Prognosis after ischemic, hemorrhagic
Cerebral hemorrhage usually occurs in a more severe form. The mortality rate in such patients reaches 70%; even after removal of the hematoma, the rate is not much lower. Unfavorable factors include:
- breakthrough of blood into the ventricles of the brain;
- uncontrolled arterial hypertension;
- large volume of hematoma;
- progressive cerebral edema;
- signs of displacement of the stem part;
- acute heart failure;
- increase in creatinine content in the blood;
- convulsive syndrome, lack of consciousness, reactions to painful stimuli for more than 3 days;
- age after 70 years.
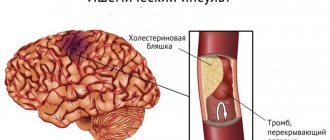
With ischemic stroke, a more benign course is observed; it is rarely accompanied by a profound impairment of consciousness. This happens with repeated vascular accidents, massive blockage of the brain arteries with cholesterol plaques, lack of treatment or complete disregard of doctors’ recommendations.
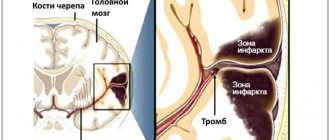
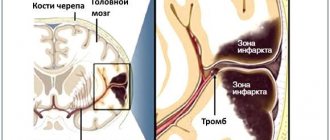
Blockage of arteries in the brain
Precoma and the first degree of coma can still give the patient a chance for recovery; with a higher degree, the prognosis is considered doubtful, and the onset of extreme coma is usually regarded as fatal.
Treatment
Treatment begins with stabilizing the respiratory rate (respiratory rate), and it is also very important to restore all functions of the cardiovascular system. The development of a treatment plan should begin only after all necessary research has been completed. It is very important to quickly replace all vital functions with artificial ones. For example, supplying oxygen to the body, stabilizing body temperature, and providing nutrition are very important.
Hemorrhagic stroke is treated only with surgery. With this operation, bleeding in the brain is eliminated and the aneurysm, which was the causative agent of the bleeding, is clogged. After all these manipulations, the swelling begins to rapidly subside. Such an operation requires a highly qualified neurosurgeon.
Duration of coma
The duration of a coma can be very different: from several hours to several days or weeks. Some patients die without regaining consciousness. Rarely does a patient remain in a coma for several months, a year, or more. But the chances of recovery after such a long coma are extremely low.
A quick exit is more likely when:
- moderate area of necrosis;
- ischemic nature of stroke;
- partial preservation of reflexes;
- young age of the patient.
Stages of medical care for patients in a coma after a stroke
Patients in a state of coma that has developed as a result of a stroke are provided with medical care at the prehospital stage by emergency physicians:
- restore airway patency;
- provide oxygen through an air duct or transfer the patient to artificial ventilation;
- prevent aspiration (foreign bodies entering the respiratory tract).
When there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure, drugs are used that have a vasopressor effect (alpha-adrenergic agonists) and improve myocardial contractility (cardiac glycosides), drugs that replenish the volume of circulating fluid (crystalloid solutions and low molecular weight dextrans). If the patient develops seizures, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are used. If necessary, barbiturates and inhalation anesthesia are used.
When a patient is admitted to the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, doctors take emergency measures:
- maintaining an optimal level of oxygen supply;
- monitoring of blood pressure and correction of cardiac activity;
- administration of pressor amines (1 ml of 1% mesotone solution intramuscularly or subcutaneously, caffeine, corticosteroids;
- constant monitoring and correction of acid-base balance in the body;
- control of swallowing (in the presence of dysphagia, a nasogastric tube is inserted to prevent aspiration bronchopneumonia and ensure adequate nutrition for the patient);
- control of the condition of the bladder and intestines.
There are currently no specific drug treatments for hemorrhagic stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are taking measures aimed at reducing the usually high intracranial pressure. At the same time, they normalize blood pressure, the state of the blood coagulation system and the permeability of the vascular wall, and support the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In the absence of contraindications, surgical interventions are performed at partner clinics. In the case of an ischemic stroke, patients are brought out of a coma and the restoration of lost functions is immediately begun using methods of drug therapy and physical rehabilitation.
