The need for self-realization is inherent in nature. Self-realization is awareness of yourself, your talents and positive aspects, and the application of the information received. The desire for self-expression forces people to seek a place in society by effectively using their abilities. If a person manages to do this, he receives complete satisfaction from life.
Consider the theory of needs
There are several theories of needs.
Maslow's theory of hierarchical needs
Maslow assumed that every need is satisfied to some extent. He suggested this arrangement:
- physiological - 80-85%;
- safety and feeling of security - 70-75%;
- love and sense of belonging - 45-55%;
- self-esteem - 40-45%;
- self-realization - 10%.
The scheme is conditional and changes with an individual approach. Thus, there are people for whom the need for self-realization and self-esteem is more valuable than the feeling of love.
Maslow argued that people's actions are not always driven by economic interests, but that their actions are often motivated by needs that cannot be satisfied by money.
Alderfer's theory of work motivation
Alderfer highlights the need for self-actualization, the need for social connections, and the desire for growth. According to his ideas, the less an individual’s needs of existence are satisfied, the more strongly they manifest themselves. Applying these principles, Alderfer proposed to motivate workers. When meeting social needs, growth needs should be supported. If they are weakly expressed, it is worth doing the opposite.
Douglas McGregor's Theory of Motivation
McGregor identified 2 approaches to management, conventionally calling them “Theory X” and “Theory Y”. The first leadership style involves an authoritarian leader and strict control over the work of employees. The second approach is based on democracy, a number of powers are transferred to employees, work is underway to improve relationships in the team, and the motivation of people and their characteristics are taken into account.
Studying the personality of each person will help you choose an approach. This is the only way to satisfy the need for self-realization of all employees.
Frederick Herzberg's two factor theory
According to Herzberg's theory, employee motivation is influenced by the hygiene factor or a set of conditions under which the employee does not receive satisfaction. This is often due to company policy, relationships with management, working conditions and pay.
Another factor was called "motivator". Thanks to this approach, employees’ motivation to work increases, and they receive satisfaction of the need for self-realization. This occurs due to the possibility of promotion, personal growth, recognition from colleagues and management, and good pay.
The theory of motivation by L. Porter – E. Lawler
The Porter-Lawler model can be described as follows: in order to get results at work and rewards for them, you need to make an effort. The latter are determined by abilities, knowledge, experience, and level of qualifications. The higher the payment, the more effort put in. A person’s awareness of his role in the work process is also important.
Scientists have come to the conclusion that productive work will satisfy the need for self-realization. Previously, it was believed that the result depended on whether the person was initially satisfied. Porter and Lawler's theory has helped in the study of human motivation.
McClelland's theory of acquired needs
McClelland emphasized the needs of achievement, participation and desire in gaining power. The combination of these desires determines the employee's motivation. If you know what motivates an employee, you can use him more effectively by offering tasks the solution to which will suit him. This will improve your workflow. Employees will have the opportunity to satisfy their need for self-realization.
Satisfying the need for creative self-realization
Creativity is the work of creating something new. During the creative process, an individual manages to most fully satisfy the need for self-expression and use all the abilities that are inherent in him. And a socially important result will lead to self-realization.
The acquired skill is not important for creativity. You need to learn to solve problems with creativity.
Creativity is not the ability to compose poetry or paint pictures, but the expression of personality traits, based on its unique traits, characteristics and qualities. Creativity lies at the heart of self-expression, contributing to the development of personal views on the world.
Self-determination and self-realization
How are self-determination and personal self-realization related to each other? Before you begin any movement forward, you need to be able to clearly understand what you are really interested in and what your strengths are.
Everyone has a different nature, so it is not surprising that people have different aspirations. The ability to set a goal correctly is the greatest blessing!
Self-determination is realized through a careful analysis of personal interests, abilities, talents and inclinations.
Professional self-determination is very connected with the life self-determination of the individual, as it directly affects the quality of a person’s life, his self-realization, self-esteem and significance.
Choosing a profession is a critical moment in a person’s life, which tears a person between individual and social needs, between what is desired and what is needed by society.
There are concepts of career guidance and career counseling that help a person in the process of professional self-determination. To help a person decide on a career choice, it is necessary:
- Help analyze all the information and decide what best suits the abilities and desires of the individual;
- Morally support in choosing and help make the final decision.
The main goal of professional self-determination is to create a willingness to independently and consciously plan one’s future and realize the prospects for one’s development.
Personal self-realization
Today, the particular relevance of the problem of personal self-realization is due to the fact that it is a specific defining criterion in the formation of personality. Usually there are two most significant areas of self-realization:
- Professional activities
- And implementation in family life
Social self-realization of an individual consists in achieving social success in life in the amount that a particular individual wants, and not in accordance with the real criteria of social success.
And personal self-realization leads to the spiritual growth of the individual and ensures in the first stages the development of personal potentials, such as responsibility, curiosity, sociability, hard work, perseverance, initiative, intellectuality, morality, etc.
Although personal self-realization is observed in the process of an individual’s life. It becomes possible only on the condition that the individual himself is aware of his own inclinations, abilities, talents, and interests. And, of course, the needs on the basis of which the individual will build goals.
In other words, the subject’s entire life is built on a series of actions. Targeted at personal self-realization and achieving life goals.
To be successful in life, certain efforts must be made, consisting of certain strategies and goals.
Self-realization in society
Man lives in society and can never achieve complete freedom from it. Self-realization in society lies in being able to build strong, trusting relationships with people around you.
Self-realization of a person is a long process. During which innate talents and acquired skills are developed and applied in everyday life.
In society, such people are perceived as accomplished, psychologically stable individuals.
Self-realization in life
What does self-realization mean in life? Do what you want? Earn a lot of money? Find a happy family? Become famous?
