Pelvic pain is pain that is localized below the navel and above the beginning of the thighs. They can be associated with different conditions. Sometimes pelvic pain does not pose any danger and goes away on its own after some time, sometimes it indicates certain diseases, and in some cases it signals that you need to urgently go to the hospital.
Sexually transmitted infections
Characteristic signs of sexually transmitted infections (STIs): pain during urination, vaginal discharge, vaginal bleeding between periods. The most common types of STIs are gonorrhea and chlamydia. The final diagnosis can be made by a doctor after laboratory tests. If you are diagnosed with a sexually transmitted disease, your partner should also be tested.
general information
The trigeminal nerve consists of sensory and motor fibers. It originates in the structures of the brain and is divided into three branches:
- ophthalmic: responsible for the eye, forehead and upper eyelid;
- maxillary: innervates the area from the lower eyelid to the upper lip;
- mandibular: involves the chin, lower jaw, lips and gums.
With neuralgia, one or more branches of the trigeminal nerve are affected, which determines the main symptoms of the pathology. People over 45 years of age are most susceptible to the disease, and women get sick more often than men.
Make an appointment
Ovarian cyst
The ovaries contain follicles - sacs in which eggs mature. A mature follicle ruptures during ovulation and releases an egg. If this does not happen, it turns into a cyst. Such ovarian cysts are usually harmless and can go away on their own, but they can cause pain and an enlarged abdomen. When the cyst is torsioned, a threatening condition occurs - severe acute pain should force you to immediately consult a doctor. Ovarian cysts are detected during a gynecological examination and ultrasound.
Treatment of trigeminal neuralgia
Treatment is aimed at:
- to eliminate the cause of damage;
- to alleviate the patient's condition;
- to stimulate the restoration of nerve structures;
- to reduce the excitability of trigger zones.
Properly selected treatment can reduce the frequency, intensity and duration of pain waves, and ideally achieve stable remission.
Drug treatment
Trigeminal neuralgia requires complex treatment using drugs from several groups:
- anticonvulsants (carbamazepine and analogues): reduce the excitability of nerve fibers;
- muscle relaxants (baclofen, mydocalm): reduce muscle spasms, improve blood circulation, reduce pain;
- B vitamins (neuromultivit, milgamma): stimulate the restoration of nerve fibers, have an antidepressant effect;
- antihistamines (diphenhydramine): enhance the effect of anticonvulsants;
- sedatives and antidepressants (glycine, aminazine): stabilize the patient’s emotional state.
For severe pain, narcotic analgesics may be prescribed. Previously, drug blockades (injecting the problem area with anesthetics) were actively used, but today this method of treatment is almost never used. It contributes to additional damage to nerve fibers.
Treatment of the root cause of the disease is mandatory: elimination of dental problems, taking medications to improve cerebral circulation, etc.
Physiotherapy and other non-drug methods
Non-drug methods complement drug therapy well and help stabilize patients’ condition. Depending on the condition and concomitant diseases, the following may be prescribed:
- ultraviolet irradiation: inhibits the passage of impulses along nerve fibers, providing an analgesic effect;
- laser therapy: reduces pain;
- UHF therapy: improves microcirculation and prevents muscle atrophy;
- electrophoresis with analgesics or antispasmodics to relieve pain and relax muscles;
- diadynamic currents: reduce the conductivity of nerve fibers, significantly increase the intervals between attacks;
- massage of the face, head, cervical-collar area: improves blood circulation and lymph outflow, improving tissue nutrition; must be carried out with caution so as not to touch trigger zones and provoke an attack; the course is carried out only during the period of remission;
- acupuncture: helps relieve pain.
Surgery
The help of surgeons is indispensable when it is necessary to eliminate nerve compression. If indicated, the following is carried out:
- removal of tumors;
- displacement or removal of dilated vessels pressing on the nerve (microvascular decompression);
- expansion of the bone canals in which the branches of the nerve pass.
A number of operations are aimed at reducing nerve fiber conductivity:
- exposure to a gamma knife or cyber knife;
- balloon compression of the trigeminal node: compression of the node using an air-filled balloon installed in close proximity to it, followed by death of the nerve fibers; surgery often leads to partial loss of sensation and decreased muscle movement;
- resection of the trigeminal node: rarely performed due to the complexity and large number of complications.
