Many specialists, including neurologists and cardiologists at MedicCity, are confident that MRI scanning of cerebral vessels should certainly be included in the program of mandatory medical examination of the population.
MRI diagnostics allows you to detect pathological changes in blood vessels at the earliest stages. This means that we are able to prevent the development of the most dangerous conditions, such as atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attack, and tumor processes. MRI angiography of cerebral vessels can save your life and the lives of your loved ones!
Diagnostics based on the phenomenon of magnetic nuclear resonance are not only extremely informative and accurate, but also do not have a harmful effect on the body and can be carried out many times.
The study of the condition of cerebral vessels makes it possible today to identify and treat diseases that for many years have robbed people of their mental and physical health at an unacceptably early age.
1 MRI of cerebral vessels
2 MRI of cerebral vessels
3 MRI of cerebral vessels
What is the difference between MRI of cerebral vessels, MRI angiography of cerebral vessels and MRI of the brain
Patients often wonder what kind of test they were prescribed and whether different types of diagnostics duplicate each other.
First of all, let's define the terms. When they talk about MRI of cerebral vessels and magnetic resonance angiography of cerebral vessels, we are talking about the same study.
At one time, angiography was quite invasive and required local anesthesia. During the procedure, the patient had a puncture of the carotid artery and a contrast agent was injected into the blood through a special needle. X-rays were then used to take a series of pictures of the area of interest.
The invention of MRI made it possible to improve the method and reduce the number of unpleasant sensations and contraindications. Now the patient does not experience pain, he is not exposed to radiation, and the scan itself has become much more informative.
Due to the fact that MRI angiography provides excellent visualization of the area under study, the study can be performed without a contrast agent. The use of contrast is resorted to in difficult cases, for example, in cancer diagnostics.
1 MRI of the brain
2 MRI of the brain
3 MRI of the brain
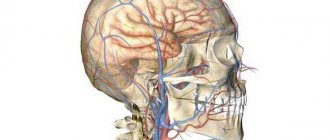
MRI angiography of cerebral vessels determines the intensity of blood flow in the arteries, veins and capillaries, helps to identify painful changes at an early stage, confirm or refute an alarming diagnosis, clarify the scope of the upcoming surgical intervention, track the dynamics of recovery after a stroke, etc.
This diagnosis differs from MRI of the brain in the nature of the visualization:
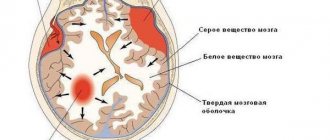
MRI of the brain is not suitable for observing blood vessels, but it makes it possible to see the structure of nervous tissue and brain matter.
MRI angiography depicts the vascular structures of the brain, but not the substance of the brain.
To obtain the most complete picture of structural changes, the techniques can be used simultaneously, complementing each other.
What does this diagnostic method provide?
- Time-of-flight diagnostics allows one to obtain sections of vessels perpendicular to the direction of blood flow.
- The phase contrast method makes it possible to determine the speed of blood flow.
- MPA with contrast enhancement allows you to study the condition of the vessel in more detail by filling it with a contrast agent, and obtain amplitude information about the speed of blood flow.
Deciphering images and making a diagnosis can only be carried out by a specialist who has the necessary knowledge. In the image, tissues and organs of different densities are expressed in different shades of a black and white palette. Seals will appear as white spots in the pictures, and liquids will appear as black spots. The specialist assesses the condition of the vessels and identifies the presence of pathologies, based on the location of the blood branch, the density of individual sections of the area under study, and shape.
The images allow the doctor to identify deviations from the norm such as:
- changes in the diameter of blood vessels, their narrowing as a result of developing arteriosclerosis or vascular spasm;
- deficiency of blood flow, indicating the development of intracranial hypertension;
- change in the position of blood vessels, indicating neoplasm or tissue swelling;
- changes in the structure and structure of the carotid artery;
- expansion of the vessel wall during an aneurysm.
MRA images allow not only to identify pathologies and dysfunctions, but also to determine the extent of the defective area.
What does MRI of cerebral vessels show?
With this research you can:
- track post-traumatic changes (possible contusions, hemorrhages, hematomas, etc.);
- detect signs/monitor the consequences of a stroke;
- detect signs of multiple sclerosis;
- identify changes associated with vascular atherosclerosis;
- identify cerebral circulation disorders;
- identify developmental anomalies;
- detect the danger of blood clots in the vessels of the head and neck;
- identify the presence of infection, inflammation, neoplasm, and many others.
1 MRI of cerebral vessels
2 MRI of cerebral vessels
3 MRI of cerebral vessels
Benefits of MRA
Benefits of MRA
- This diagnostic procedure allows specialists to obtain a clear and detailed image of the blood vessel without the use of catheterization. This means that the risk of arterial injury and complications after the procedure is completely eliminated.
- The time required for non-contrast MRA is significantly shorter than the period for CT or radiography, since no prior patient preparation is required.
- Non-contrast MR angiography costs less than CT examination of blood vessels due to the absence of the need to purchase a contrast agent.
- The method is absolutely safe, while CT and X-ray examinations expose the patient to radiation. The procedure takes place without pain or unpleasant physical sensations, so it can be used for children and people with a low pain threshold.
For whom is MRI of cerebral vessels recommended?
MRI angiography of cerebral vessels is usually required by such conditions and diseases as:
- previous head injuries (TBI, SHM);
- strokes, micro-strokes;
- frequent headaches of unknown origin;
- frequent dizziness;
- episodes of loss of consciousness;
- coordination problems;
- visual or auditory dysfunction;
- epilepsy;
- rapidly developing diabetes mellitus;
- suspicion of a tumor process;
- tracking the results of conservative or surgical treatment, etc.