Psychologists say that self-realization is a person’s desire to fully reveal his potential and capabilities. The result is a feeling of happiness from what you do.
To evaluate how self-actualized you are, there must be an evaluation criterion!
Let's say you want to realize yourself as a doctor. Then the evaluation criterion may be the number of patients whom you helped recover.
At the same time, recognition is the recognition of patients (not colleagues), and self-affirmation is your level of professionalism.
Another obstacle is solipsism, which proudly declares: “I will make myself!” But self-realization, whether we like it or not, occurs in connection with another person. She needs friendly support, tenderness, love and trust in others.
Social affiliation
Human needs human. After the first two steps of the hierarchy have been completed: the person is well-fed, everything is fine financially, and he is safe, he understands that he is lonely and this weighs on him. He begins to look for a soul mate.
He needs support from others, he needs to know that he is accepted for who he is. He needs companionship, friends, family, love who will accept him as one of their own so that he can be comfortable with them. He needs to know that he belongs to a certain group of people, clan, team, class.
If this need is not satisfied, then the person simply will not be able to live in society, he will experience social maladjustment, and other more serious problems are possible.
Self-affirmation and its pitfalls
From 19 to 30 years old (approximately) we live the next period in life. At this time, we learn to earn money on our own; some succeed, others don’t. Relationships with money at this stage are associated with the degree of psychological maturity and “adulthood”. The dominant needs in this period are professional and career ambitions, as well as the desire to find a soul mate, have a family and children. These two spheres mutually stimulate each other, encouraging young people to create a material basis and gain a certain status in society. Money as a factor of social success becomes the cornerstone; its availability, the ability to earn it and the ability to handle it determine personal maturity.
According to Maslow’s pyramid, with the help of money at this stage we assert ourselves, realize social needs and provide the basis for the realization of biological needs, for example, procreation. And this corresponds to the opening of the first three chakras. It is clear that here there is a serious stratification of people according to value orientations, according to the degree of psychological maturity, and according to the degree of success. Those who have won their place in the sun feel more confident and calm, and those who have not succeeded continue the “race”. At the same time, both of them, for the most part, fall into the money trap. Feeling their strength and power, successful people cannot stop and continue to increase their capital, although on a psychological level the level of happiness no longer increases. This is confirmed by research by American scientists.
It turned out that there is no certain amount of money, after receiving which a person feels completely happy. A person can feel comfortable if his income exceeds the income of the people around him (colleagues, relatives, acquaintances). In this case, there is no specific number - a thousand, ten thousand or a million monetary units, the main thing is to be richer than the rest. But there is an amount beyond which the feeling of inner comfort does not increase. This is approximately 50-100 thousand dollars per year. And even if a person becomes a millionaire, the level of happiness remains the same. A good illustration of the revaluation of attitudes towards money is the film “Duhless” based on the book by Sergei Minaev. There is another category of successful people who strive for independence and freedom with the help of money. These are those who decide that they will no longer work for others and become entrepreneurs and businessmen. Many of them sincerely say: “I created a business to be free, to live the way I want, to have enough money, to have a lot of free time, to not depend on anyone or anything.”
But as a result, it turned out that instead of working for the state or for another person 5 days a week for 8 hours, you now have to work for yourself for 16 hours, 7 days a week. At the same time, there is no opportunity to freely manage money; due to lack of time, such people do not read books, do not go to theaters, cinema, communicate little with loved ones, children, rarely rest... And this money trap is very powerful: gradually - this is how our psyche - people begin to experience pleasure from their position. This phenomenon was even called the “Stockholm syndrome” (once in Stockholm, terrorists took plane passengers hostage, and they, being on the verge of life and death, experienced a strange pleasure, which is why later, at the trial, they even acquitted the aggressors ). It’s the same in business - the owner enjoys working on weekends, and on Monday he arrives at the office before everyone else.
The next category of people - those who have not achieved success, with low self-esteem - hide behind money and strive to use it to strengthen their position, at least in their own eyes. Their inherent anxiety is reflected in worries about spending, saving, and a lot of fantasizing about money. Some people include a psychological defense such as “money doesn’t buy happiness,” deliberately belittling the importance of money and thus maintaining their self-esteem.
And there are those who have found a “golden mean” in their relationship with money - these are people who have learned to earn enough to satisfy their needs, who have not fallen into the traps of money and become dependent on it.
- 2.1. Physiological needs
- 2.2. Needs for security and confidence in the future
- 2.3. Social needs (needs of belonging and involvement)
- 2.4. Need for respect (recognition and self-affirmation)
- 2.5. The need for self-realization (self-expression)
- 2.6. Self-actualization assessment
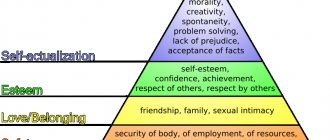
Chapter 2. Hierarchy of human needs. Maslow's model
None of the existing theories of motivation has such an impact on the thinking of managers as the theory of needs, developed by the great motivation specialist Abraham Maslow.
Maslow's theory allows managers to more fully understand the aspirations and motives of employee behavior. Maslow proved that people's motivation is determined by a wide range of their needs. If earlier managers motivated subordinates almost exclusively only with economic incentives, since people’s behavior was determined mainly by their needs at lower levels, then thanks to Maslow’s theory it became obvious that there are also non-material incentives that force employees to do what the organization needs.
Maslow identified five main groups of human needs, which are in a dynamic relationship and form a hierarchy (Diagram 1). This can be depicted as ascending steps.
Scheme 1. Hierarchy of human motivation needs in order of priority
The theory of the hierarchy of human needs is based on a pattern: when a need at one level is satisfied, a need at the next, higher level arises. A satisfied need ceases to motivate.
