- Time: 30-60 seconds, with contrast - 20 minutes
- The need to administer a contrast agent: yes
- Necessity of preliminary preparation: no
- Presence of contraindications: yes
- Limitations: weight - up to 200 kg
- Conclusion preparation time: 15-20 minutes
- Children: from 14 years old
What is CT angiography of cerebral vessels?
Cerebral CT angiography is a diagnostic technique that creates a three-dimensional image of the arteries, veins and venous sinuses of the brain.
The study of the Circle of Willis, which underlies the circulatory system of the brain and is located in its ventral (lower) region, deserves special attention.
This procedure is performed in the presence of headaches, if various brain abnormalities and other neurological abnormalities are suspected.
If the patient has not previously been given a specific diagnosis, then at the same time as the vessels of the brain, the vessels of the neck are checked.
This is due to the fact that some pathologies related to the brain may arise due to impaired blood flow in the neck.
Advantages of CT angiography of cerebral vessels
CT not only displays the vascular network in three dimensions, but also allows you to study in detail any large or small vessels. This research method is considered the most useful and effective, since it makes it possible to diagnose almost any dangerous disease at an early stage.
During CT angiography, you can examine the structure of the vascular wall and the tissue that surrounds the veins and arteries. This provides valuable information necessary, for example, for the early detection of hemorrhagic stroke. In the images, you can see the size of the hematoma, study the degree of damage to the brain centers and nuclei, and also assess the level of compression of the brain matter.
There is no pain during the examination.
How the study is performed
Cerebral angiography is performed in the operating room of the cath lab department. The patient's head is gently fixed to the table with a special tape passing through the frontal area. This is necessary to eliminate head movements during the examination and obtain a high-quality “unblurred” image.
In the department, before transportation to the operating room, premedication is carried out using a mild sedative and an antiallergic drug.
The puncture site in the area of the femoral artery through which the examination is carried out must first be shaved the day before and treated with an antiseptic in the operating room. The examination is performed under local anesthesia. Through a small incision with a diameter of 2.0-3.0 mm, a catheter is inserted into the mouth of the arteries of the brain, through which contrast is injected, and the image is recorded on a computer. If there is pathology of the cerebral vessels, this will be reflected in the resulting image. After completion of the study, a pressure aseptic bandage is applied to the puncture site. For 12 hours after the examination, it is necessary to remain in bed in a position with the lower limb extended on the side where the intervention was performed. After completing the study, it is recommended to drink at least 0.5-0.7 liters of clean water to ensure rapid removal of the contrast from the body.
Alternatives to CT scan of the brain
Alternative diagnostic methods include primarily MRI. But it is not recommended if the patient has any metal elements in the body: a pacemaker, vascular clips, etc. X-ray angiography is also sometimes used.
If you want to know where is the best place to get a CT scan of the brain, contact us - we will sign you up for a study at a clinic where they conduct the study using the latest equipment and guarantee high-quality diagnostic results.
CT angiography on a multislice tomograph (MSCT angiography)
In multislice (multi-layer, multi-slice) computed tomographs (MSCT), unlike tomographs of previous generations, not one, but two or more rows of detectors are located around the circumference. This technology significantly increases the speed and information content of studies, and also reduces the radiation dose to the patient. MSCT has a number of advantages over conventional computed tomography:
- improved time resolution;
- improved spatial resolution along the longitudinal z-axis;
- increasing scanning speed;
- improved contrast resolution;
- increase in signal-to-noise ratio;
- effective use of the X-ray tube;
- large anatomical coverage area;
- reducing radiation exposure to the patient;
Indications
- Presence of headaches of unknown origin;
- Detection of atherosclerosis, in order to identify the risk of stroke;
- Presence of head injuries;
- If other diagnostic methods do not provide convincing information regarding the diagnosis;
- Systemic and cerebral vasculitis;
- Risk of hemorrhage;
- To assess the patient’s condition after surgery;
- The presence of malignant and benign neoplasms in blood vessels;
- Any abnormalities in vascular development.
Why is the research being done?
Cerebral angiography is used to detect or exclude pathologies of the blood vessels of the brain, such as:
- abnormal blood vessels (vascular malformation);
- aneurysms;
- narrowing of the arteries of the brain;
- vasculitis;
The study is also used for:
- confirmation of the presence and location of a brain tumor;
- assessment of the head and neck artery before surgery;
- determining the presence of blood clots in the vessels of the brain, which may cause a stroke.
In some cases, this procedure is used to clarify the diagnosis after abnormalities have been identified according to MRI or CT. Contrast that extends beyond the outline of a blood vessel may be a sign of internal bleeding. Narrowing of the arteries may indicate cholesterol deposits, spasms, or hereditary diseases. Abnormally developed blood arteries may be associated with brain tumors, intracranial bleeding, aneurysm (bulging of the artery wall), or arteriovenous malignancy.
Cerebral angiography is also performed to prepare for x-ray surgery to eliminate malformation, aneurysm or thrombosis of cerebral vessels.
Contraindications for CT scanning
Computed tomography is prohibited at any stage of pregnancy, since X-rays can cause abnormalities in the development of the fetus.
