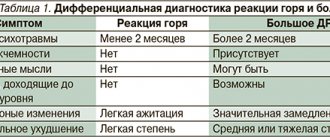
Severe neurosis and asthenic neurasthenia
Reactive severe asthenia can occur with severe neuroses. The disease is complemented by the following clinical signs:
- absentmindedness;
- forgetfulness;
- autonomic disorders - unexplained difficulty breathing, sweating, changes in blood pressure, increased heart rate;
- high level of anxiety;
- increased fears and phobias;
- decreased sex drive;
- fluctuations in appetite;
- increased sensitivity to bright light and loud sounds;
- impaired speed and quality of thinking (cognitive dysfunction);
- concomitant depressive (affective) clinic.
However, the diagnosis of neurasthenia has now lost its relevance; it was removed from the ICD 11th revision (2019). The problem lies in the inaccuracy of the pathogenetic mechanisms, and the symptoms can be placed within the framework of other diseases and conditions.
In adult men
The course of affective disorders is individual, the dependence on gender is almost not expressed. However, men may have other prerequisites for developing the disease. For example, they more often become participants in hostilities or suffer financial (career) failures more difficult.
The social roles that are imposed on boys from an early age increase the demands placed on themselves. Young men start working earlier in an effort to achieve success, which exposes them to high levels of stress. We must not forget that personal characteristics are different for all people, that is, not everyone can withstand the pressure applied.
Over the years, the condition worsens due to chronic fatigue, family problems, and aging. Losing a job or wife in middle age often becomes a critical moment when adaptation mechanisms are disrupted. At the same time, men are less likely to go to doctors, not wanting to show their own weaknesses, or even completely deny the existence of a problem.
Among women
Now women are trying to share the same social functions as men, while caring for children and maintaining everyday life. An exaggerated sense of responsibility leads to them taking on too many responsibilities. Unofficially, psychiatrists call this the “hunted horse” syndrome.
Prolonged intellectual and psychophysical overstrain becomes a trigger for the development of affective disorders. Another common cause of asthenic depression in women is the pre/postpartum period. Violations are aggravated against the background of hormonal imbalance, as well as in the absence of support from loved ones.
In children
Unfortunately, children are also susceptible to developing the disease. The normal development of the psyche largely depends on obtaining a positive emotional experience, adequate upbringing, and a “healthy” social environment. Vulnerability is determined not only by age, but by a person’s personal characteristics.
Children may experience all the symptoms characteristic of asthenic depression. However, they cannot always correctly formulate their concerns or are completely silent about them. The painful condition is hidden behind complaints of boredom, strange pains, and restless sleep.
As the disorder worsens, the child begins to distance himself from others, stops taking part in games, and moves away from peers. A decline in academic performance leads to conflicts in the family and school. It is not uncommon to skip classes, run away from home, and spend time alone.
The appearance of depressive behavior at a young age should alert parents and teachers. Children often remain silent about bullying at school, cases of violence (including sexual violence), and disharmonious relationships in the family. Lack of timely treatment causes delayed psychomotor development, the occurrence of more severe diseases, and suicidal behavior.
Causes of the disease and risk group
Not every person becomes neurasthenic, even under enormous loads and stress. Most often, asthenic neurosis affects people with the following characteristics of character and lifestyle:
- having an asthenic type of character, the main features of which are vulnerable pride, an exaggerated sense of one’s own inferiority, isolation, shyness, irritability, dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, suspiciousness, anxiety, increased exhaustion;
- those who deliberately neglect proper rest are workaholics;
- those who do not know how to properly organize the work process;
- those who strive to bring work to perfection, even to the point of missing deadlines, are perfectionists;
- overly responsible, striving to complete work on time and in full at any cost;
- those who have taken on an overwhelming amount of worries - those working in several places, students with part-time jobs, housewives with children and sick elderly relatives, etc.
The character traits described may be the result of personality traits, or too strict upbringing with exorbitant demands, or heredity to asthenia. People with neurotic character traits are a risk group for the appearance and development of asthenic neurosis, but character traits are not enough; a psychotropic factor is also needed, which gives impetus to the onset of the disease.