People need to satisfy needs in a certain order - when one group is satisfied, another comes to the fore.
A person rarely achieves a state of complete satisfaction; throughout his life he desires something.
It is necessary to consider motivational groups in more detail.
2.1. Physiological needs
The needs of this group consist of basic, primary human needs, sometimes even unconscious. Sometimes they are called biological needs. These are human needs for food, water, warmth, sleep, rest, clothing, shelter, and the like, necessary for the survival of the body, maintenance and continuation of life. In relation to the working environment, they manifest themselves as the need for wages, favorable working conditions, vacation, etc.
High earnings provide a decent living, for example, the opportunity to live in a comfortable apartment, eat well, wear necessary, comfortable and fashionable clothes, etc.
To pay for the basic needs of life, employees must be motivated by long-term benefits, providing them with a tangible high income and sufficient remuneration, and providing them with breaks from work, weekends and holidays to recuperate.
If a person is dominated only by these needs, crowding out everything else, then he has little interest in the meaning and content of work, and cares mainly about increasing his income and improving working conditions.
If a person is deprived of everything, he will first of all strive to satisfy his physiological needs. As a result, his views on the future may change.
A person’s dissatisfaction may also indicate the dissatisfaction of needs at a higher level than the level of the need about which the employee complains. For example, when a person thinks he needs a rest, he may actually be feeling the need for security rather than a day off or a vacation.
2.2. Needs for security and confidence in the future
If a person has sufficient physiological needs, then he immediately has other needs related to the safety of the body.
This group ? one of the main life motivators, it includes both physical (safety precautions, labor protection, improvement of working conditions, etc.) and economic (social guaranteed employment, social insurance in case of illness and old age) security. Satisfying the needs of this group provides a person with confidence in the future and reflects the desire to protect oneself from suffering, dangers, illnesses, injuries, losses or deprivations. Confidence in the future is acquired through guaranteed employment, purchasing an insurance policy, pension provision, the ability to store money in banks, and by creating insurance potential through receiving a decent education.
For those who have suffered severe hardship at some significant period in their lives, this need is more urgent than for others.
To address workers' safety needs, employers need to:
1) create safe working conditions for employees;
2) provide workers with protective clothing;
3) install special equipment at workplaces;
4) provide workers with safe tools and devices.
2.3. Social needs (needs of belonging and involvement)
After physiological and safety needs are satisfied, social needs come to the fore.
In this group? needs for friendship, love, communication and emotional connections with each other:
1) have friends and colleagues, communicate with people who pay attention to us, share our joys and concerns;
2) be a member of a team and feel the support and cohesion of the group.
All this is expressed in the desire for warm relationships with people, participation in joint events, and the creation of formal and informal groups. If a person is satisfied with social needs, then he considers his work as part of a joint activity. Work is a cementing environment for friendship and camaraderie.
A reduction in social relationships (work contacts and informal friendships) often leads to unpleasant emotional experiences, the emergence of an inferiority complex, a feeling of being an outcast from society, etc.
To address the social needs of employees, management must:
1) inspire employees to create groups and teams;
2) create conditions and allow the same group of people to work and play together in order to strengthen and facilitate their relationships;
3) allow all groups to be different from other groups;
4) hold meetings to exchange professional issues, discuss matters of interest to everyone and contribute to the solution of professional problems.
2.4. Need for respect (recognition and self-affirmation)
When the needs of the three lower levels are satisfied, the person focuses his attention on satisfying personal needs. The needs of this group reflect the desires of people to be strong, competent, confident in themselves and their own position, striving for independence and freedom. This also includes the needs for prestige, reputation, career and professional growth, leadership in a team, recognition of personal achievements, and respect from others.
Every person enjoys feeling that he is indispensable. The art of managing people is the ability to make each employee understand that their work is very important for overall success. Good work without recognition leads to disappointment in the employee.
In a team, a person enjoys his own role and feels comfortable if he is given and addressed well-deserved privileges, different from the general reward system, for his personal contributions and achievements.
The most objective and stable self-respect is based on the deserved respect of others, and not on external fame, fame or undeserved adulation.
2.5. The need for self-realization (self-expression)
These are spiritual needs. The manifestation of these needs is based on the satisfaction of all previous needs. New dissatisfaction and new anxiety appear until a person does what he likes, otherwise he will not find peace of mind. Spiritual needs find self-expression through creativity and personal self-realization.
A person must become what he can be. Every person is amazingly rich in ideas, but he needs to be convinced of this.
A person’s desire to fully reveal himself, use his knowledge and skills, implement his own plans, realize individual talents and abilities, achieve everything he wants, be the best and feel satisfied with his position is currently undeniable and recognized by everyone. This need for self-expression is the highest of all human needs.
In this group, the best, more individual sides and abilities of people appear.
To effectively manage people you need:
1) assign them personal responsibility for the fulfillment of production tasks;
2) give them the opportunity to express and realize themselves, giving them unique, original work that requires ingenuity, and at the same time providing them with greater freedom in choosing the means to achieve their goals and solve problems.
People who feel the need for power and influence over others and even peers are motivated by the opportunity to:
1) manage and control;
2) persuade and influence;
3) compete;
4) lead;
5) achieve goals and objectives.
All this needs to be supported by praise for good work. It is important for people to feel that they are performing well and being individuals in their own way.
An important fact for managers is that all human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order.
Low level needs.
1. Physiological needs.
2. Needs for security and confidence in the future.
3. Social needs (needs of belonging and involvement).
4. The need for respect (recognition and self-affirmation).
Higher level needs.
5. The need for self-realization (self-expression).
First, the needs of lower levels must be satisfied first, and only then can the needs of higher levels be addressed.
