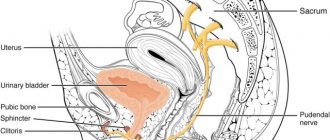
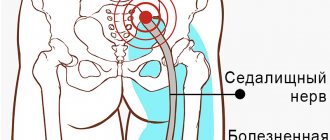
Carpal - This word comes from the Greek Karpos, which means "wrist". The wrist is surrounded by bundles of fibrous tissue, which normally serves as a support for the joint. The limited space between these fibrous bands of fibrous tissue and the bony structures of the wrist is called the carpal tunnel. The median nerve, which passes through the wrist, provides sensation to the thumb, index and middle fingers. Any condition that causes swelling or changes in the position of tissue in the wrist can result in compression and irritation of the median nerve. Irritation of the median nerve in such cases leads to tingling and numbness in the thumb, index and middle fingers, a condition known as “carpal tunnel syndrome.”
Causes of carpal tunnel syndrome
Given the limited space in the carpal tunnel, any swelling in this area can put pressure on the median nerve, causing symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. There are many different reasons that lead to the development of this syndrome, but often the exact cause cannot be determined. Some people have an anatomically narrower carpal tunnel to begin with, making them more at risk for developing carpal tunnel syndrome. It is believed that this tendency may be genetically determined, and if there is a family history of this syndrome, then the likelihood of pressure on the median nerve increases significantly. You are also more likely to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if you are overweight, smoke, or drink excessively. Another risk factor is age – the older a person is, the higher the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Women are more predisposed to this syndrome than men due to the narrower carpal tunnel. There is also a greater tendency to develop carpal tunnel syndrome if there has been a wrist injury (rupture or sprain) or there are diseases such as:
- diabetes
- osteoarthritis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- hypothyroidism
It is possible that hormones play a role in the development of carpal tunnel syndrome, as some women develop the syndrome during pregnancy or menopause. Hormones produced during pregnancy can lead to fluid retention, which in turn can cause swelling in the wrist. It has been noted that performing certain types of activities can lead to the development of this syndrome. People who do a lot of heavy manual work or repetitive movements of the wrist, such as on an assembly line or working with their hands in cold temperatures, also have a greater risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. But the probability increases significantly if the load is combined with the presence of systemic diseases.
Pinching of the radial nerve in the arm. What is dangerous and how to treat it
Pinching of the radial nerve in the hand can occur in the following cases:
- as a result of injuries and bruises of the shoulder
- congenital anomalies of bone structures
- for fractures of the lower extremities and long-term use of crutches
- when you put your hand under your head while sleeping
- during surgical operations
- due to a tumor
- incorrectly given injection in the shoulder area
- past viral or bacterial diseases
- hypothermia
- stress
- alcohol or lead poisoning
Our doctors
Meet our specialists
Work experience 30 years Status Orthopedic traumatologist Qualification Doctor of the highest category
Donskoy E.O. Chief physician of the medical center "MEDICUS". Receives patients with diseases of the joints and spine.
Work experience 35 years Status Orthopedic traumatologist Qualification Candidate of Medical Sciences
Averyushkin A.V. Engaged in conservative and surgical treatment of injuries and orthopedic pathologies, Candidate of Medical Sciences, author of scientific works.
Work experience 45 years Status Orthopedic traumatologist Qualification Doctor
Khudoleev M.V. Traumatologist-orthopedist, surgeon, sports medicine doctor.
Work experience 15 years Status Orthopedic traumatologist Qualification Doctor of the highest category
Malofeev V.A. He is fluent in all the necessary methods of diagnosing and treating orthopedic pathologies and successfully restores patients.
Work experience 5 years Status Masseur Qualification Massage
Zolotukhin V.V. Massage therapist at LDC MEDICUS. Viktor Vasilyevich’s magical hands put hundreds of patients on their feet and relieved pain.
Work experience over 30 years Status Nurse Qualification Nurse
Pugacheva O.N. Graduated from Leningrad Medical School. Works as a nurse.
Work experience 10 years Status Physiotherapy nurse Qualification Highest category
Murzakova A.Z. In 1981 she graduated from the Ufa Medical School. In 2012 - “Center for Advanced Training of Specialists No. 1”. Specialty: physiotherapy.