If signs of coma appear, the patient should be placed on a horizontal surface, turn his head to the side and call an ambulance. Call and alert the clinic staff about the current situation. The Yusupov Hospital employs professors and doctors of the highest category who use modern equipment and medications that allow them to do everything possible to bring a patient out of a coma after a stroke.
What is coma and stupor?
Coma is a disorder of the central nervous system. A person has no consciousness, reflexes or reactions to external stimuli. There is a failure in all the most important life processes.
There are primary and secondary coma. The first occurs with focal brain damage. These could be injuries, tumors, apoplexy. The second is a consequence of some pathological process.
Stupor is one of the stages of coma. It is also characterized by depression of the central nervous system. The patient's reflexes are preserved, but he does not react in any way to the environment. In fact, stupor is an intermediate state between stunned consciousness and coma.
- On the verge of life and death: extensive cerebral stroke. What are the chances of survival?
Why do people fall into a coma?
The main reason for the development of coma after a stroke is cerebral hemorrhage or apoplexy. Several factors can provoke it:
- Heavy bleeding.
- Insufficient or completely absent blood circulation in the brain.
- Brain swelling.
- Atheroma. This is a disease associated with blood vessels.
- Poisoning with chemicals or other substances hazardous to the body.
- Callagenosis. Represents pathological changes in connective tissue.
- Angiopathy. This is a condition characterized by the accumulation of a specific protein in the blood vessels of the brain.
- Acute stage of vitamin deficiency.
- Infectious and autoimmune diseases of the circulatory system.
- Most often, the listed pathologies develop with hemorrhagic stroke.
Ischemic stroke very rarely leads to coma. Even if a coma does occur, the chance that a person will come out of it is great. In the hemorrhagic form, the death of brain tissue occurs, which entails serious complications.
Degrees of coma
Depending on how damaged the brain is after a stroke, there are 5 stages of coma:
Prekoma. This is a state when there is no coma yet, but brain functions are weakening. Its duration ranges from 2 hours to several days. The patient's consciousness is confused, his mood often changes, and coordination of movements is impaired. However, all the reflexes necessary for life are preserved. The body reacts to stimuli. A person feels touch.
Coma of the first degree of severity is considered to be stupor. It is characterized by lethargy, difficulties with communication and establishing contact, and increased muscle tone. The patient has difficulty eating. He can only eat liquid meals or drink water.
Second degree. Brain activity is greatly reduced. The patient does not respond to attempts to establish contact with him. However, there is a reaction to loud sounds and bright light (the pupils are constricted). Muscle tone either increases or decreases. Muscle fibers contract chaotically. Reflexes are also inconsistent. In some cases, spontaneous urination and defecation occur. Experts consider the second degree to be a borderline state.
The third degree is the coma itself. The person is in an unconscious state. He has no reaction to stimuli, reduced muscle tone, and muscle twitching is observed, for example, as a response to pain. The functioning of almost all organs and systems is disrupted. Blood pressure drops, heart rate decreases, and breathing slows down.
Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke
This type of stroke is characterized by extensive bleeding in the brain. Bleeding can begin after damage to the vessel (due to external mechanical trauma), due to rupture of an aneurysm, or damage by a blood clot. In addition, there are often cases when there is a congenital pathology in which the permeability of the vessel is increased. Naturally, with this type of stroke, the prognosis is greatly worsened, since the consequences are very serious, and the rehabilitation period increases. It is also worth noting that with a hemorrhagic stroke, coma is very severe.
With any type of stroke, coma can develop, but with hemorrhagic stroke it appears most often, it develops faster and has a number of complications and aggravating factors.
How does a person feel
There is no clear and uniform answer to the question of how a person feels while in a coma. But scientists have recorded brain activity when visiting relatives or changes in breathing and heartbeat when trying to communicate with a patient. Many relatives wonder: can a person in a coma hear them?
The people themselves who have experienced such an experience describe their sensations differently: some were conscious, but could not show it, some saw various dreams, and some communicated with deceased loved ones; there are also cases when patients couldn't remember anything.
What can't you do?
Before the doctor arrives, you need to help the patient, but avoid unnecessary manipulations that will aggravate his situation. You cannot do the following:
- Hit and shake a person, trying to bring him to his senses. If the patient is in a comatose state, this will not help him regain consciousness. You may injure the patient.