In other words, a person experiencing hunger will first seek to find food, and only after eating will he try to build a shelter. You can no longer attract a well-fed person with bread; bread is only interested in those who don’t have it.
Living in comfort and security, a person will first be motivated to activity by the need for social contacts, and then will begin to actively strive for respect from others.
Only after a person feels inner satisfaction and respect from others will his most important needs begin to grow in accordance with his potential. But if the situation changes radically, then the most important needs may change dramatically. For example, at some point an employee may sacrifice a physiological need for the sake of a safety need.
When a worker whose lower-level needs have been satisfied is suddenly faced with the threat of job loss, his attention immediately shifts to the lowest level of needs. If a manager tries to motivate workers whose safety needs (second level) are not yet met by offering a social reward (third level), he will not achieve the desired goal-oriented results.
If at the moment the employee is motivated primarily by the opportunity to satisfy safety needs, the manager can be confident that once these needs are satisfied, the person will look for opportunities to satisfy his social needs.
A person never experiences the feeling of complete satisfaction of his needs.
If the needs of a lower level are no longer satisfied, the person will return to this level and remain there not until these needs are fully satisfied, but when these needs are sufficiently satisfied.
It must be taken into account that the needs of the lower level form the foundation on which the needs of the higher level are built. Only if lower-level needs remain satisfied does the manager have a chance to succeed by motivating employees through satisfying higher-level needs. In order for a higher level of the hierarchy of needs to begin to influence human behavior, it is not necessary to satisfy the need of the lower level completely. For example, people usually begin to seek their place in a certain community long before their security needs are met or their physiological needs are fully satisfied.
The key point in the concept, Maslow's hierarchy of needs, is that needs are never satisfied on an all-or-nothing basis. Needs overlap, and a person can be motivated at two or more levels of needs simultaneously.
Maslow suggested that the average person satisfies his needs something like this:
1) physiological – 85%;
2) safety and protection – 70%;
3) love and belonging – 50%;
4) self-esteem – 40%;
5) self-actualization – 10%.
However, this hierarchical structure is not always rigid. Maslow noted that although “hierarchical levels of needs may have a fixed order, in fact this hierarchy is far from being so “rigid.” It is true that for most people their basic needs fell roughly in the order presented. However, there are a number of exceptions. There are people for whom, for example, self-respect is more important than love.
From Maslow’s point of view, the motives for people’s actions are mainly not economic factors, but various needs that cannot always be satisfied with money. From this he concluded that as the needs of workers are met, labor productivity will increase.
Maslow's theory has made important contributions to understanding what makes workers more effective. People's motivation is determined by a wide range of their needs. Individuals with high power motivation can be divided into two groups.
The first group includes those who strive for power for the sake of domination.
The second group includes those who strive for power in order to achieve solutions to group problems. Particular importance is attached to the need for power of the second type. Therefore, it is believed that, on the one hand, it is necessary to develop this need among managers, and on the other, to give them the opportunity to satisfy it.
People with a strong need for achievement are more likely than others to become entrepreneurs. They like to do things better than their competitors and are willing to take on responsibility and quite a lot of risk.
A developed need for power is often associated with reaching high levels in the organizational hierarchy. Those who have this need have a better chance of making a career, gradually rising up the job ladder.
2.6. Self-actualization assessment
The lack of an adequate assessment instrument to measure self-actualization initially thwarted any attempt to validate Maslow's basic claims. However, the development of the Personal Orientation Inventory (POI) has given researchers the opportunity to measure values and behaviors associated with self-actualization. It is a self-report questionnaire designed to assess various characteristics of self-actualization according to Maslow's concept. It consists of 150 forced choice statements. From each pair of statements, the respondent must choose the one that best characterizes him.
The POI consists of two main scales and ten subscales.
The first main scale measures the extent to which a person is self-directed rather than others-directed in the search for values and meaning in life (characteristics: autonomy, independence, freedom - dependence, need for approval and acceptance).
The second main scale is called “time competence.” It measures the extent to which a person lives in the present rather than focusing on the past or future.
Ten additional subscales are designed to measure important elements of self-actualization: self-actualization values, existentiality, emotional reactivity, spontaneity, concern for one's interests, self-acceptance, acceptance of aggression, capacity for close relationships.
POI also has a built-in lie detection scale.
Numerous studies allow us to consider the validity of POI proven.
The only major limitation to using the 150-item POI for research purposes is its length. Jones and Crandall (1986) developed a short self-actualization index. The scale consists of 15 items.
1. I am not ashamed of any of my emotions.
2. I feel that I have to do what others expect of me (N).
3. I believe that people are essentially good and can be trusted.
4. I can be angry with those I love.
5. It is always necessary for others to approve of what I do (N).
6. I do not accept my weaknesses (N).
7. I may like people whom I may not approve of.
8. I'm afraid of failure (N).
9. I try not to analyze or simplify complex areas (N).
10. It's better to be yourself than to be popular.
11. There is nothing in my life to which I would particularly devote myself (N).
12. I can express my feelings even if it leads to undesirable consequences.
13. I am not obliged to help others (N).
14. I'm tired of inadequacy (N).
15. They love me because I love.
Respondents answer each statement using a 4-digit scale:
1) disagree;
2) partly disagree;
3) partially agree;
4) I agree.
The symbol (N) following the statement indicates that when total values are calculated, the score for this item will be inverted (1 = 4, 2 = 3, 3 = 2, 4 = 1). The higher the total value, the more self-actualized the respondent is considered.
In a study of several hundred college students, Jones and Crandall found that self-actualization index scores were positively correlated with all scores on the much longer POI (r = +0.67) and with measures of self-esteem and “rational behavior and beliefs.” The scale has some reliability and is not susceptible to “social desirability” response selection. It was also shown that college students who participated in self-confidence training had significant increases in self-actualization as measured by the scale.