Make an appointment
Pelvic organ prolapse
With age or during pregnancy and childbirth, the pelvic floor muscles may weaken, causing the uterus, vagina and bladder to move downwards. This is not a dangerous condition, but it leads to a feeling of discomfort and makes sexual intercourse painful. Special Kegel exercises help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Varicose veins of the pelvic veins
Varicose veins can occur not only on the legs. Dilatation of the pelvic veins leads to pain, which intensifies when the woman sits or stands. When lying down, symptoms decrease or disappear. Varicose veins of the pelvic veins are treated surgically.
Numbness of the face
Stroke
Diabetes
34730 March 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Numbness of the face: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Numbness of the face occurs when the sensitivity of skin and muscle receptors to various impulses is impaired. This symptom may develop gradually or appear suddenly. Loss of facial sensitivity is described as burning, tingling, sometimes pain, and in some cases as a complete absence of sensation. When the face is numb, the color of the skin over the affected area may change in the form of pallor or redness.
In severe cases, sensory impairment is accompanied by a decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles.
Types of facial numbness
Any external influence, be it heat or cold, light touch or strong pressure, leads to activation of skin receptors and muscle structures. Each receptor is associated with a specific type of nerve fiber that transmits a specific type of sensitivity (sensation of pressure on the skin, vibration, stretching of the skin, and temperature sensitivity). An impulse is generated in the receptor, which is sent through nerve fibers at high speed to the nerve ganglia, which are a collection of sensory neurons. This is where primary information processing occurs to activate vital reflexes. Subsequently, the impulse goes to the brain, where it is processed in special nerve centers, and the person feels pain, pressure, vibration, etc. Thus, we can talk about the following types of sensitivity disorders:
- Violation of surface sensitivity
occurs when receptors (temperature, tactile, pain, etc.) and nerve fibers of the facial skin are damaged. - Violation of deep sensitivity
occurs when the receptors and nerve fibers of the facial muscles are damaged. - Violation of complex types of sensitivity
. A similar type of disorder occurs when the cerebral cortex is damaged. There is no recognition of two different stimuli that simultaneously affect the skin, or the person cannot determine the location of the touch.
Possible causes of facial numbness
In many cases, numbness in different parts of the face is short-term, passing within a few minutes.
Such episodes can occur when the head is positioned in an awkward position, for example during sleep.
This occurs due to compression of the nerve fibers and a temporary disruption of impulse conduction. There is a burning and tingling sensation in the affected area. Partial loss of sensitivity is observed with prolonged exposure to the cold due to vasospasm. After gradual warming of the skin, sensitivity is restored.
However, facial numbness can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Acute cerebrovascular accident, or stroke
– a common cause of sudden numbness of the face in combination with a violation of facial activity. Hemorrhage or blockage of brain vessels by a thrombus (blood clot) occurs, acute oxygen deficiency and damage to neurons with disruption of their functions develops. Symptoms develop unexpectedly, sometimes accompanied by headache.
The main signs of a stroke are: numbness of the face and limbs on one or both sides, sudden weakness, speech impairment (inability to clearly pronounce words), drooping of the corner / corners of the mouth, uncoordination of movements.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. A cerebral aneurysm
can cause numbness in the face due to compression of nerve fibers and sensitive centers of the brain. It usually develops gradually; at the onset of the disease, symptoms may be completely absent. Numbness first affects one area of the face (for example, perioral), and with further growth of the aneurysm, the affected area gradually expands. Sensations may also change: from tingling, burning at first - to a complete absence of sensations later.
There is a danger of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm; in this case, the symptoms are similar to those of a stroke and appear quickly.
Trigeminal neuritis
often accompanies inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries, periodontitis), ear (otitis), paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis), parotid glands (mumps). The branches of the trigeminal nerve are irritated, which can lead to numbness in the corresponding areas of the face.
Impaired sensitivity with increased tone of the masticatory muscles
occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve by muscle fibers. Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles is characteristic of damage to the temporomandibular joint due to arthritis and arthrosis, incorrectly selected braces, and certain diseases of the pharynx, for example, peritonsillar abscess.
Diabetes
– with this disease, the process of utilization of glucose from the blood is disrupted, which leads to damage to the vascular wall and disruption of the nutrition of nerve bundles. In the absence of maintenance therapy, tingling and partial loss of sensitivity in areas where the blood supply is impaired may occur.
Numbness of the face in multiple sclerosis
occurs due to demyelination (disappearance of the outer sheath) of the nerve fibers of the trigeminal nerve. Numbness is often preceded by severe pain not only in the face, but also in the limbs.
Tumors of the brain and its membranes
lead to impaired sensitivity in the facial area due to compression of the neurovascular bundles or tumor growth in them.
Which doctors should I contact if I have facial numbness?
