food.
Other types of cancer can also be localized in the head and neck area, but their diagnosis and treatment are very different.