Named after the researcher who discovered it, the circle of Willis is a vivid illustration of the concept of “anastomosis”.
This is the name given to a system of communication-connections in the form of short bridges between adjacent blood vessels, in this case arteries, forming a closed ring (circle) at the base of the brain.
Since we are talking about a communication system that supplies the entire brain with glucose and oxygen, there is no need to talk about the importance of the existence of this vascular formation - it is obvious.
The variety of options for the circle of Willis is created by the presence of different ways to connect these main arterial blood supply lines.
General information about the basal circulation, its vascular structure and its functions
The circle of Willis is the very beginning of the entire circulatory network, rising from the base of the brain up both along its surface and in the depths, in order to further, endlessly branching, reach each individual cell in its tissues and structures.
The arterial system, closed in a ring, allows it to carry out its main function (uninterrupted blood supply to the brain) as successfully as possible, because when there is a power interruption from one vessel, an automatic switch to blood supply from another occurs.
And power interruptions can occur due to the appearance in one of the arterial branches:
- spasm;
- narrowing of the lumen of another etiology (due to the formation of cholesterol deposits, blood clot, thickening of the wall from scar formation, due to compression from the outside);
- aneurysmal deformation of the lumen;
- atrophy or neglect (collapse with closure of the lumen - obliteration).
Or it could be a consequence of hypoplasia (congenital underdevelopment) that occurred at a critical moment.
The role of the Circle of Willis
The circle of Willis is a mechanism of protection, compensation for impaired blood circulation, provided by nature to provide blood to the brain when specific arteries are damaged. If obstruction, rupture, compression occurs, or there is congenital underdevelopment of the branches of the arterial bed, then the vessels of the opposite side will take over the function of blood supply, delivering blood through collaterals - connecting arteries.
Considering the functional importance of the arterial network at the base of the brain, it becomes clear why these arteries are so important. We are not just talking about serious illnesses like stroke or aneurysm. The circle of Willis helps to maximally supply the brain with blood in case of functional disorders (spasm), some variants of the structure of the arteries, when the vascular ring still remains closed, but the diameter of individual vessels does not allow the delivery of the required amount of blood.
The role of the circle of Willis increases sharply with complete occlusion of any of the arteries. Then the prognosis, the rate of increase in symptoms, and the volume of damage to the nervous tissue will depend on how this ring is formed and how capable it is of redirecting blood to those areas of the brain that do not receive enough nutrition. It is clear that a properly formed vascular system will cope with this task better than one where there are anomalies in the development of blood vessels or even a complete absence of specific branches.
About the structure of this part of the circulatory system
There are many options for constructing the arterial ring of the base of the brain, but its mandatory components are arteries:
- forebrain (its initial fragment);
- posterior medulla (at its initial segment);
- connecting (front and rear);
- internal carotid (its suprasphenoid fragment).
The main vascular arteries are 2 carotid and 2 vertebral arteries (one on each side of the body). Carotid animals enter the cranial cavity through the carotid canal, which passes through the pyramid of the temporal bone and opens at its apex; vertebrates enter by passing the foramen magnum.
The blood supply is created by intermediate “bridges” that have individual characteristics: they can be completely absent, be in a state of aplasia, hypoplasia, or be tripled (the presence of three elements instead of two, or the phenomenon of trifurcation).
In the classically symmetrical version, the vertebral arteries merge to form one powerful basilar (main) one, running along the pons and giving branches to supply the cerebellum and medulla oblongata. Anteriorly, it is divided into 2 posterior connective (right and left), at the same level creating also 2 posterior cerebral.
At the level of its confluence with the internal carotid, on both sides of the anastomosis, the central cerebral arteries (left and right) branch in the distal direction. The branches of both internal carotid cells close in front, forming a semicircle, from which 2 parallel anterior cerebral arteries extend forward. The single anterior connecting bridge connecting them from behind is part of the arch formed by the fusion of the branches of the internal carotid arteries.
When is treatment needed?
Therapy is not always required. Some of the riskier options include:
- Complex forms of absence of connecting arteries and collaterals. In this case, the risks of migraine, stroke, and dyscirculatory encephalopathy increase. Correction is required to prevent violations that have not yet occurred. This is the main direction.
- Hypoplasia of the vertebral arteries and other structures of the circle of Willis. Requires immediate medical attention, because it poses a threat of ischemia and early stroke. It is necessary to prevent the deposition of cholesterol plaques and arterial stenosis.
Pre-stroke symptoms are described in detail in this article.