Work experience over 20 years Status Chiropractor Qualification Highest category
Azimov O.A. Specializes in the treatment of diseases of the joints and spine, rehabilitation after injuries and fractures. Works as a chiropractor at the Medical Center MEDICUS.
Work experience 4 years Status Nurse Qualification Junior nurse
Semenyuk E.B. Graduated from St. Petersburg Medical College No. 2. Works as a nurse at the Medical Center MEDICUS.
Work experience 30 years Status Nurse Qualification Highest qualification
Gadzhieva L.A. Graduated from Leningrad Medical School. Works as a senior nurse at the Medical Center MEDICUS.
Symptoms of a pinched nerve
- First of all, a person is tormented by severe pain in the hand, its sensitivity decreases. The hand and fingers bend with difficulty. Muscle weakness appears, or vice versa, muscle tension. Depending on the location of the pinched radial nerve, their characteristic signs are distinguished.
- Pinching in the armpit. In this case, the forearm, the back of the hand and the first three fingers are affected. Their sensitivity and motor function are impaired. Drop hand syndrome is observed.
- Pinched median nerve. Numbness occurs on the inside of the hand. The muscles of the thumb atrophy and it becomes immobile.
- Pinching in the area of the ulnar nerve. Pain occurs in the area of the shoulder and elbow. Pain occurs when moving the hand and squeezing the fingers. The forearm muscles weaken and lose their volume.
Treatment methods
Joint reconstruction
1 procedure per course FREE!
Introduction of organic serum with hyaluronic acid into the joint capsule. As a result, cartilage reconstruction occurs Read more…
Neuroprotective therapy
Discount -10%! Only 3 days!
Neuroprotectors are new generation drugs that can restore the conduction of impulses in nerve tissues. Read more…
Plasmacytopheresis
1 procedure for the course is FREE!
Treatment and healing of cartilage with growth factors. Restoration of joint tissue with purified platelet blood. Read more…
Transdermal therapy
Discount -25%! Only 3 days!
The introduction of titanium glycerosolvate into a diseased joint is a unique method of drug delivery without surgery or painful injections. Read more…
Ultraphonophoresis
Discount -25%! Only 3 days!
This is an innovative way to administer medications using ultrasound, which has the unique ability to loosen tissue. Read more…
EHF therapy
Discount -25%! Only 3 days!
This is a promising method of physiotherapy with a great future. In life, waves of this range do not reach the ground, being dispersed in the atmosphere. The device generates these waves itself. Read more…
Infusion therapy
Combinations of drugs for drip administration through a vein. High digestibility and rapid achievement of therapeutic action make infusion therapy Read more…
Blockade
1 procedure for the course is FREE!
A joint or spinal block is a way to quickly help a joint or back. In case of acute pain, the blockade helps to quickly relieve pain and help locally Read more…
Introduction of chondroprotectors
"HONDRO" in Latin means "cartilage" and that says it all. Injection of cartilage cells into damaged segments of the spine Read more...
Autohemotherapy
Treatment using the patient's autologous blood cells. Blood is administered intramuscularly, which provokes the body to intensify the fight against chronic infection, suppuration and trophic ulcers, the immune system is strengthened and effectively resists new infections. Read more…
Laser treatment
Infrared healing with a wavelength of 0.8-0.9 microns affects the internal source of the problem. This relieves inflammation, swelling and pain in the joint. Degenerative processes in the joint fade away as metabolic processes inside the joint accelerate many times. Read more…
Peloid therapy
Nutrition and growth of cartilage cells using peloid dressings. The base comes from Lake Sivash, where mud with a high concentration of Dunaliela Salina microalgae, which is rich in beta-carotene, is extracted.
Diagnostics
If this problem is not addressed to a specialist, the symptoms of pinching will intensify. And in rare cases, this can lead to tissue death in the hand. Therefore, it is important to take timely measures for diagnosis and treatment. To do this, you must first contact a diagnostic center, where the doctor will conduct a survey and a neurological examination in order to identify the location of the pinching and the reasons that caused it. And then he will prescribe a series of studies:
- blood and urine tests. Allows you to identify inflammatory processes in the body.
- X-ray of the spine and arm. It is carried out to identify joint pathologies.
- MRI of the injured arm, thoracic and cervical spine. Used to determine the location of pinching and the condition of tissues, vessels and joints in this area. As well as identifying possible tumors.