If your face becomes numb, you should consult a neurologist or therapist. In some cases, consultation with an otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, or dentist may be required.
Diagnosis and examinations for facial numbness
Depending on the suspected cause of facial numbness, the following laboratory and instrumental studies may be required:
- clinical blood test;
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS)
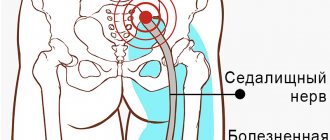
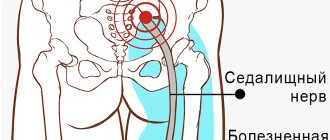
Quite often, the source of pelvic pain is the muscles and ligaments. This condition is called myofascial pain syndrome and has the following causes:
- muscle and ligament sprains;
- bruises;
- frequent minor muscle injuries, for example, during heavy physical work or sports;
- overstrain of the pelvic muscles, when you have to maintain an uncomfortable position for a long time;
- Sometimes the cause is hypothermia and frequent stress.
There can be many causes of pelvic pain. Sometimes it is difficult for a doctor to determine the cause of this condition without additional examinations. If you are worried about pelvic pain, make an appointment with a gynecologist at ProfMedLab, our phone number: +7 (495) 120-08-07.
Need more interesting articles:
13 reasons to get tested for hormones 02/08/2017
Working night shifts increases the risk of developing breast cancer 07/08/2019
Why is it good to cry? 05/19/2017
Prevention
Prevention of trigeminal neuralgia is a set of simple measures that significantly reduce the risk of developing pathology. Doctors recommend:
- undergo regular preventive examinations;
- at the first signs of the disease, seek help (the sooner treatment is started, the greater its effect will be);
- eat right, get the required amount of vitamins, minerals, unsaturated fatty acids;
- regularly engage in light sports and gymnastics;
- get enough sleep and rest;
- minimize stress and physical overload;
- avoid hypothermia and harden yourself;
- to refuse from bad habits.
Treatment of pectoralis minor syndrome
Treatment of pectoralis minor syndrome is divided into primary and auxiliary. The main thing is gentle manual therapy. It differs radically from conventional manual therapy not only in its safety and higher efficiency. Its main advantage is that it copes excellently with muscle tension. Using special musculofascial techniques, gentle manual therapy relaxes tense muscles and eliminates not only the symptoms, but also the very cause of pectoralis minor syndrome.
Treatment for pectoralis minor syndrome is performed by a chiropractor. It is better if it is a chiropractor-neurologist. He will be able to conduct a better and more detailed examination, diagnosis and treatment of your problem. Moreover, advanced and chronic cases may require additional medications, physiotherapy or exercise therapy. In general, treatment tactics and recovery time largely depend on whether we are dealing with a “fresh” or chronic case of pectoralis minor syndrome. Keep this in mind, don't start it and take care of yourself.
Pectoralis minor syndrome
Pectoralis minor syndrome is when this muscle pinches the nerves and vessels located next to it.
Pectoralis minor syndrome is also called Wright's syndrome, Wright-Mendlovich syndrome or hyperabduction syndrome. It was described in 1945 by two American doctors - Wright and Mendlovitch, independently of each other. The word "hyperabduction" means significant abduction of the arm to the side.
The pectoralis minor muscle is located on the ribs, just below the collarbone. It has the shape of an elongated triangle, the apex of which faces the shoulder joint and the base faces the sternum. Directly under the muscle, more precisely, between the muscle and the ribs, nerves and blood vessels pass. They go from the cervical spine to the arm to provide innervation and blood supply to the arm. This arrangement of the neurovascular bundle, when it lies on the ribs and is covered with muscle on top, resembles a tunnel. When there is spasm or shortening of the pectoralis minor muscle, in this tunnel, between the muscle and the ribs, pinching of the neurovascular bundle occurs - this is the pectoralis minor muscle syndrome or Wright Mendlovich syndrome. And at its core, this is tunnel syndrome. It can occur when the arm is moved to the side for a long time, when the muscle tightens and presses the bundle to the ribs. This is possible during surgery, an IV, deep sleep, or during certain types of work that require this hand position. Significant abduction of the arm - hyperabduction - gave another name to this syndrome - hyperabduction syndrome.