- Lack of closure of the vascular ring. Therapy is aimed at preventing complications and correcting symptoms. The open form of the anomaly is considered especially dangerous. The most threatening of them all. Therefore, treatment continues throughout life under the constant supervision of doctors.
Eliminating the structural disorder itself is a key task. Others are aimed at restoring normal functional activity of the brain.
Drug therapy
Symptomatic correction is required, for example, in the context of migraine and its frequent attacks. Encephalopathy, neurological deficit in this regard.
Several types of medications are prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory non-steroidal origin, Ketorol, Nimesulide, Diclofenac. Other. In addition to the main effect, they have the ability to relieve pain, which is used in therapeutic practice.
- Antispasmodics. Drotaverine, Papaverine, other names. They relieve vascular stenosis, excessive abnormal narrowing of the arteries. In most cases, medications are prescribed as a symptomatic measure. To fix the problem here and now.
- Nootropics. Accelerate metabolic processes in the brain. Prevents early destruction of cerebral structures. Such names as Phenibut, Glycine are used.
- Cerebrovascular. To accelerate blood flow in the central nervous system. The technique allows you to restore trophism and eliminate ischemic phenomena. Piracetam, Actovegin. The latter has an antianginal effect. Reduces tissue need for oxygen, optimizes nutrition and metabolic processes.
- It is possible to use angioprotectors. Anavenol, others as part of strengthening the vascular wall. Restoring its elasticity, firmness and ability to withstand, including increased loads.
Lifestyle change
A big role is given to giving up bad habits and changing your lifestyle.
- Avoidance of smoking and drinking alcohol is indicated. It is also undesirable to drink coffee; it is better to replace it with herbal infusions or chicory.
- In addition, the use of salt is limited to 5-7 grams per day, so as not to cause an increase in blood pressure.
- Nutrition involves the inclusion of plant foods in the diet. Exclusion of semi-finished products and smoked meats. Also less fried, salty, fatty.
You need to eat meat, but it is better to limit yourself to certain types of poultry: turkey breast, chicken.
Surgical correction
In difficult cases, surgery cannot be avoided. The task is to restore the normal structure of the Circle of Willis in a certain part.
For example, creating a bypass for blood flow (shunt), mechanical expansion of the lumen of the artery (stenting, ballooning).
Often, a complication of improper development of the ring-shaped structure is aneurysms of the vessels included in the structure: sac-like expansions of the walls that can burst at any time. This is also an absolute indication for surgery.
The question of choosing tactics falls on the shoulders of the doctor.
Development and formation options
Scientists' opinions about the frequency of occurrence of the classic variant differ greatly from each other: according to some data it is 50%, according to others - 25, according to others - even less. Depending on the method of vessel branching, determined by the characteristics of intrauterine development, both the presence and degree of development of some segments of the system will differ from the canonical one.
Possible options for absence are cases when there are no arteries:
- basilar;
- all connecting;
- connecting front;
- connecting rear (one or both);
- connecting front and one of the connecting rear.
Cases of anterior or posterior trifurcation can also be represented by variations in the origin of the arteries:
- posterior cerebral from the internal carotid (a separate option - with the simultaneous absence of the anterior connective);
- both forebrain from one of the internal carotid.
It is also possible that:
- hypoplasia of one of the hindbrain;
- incomplete duplication of the anterior cerebral branch.
The most common occurrence is the presence of a posterior trifurcation of the internal carotid axis (with the origin of three cerebral arteries at once: posterior, anterior and middle), and the posterior cerebral artery departs from the posterior communicating artery. Such an anomaly, having arisen in a 16-week fetus, can persist or undergo a gradual transformation into a fully vicious circle.
The situation with aplasia of the posterior connecting branch is no less common, when there is a connection between the basilar and internal carotid arteries only on one side, and on the other the circle is not closed.
In the less commonly diagnosed absence of the anterior connecting bridge, there is no communication between the carotid arteries, which can lead to the impossibility of pumping blood from one side to the other.
With aplasia of the anterior communicating branch, disconnection occurs between the carotid arteries, and with unformed posterior segments of the circle of Willis, connecting the posterior and anterior segments, they are practically not connected to each other.
Rarer findings during the study include cases:
- the presence of a median trunk of the corpus callosum;
- fusion of both anterior cerebral arteries into one trunk or their parietal contact with each other;
- anterior trifurcation (with the departure of both forebrain from the same carotid);
- the presence of bilateral trifurcation of the carotid arteries;
- absence of both posterior communicating branches;
- the presence of a double anterior communicating artery.
Diagnostics
The examination is carried out under the supervision of a vascular surgery specialist. It is possible to involve a neurologist.