- electromyography. This method allows you to determine the degree of muscle damage.
Results of our patients BEFORE and AFTER treatment
Evgenia Semenovna, 67 years old.
Arthrosis of the knee, stage 3, was sent for joint replacement surgery. With the help of plasma, I coped with arthrosis in 3 sessions. Refused the cane. Avoided surgery. There is no pain, the cartilage and joint capsule have been restored. The duration of treatment is a week.
Pavel Ivanovich, 73 years old
Periarthrosis of the shoulder joint stage 2. I was treated by chiropractors, with leeches and needles - it didn’t help. The plasma caused the regeneration of lost tissue. Full mobility returned, chronic pain of 15 years went away. The treatment period is 10 days.
Natalya Igorevna, 59 years old
Osteochondrosis complicated by hernia formation. Excruciating back pain was relieved in one session. Neurological manifestations - goose bumps in the legs, numbness in the lower leg - disappeared after the second procedure. Course - 2 weeks.
Taisiya Romanovna, 82 years old
Arthrosis of the hip joint stage 3. The operation was refused due to his age and heavy weight. Plasmacytopheresis restored the joint capsule, restoration of articular cartilage and joint lubricating fluid production occurred. Course - 7 days.
Roman Stepanovich, 73 years old
Headaches, cervical osteochodrosis and vertebral hernias. As a result of treatment, headaches disappeared and pain in the cervical spine decreased. The pictures show restoration of the paravertebral tissues, reduction of the hernia.
Radial nerve entrapment treatment
After the examination and the data obtained from it, the doctor prescribes treatment. It depends on the patient’s condition, the location and degree of pinching and the causes that caused it. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. The conservative treatment method is aimed at relieving the patient of pain symptoms and restoring the damaged area. This method includes: taking medications (anti-inflammatory, painkillers, antispasmodics, B vitamins, diuretics, chondroprotectors), blockades, physiotherapy, massage, acupuncture, physical therapy. If a fracture occurs as a result of a nerve rupture, then in this case a surgical operation is performed to stitch it together. Surgery is also used to remove tumors.
At the MEDICUS clinic, experienced specialists will help you navigate the choice of diagnostic methods to detect pinched radial nerve and prescribe the most effective treatment that is suitable for you. You can make an appointment with a doctor through our website or by calling 986-66-36.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Patients with carpal tunnel syndrome initially feel numbness and tingling in the hand along the median nerve (thumb, index, middle, and part of the fourth finger). These sensations are often more pronounced at night and may even lead to awakening from sleep. The cause of increased symptoms at night may be due to the flexed position of the wrist during sleep and/or the accumulation of fluid around the wrist and hand while it is in a horizontal position. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be a temporary condition that resolves completely on its own, or symptoms may persist and progress.
As the syndrome progresses, patients may develop a burning sensation and/or experience hand spasms and weakness. Decreased grip strength can cause objects to frequently fall out of your hand. Sometimes sharp shooting pains can also be felt in the forearm. Chronic carpal tunnel syndrome can also cause muscle atrophy in the hand, especially the muscles at the base of the thumb on the palm of the hand.
Causes
The anatomical narrowness of the canal is only a predisposing factor in the development of tunnel syndrome. In recent years, evidence has accumulated indicating that this anatomical feature is genetically determined. Another reason that can lead to the development of tunnel syndrome is the presence of congenital developmental anomalies in the form of additional fibrous cords, muscles and tendons, and rudimentary bone spurs. However, predisposing factors alone for the development of this disease are usually not enough. Some metabolic and endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus, acromegaly, hypothyroidism), diseases accompanied by changes in joints, bone tissue and tendons (rheumatoid arthritis, rheumatism, gout), conditions accompanied by hormonal changes (pregnancy), space-occupying formations can contribute to the development of tunnel syndrome the nerve itself (schwannoma, neuroma) and outside the nerve (hemangioma, lipoma). The development of tunnel syndromes is facilitated by frequently repeated stereotypical movements and injuries. Therefore, the prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome is significantly higher in people engaged in certain activities and in representatives of certain professions (for example, stenographers have carpal tunnel syndrome 3 times more often).