- Place the patient on his back. The optimal body position is on the side. A tilted head will prevent vomit from coming out. The patient may choke.
- Give alcohol. If a person has come to his senses, there is no need to give him alcohol to get a hangover. You should not increase the amount of ethanol in the blood, as this can again lead to coma or binge drinking. If after some time the patient experiences severe withdrawal symptoms, it is better to call a doctor and put on a drip.
- Douse with cold water. On the contrary, you need to try to warm the patient. Cold water will not revive him, but will only lower his body temperature and blood pressure and slow down his pulse.
If the patient regains consciousness, do not force him to get up. You need rest, good sleep and plenty of fluids for some time. Also, you should not leave a person alone in a comatose state. Constantly measure his pulse and check his breathing. If you have a tonometer, it is advisable to also measure blood pressure.
It is not recommended to flush a person’s stomach before the doctor arrives, especially if he is unconscious. You can injure the larynx and cause asphyxia .
How long does a drug coma last?
The coma state is conventionally divided into 4 stages:
- Falling asleep
- Superficial stage
- Deep coma
- Death or recovery from a coma.
If a person falls into a deep coma while in a medical facility, a person can remain there for quite a long time. However, such an experience is extremely painful for the body and carries many negative consequences for the body. Therefore, it is very important to prevent this stage from occurring. To do this, it is necessary to provide the victim with medical assistance as soon as possible.
REMOVAL AT HOME
Stages
A person begins to feel unwell when the blood alcohol concentration reaches 300-500 ml, serious toxic syndrome develops at 1600 ml, and coma - from 1800 ml. Sometimes the condition can occur after a small dose of alcohol.
The condition goes through three stages:
- • Superficial or first stage. The person faints, vomits, and salivates uncontrollably. The pupils narrow, the face takes on a bluish tint, the muscles are tense, and the thermoregulation mechanism is disrupted.
- • Second stage. The pressure drops, breathing slows down and is hard to hear, the pulse becomes weak and frequent. Reflexes of muscles and tendons are absent. Involuntary urination and defecation may occur. There is a poor reaction to light, sounds, and possible development of seizures.
- • Deep or third stage. The pulse is difficult to palpate, breathing is barely perceptible, the rhythm of the heart and breathing is lost, and there are no reflexes. The pupils dilate, the face acquires a pronounced blue tint. If the amount of alcohol in the blood continues to rise, the person is at risk of cardiac or pulmonary arrest. If qualified assistance is not provided, a person may suffocate in vomit or die due to failure of one of the internal organs.
Why should you contact the New Method clinic?
We provide services for the diagnosis and treatment of alcoholism and its consequences. The clinic has all the necessary equipment to help a person in a coma. We make house calls or provide home assistance.
reasons to contact us :
- A staff of experienced specialists (narcologists, resuscitators, psychiatrists);
- Using only proven and high-quality drugs;
- Guarantee of complete anonymity;
- Versatile comprehensive treatment;
- Reasonable prices;
- Psychological support for patients.
If a coma appears as a result of chronic alcoholism, you can undergo treatment in a hospital (stay for up to 8 months). We provide a lifetime guarantee against relapse. We do not forcefully treat. Psychologists and psychiatrists use psychological influence techniques to gently convince the patient that it is time to take the path of recovery.
We also work with relatives, helping to restore lost social connections, find a job or return to school. At all stages of treatment, our patients receive legal support .
You can call a doctor to your home if your friend or relative is in a coma . We will deliver him to the clinic ourselves. The doctor arrives at your home within 40 minutes.
Anti-binge drip
From 3100 ₽/dropper
Removing withdrawal symptoms
From 9000 ₽
Drug treatment clinic
From 40,000 ₽/month
Teenage alcoholism
From 3200 ₽/day
Esperal coding
From 8500 ₽
24-hour drug treatment assistance
From 40,000 ₽/month
Coding for alcoholism at home
From 3100 ₽
Diagnostics
Alcoholic coma can be determined by symptoms, characteristic odor on exhalation, and the presence of a coma state. After providing first aid, specialists must make sure that other types of coma are not connected to the main comatose state. For example, alcoholic coma often goes side by side with neurological, somatic and toxic ones.
