Feeling weak in your hand? Do you feel a sharp numbness in your fingers? Can't perform basic hand movements? Having trouble moving your hand? Perhaps we are talking about the problem of ulnar nerve neuropathy, which requires complex treatment under the supervision of professionals.
At Medical, they will help you determine the exact causes of ulnar nerve neuropathy, prescribe treatment and prevention of the disease, help you quickly relieve pain and recover as quickly as possible.
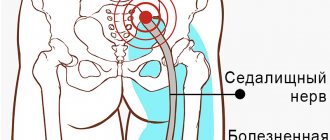
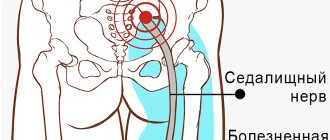
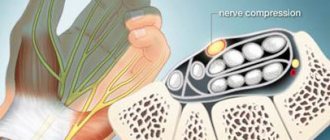
Ulnar nerve neuropathy is a common condition in which the nerve becomes compressed or pinched. It is this nerve that is responsible for the sensitivity of the fingers (little and ring fingers), and also plays an important role in the movement of the hand. It is considered the longest nerve of the brachial plexus.
Symptoms of ulnar nerve neuropathy
- the elbow and arm become weak;
- obvious motor impairments, when it is impossible to move the elbow or the whole arm;
- decreased hand sensitivity;
- the little finger and ring finger go numb;
- when a person makes a fist, the fingers do not touch the palms;
- when the patient puts his hand on the table, it becomes difficult for him to lift or even move his little finger;
- the shape of the hand becomes similar to a “bird’s paw” due to developing atrophic processes.
To confirm the diagnosis against the background of these symptoms, the neurologist performs tests. MRI diagnostics may also be needed to determine the level and nature of the lesion.
What to do at home if your elbow hurts
Elbow pain can appear suddenly in a person or increase gradually. Their causes can also be obvious (trauma, inflammation) or completely unclear (slowly developing chronic inflammatory and degenerative pathological processes).
In any case, if you experience constant pain, you should not:
- treat yourself with folk remedies or medicines that helped a neighbor;
- panic – all this can be treated, but only by specialists; You will be helped in a medical clinic, Moscow - the clinic’s specialists have extensive experience in the treatment of pain syndrome of the elbow joint.
How to treat a sore elbow at home
There is no point in delaying a visit to the doctor. But sometimes circumstances develop in such a way that pain in the elbow needs to be relieved urgently, but there is no way to see a doctor. To temporarily eliminate pain in the elbow, you can use medicinal and non-medicinal means, but you need to remember that this will not cancel a visit to the doctor:
- Painkillers in tablets:
- paracetamol (trade names Efferalgan, Panadol, Paracetamol) – for pain you can take a 500 mg tablet; contraindications: severe liver disease, chronic alcoholism;
- medications from the group of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - ketoprofen (Ketonal, Artrum) has the most powerful analgesic effect; You can take a 100 mg tablet once; contraindications: gastrointestinal ulcers, severe kidney and liver diseases;
- nimesulide (Nise) is a medicine from the NSAID group that does not cause significant side effects from the gastrointestinal tract; for pain, you can take a 100 mg tablet.
- Pain-relieving ointments, creams, gels – applied externally and can be no less effective than tablets; Moreover, they have no side effects (except for allergies) and contraindications:
- ointments with diclofenac : Voltaren emulgel, Diclofenac gel;
- ointments with ketoprofen : Bystrumgel, Artrum gel, Ketonal cream and gel;
- ointments with nimesulide : gels Nise, Nimulid, Nimesulide.
- Injections (injections of medicinal solutions). Many patients do not have a medical education, so it is better to replace injections with rectal (introduced into the rectum) suppositories (suppositories). In terms of absorption rate and effectiveness, this corresponds to intramuscular injections. The following rectal suppositories can be used:
- Diclofenac – at a dose of 100 mg; contraindications: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
- Ketonal – at a dose of 100 mg; contraindications as for Diclofenac;
- Indomethacin – 100 mg; contraindications, like Diclofenac.
Well, if you still know how to give injections, then you can administer 75 mg of Diclofenac intramuscularly (a medicinal solution of 3 ml is produced in ampoules, 25 mg in 1 ml, a total of 75 mg in an ampoule).
Drugs for treating acute pain in the elbows at home
Exercise therapy exercises will also help. If you experience significant pain before training, it is better to consult your doctor. But sometimes you can start doing the simplest light exercises on your own.
The main thing is to continue training every day, but do not overdo it, do not make sudden movements and do not continue training when the pain increases.