Characteristics of self-actualizing people.
1. More effective perception of reality.
2. Acceptance of yourself, others and nature (accept yourself as they are).
3. Spontaneity, simplicity and naturalness.
4. Focused on the problem.
5. Independence: need for privacy.
6. Autonomy: independence from culture and environment.
7. Freshness of perception.
8. Summit, or mystical, experiences (moments of great excitement or high tension, as well as moments of relaxation, peace, bliss and tranquility).
9. Public interest.
10. Deep interpersonal relationships.
11. Democratic character (lack of prejudice).
12. Distinction between means and ends.
13. Philosophical sense of humor (friendly humor).
14. Creativity (ability to create).
15. Resistance to culturalization (they are in harmony with their culture, maintaining a certain internal independence from it).
From the point of view of humanistic psychology, only people themselves are responsible for the choices they make. This does not mean that if people are given freedom of choice, they will necessarily act in their own interests. Freedom of choice does not guarantee the correctness of the choice. The main principle of this direction is the model of a responsible person who freely makes a choice among the opportunities provided.
Table of contents
Hierarchy of needs theory
Maslow distributed needs in order of decreasing importance, explaining this construction by the fact that a person cannot experience high-level needs while he needs more primitive things. The basis is physiology (quenching hunger, thirst, etc.)
A step higher is the need for security, above it is the need for affection and love, as well as the need to belong to a social group. The next step is the need for respect and approval, above which Maslow placed cognitive needs (thirst for knowledge, desire to perceive as much information as possible). Next comes the need for aesthetics (the desire to harmonize life, fill it with beauty and art). And finally, the last step of the pyramid, the highest, is the desire to reveal inner potential (this is self-actualization). It is important to note that each of the needs does not have to be satisfied completely - partial saturation is enough to move to the next stage.
“I am absolutely convinced that a person lives by bread alone only in conditions when there is no bread,” explained Maslow. - But what happens to human aspirations when there is plenty of bread and the stomach is always full? Higher needs appear, and it is they, and not physiological hunger, that control our body. As some needs are satisfied, others arise, higher and higher ones. So gradually, step by step, a person comes to the need for self-development - the highest of them.”
Maslow was well aware that satisfying primitive physiological needs is fundamental. In his view, an ideal happy society is, first of all, a society of well-fed people who have no reason for fear or anxiety. If a person, for example, is constantly lacking food, he is unlikely to be in dire need of love. However, a person overwhelmed with love experiences still needs food, and regularly (even if romance novels claim the opposite). By satiety, Maslow meant not only the absence of interruptions in nutrition, but also a sufficient amount of water, oxygen, and sleep.
The forms in which needs manifest themselves can be different; there is no single standard. Each of us has our own motivations and abilities. Therefore, for example, the need for respect and recognition may manifest itself differently in different people: one needs to become an outstanding politician and win the approval of the majority of his fellow citizens, while for another it is enough for his own children to recognize his authority. The same wide range within the same need can be observed at any stage of the pyramid, even at the first (physiological needs).
Abraham Maslow recognized that people have many different needs, but also believed that these needs can be divided into five main categories:
Physiological: hunger, thirst, etc. Security needs: comfort, consistency of living conditions. Social: social connections, communication, affection, caring for others and attention to oneself, joint activities. Prestigious: self-esteem, respect from others, recognition, achieving success and high praise, career growth. Spiritual: cognition, self-actualization, self-expression, self-identification.
There is also a more detailed classification. The system has seven main levels (priorities):
- (lower) Physiological needs: hunger, thirst, etc.
- Security needs: a feeling of confidence, freedom from fear and failure.
- The need for belonging and love.
- Esteem needs: achieving success, approval, recognition.
- Cognitive needs: to know, to be able to, to explore.
- Aesthetic needs: harmony, order, beauty.
- (highest) The need for self-actualization: the realization of one’s goals, abilities, development of one’s own personality.
As lower-lying needs are satisfied, higher-level needs become more and more relevant, but this does not mean that the place of the previous need is taken by a new one only when the previous one is fully satisfied. Also, the needs are not in an unbroken sequence and do not have fixed positions, as shown in the diagram. This pattern is the most stable, but the relative arrangement of needs may vary among different people.
You can also pay attention to some overlap with Gumilyov’s theory about the development of cultural needs with the growth of the level of civilization and their rapid degradation (for example, when the base of Maslow’s pyramid is violated, that is, physiological or protective needs).
Theory of origin and brief description of the pyramid
The famous American psychologist Maslow was one of the first to draw attention to the fact that human behavior can be studied from the perspective of the norm, that is, positively. Before this (until approximately 1920), all studies in the field of psychotherapy were limited to the study of individuals with deviations, outside the norm.
Freud and Jung alone are worth something! Some of their ideas are still either ridiculed, confirmed or refuted. But these, one might say, are the pillars of psychotherapy!
But we will return to Maslow. In 1954, in his work “Motivation and Personality,” he proposed that all human needs are innate and have their own system. This system consists of five levels, which are arranged in a pyramid.
The main idea of this division is that the pyramid is based on human physiological needs. So, until the previous “layer” of the pyramid is resolved, overcome, satisfied, there can be no talk of any next one. If, for example, you are hungry, then you have no time to think about the “higher matters” of human psychology.
Maslow built his pyramid on the principle of decreasing importance of the previous level. He was of the opinion that a happy society begins with satiety. Satiety means not only food, but also a constant and sufficient supply of water, oxygen, sleep and sex.
It is this position that is the basis for criticism of his theory. After all, it is difficult to find a person for whom everything will be enough.