In addition to the personality psychotype, the main causes of asthenic neurosis lie in the negative impact of an endogenous or exogenous nature on the human psyche:
- excessive physical or intellectual stress leading to exhaustion of the nervous system;
- excessive demands made by management, colleagues, relatives, excessive criticism on their part, contributing to the development of an inferiority complex;
- an unhealthy environment (prejudice, bullying) in the workplace, at an educational institution or in the family, in which a person is constantly in anticipation of a scandal, insult, or physical violence;
- work or study in a highly competitive environment that does not provide the opportunity to fully rest and relax;
- incorrect choice of type of activity, education, including at the insistence of parents or other relatives, the need to engage in unloved work;
- chronic diseases that weaken health and complicate the performance of professional duties;
- endocrine diseases that disrupt the balance of the autonomic nervous system;
- stimulating the nervous system with alcohol and drugs;
- unhealthy, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, obesity, leading to metabolic and hormonal imbalances;
- long-term financial problems causing feelings of inadequacy.
Crashed Horse Disease: The Face of Modern Depression
According to WHO experts, depressive disorders as a cause of temporary disability and in terms of the degree of economic damage caused will soon take one of the leading, if not first, places. At the same time, psychiatrists, psychotherapists, and doctors of other specialties are increasingly noticing that patients suffering from depression have, for quite some time now, almost completely lost their classic “look” described by Jaspers and complain about anything, but not low mood, a feeling of melancholy or lethargy . The so-called atypical, masked or larvae depression has become, perhaps, excuse the pun, the most typical. This makes it difficult to identify it and, naturally, provide effective, timely assistance. Patients spend months, and sometimes years, visiting the offices of therapists, surgeons, neurologists, cardiologists, gastroenterologists, undergoing expensive tests, and “testing” dozens of medications. Increasingly, we observe that internists, despairing of helping a patient with persistent arterial hypertension, arrhythmia, peptic ulcer disease or colitis, who does not have clear signs of a depressive disorder, add an antidepressant to therapy and achieve rapid improvement in the treatment of a seemingly purely somatic illness.
What is the reason for such an obvious, rapid, if not catastrophic pathomorphosis? The explanation lies in the dramatic changes in the living conditions of modern man and Russians in particular. We, who have been in the “sleepy stupor of stagnation” for decades, and are now forced with our elbows, fists, other places and, fortunately, more and more often, with our brains, to win a worthy place in the sun. But, as they say, every good has its silver lining, the ever-accelerating pace of modern life, all these information and technological “explosions,” and the ruthlessness of competition inevitably give rise to a real epidemic of chronic stress, affecting almost all layers of our society. However, stress, you say, is a well-known and well-studied problem, what does depression have to do with it? And despite the fact that it is stress that increases the number of “exhaustion depressions,” “vegetative,” “somatized,” “larved” and other similar atypical depressions, which are based on special mechanisms that bring originality to the clinical picture of depressive disorders. In the anamnesis of such patients, there is usually no trace of hereditary burden or specific “fresh” psychotrauma, there are no clearly defined “episodes” or “phases”, and more often there is a hot “burning” at work, a series of “blows of fate”, simply unabated pain over the years , lived aimlessly or in pursuit of a mirage, concern for children rushing in vain in attempts to become “people” or, on the contrary, who have broken out, and are now reaping the fruits of success, which are very reminiscent of apples from the famous tree in the Garden of Eden. In the behavior of these people there is usually no “notorious” psychomotor retardation, at times they may even seem active, “lively”, only sometimes their eyes seem to dim or a “cloud” appears on their face, especially if they manage to find something truly important for this person, “ sore subject. Such patients characterize their mood as “normal” or, in extreme cases, unstable. Only with more careful questioning does it become clear that periodically and over time, more and more often, they feel “tired of life,” twitchiness, irritation, internal tension, anxiety, and the inability to relax. Often there is no feeling of rest after sleep, weekends or vacations, apathy and “laziness” set in, or life loses its fullness and brightness and proceeds as if on “autopilot”; A person accidentally pulled out of the everyday bustle becomes confused - he doesn’t know what to do, what to want. In most cases, the complaints of such patients are purely somatic in nature, and at the same time, there are often somatic diseases that explain these complaints, quite real, confirmed by paraclinical studies. Only sometimes experienced internists can notice that, for example, the severity and persistence of pain in osteochondrosis or gastritis or other symptoms are exaggerated, that is, they seem to be aggravated, and they are usually resistant to treatment. The symptoms of such depressive states are practically indistinguishable from the so-called “chronic fatigue syndrome”, characteristic of long-term viral infections, and depression should be differentiated from this syndrome first of all. True, such differential diagnosis is quite technically complex and requires high professionalism of specialists and modern laboratory and instrumental base.