Effective exercises:
- bending all the way and straightening the arms at the elbows; repeat 15 times;
- rotational movements with arms bent at the elbows; do first 10 times to the left, then 10 to the right;
- simultaneous squeezing of a tennis ball with the right and left hands; repeat 10 times.
What not to do if you have elbow pain
If you have constant pain in your elbow, then you shouldn’t:
- lift weights;
- constantly perform the same professional movements with a load on the elbow joint; if this is not possible, then you should change your job or give up playing sports such as tennis, basketball;
- supercool;
- constantly expose yourself to stress and overload at work;
- smoking, regularly drinking alcohol;
- self-medicate.
When you need to see a doctor urgently
This must be done if you have pain in your elbow:
- accompanied by swelling and redness of the skin, increased body temperature;
- do not go away, despite eliminating stress and taking painkillers;
- accompanied by impaired movement and numbness of the hand;
- increase during movements in the joint;
- arise against the background of deformation of the elbow area.
If such symptoms appear, you cannot postpone visiting a doctor; this can lead to serious complications.
Effective treatment for ulnar nerve neuropathy
It is important! Treatment is selected based on the causes of the disease. Basically, the following methods are used:
- hand fixation to limit mobility;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- massotherapy;
- manual therapy;
- physical therapy for recovery;
- taking medications.
You will always be provided with comprehensive assistance at Medical. You can make an appointment with a specialist by phone. Do not tolerate pain, which with the right approach can always be eliminated by determining the exact cause of the disease and undergoing comprehensive treatment.
What exactly hurts
The elbow joint is a complex joint consisting of three bones (ulna, radius, humerus) and interconnected joints: radioulnar, humeroulnar and humeroradial. The radial side of the joint is on the outer (lateral) side of the arm, the ulnar side is on the inner (medial). The complex joint is surrounded by a dense capsule that protects it from external influences.
The inner lining of the capsule is called synovial. It secretes synovial fluid, which is the “lubricant” of the joint and supplies nutrients to the cells of the hyaline cartilage that covers the articular surfaces of the bones. Around the joint between the bone and tendon-ligament tissues there are 3 bursae - articular capsules containing synovial fluid (interosseous ulnar, radioulnar and ulnar subcutaneous). They improve the process of sliding of joint tissues during movement and prevent injury.
The joint is strengthened by four ligaments: two lateral (ulnar and radial), annular (fixes the head of the radius) and quadrate (fixes the connection of the radius and ulna). In the area of the elbow, the tendons of the flexor and extensor muscles of the shoulder are attached and the tendons of the forearm, which are involved in the movement of the arm below the elbow joint, originate. Joint movements: flexion-extension, supination-pronation (rotation of the forearm in and out).
The structure of the elbow joint
The elbow is the elbow joint and the soft tissues surrounding it - tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, nerves, subcutaneous tissue and skin. Elbow pain can occur due to pathology in any of these structures.
Causes of elbow pain
Elbow pain can be a consequence of many diseases and injuries:
- Acute and chronic arthritis (inflammatory processes) of the elbow joint. The reason is infection entering the joint cavity, autoimmune (allergy to one’s own tissues) processes. In acute arthritis, redness, swelling, increased skin temperature over the joint, pain, and sometimes fever and general malaise appear. When arthritis takes a chronic course, the pain becomes moderate and aching, the swelling is insignificant, and there is no redness. You need to start treatment as early as possible; for this, in case of acute arthritis of one joint, you need to consult a surgeon; if several joints are affected at once or the process is erased, then consult a rheumatologist.
- Bursitis is an inflammation of the periarticular bursa (bursa). The disease develops against the background of microtrauma during constant performance of certain movements. Bursitis most often develops in the subcutaneous ulnar bursa (see Fig.), but can also occur in the radioulnar and interosseous ulnar bursa. It manifests itself as moderate pain and the appearance of a lump of dense elastic consistency in the elbow area. Bursitis is treated by an orthopedist-traumatologist.
- Epicondylitis, an inflammation of the muscle tendon where it attaches to the bony joint structure, can also cause elbow pain. Ulnar epicondylitis is divided into internal - with damage to the tendons of the flexor muscles attached to the inner surface of the head of the humerus and external - with pathology of the extensor muscles attached to the outer surface of the head of the humerus. Pain in this case appears respectively when flexing and extending the arm in the right or left elbow, as well as when pressing on the outer or inner surface of the head of the humerus. The reason for the development of epicondylitis is microtrauma during regular performance of monotonous work (painters, cooks) and sports activities (tennis, golf). Treatment consists of limiting exercise and anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Arthrosis is degenerative-dystrophic changes in the elbow that develop after injuries, inflammatory processes and in the second half of life, after the age of 50 years. Painful sensations of an aching nature, it is difficult to bend and straighten the arm at the elbow.