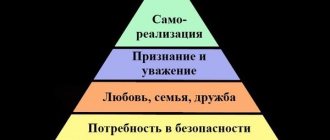
Hierarchy of needs – 5 steps
Initially, the psychologist identified 7 levels, examples and their names a little later. A little later, Maslow’s followers narrowed the pyramid to 5 steps of basic human needs. But the basic idea of hierarchy remains the same.
5 levels of Maslow's pyramid
Physiological needs
This is the first level of the pyramid. We cannot live without satisfying our physiological needs. A person needs them to save life. After all, what will happen to him if he doesn’t take care of food or sleep? Let problems begin, the kind that you want or don’t want, but you have to eat and sleep.
Many psychologists argue that until this basic need is satisfied, the human brain cannot think about anything else. But there are exceptions to every rule. I know cases when a person had no time to sleep and eat until he finished his dissertation, being at the finish line.
Need for security
The instinct of self-preservation plays a role here.
Even in ancient times, it was important for a person to feel safe, so we build houses, fences, and create personal boundaries. If for some reason we fail to satisfy it, life goes “awry”
The person becomes suspicious, fear and anxiety appear. They, of course, can appear for other reasons...
Need for love, friendship, belonging
From this stage we begin to talk about human values. It is his environment that defines them
It is important for any person to feel in a group of people similar to him, to be accepted in it and to find among such group members the closest ones who would become friends
Currently, the family is the only group where a person is accepted unconditionally. Of course, we are talking about a real family, where everyone respects and takes each other into account, where everyone is valuable and needed. In such a family, a person learns what love, a sense of security and acceptance means. The fact has already been scientifically proven: the more healthy love and acceptance a child receives in the family, the better he adapts to society.
Need for self-realization
At the top of the pyramid is a person’s desire to realize himself. It is also called cognitive need. The basis is the path to knowledge and self-development. This is a person’s desire to learn new things, to discover unknown sides of the world. In children, it is expressed in disassembling toys, understanding the structure of objects and phenomena. Adults realize it through science, religion, and travel.
Such a need cannot be satisfied without internal motivation for change, the beginning of a new life. This is the highest need of a person, which makes him wiser and happier. Maslow argues that not all people can achieve its satisfaction. If a person finds himself in a friendly environment, he has adequate self-esteem, he is not afraid to express himself and develop, then he will be able to realize himself.
It should be noted that the forms of manifestation of these needs manifest themselves differently in each person. For some, it’s enough to be told pleasant words, while others seek recognition on stage. Some people want to gain the respect of the whole country, while others just need handshakes and joy after defending their dissertation.
If we talk about an expanded pyramid with 7 levels, then it represents the following hierarchy of needs:
- Physiological - hunger, thirst, sexual desire, etc.
- Security - to feel protected, not to experience fear of failure.
- Belonging and love – belonging to a community, feeling accepted, loving, accepting love.
- Respect, veneration - achieving success, recognition, approval, competence.
- Cognitive – understanding, skills, knowledge, research.
- Aesthetic – beauty, taste.
- Self-actualization is development, achieving harmony with oneself.
At the top of the pyramid is a person’s ideal sense of harmony with oneself. The essence of this theory is precisely that when all needs are satisfied, a person achieves an ideal feeling.
Drawing of Maslow's 7-level pyramid
Application of Maslow's pyramid in areas of life
Some people say: “This, of course, is all cool, but why do I need this pyramid?” You may not need it now, but don’t rush to dismiss it. We become familiar with the described scheme from the birth of the baby.
If you have already had such a happy experience, remember whether a 3-6 month old child smiles at you with pleasure or communicates if he is really hungry? Of course not! Until you feed the little “glutton”, there is no talk of any cute baby, you see in front of you an indignant and screaming little man whom you can’t even try to feed!
The same applies to family relationships. If you and your spouse have different needs, sooner or later problems will begin in such a marriage. For example, you like active recreation, she doesn’t. You strive to attend theaters and cultural events, but he spends all his free time playing computer games and cannot put two words together in a sentence...
It is not only the spouses who interact in the family. You also need to build relationships with your teenagers. For example, take the need for belonging in a teenager. In an effort to satisfy her, such “children” can forget about their studies, moral values, and behavior within the framework of the law.
Well, are we all about family, but about family (although this is my favorite topic!)? Let us now consider the sphere of human work. If he struggles and struggles, but is unable to provide for himself while working “on his own,” then he loses calm, restless sleep, anxiety, and everything is bad. Why? Because he doesn’t get enough sleep (minus 1st level) and doesn’t feel secure for tomorrow (minus 2nd level). What kind of development can we talk about?
When you can’t make money this way, find a job, even if you don’t love it, but which will give you the opportunity for several months not to think: “What should I eat tomorrow?”
Why is it that now many advertisements on billboards and pictures on TV are full of half-naked women and slowly flowing, eating or chewing food? It's simple. Marketers successfully use Maslow's pyramid to stimulate your interest in a product through basic physiological needs!
Methods of self-organization
So, let's look at the basic methods of self-organization that you can use to learn how to manage yourself.
Method 1. Time management. The first thing you need to do to increase your level of self-organization is planning your time, that is, time management. But not just planning, but also following the plans. You also need to manage yourself and your time wisely. Learn the basic principles of time management and think about how to apply them more effectively specifically to your situation. Time management is actually a very broad concept, a whole science, and therefore requires serious study.
Method 2. Developing habits. To learn how to perform the necessary regular actions without any problems, you just need to turn them into a habit. And this can be done by using the simple rule of 21 days - this is the number of days needed for any, even the most hated, action to become a habit. By acquiring necessary, useful habits in this way, you will significantly increase your level of self-organization.