The measures are mostly standard; it is necessary to carefully evaluate the anatomical structure of the circle of Willis.
- Angiography. Essentially an x-ray with contrast. A special drug is introduced, which, accumulating in the blood, enhances the pattern. Then doctors take a series of photographs and, based on the results, evaluate the nature of the structure of the ring-shaped structure. It is considered an accessible and relatively simple diagnostic method with a minimum of contraindications.
- Dopplerography of cerebral vessels. Required to assess the speed and quality of blood flow in cerebral structures, used as part of a functional examination. Prescribed in all cases.
- MRI. To identify complex forms of anomaly. This is perhaps the most informative technique among others. Maximum safe, does not create a load on the body, and is not accompanied by pain. But the research costs on average more than its analogues. That’s why they resort to this method when others have failed.
- It is possible to prescribe invasive, selective angiography.
Activities can be adjusted during the examination and supplemented with other techniques. The issue is resolved at the discretion of the specialist.
Pathological structure of the arterial basilar circle
The vessels of the anterior half (carotid and anterior cerebral) are distinguished by the greatest stability of development, while the anatomy of the posterior cerebral and connecting parts is characterized by great variability in branching.
However, deviations in the structure of the anterior half are much more important due to the significant severity of clinical symptoms and the greater severity of the prognosis. In addition to the ideal (closed) there are options for the open basilar circle:
- fully;
- not completely.
In the first case (in the absence of connecting branches), the communication between the anterior and posterior sections is completely absent; in the second (with their preservation, but in a state of stenosis or hypoplasia), they speak of incomplete opening of the basilar circle, allowing it to function not at full capacity.
Signs of structural anomalies
Anomalies in the structure of blood vessels may not manifest themselves for years, until reaching an age when the changes become stable and the level of cerebral circulation becomes unstable, but they can appear already in young years.
The most constant ones include the appearance of:
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- decreased attention, memory (in severe cases, intellectual capabilities).
Due to the presence of cerebral ischemia involving fine brain structures, both neurological and mental abnormalities appear - from emotional instability to neuroses and panic attacks.
The most characteristic symptom of circle of Willis pathology is migraine attacks. The most susceptible to it are people with open circles or anomalies in the development of the posterior half of the system:
- posterior trifurcation;
- hypo- or aplasia of the posterior communicating branches.
Due to ischemia of the areas of the brain responsible for vision, the onset of an attack is preceded by the appearance of a visual aura (bright zigzags, flashes and sparks in the eyes).
Other symptoms of insufficient blood supply are signs of DEP (dyscirculatory encephalopathy) with a disorder in both the emotional-volitional and purely physical spheres - from unreasonable weakness to decreased ability to work.
The peak of dysfunction in the abnormal structure of the basal circle is the development of stroke with the development of paralysis and paresis, sensory and motor disorders, and in severe cases - with the onset of coma.
The emergence and development of an aneurysm may also not manifest itself for decades and is often an accidental finding during the study of cerebral vessels.
About the causes of pathologies
Deviations in the development of structures of the circle of Willis occur, as a rule, during intrauterine development, the course of which can be caused by abuse on the part of the pregnant mother:
- her smoking;
- her use of alcohol or drugs;
- overdose of sleeping pills and sedatives;
- unauthorized use of medications not prescribed by a doctor.
The course of pregnancy can be affected by chronic or acute stress of high intensity, viral infection, etc.
The cessation of the functioning of the existing and developed system of messages at the base of the brain can be caused by both the same chronic household intoxications and changes in the properties of blood (due to its high coagulability), as well as diseases that cause degeneration of the vascular wall or narrowing (closing) of the lumen of blood vessels:
- atherosclerosis;
- thrombosis;
- fat or air embolism when large arteries are injured by sharp edges of bones during their fracture, or other acute and chronic causes.
Signs and diagnosis of anomalies of the circle of Willis
Clinical signs of abnormalities in the branching of vessels in the circle of Willis occur when blood flow through collaterals becomes insufficient for various reasons. For example, fatty plaques have formed in the arteries, a blood clot has appeared or an embolus has migrated from the left side of the heart, or an aneurysm has ruptured. A healthy person does not feel non-classical branching of blood vessels, since his brain does not experience the need for bypass blood flow paths.
development of stroke/disorders associated with insufficient blood supply to the brain area
Symptoms of obstructed blood flow can vary widely. If we are not talking about a stroke, then patients complain of dizziness, headaches, decreased intellectual abilities, memory, and attention. Psychological problems are also common - often abnormal branching of blood vessels is accompanied by neuroses, panic attacks, and emotional lability of its owners.