Contraindications to MRI of cerebral vessels
This diagnostic procedure has a fairly narrow list of contraindications. Among them:
- patient weight over 120 kg;
- severe form of claustrophobia;
- inability to lie in one position for a long time and motionless;
- early stages of pregnancy;
- the presence in the body of metal implants, prostheses, insulin pumps, vascular clips and devices (pacemakers, defibrillators, etc.).
1 MRI of the brain
2 MRI of the brain
3 MRI of the brain
When is angiography performed?
Angiography is performed before surgery, as a postoperative study and as a diagnostic method for suspected vascular pathologies. If the patient comes with complaints of:
- regular loss of consciousness
- headache,
- frequent dizziness,
- hearing loss,
- numbness of the limbs,
- spontaneous hematomas, MRA cannot be avoided.
The procedure is also prescribed after:
- traumatic brain injury,
- with a sharp drop in visual acuity,
- after a stroke,
- if you suspect vascular disorders of a diabetic nature.
How to prepare for MR angiography
There is no special preparation for this examination.
Before lying on the tomograph table, the patient must get rid of electronic gadgets and remove all metal objects and jewelry.
You can take earplugs with you for comfort - the equipment creates quite intense noise during operation.
The procedure may take 30-60 minutes, so you need to be patient.
There is no need to be afraid - if the patient experiences any unpleasant sensations, the procedure can be interrupted at any time (although this is usually not required; the examination can be tolerated without problems even by children).
Once the diagnosis is complete, the patient is released and the MRI physician begins to interpret the results.
How is the procedure done?
To perform MRA, a conventional magnetic resonance scanner is used. The procedure, depending on the type of study, takes from 10 minutes to an hour. The main condition for a successful study is immobility during scanning. If the patient finds it difficult to remain in one position, he is prescribed a sedative to put him into a short-term sleep.
During the study, the patient may hear noises made by operating equipment. To reduce discomfort from constant loud sounds, the patient is asked to wear headphones, through which the doctor will tell the person being examined how the procedure is going.
Indications and contraindications
Currently, MR angiography of cerebral vessels is used:
- if a cerebral aneurysm is suspected;
- as a method of preoperative diagnosis;
- when determining thrombosis or stenosis of cerebral vessels and great vessels of the neck;
- in order to determine the sources of blood supply and assess the relationship with large arteries of brain tumors, primarily located at the base of the skull, for preoperative planning of access and the volume of removal (meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, etc.);
- in the diagnosis of arteriovenous malformations;
- for diagnosing congenital anomalies;
- for vascular diseases of the brain ( stroke - differential diagnosis of hemorrhagic and ischemic variants, determination of the duration of the event);
- indications for prescription may include patient complaints of dizziness; severe and prolonged headaches of unknown origin; decreased memory and orientation; confusion; double vision; when seizures occur or the frequency of seizures increases; the appearance of weakness in the limbs, etc.
- in case of chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency (in the period after a stroke, in the presence of transient ischemic attacks, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, etc.);
- An indication for prescribing MRI may be dynamic monitoring of the patient - i.e. conducting control studies at intervals recommended by the doctor to identify positive or negative changes;
- assessment of the effectiveness of surgical treatment and diagnosis of complications;
- the need for spatial visualization, construction of 3D reconstructions.
Contraindications:
- metal implants;
- epilepsy, schizophrenia;
- pregnancy;
- serious condition of the patient;
- inability to remain still during scanning;
- large body weight;
- severe claustrophobia.
1.What is MR angiography
MR angiography (magnetic resonance angiography) is a technique that allows you to examine the blood vessels of the brain. The result of such diagnostics is a three-dimensional image of the entire vascular system of the area under study. These data provide the doctor with information not only about the anatomical features, but also about the functional viability of the vessels. The result of MR angiography of the cerebral arteries is an accurate diagnosis or confirmation of the suspected disease, which serves as the basis for a further treatment plan. MR angiography is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of already used therapy or surgical assistance.
MR angiography is a safe study that even excludes arterial puncture. Diagnosis can be done with or without contrast agent. At the same time, the information content and accuracy of such a survey is higher than that of many other methods. MR angiography of the cerebral arteries is a radiation diagnostic method, but the radiation parameters of the tomograph are completely safe. The procedure is carried out using a magnetic resonance tomograph with a field strength of 0.5 Tesla.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
4.What results does MR angiography of the cerebral arteries give?
The volumetric 3D image obtained by the doctor on the tomograph monitor makes it possible to comprehensively study the anatomy and functions of the vascular system of the brain. In this case, aneurysms, vascular occlusions, vascular malformations, places of stenosis and atherosclerotic changes are clearly visible.
Many chronic conditions - headaches of unknown origin, tinnitus, dizziness - may have vascular disorders as their root cause. Often, only through MR angiography can a clear connection be established between a particular manifestation and a specific organic or functional abnormality and adequate treatment, therapeutic or surgical, be prescribed.
The following diseases are most often diagnosed during MR angiography of cerebral arteries:
- aneurysm;
- vascular wall dissection;
- vascular stenosis;
- vasculitis;
- atherosclerosis.
MR angiography in Volyn hospital
Magnetic resonance imaging room of the Volyn hospital with two of the most modern tomographs with a magnetic field induction of 1.0 and 1.5 Tesla. Doctors at the MRI office are at the forefront of the development of magnetic resonance imaging in Russia and have unique, vast experience and original research methods. Highly qualified personnel and the latest software allow us to conduct the widest range of research. The department has extensive experience in magnetic resonance angiography (MR angiography).