Method 3. Self-motivation. Another good method of self-organization is self-motivation. These words are similar, but their meanings are different. Self-motivation is the definition of some motives for yourself, the presence of which will increase interest in performing the necessary actions or achieving goals. Here, too, you should study the basic methods of self-motivation, decide which possible motives are most important specifically for you, and use them.
Method 4. Social circle. Success in self-organization largely depends on the social circle in which a person finds himself. For example, if all colleagues in one office room are accustomed to “playing the fool,” then even the most notorious workaholic, once in this team, will also significantly reduce his productivity. Therefore, it is worth forming your social circle from people with a high level of self-organization, from whom, in your opinion, there is something to learn in this regard. And, on the contrary, exclude communication with those people who do not know how to manage themselves, do not strive for this, and even dissuade you, they say, who needs all this.
Method 5: Teaching others. And the last interesting method of self-organization that I want to consider is teaching it to someone else. The fact is that when a person teaches others, he subconsciously improves his knowledge and skills; he must be more competent and professional than the students. And in order to teach someone, it is not at all necessary to get a job as a teacher. For example, parents can teach their children, because self-organization will never be superfluous for them either. Older brothers and sisters - younger ones. Finally, you can, by mutual agreement, start teaching your boyfriend or girlfriend. And in all these cases, you will have to, first of all, set a personal example, which will be of great benefit to yourself.
In conclusion, I want to emphasize once again: self-organization is very necessary and important - remember this well. If there were no self-organization, there would be no, for example, the Financial Genius website, and many other things that are created by a variety of people. Those who are able to manage themselves will definitely achieve great success in life and will be able to do great things. And those who don’t even think about it will live “like everyone else.” See for yourself what is more interesting for you...
Now you have some idea of what self-organization is, how to manage yourself, what methods of self-organization can be used for this. Study this topic more deeply, put it into practice, and you will probably soon see the first positive changes.
That's all, I wish you success in achieving your goals! See you again on the pages of the site!
How to apply the pyramid on yourself?
Skillful use of the pyramid, for example, in management or a team, will help you solve problems or prevent them altogether. By using some techniques to highlight a person's strengths, talents and importance in the team, you can properly motivate your staff to achieve success.
You can interact much more effectively with the same children if you take into account their needs and desires.
In order to climb up the pyramid, you can read many books and articles about motivation, but it is better to take an online course or training once. Learning from a person who has walked this path will help you believe in yourself and achieve what exactly you want in this life. Under no circumstances should you listen to amateurs who shout at every corner: “Pay me and you’ll get rich!”
For me, such a person is Pavel Volya.
His online course “Improver Express” will teach 3 main things: initiative, action and efficiency.
The training consists of 23 chips. It was they who helped Volya turn from a simple beggar Penza guy into the highest paid presenter of the TNT channel and my favorite stand-up comedian. According to Forbes magazine, Pavel earns $2.5 million annually.
The course is suitable for both men and women from 16 years of age.
How the training will take place:
- You receive theory and practical assignment.
- Do it.
- If you did it right, move on to the next one.
If you don’t mess around and do all your homework responsibly, then pleasant changes await you: at work, in your personal life, with relatives and friends. This will lead to more money, connections and success.
Cost – 15,000 rubles. with access forever, but there is also the opportunity to take the course for 3,000 rubles.
If within 2 weeks you decide that the course is not suitable for you, your money will be returned.
After registering for training, a girl from Pavel’s team will contact you and answer all your questions regarding the training. You will discuss payment terms with her.
Also in this article you will find reviews of all courses of the “Willpower” project from Pavel and Laysan Utyasheva.
Money and choice of profession
In adolescence (16-18 years old), young people think about their future, about choosing a profession, about how they would like to live their lives, based on their childhood experiences and the experiences of their parents. At this age, ideological positions are also formed. And money plays an important role in these processes.
Very important decisions regarding the future are made based on childhood experiences with money. For example, those who had a lack of money in their family decide to choose a profession or job that would bring a large financial income. In this case, such a factor as the substantive attractiveness of the future work may be ignored. That is, a profession or job is chosen not to one’s liking, not in accordance with what the young person likes, but according to the principle of “earning as much as possible.” It is clear that there are those who, despite financial difficulties in their family, choose a profession based on their interests, hobbies and abilities. At the same time, those who were brought up in wealthy families do not always choose a profession according to their interests.
Parents can have a great influence when they decide for their child where to study, since they have the money. At this stage, money acts as a kind of “arbiter of future destiny.” And depending on what decision is made, such will be the future fate of the young man. Boys and girls understand and feel the power of money even more. Some people succumb to it, while others have it in mind, but follow their personal preferences and already established values.
Criticism
Many psychologists still criticize the theory of the pyramid of needs. They justify this by the fact that the economic situation at the time the theory was created left much to be desired, so the opinion about the dissatisfaction of basic needs was relevant. Now a person is fed up with various services, and he no longer needs to suffer from a lack of something, he no longer has to survive.
Modern researchers confirm that now a person does not have the same sequence of needs as in the pyramid. It is not at all necessary to receive love first, and then value, and then development. Now motivation has changed a little; there are other motivators that help you achieve success and change. Read more about this in the article.
When spirituality comes
After 30 years, many realize the fact that all desires cannot be satisfied, all money cannot be earned. People are beginning to lean toward a settled life, looking for comfort, coziness, and security. A certain result of the previous stage of life is summed up, the place of money in the value system is revised. With the healthy development of the situation, the importance of money decreases and values such as family, children, interests, and hobbies come to the fore. In the case of an unhealthy trend, money remains a super value or is pushed far into the background. This period lasts until approximately 35-37 years.