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome can be made based on symptoms and characteristic areas of numbness in the hand. But at the same time, it is often necessary to exclude other possible causes of symptoms that simulate carpal tunnel syndrome. This could be a neck, shoulder or elbow problem. The doctor examines the wrist to detect swelling, local fever, pain, and discoloration. Sometimes pressing on the front of the wrist can produce a tingling sensation in the hand and this is called the Tinel sign, characteristic of carpal tunnel syndrome. Symptoms may also occasionally be reproduced by flexing the wrist forward (called Phalen's sign). A definitive diagnosis can be made with ENMG. Typically, with carpal tunnel syndrome, there is a slowdown in nerve impulse transmission after the nerve passes through the wrist.
Extremity muscle testing, an electromyogram, is sometimes performed to rule out or detect other conditions that may mimic carpal tunnel syndrome.
Laboratory tests may be performed to help diagnose conditions associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. These tests include thyroid hormone analysis, general blood tests, blood sugar levels, etc. X-rays of the hand may also be ordered to determine the presence of bone changes (abnormalities of the bones and joints of the wrist). MRI is necessary in cases where it is necessary to visualize changes in ligaments and cartilage.
Treatment
In mild cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, ice compresses and a decrease in load can help. If this does not help, the following measures must be taken: 1. Immobilization of the wrist. There are special devices (splints, orthoses) that immobilize the wrist and are convenient to use (Fig. 1). Immobilization should be carried out at least overnight, and preferably for 24 hours (at least in the acute period). 2. NSAIDs. Drugs from the NSAID group will be effective if the inflammatory process dominates in the pain mechanism. 3. If the use of NSAIDs turns out to be ineffective, it is advisable to inject novocaine with hydrocortisone into the wrist area. As a rule, this procedure is very effective. 4. In outpatient settings, electrophoresis can be performed with anesthetics and corticosteroids. 5. Surgical treatment. For mild or moderate carpal tunnel syndrome, conservative treatment is more effective. In cases where all conservative treatment options have been exhausted, surgical treatment is resorted to. Surgical treatment consists of partial or complete resection of the transverse ligament and releasing the median nerve from compression. Recently, endoscopic surgical methods have been successfully used in the treatment of carpal syndrome.
Treatments for carpal tunnel syndrome
The choice of treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome depends on the severity of the symptoms and the underlying medical condition that may be causing the symptoms.
In the first stage, treatment usually includes rest, immobilization of the wrist in a brace, and sometimes local cold. If the patient’s profession involves stress on the wrist, then it is necessary to change activities for a while. In addition, it is possible to improve the ergonomics of the workplace, for example, you can adjust the computer keyboard and the height of the chair and optimize the load on the hands. These measures, as well as periodic episodes of rest and wrist stretching exercises, can actually prevent the development of carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms, which are caused by repetitive, excessive movements of the wrist. If there are systemic diseases or injuries, then individual treatment of these diseases is carried out. Fractures may require orthopedic correction (plaster, orthosis). Overweight patients should be advised to lose weight. For rheumatoid arthritis, specific treatment is carried out for the inflammatory autoimmune process. Wrist swelling, which may be associated with pregnancy, disappears after the baby is born.
Drug treatment
Several types of medications may be used to treat carpal tunnel syndrome. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is quite often prescribed in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome and, although the mechanism of therapeutic action is not entirely clear, nevertheless, many doctors note a certain effect of using this drug. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may also be helpful in reducing inflammation and pain. But these drugs have side effects and therefore this must be taken into account when prescribing them. Corticosteroids may also be used. They can be given orally or as injections into the affected wrist joint. Corticosteroids can lead to rapid relief of symptoms, but the side effects of these drugs do not allow them to be prescribed long-term and in the presence of some conditions (for example, in diabetes mellitus, their use can lead to a worsening of the condition). They should also not be prescribed in the presence of infections. In addition to drug treatment, physiotherapy and acupuncture also provide a certain therapeutic effect. Most patients with carpal tunnel syndrome can be treated with conservative therapy. But sometimes chronic pressure on the median nerve can lead to permanent numbness and weakness. To avoid serious and permanent nerve and muscle damage, surgical treatment may be recommended in such cases. Surgery involves excision of tissue putting pressure on the median nerve. This surgical procedure is called a "carpal tunnel release." Currently, such an operation can be performed using endoscopic techniques, which allows for minimal tissue trauma and rapid restoration of nerve conduction. After surgical treatment, it is necessary to use exercise therapy to restore hand function.