Migraine is considered a characteristic manifestation of the non-classical development of the circle of Willis. Many observations have been devoted to the issue of the relationship between the structure of the cerebral arteries and migraine, which indicate that the majority of patients with migraine have certain anomalies. Especially often with migraine, deviations in the structure of the posterior part of the arterial system are diagnosed. When the circle of Willis is open, hypoplasia or aplasia of the posterior communicating arteries, the posterior trifurcation, those parts of the brain that are responsible for vision do not receive enough blood, therefore an intense headache is preceded by a visual aura in the form of flashes, zigzags, etc.
A decrease in blood flow through the vessels of the arterial ring of the brain can provoke periodic headaches and disorders similar to dyscirculatory encephalopathy - apathy or irritability, decreased performance, fatigue, etc. Typically, such a conclusion can be found in the results of MR angiography and it indicates hypoplasia of those or other vessels.
In case of aplasia of the arterial trunks, when some vessels are absent at all, the absence of blood flow is recorded during the study. For example, aplasia of the posterior communicating arteries will be accompanied by a lack of blood flow through them, respectively. Such aplasia can also be asymptomatic, but only when a sufficient amount of blood passes through the main arteries. With atherosclerosis or spasm of the arteries, signs of insufficient blood supply to the brain will not be long in coming.
% distribution of aneurysm cases among cerebral arteries
If, against the background of an abnormal structure of the arteries at the base of the brain, an acute circulatory disorder occurs, then the clinic will have obvious symptoms of a stroke - paresis and paralysis, speech disorders, pathological reflexes, impaired consciousness up to coma.
Separately, it is worth mentioning aneurysms - dilations of blood vessels in the brain. According to statistics, it is in the arteries of the Circle of Willis that the greatest number of them are found. An aneurysm of the arteries in this area is fraught with rupture and massive subarachnoid hemorrhage with clinical stroke, coma and severe neurological manifestations.
Aneurysm is an independent pathology, and not a variant of individual branching of vessels, but it much more often accompanies non-classical types of the circle of Willis.
The diagnosis of a particular anomaly in the development of the circle of Willis can only be established with the use of modern instrumental examination methods. Opportunities in diagnostics have given specialists a chance to analyze the nature of the prevalence of variants in the structure of brain vessels and their varieties, but until relatively recently, conclusions could be drawn mainly from the results of autopsies of deceased patients.
The development of ultrasound Dopplerography and magnetic resonance imaging techniques has made it possible to make the study of the nature of the structure of the Circle of Willis a publicly accessible and safe event. The main methods for diagnosing variants of the vascular system of the brain include:
- X-ray contrast angiography is one of the most informative methods, but has contraindications associated with the need for contrast (liver, kidney pathology, allergies to contrast, etc.);
- Transcranial Doppler ultrasound - the procedure is safe, affordable, and requires devices with a Doppler sensor, which are available in many medical institutions;
- MR angiography - performed on a magnetic tomograph, has contraindications, a significant drawback is its high cost.
Circle of Willis on a diagnostic image
Selective angiography of the cerebral vessels is an invasive procedure in which a catheter is inserted into the femoral artery and advanced to the area of interest in the cerebral arteries. When the desired area is reached, a contrast agent is applied. The method is most often used during surgical treatment (stenting, angioplasty).
, CT angiography can be used when a contrast agent is injected intravenously, and then pictures of the head are taken in different projections and sections. Subsequently, a three-dimensional image of the vascular structures of the brain can be recreated.
Transcranial Dopplerography makes it possible to determine the nature of blood flow in the vessels of the brain (reduced, absent), but it does not provide enough data regarding the anatomical structure of the arteries. Its important advantage is considered to be the almost complete absence of contraindications and low cost.
MR angiography is one of the most expensive, but at the same time quite informative methods for diagnosing the structure of the circle of Willis. It is performed in a magnetic tomograph and the contraindications for it are the same as for conventional MRI (high degree of obesity, claustrophobia, the presence in the body of metal implants that conduct a magnetic field).
The MRI picture shows the structure of the vessels of the circle of Willis, the presence or absence of connections between them, aplasia or hypoplasia of the arteries. When assessing the result, a specialist can determine the diameter of each artery and the characteristics of its branching.
Video: example of MR angiography of the brain
(The circle of Willis is closed; a convoluted S-shaped course of the intracranial section of the left vertebral artery is determined; a C-shaped course of the basilar artery; otherwise, in the segments of the ICA and paired arteries of the ring of the base of the brain, no data were obtained for the presence of hemodynamically significant stenoses or pathological tortuosities).