At this age, the so-called essential crisis occurs. The needs of the soul come to the fore. Many people develop a vague longing for something sublime, a need arises for higher values and meanings. That is, according to Maslow, basic and social needs have already been realized to one degree or another, the turn of mental and spiritual needs comes, and the fourth chakra, Anahata, is “turned on.” If this happens, then money becomes a good support in the spiritual development of the individual.
A certain part of people begins to participate in various trainings and practices, allocates an expense item for this, which ultimately becomes an investment in unlocking their human potential. Most people continue the “race for happiness and freedom,” assuming that these states are directly related to money. Some of those who have never achieved financial and social success devalue the importance of money in their lives and also become involved in the “spiritual” life. But such spirituality becomes an escape from ourselves, compensation for the failures of the previous stage of life.
Advantages and disadvantages
As I already wrote, many recognized the fact that Maslow saw in his theory only ideal people who strive for self-actualization, who are characterized by a hierarchy of need satisfaction.
But the Australian John Barton put forward the idea that all needs are important to a person, regardless of the order in which they are found. And by the way, achieving self-actualization is not important for everyone. This is a short summary of the cons.
The advantage of this classification of needs is that Maslow was the first to talk about human values, describe and characterize the needs and motivation of the individual.
Self-realization goals
The need for self-realization lies not only in the desire to improve self-knowledge, but also manifests itself as a result of working with the inherent potential and constant growth. People who have realized their own internal resources are usually called successful in life. The psychological problem of personal self-realization contains a discrepancy between the energetic and mental capabilities of the individual and the level of his actualization. In other words, due to various life situations, the real potential of the subject may not coincide with the final result of his activities, which often leads to a feeling of dissatisfaction with his life. However, despite this, the need for personal self-realization is preserved in each subject.
Although personal self-realization is observed in the process of an individual’s life, it becomes possible only on the condition that the individual himself is aware of his own inclinations, abilities, talents, interests and, of course, needs, on the basis of which the individual will build goals. In other words, the subject’s entire life is built on a series of actions aimed at personal self-realization and achieving set life goals. To be successful in life, certain efforts must be made, consisting of certain strategies and goals. The main condition for personal self-realization is the implementation of such strategies and achievement of goals.
As an individual grows, his needs also change, therefore, goals and strategies also change. For example, in childhood, the main goal of an individual is study, and in adolescence, goals related to determining the choice of profession and resolving issues of intimate life begin to prevail. After achieving the first strategy or stage of self-realization, when the individual has already started a family and has decided on a profession, the mechanism for correcting and transforming strategies and goals comes into play. So, for example, if the need for career growth is satisfied and the individual receives the position he sought, then this goal goes away and the process of adaptation to the position, colleagues, etc. begins. Something similar happens in family relationships. The choice of self-realization strategies and setting current goals takes into account the age category of the subject, his character and immediate needs.
Self-realization in life has its own specific methods and tools for implementation. Every day an individual reveals himself in work, hobbies and interests, etc. However, today the main and important tool through which the full potential of an individual is revealed is creativity. Many psychologists believe that only with creative activity does an individual engage in excess activity without pursuing a specific goal. In other words, creative activity acts as a voluntary activity, for which an individual is ready to expend all his potential, all his strength in order to express himself and his own potential. And the following universal human values, mechanisms and needs motivate an individual to painstakingly and long-term work on himself:
need for recognition in a team;
in the development of intelligence;
desire to start a family;
the desire to achieve success in sports or become physically developed;
the need for an elite profession, career growth and work with high earnings;
the desire to constantly improve oneself;
desire for social status.
Satisfying the need for self-realization in the profession
Personal expression plays an important role today. High demands are placed on a person for two reasons:
- Competition in the labor market.
- Difficult life circumstances.
Satisfaction of the need for self-realization is expressed externally and internally. External manifestation implies achievements, for example, receiving a promotion, an increase in wages, respect from colleagues. Internal self-realization is the development of useful qualities, gaining knowledge and improving skills.
This type of self-realization is characterized by continuity, creativity, setting and achieving goals. Here you can add the disclosure of personal potential, recognition from people engaged in a similar type of activity and other things.
Self-realization in the profession is strongly influenced by personal traits, for example, flexibility of thinking and behavior, ability to organize, communication skills, and the ability to work in a team.
Bottom line
The definite result is the age of 50 years. Those people for whom the needs of the soul have not become dominant stop in their development, many begin to get sick, stagnation arises in their mental life, the egocentric position intensifies even more, life goes into decline, no matter how much money is made. The passing away of many rich and famous people after 50 is proof of this.
How to survive the age crisis without losses
Those for whom the needs of the soul have prevailed continue their development; many are carried away by one or another type of creativity, thus opening the fifth chakra - Vishuddha. And money at this stage continues to be a good help and finally turns into a means for further development. This movement continues until the end of life
And it no longer matters whether a person manages to fully reveal his potential, whether he manages to open the higher chakras (sixth and seventh) - his life was not lived in vain, he realized most of the needs of his soul
Main factors in the development of personal self-realization
The main factors are considered:
- Internal . Perception of the surrounding world, personal interests, preferences, attitude to rules, laws.
- External . Relationship with parents and pedagogical education.
- Public . The human environment, society, laws and customs of the state where the person was born and lives.
- Hereditary . Genetics is important for self-realization. Children receive the traits of their parents at the biological level and adopt talents. Unique abilities can be developed.
For each individual, the development of personality takes place according to a special program. This confirms the uniqueness of each of us.
More than 9,000 people have gotten rid of their psychological problems using this technique.
The methods of self-realization for a woman may differ from the methods chosen by men. Age, country of residence, and genetics matter. But based on the characteristics of the factors, it is possible to assess the level of a person’s self-realization and the desire for it.
Read our article on the secrets of self-confidence →