Types of damage
Damage to the nerves of the hand is represented by the following groups.
- Complete rupture of a nerve is called neurotmesis. Surgical treatment is indicated. Recovery occurs over months or years depending on the severity of the damage.
- Partial rupture accompanied by various disorders - neuropraxia - occurs with closed injuries. A condition with preserved nerve sensitivity, when the lack of conduction is temporary.
- Neuropathy is a disorder resulting from a fracture, bruise or cut in the hand area.
- A pinched nerve occurs when the patient cannot bend the wrist. The little finger is completely immobilized, the ring finger is partially immobilized, the thumb moves with difficulty. The pain radiates to the little finger.
Treatment of radial neuritis
To cure radial neuritis, it is necessary to first eliminate the cause of its development. Specific measures here depend on its nature:
- if neuritis is provoked by an infectious disease, then antibiotic and antiviral agents are prescribed;
- if the disease is caused by blood supply disorders, then in most cases vasodilator drugs are prescribed;
- If the disease is traumatic, it is necessary, first of all, to completely immobilize the affected limb and eliminate its use as much as possible.
To stop inflammation, the doctor prescribes anti-inflammatory and decongestant drugs, analgesics, and B vitamins. Anticholinesterase drugs and biogenic stimulants are also successfully used.
Successful treatment of neuritis is facilitated by a course of physiotherapy, which can be carried out after 1 week of drug treatment. Physiotherapeutic agents that have proven effectiveness in the treatment of radial neuritis include:
- ultraphonophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- exposure to pulsed currents;
- electrical stimulation;
- UHF therapy;
- acupuncture.
Massages of the area innervated by it and exercise therapy can also speed up the restoration of the functions of the affected nerve.
Why are the nerves compressed?
Nature has provided a muscular-osseous or muscular-fibrous bed for the nerve. The causes of compression are different:
- congenital narrowness of the bone canal;
- swelling due to constant overload;
- abnormal bone growth or acromegaly;
- inflammation of nearby joints;
- tendon inflammation;
- degenerative changes in bones – arthrosis and arthritis;
- too large callus after a fracture;
- endocrine and metabolic diseases in which tissue nutrition is disrupted - diabetes mellitus, myxedema.
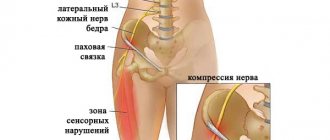
Each peripheral nerve along its length passes through narrow places in which it can be compressed. This primarily concerns the median nerve of the arm, which has to overcome three tunnels - at the wrist, forearm and in the lower third of the shoulder. The ulnar nerve may become compressed at the elbow joint and under the palmar ligament. The obturator, lateral cutaneous, sciatic, tibial, and plantar digital nerves may be compressed in the leg.
Diagnosis of neuritis
The success of treating this disease depends on many factors, and important here are the age of the patient and the stage at which the disease was detected. That is why early detection of pathology plays such a significant role.
Since the symptoms of neuritis are in many ways similar to the clinical manifestations of cerebrovascular accidents, multiple sclerosis and brain tumors, a careful differential diagnosis is required. It must be carried out by a qualified neurologist.
The doctor receives valuable data from a survey and physical examination of the patient, checking reflexes, muscle strength and other parameters. If necessary, the patient may be recommended to consult with specialists.
To clarify the diagnosis, the following studies may be prescribed:
- blood tests (clinical and biochemical),
- general urine analysis;
- radiography;
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging);
- electroneuromyography (ENMG);
- CT (computed tomography).
Clinical manifestations
The main symptoms of cubital tunnel syndrome are pain, numbness and/or tingling. Pain and paresthesia are felt in the lateral part of the shoulder and radiate to the little finger and half of the fourth finger. At first, discomfort and pain occur only when pressure is applied to the elbow or after prolonged bending. In a more severe stage, pain and numbness are felt constantly. Another sign of the disease is weakness in the arm. It manifests itself as a loss of “confidence” in the hand: suddenly objects begin to fall out of it during some habitual actions. For example, it becomes difficult for a person to pour water from a kettle. In advanced stages, the hand on the sore arm begins to lose weight, and pits appear between the bones due to muscle atrophy.