- Joint dislocation is a complete or partial (subluxation) divergence of articular joints. A dislocation develops when you fall backwards or forwards onto a straight arm, as well as from a direct strong blow to the joint. Symptoms: severe sudden pain, aggravated by moving the hand and clenching it into a fist, increasing tissue swelling. If such symptoms appear, you need to provide emergency assistance to the victim (see above) and call an ambulance. Reducing a dislocation on your own is strictly contraindicated: this can lead to a bone fracture, pinched nerves and blood vessels. In the hospital, diagnostics are first carried out, and then, under local or general anesthesia, the dislocation is reduced with the application of an immobilization bandage.
- Joint fracture - develops during acute injury, can be open (with a violation of the skin and protrusion of bone fragments onto the surface) and closed. Bone fragments may remain in the same position as normal (undisplaced fracture) or move (displaced fracture). Symptoms: severe sudden pain in the elbow, dry cracking, change in joint configuration and increasing swelling. After emergency assistance is provided, the victim is hospitalized and urgently examined. In case of a non-displaced fracture, an immobilization bandage is applied. A displaced fracture is operated on, the bones are connected, and only after that immobilization is carried out.
Elbow fracture a) without displacement of fragments, b) with displacement
Rehabilitation after neurolysis
Recovery after the intervention begins with the restoration of sensitivity and the cessation of painful sensations. This happens by relieving pressure on the nerve. All other functions are restored somewhat more slowly. The sooner the operation is performed, the easier the rehabilitation will be. After the operation, gradually:
- The functionality of the nerve improves or is completely restored.
- The pain disappears.
- The ability to feel is restored.
- Sweating returns to normal.
Diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome
Usually, to make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to know the characteristic symptoms of the patient. In this case, it is convenient to use a set of special tests that make it possible to identify different types of tunnel neuropathies.
Find your dream career with the help of the proven expertise of GeekBrains specialists
Alexander Volchek
CEO of top Russian companies
To make work enjoyable, you must first find the right profession.
We have prepared documents that will help you make the right choice and determine which IT profession is right for you.
Thanks to these guides, 76% of our students were able to find the in-demand profession of their dreams.
Typically these documents are only available to our students; we will be giving them away for free for a while, but will remove them from public access very soon.
Download and use today:
Guide to IT professions
5 professions with skills and average salaries
Checklist for effective learning from Geekbrains
6 Rules to Follow to Make Learning Easier
All professions that exist in the IT field
63 professions and the skills required for them
Book recommendations for in-demand professionals
6 areas of activity and useful literature on each of them
If a number of signs suggest that a patient has compression-ischemic damage to the peripheral nervous system, standard testing is performed. It includes the following activities:
- general somatic examination with identification of basic vital functions;
- neurological diagnostics using special tests;
- radiography of the affected area to identify additional ribs, bone processes or calluses, fractures, dislocations, etc.;
- neuroimaging using MRI and CT techniques of the affected areas of the nerve trunk, spine, etc.;
- electrophysiological diagnostics using the results of electroneuromyography, which makes it possible to determine the speed of the impulse in the nerve canal and clarify the degree of damage to this nerve;
- Dopplerography of the vessels of the extremities with flexion-extension tests;
- Ultrasound of the affected area, which allows us to identify pathologies that in turn lead to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Also during diagnosis, it is necessary to exclude concomitant somatic pathologies, which are often caused by progressive tunnel neuropathy. To do this, a number of additional examinations are carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of blood glucose levels;
- determination of thyroid-stimulating hormones;
- rheumatoid factor analysis;
- determination of C-reactive protein;
- determination of the antistreptolysin-O indicator;
- analysis of circulating immune complexes.
First signs
The disease usually begins to develop with damage to thick or thin nerve fibers. Often, axonal polyneuropathy has a distal symmetrical distribution on the hands or feet. Neuropathy most often affects the lower extremities first and then spreads symmetrically up the body. The most common primary symptoms of damage include:
- muscle weakness;
- pain syndrome in the limbs;
- burning;
- crawling sensation;
- numbness of the skin.
Symptoms are most pronounced in the evening and at night.
Carrying out the operation
The operation is carried out in several stages:
- Introduction of anesthesia.
- Opening the connective tissue with a scalpel along the entire length of the nerve.
- Detection of fiber bundles, excision of the scar between them.
- Access to the nerve is open, it is isolated from the surrounding tissues.
- The scarring area is determined by palpation. The scar is found and removed.
- Excision can be carried out only over the nerve, bypassing the sides, to avoid damage to blood vessels and other structures.
- Application of miniature sutures.
- Placement of the nerve into the resulting muscle space.
- After these manipulations, the tightness disappears, and previously lost sensitivity appears.