What are the pathogenetic mechanisms of the type of depression under discussion? To explain their development, the most acceptable concept is nonspecific protective-adaptive reactions of the nervous system, proposed by Yu.L. Nuller. When, as a result of prolonged debilitating effects (chronic stress), a general deficiency of the body’s energy resources develops (primarily the resources of the nervous system), a nonspecific anxiety reaction is activated through the feedback chain (sometimes patients feel this physically - they complain of worsening sleep, internal tremors, muscle tension , symptoms appear that are considered “neurotic” - persistent cephalgia in the form of a “helmet” on the head, a “lump” in the throat or difficulty swallowing, a feeling of lack of air or increased heartbeat). In parallel, according to the law of locus minoris resistencia, old or dormant somatic diseases are exacerbated, which also does not contribute in any way to identifying the true triggers of health disorders. Since the alarm reaction (nonspecific activation) does not solve the problem, and the depletion of the nervous system continues, the second, deeper “echelon” of defense is activated - depression, which, within the framework of this concept, is not a disease, but a special mechanism of protective inhibition developed by evolution that does not allow wasting the last, “untouchable” reserve of strength. But for a reasonable person living in society, this mechanism loses its protective meaning - he cannot “hide” from life, driven by a sense of duty, responsibility, obeying generally accepted rules and social laws, and finally, simply by inertia, he continues to fuss and at the same time constantly receives signals from his nervous system about approaching internal “bankruptcy”. Possessing the ability to predict, such a person, on a conscious or subconscious level, seems to constantly ask the question: “How to live on, being in a state of squeezed lemon?” And he vaguely senses or imagines the possibility of a complete collapse in all directions. This gives rise to increased anxiety, periodically reaching the level of despair or panic. The latter is often accompanied by vegetative “storms” (in the form of blood pressure fluctuations, arrhythmias, gastrointestinal dyskinesias), which were previously usually classified as vegetative-vascular dystonia or diencephalic (hypothalamic) crises, and are now increasingly called “panic attacks.”
When such crises or attacks are repeated, obsessive-phobic mechanisms are activated, which, along with the protective and adaptive reactions described above, form a vicious circle of self-maintenance of depression. And when all these mechanisms, operating not only at the psychological, but also at the biological level, are turned on, the patient, unfortunately, is often no longer able to help either proper rest or the most sophisticated psychotherapeutic techniques. We need means that reliably break the vicious circle of “exhaustion – anxiety – exhaustion” and block the adaptive reactions of the nervous system, which have lost their protective meaning in a person and only support the state of the disease.
So far, only tranquilizers and antidepressants can claim to be such drugs.
In addition, treatment for depression always requires an integrated approach. Along with a comprehensive examination (due to the difficulties described above in distinguishing between somatic and “depressogenic” symptoms), treatment with antidepressants should be combined with psychotherapy and psychological counseling. At the same time, psychotherapy and the work of a psychologist, regardless of the techniques used, are designed to provide solutions to the following fundamentally important tasks.
- Description (in a form accessible to the patient) of the nature, mechanisms of development and, most importantly, the reversible nature of depressive disorders.
- Familiarize the patient with the peculiarities of the effects of the drugs used and the need to strictly follow the recommendations given by the doctor!
- Identification of the main debilitating factors - overload, external and internal conflicts, addictions, “dysfunctional” relationships and cognitive processes, and in the longer term - the formation of a new, less “cruel” lifestyle in relation to the nervous system and the body as a whole. This process is complex, time-consuming and leads to success only if it is started on time - when the patient already has the desire and strength to change something, and he himself is looking for “new ways”, and the psychotherapist, as required by one of the basic laws of this profession, plays not a directive, indicating, but an accompanying (“facilitating”) role. At the same time, we must help the patient understand that otherwise (if such searches are abandoned), the risk of at least repeated courses of antidepressant treatment remains.