As you can see, each method has both advantages and disadvantages, so they are combined to obtain accurate conclusions regarding the arteries of the brain. An integrated approach makes it possible to determine the anatomy of the vessels and the nature and direction of blood flow through them, which is very important in assessing the degree of risk of vascular accidents and possible prognosis.
Many people who have discovered any variant of the structure of the Circle of Willis are immediately interested in treatment methods. Since deviations in the branching of blood vessels are not considered an independent disease, treatment as such is not required. Moreover, in the absence of a clinic for blood flow insufficiency, it does not make sense.
In cases where there are specific complaints (migraines, decreased mental capacity, etc.), you need to seek help from a neurologist who will prescribe vascular drugs (nootropil, fezam, actovegin), drugs to improve metabolism in the brain (mildronate, vitamins B), if necessary - sedatives, tranquilizers, antidepressants, in case of migraine - analgesics, anti-inflammatory, specific anti-migraine drugs (ketorol, ibuprofen, paracetamol, askofen, triptans).
Surgical treatment is indicated for severe circulatory disorders with progression of vascular encephalopathy, diagnosed aneurysm, and sometimes after a stroke. It consists of stenting, clipping or exclusion of the aneurysm from the bloodstream, and balloon angioplasty for narrowing of the arteries.
About treatment for dysfunctions
It is prescribed and carried out in the presence of documented pathology, accompanied by patient complaints and the presence of a clinical picture of a particular syndrome.
Depending on the prevalence of manifestations, conservative treatment is carried out with the following means:
- general vascular (antispasmodics, sedatives);
- tranquilizers;
- antidepressants;
- anti-inflammatory and analgesic (categories of Ibuprofen and Ketorol).
Cases of migraine deserve separate study and differentiation from similar conditions, after which therapy adequate to the diagnosis is prescribed.
If drug treatment is ineffective or acute pathology occurs, microsurgical treatment is used using the following techniques:
- stenting;
- clipping;
- balloon angioplasty.
On the prevention of conditions caused by pathology of the circle of Willis
It consists in the pregnant woman following recommendations on the range, dosage, frequency of taking medications, and using only medications prescribed by a doctor. It is necessary to protect yourself as much as possible from viral infection and avoid stressful situations in every possible way (family members and colleagues of the pregnant woman are also encouraged to do this).
Prevention of life-threatening acute vascular conditions should be achieved by maintaining a maximally active lifestyle in order to prevent problems with blood vessels, and if they occur, active cooperation with the attending physician with unconditional compliance with his instructions is necessary.
What do various options for the development of VC mean in practice?
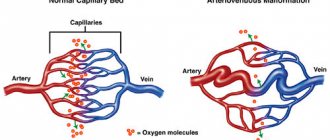
The asymmetry of the structure of the VC leads to a significant asymmetry of blood flow and is an important factor in the development of intracranial aneurysms and ischemic strokes. These disorders typically occur in elderly patients in whom an open VC limits the ability to compensate for acute changes in the arterial blood supply to the brain.
Before the development of these diseases or their complications, a person does not even know that he has anomalies in the development of cerebral vessels.
Aneurysms of the VC vessels
An aneurysm is a protrusion of the vascular wall. Aneurysms of the vessels included in the VC are the most common cerebral aneurysms. Most often they arise in the ACA, at the bifurcation (bifurcation site) of the ICA and in the PCA, at the bifurcation of the BA.
Most brain aneurysms do not cause any symptoms until they rupture. However, with large protrusions, compression of nearby tissues of the central nervous system may occur, which in some people leads to:
- double vision;
- pupil dilation;
- pain behind the eyeballs;
- headaches.
When an aneurysm of the vessels entering the VC ruptures, hemorrhage develops in the space around the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage), the symptoms of which include:
- Sudden onset of severe headache.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Stiffness in the neck.
- Temporary loss of vision or consciousness.
Ischemic stroke with various variants of the VC structure
Disruption of the symmetry of blood flow through the arteries of the brain can contribute to the development of atherosclerotic lesions, which increases the risk of ischemic stroke. An open VC does not provide good collateral blood flow, so the size of the stroke may increase.
Symptoms of ischemic stroke:
- Sudden onset of numbness or weakness in the muscles of one side of the body.
- Sudden deterioration of consciousness, difficulty speaking or understanding speech.
- Sudden visual disturbances.
- Sudden disturbances in walking, dizziness, loss of balance and coordination of movements.
- Sudden onset of headache.