Causes of alcoholic polyneuropathy
The disease is provoked by alcohol intoxication and the associated toxic effect on peripheral nerves, their damage, and metabolic disorders. There are several additional factors that cause alcoholic polyneuropathy:
- "dietary". Unbalanced, poor nutrition often accompanies alcohol addiction. The diet contains an excess of carbohydrates and a lack of vitamins. Deficiency of folic acid, thiamine, and other B vitamins slows down the utilization of ethyl alcohol and its breakdown products, which increases the toxic effect of alcohol;
- oxidative stress. With constant consumption of alcohol, excessive formation of free oxygen radicals occurs, and the activity of antioxidants decreases. The balance of pro-oxidant and antioxidant systems shifts, which causes disturbances in the activity of cellular structures, and, in particular, in the work of endothelial cells (“responsible” for the metabolic support of the brain, regeneration, tissue growth, and perform barrier functions). A decrease in endothelial activity provokes endoneurial hypoxia, against which neuropathy appears;
- direct damage to the peripheral nervous system. Occurs under the influence of alcohol and ethyl alcohol metabolites. Acetaldehyde destroys the barrier protection of the nervous system and damages the nerve fiber.
How does the disease manifest?
Alcoholic polyneuropathy has a set of characteristic symptoms that gradually become more pronounced:
- the muscles of the arms and legs become weak. At first, mild weakness is felt in the palms and feet, and then spreads and becomes more noticeable;
- decrease in sensitivity, its gradual decrease until disappearance;
- decrease in the severity of reflexes up to their absence;
- pain syndrome. The pain may increase gradually or be immediate and severe. Usually pain is not associated with any “external” causes (injuries, stress);
- swelling of the legs, arms;
- the appearance of goosebumps, burning, and other sensations in the limbs;
- tremors, tics, muscle twitching, finger trembling;
- problems with the cardiovascular and respiratory systems (shortness of breath, breathing problems, rapid pulse, arrhythmia);
- sweating (appears unexpectedly and is not associated with exercise, body temperature or heat);
- impaired coordination of movements, dizziness, problems with balance.
Symptoms can increase sharply after severe alcohol intoxication or binge drinking; they often manifest themselves acutely after hypothermia. In other cases, they intensify gradually, against the background of a general deterioration in health due to chronic alcohol dependence. More often, the disease develops subacutely over several weeks or months: the sensitivity of the arms or legs is impaired, and the calf muscles become painful. When squeezed, the pain intensifies. Without treatment, muscle weakness appears - up to paralysis and atrophy.
Order alcoholism treatment
We work around the clock, experienced doctors, 100% anonymous.
Forms of alcoholic polyneuropathy
They differ in the set of symptoms and clinical picture.
Sensory. It manifests itself as pain in the hands, feet (the latter is more common), numbness or burning, cramps, and a feeling of chilliness. The sensitivity of the palms to temperature or pain stimuli may become more acute or, conversely, reduced. Sensory disturbances may be segmental. They often occur together with noticeable vegetative-vascular disorders (sweating, marbling of the skin on the feet or palms, or a change in its shade to bluish). A number of reflexes may decrease.
Motor. Sensory disturbances in this form are mild, most often affecting the legs. The muscles are weakening. The tibial nerve is often affected, causing the flexion of the feet and toes to be impaired, a person may walk on their toes, and the extensors of the foot and toes do not work properly. In the area of the legs and feet, muscle atrophy may develop or increased muscle tone may appear. Without treatment, paresis (muscle weakness) intensifies to the point of paralysis, pain, numbness, and sensory disturbances may appear. The same symptoms can occur in the hands.
Ataxic. Coordination of movements and gait are impaired due to a decrease in deep sensitivity. A feeling of numbness appears in the legs, the feet and palms become numb, and reflexes are reduced.
Mixed. With this form of polyneuropathy, there are symptoms characteristic of the motor and sensory forms: pain, decreased sensitivity, weakness of the muscles of the arms and legs, changes (usually decreased) reflexes.
Alcoholic polyneuropathy can be asymptomatic (almost all patients with chronic alcoholism have it). In the chronic form, symptoms increase gradually over a year or more. In acute or subacute form, it develops over several weeks and is more pronounced.
Order alcoholism coding
Experienced doctors and narcologists. In hospital or at home. 24-hour service in Moscow and the region. Professional, anonymous, safe.
Treatment with folk remedies
The following recipes help with numb hands:
- as a compress or therapeutic bath, use a mixture of 2 liters of milk, 600 g of salt and 50 g of honey, heated to 60? C;
- apply an infusion of wild rosemary with apple cider vinegar (1:3) 3 times a day;
- infusion of garlic (several cloves) in vodka (400 ml) taken orally, 3-5 drops dissolved in water;
- for 1 liter of vegetable oil - 100 g of ground black pepper, cook for 30–40 minutes, rub the cooled product into the skin of the affected limb.