Therapy for modern depression is usually an effective process, but it is far from simple and cloudless; relapses are quite common, and there is often a tendency towards chronic depressive disorders.
An ideal antidepressant has not yet been proposed that combines high activity, “strength”, broad spectrum of action with the absence of side effects. The Regional Consultative and Diagnostic Center widely uses the most modern treatment regimens and combinations of drugs, which are more reliable, versatile and have minimal side effects and are recommended by leading specialists in neurology and psychotherapy.
Psychotherapist Vladimir Mikhailovich Podgrushny conducts consultations at OKDC and is ready to help in a difficult situation.
share information
0
Social buttons for Joomla
Symptoms and signs of asthenic neurosis
Experienced specialists are able to identify asthenic neurosis at an early stage of its appearance. The symptoms of the disease depend on its clinical form. General signs of the presence and development of neurasthenia are the following symptoms, characteristic of all phases:
- rapid physical and mental fatigue, decreased performance due to difficulties concentrating;
- increased anxiety and irritability, sudden mood swings;
- headache of a diffuse nature that occurs in the evening, which is characterized by a feeling of squeezing;
- dizziness that occurs during physical and nervous overstrain with a feeling of rotation in the head, rather than objects in the visual zone;
- cardiovascular disorders - stabbing or pressing pain in the heart area, arterial hypertension, palpitations, tachycardia, pallor or redness of the skin even with slight excitement;
- dyspeptic disorders - heaviness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, flatulence, as well as constipation and diarrhea without changing the menu and diet;
- deterioration or exacerbation of appetite;
- increased urge to urinate in a tense situation;
- decreased libido in men and women, erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation in men;
- sleep disorders.
If treatment is not started on time, the disease develops with intensification of symptoms and transition to another, more severe form.
Depression: can you recognize it yourself?
Not everyone should overreact to tiredness and fatigue and associate it with depression. After all, such symptoms are an adequate response of the body to stress. You should be wary if symptoms do not go away for 14-20 days, even with prolonged rest or a change in activity from active to passive and vice versa.
The main 7 manifestations of depression, by which you can identify it yourself, look like this:
- Sleep is disturbed. The patient cannot fall asleep for a long time or sleeps restlessly, and then during the day he suffers from lack of sleep all the time.
- Rest does not help overcome fatigue. Even if for 7-10 days you try to rest, lie down, walk in your favorite places, your mood is not restored.
- Nothing makes me happy. Things that previously caused joy and positive emotions (watching TV, hobbies, talking with a friend) begin to openly irritate and even bring you to tears.
- The mood is statically negative. Neither bad nor good events help change your own mood.
- Mental abilities are reduced. Concentration on standard activities, daily routines and absent-mindedness are impossible.
- Feeling overwhelmed. Most often occurs after exercise. We are talking about a standard load, which was previously tolerated calmly and did not cause discomfort.
- Sensitivity to irritants. A depressed person reacts to bright lights and loud sounds absolutely negatively.
How depression is diagnosed and treated by specialists
If you don’t want panic attacks based on vegetative crises to join your depression in addition to fatigue and irritability, you should get treatment. Moreover, fear can reach such a level that a person simply “locks himself at home” - he is afraid of everything, even going outside. No wonder: panic attacks are accompanied by cold sweat, strong heartbeat, panic, and a feeling that it is impossible to breathe air.
Therefore, to determine the causes of astheno-depressive disorders, neurology resorts to the following methods:
- Clinical and anamnestic examination. It involves a conversation with a psychotherapist. A highly qualified specialist with knowledge and experience will quickly identify symptoms and assess what exactly caused the disease.
- Study. A medical psychologist works with pathologies, recording deviations from the norm. Typically, the examination is carried out using tests on the level of thinking, attention and memory.
- Instrumental and laboratory methods. They allow for differentiated diagnosis to distinguish depression from organic disorders and endogenous diseases.