Doctors resort to special tests and studies to diagnose alcoholic coma and associated types of coma. In a normal situation, a series of tests and tactile examination are enough. Sometimes echoencephaloscopy and lumbar puncture are used.
Often the process started by a coma causes serious disruptions in the functioning of internal organs: kidneys, liver, pancreas. Metabolic processes are disrupted.
Causes
Coma occurs when a person:
- • takes alcohol on an empty stomach;
- • lowers the alcohol level instead of increasing it;
- • drinks too much ethyl alcohol in a short time.
Sometimes you don't have to be an alcoholic to experience an alcoholic coma. Vulnerable people who only need a small amount of ethanol to cause poisoning include:
- • teenagers;
- • aged people;
- • people taking potent drugs;
- • people with weakened metabolism.
Recovery after a coma
Rehabilitation after a coma becomes extremely important: a set of measures that can help you get closer to or return to your previous way of life. Everything is subject to calculation - from the load level to the program itself. The Clinical Brain Institute has been successfully dealing with these problems for quite a long time. We are ready to offer effective rehabilitation programs developed with special care, which are selected individually for each patient. Our specialists, being professionals in their field, are also very responsive and attentive people, which is something that patients so often lack!
Types of drug coma
Depending on the drug used, there are several types of narcotic coma. To administer the necessary antidote, predict the situation and carry out relevant resuscitation measures, it is important for doctors to know which drug resulted in intoxication.
Heroin coma
Heroin coma most often occurs from an overdose of this drug. Intoxication with this drug leads to the rapid development of severe complications. To remove heroin particles from the body, effective antidotes are used - Naltrexone or Naloxone. If you suspect that a loved one is using heroin, it is better to buy an ampoule of the medicine at the pharmacy in advance, so that if necessary, you can immediately administer the drug, without causing more serious consequences.
HEROIN ADDICTION TREATMENT
Toxic coma
Low-quality drugs prepared in an artisanal way are a common cause of toxic coma. This is especially true for synthetic substances, which may contain ammonia, detergents, manganese and other life-threatening substances.
Opiate coma
When a coma occurs as a result of an overdose of opiate drugs, hardware detoxification with the help of Naloxone is most often performed. A large amount of this drug, which is an opiate antidote, is injected into the body to bind narcotic toxins and remove them from the body.
Coma after an overdose of pills
Drug overdose can occur as a result of:
- erroneously taking a potent drug in large quantities,
- intentionally taking drugs in greatly increased dosages to obtain a narcotic effect.
As a result of an overdose of tablets, there is a high probability of a drug-induced coma. Most often, intoxication occurs due to exceeding the dosage of the following drugs:
- sleeping pills,
- sedatives, painkillers,
- nootropic drugs,
- cardiac drugs.
Find out treatment recommendations without leaving home for free
To select a treatment plan, you just need to leave a request, we will contact you to select the time and specialist you need
Submit your application
Consequences of alcoholic coma
A comatose state is fraught with a number of consequences:
- • swelling;
- • change in urine color from yellow to brown or dark red;
- • disruption of the heart and lungs (possible);
- • hyperkalemia;
- • trophic changes (skin tissue deformation, ulcers);
- • muscle atrophy (loss of muscle mass, hypotonia);
- • hemorrhagic syndrome (bleeding of mucous membranes);
If you do not ensure that a person receives quality treatment, his health can seriously deteriorate. Medical offers its assistance in giving up alcohol addiction and eliminating the consequences after a coma. Just call us!
First aid before the ambulance arrives
- Place the patient on his stomach, turning him slightly on his side, with his head hanging down. This will reduce the chance of suffocation.
- The patient's thermoregulation is impaired, so it is necessary to cover him with a blanket. If the incident happened on the street, then it is necessary to bring the patient indoors.
- Invite the patient to sniff cotton wool with ammonia to return the person to consciousness.
- If the person can drink, offer warm drinks: tea, water to replenish the lack of fluid in the body.
If a person is at the stage of a severe coma, then resuscitation measures may be required: artificial respiration, chest compressions.