Also, diagnostics are not recommended for people with a body weight exceeding 200 kg.
Since CT is based on the use of contrast, it has a number of additional limitations:
- Since iodine is used as a contrast agent, it can cause allergic reactions in patients. This is why the procedure is not prescribed to people allergic to iodine;
- If the patient has previously been diagnosed with renal failure, this is a contraindication for CT scanning, as it can lead to serious consequences;
- Since the contrast penetrates into milk, the procedure is not prescribed to women during breastfeeding;
- If the patient has severe injuries or shock, computed tomography with contrast is also not recommended.
How to prepare for the test
Before the study, be sure to inform your doctor about the presence of:
- allergies to strawberries, shellfish, seafood or iodine-containing substances;
- history of bleeding of unknown origin;
- an allergic reaction to a contrast agent in the past;
- pregnancy.
Before the study, it is necessary to exclude food and liquid intake for 4-8 hours. Before the examination, you need to remove all jewelry, decorations and costume jewelry to prevent their contours from interfering with the resulting image.
Preparation
- make sure that the patient is not allergic to iodine preparations;
- take a blood test for creatinine;
- do not eat 3 hours before the procedure;
- stop medications that lower blood sugar 2-3 days before;
Read more about preparation. Before carrying out the procedure, study the contraindications. The main contraindications include:
- make sure that the patient is not allergic to iodine preparations;
- pregnancy;
- hyperthyroidism;
- heart failure;
- renal failure.
CT scan of head and neck vessels with contrast
Since the vessels practically do not stand out against the background of other tissues, CT angiography of the head and neck is necessarily performed with contrast. To improve the clarity of images, iodine-containing preparations are used for injection into the blood. By staining arteries, veins and capillaries, contrast agents visualize the smallest vessels, as a result of which diagnostic possibilities are significantly increased.
Computed angiography is especially informative when:
- inflammation of blood vessels;
- the need to study the blood supply to tumors;
- suspected compression of blood vessels by neoplasms or spread of metastases to the walls of veins and arteries.
Often, the introduction of contrast causes the appearance of specific sensations. A person may feel heat, a rush of blood to the face, and a metallic taste in the mouth. Occasionally, complications occur in the form of nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, low blood pressure, redness and swelling at the injection site. You must inform your doctor about any changes in your condition without waiting for the end of the diagnostic procedure.
The contrast agent is eliminated from the body approximately one day after the injection. To speed up this process, it is recommended to drink plenty of fluids.
CT scanner and contrast bolus injection system (pictured left)
If you have already had an X-ray or contrast test two to four weeks before your angiography, tell your doctor about it. It is possible that the specialist will recommend rescheduling the date of the procedure.
Multislice CT angiography in Volyn hospital
The computed tomography room of the Volyn Hospital is equipped with a modern spiral tomograph “Bright Speed Elite”. Doctors at the CT office are at the forefront of the development of computed tomography in Russia and have unique, enormous experience and original research methods. Highly qualified personnel and the latest software allow us to conduct the widest range of research.
The department has extensive experience in computed tomography (CT) of the spine and extremities for degenerative diseases, trauma, tumors and inflammatory diseases. Three-dimensional and multiplanar image reconstructions are widely used.
How to do a CT scan of the vessels of the head and neck
It is better to come to the diagnostics in loose clothes made of natural fabric. It is important to make sure that there are no fittings, decorative elements or metal threads on it. Before the examination, remove jewelry, glasses, watches, and warn the staff about the presence of dentures or implants.
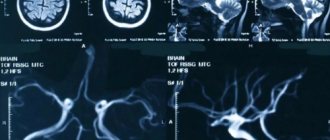
CT angiography of the brain - photo (3D reconstruction)
CT angiography of the vessels of the brain and neck proceeds as follows:
- the patient lies down on the tomograph couch;
- the radiographer administers a radiopaque solution through a dropper;
- the table moves towards the scanning system so that the head is in the radiation zone;
- the x-ray tube and sensors rotate inside the tomograph ring, the device takes pictures and transmits them to the computer;
- At the end of the study, the device turns off.
Analysis of cerebral vessels is a painless procedure. The only thing that can cause minor discomfort is the noise and crackling of a working tomograph. To combat this problem, many clinics provide hearing protection or earplugs.
The scan lasts 20-30 minutes. During this time, you should lie still and not move, so as not to spoil the quality of the pictures.
Instruction before the computed tomography procedure
The information obtained during angiography is processed in a special program. The results are saved to disk or, at the patient’s request, printed on film.
Preparation for angiography
Computed tomography of the head and neck does not require complex preparation. To reduce side effects from contrast contrast, a light snack (sandwich, yogurt or fruit) is advisable before leaving home. Breastfeeding mothers need to express and store milk, since after angiography you cannot immediately put the baby to the breast.
CT of the head and neck vessels requires blood test results for creatinine. In some diagnostic clinics, a rapid test is performed right on the spot. You can find out about the availability of such a service when making an appointment for an examination. The patient must inform the doctor about the medications he is taking: a number of medications cannot be combined with iodine-containing drugs. In agreement with the specialist, they are canceled or replaced at least 12 hours before the procedure.
Drawing blood for creatinine testing