- Consultations from other specialists. This usually includes a neurologist and a psychiatrist.
Hypersthenic form
The first phase of asthenic neurosis is characterized by the dominance of excitability, irritability, and emotional instability. A neurasthenic person is not restrained in emotions, raises his voice in normal conversation, shouts during an argument or quarrel, and allows insults. The absent-minded attention of the sick person leads to a decrease in the productivity of any type of activity, since he is constantly distracted by irritants and has difficulty returning to the work process. The patient is haunted by dreams related to daytime events and problems. Having difficulty falling asleep, he often wakes up, and in the morning he feels exhausted and unrested.
Irritable weakness
This is the next phase of the disease if adequate treatment was not carried out in the first. From the name it is clear that the stage is characterized by increased irritability against the background of increasing mental exhaustion. Easily excited for any reason, the patient, after a short-term, bright burst of temper, feels powerless. The state of excitement is easily replaced by a feeling of resentment and crying. Concentration and concentration are difficult, causing fatigue, headaches and other painful sensations of various localizations. Repeated distractions from the work process with the desire to take a break do not relieve fatigue, and returning to work does not bring the expected results, which leads the neurasthenic to severe mental exhaustion.
Hyposthenic form
It can develop as the next phase of asthenic neurosis or occur immediately in people with an asthenic psychotype. At this stage, a patient with neurasthenia suffers from mental and physical weakness, lethargy, low mood, lack of interest in any activity, and passivity. Feelings of sadness and anxiety haunt him constantly, causing emotional instability. A neurasthenic person is prone to tearfulness, touchiness, and complaints about his health. Being focused on his sensations, he cannot concentrate to perform intellectual tasks or physical work. Asthenic neurosis can be either an independent disease or a harbinger or manifestation of more serious, difficult to treat mental disorders - schizophrenia, atypical depression. Neurasthenia can also be a symptom of somatic diseases - HIV, tuberculosis, oncology, etc. Therefore, it is so important to consult a specialist in time when the first signs of the disease appear. An experienced psychiatrist or psychotherapist at the Neopsy Mental Health Center is able to differentiate this disorder from other diseases and prescribe effective treatment with a lasting positive therapeutic result.
Treatment of asthenic neurosis at Neopsy
Methods for diagnosing asthenic neurosis at the Center include the clinical-psychopathological method - a conversation with the patient (with his consent - with relatives), studying the medical history at the first consultation during the collection of anamnesis. Usually this is enough for our experienced specialists to identify neurasthenia. But to make a more accurate diagnosis, in the presence or suspicion of the possibility of somatic diseases, additional laboratory and hardware examinations and consultations with related specialists are prescribed. After confirmation of the diagnosis, an individual treatment plan is developed, which includes psychotherapeutic methods of influence, physical and dietary therapy, and drug treatment.
The Center’s specialists are fluent in all modern methods of psychotherapeutic assistance for asthenic neurosis, including hypnotherapy, relaxation, resource trance, autogenic training, etc. Together with the patient, a psychiatrist or psychotherapist develops a way to reduce physical and intellectual stress (up to changing jobs, giving up part-time work). etc.), rest, sleep and nutrition regime. The high professionalism of the specialists at the Neopsi Center for Mental Health allows us to treat asthenic neurosis with high efficiency. Contact us for help through the website services or call the specified phone number.
Call and we will help solve your problems!
Diagnostics
The main problem is that only a few patients get an appointment with a specialized specialist on time; the majority turn to therapists, cardiologists and other doctors. Naturally, a person can regularly take medications prescribed by a doctor for years without any effect, while his psycho-emotional state will rapidly deteriorate. By the way, this can cause not only a relapse, but also serious health problems caused by psychosomatics.
Doctors pay primary attention to collecting anamnesis and analyzing complaints. It is equally important to exclude organic causes of asthenic syndrome. Therefore, it is mandatory to undergo general clinical and biochemical blood tests, undergo an ultrasound of internal organs, Dopplerography of cerebral vessels, ECG, Echo-CG, X-ray of the chest and spine. According to indications, EEG, tomography and other more in-depth studies are additionally prescribed.