Neurosis of the stomach and intestines often occurs due to stress and poor lifestyle. This means that most modern people are at risk. Delayed diagnosis will lead to progression of the disease and increased damage to health. The consequences can be serious weight gain, ulcers, chronic intestinal diseases and much more.
In this article we will talk about the symptoms and treatment of gastric neurosis. We will also try to find out what causes the disease and how to prevent it.
Why does the disease occur?
When we talk about the common causes of intestinal and stomach diseases, they are often caused by bacteria, hereditary predisposition, and acquired chronic pathologies.
But do not forget that the vagus nerve is involved in organizing proper gastric secretion. When it is at rest, secretion occurs normally and the person feels comfortable. But psychological shocks and past illnesses, as well as simply constant anxiety, can lead to serious problems.
Among the common causes of gastric neurosis are:
- Problems of a psychological nature. They arise when a person feels constant anxiety, is dissatisfied with himself, or experiences a tragic event. Psychologists note that neurosis can cause a break with a loved one, being in a negative environment in a team at work, or the loss of a relative.
- Wrong lifestyle. The nervous system suffers due to lack of sleep, poor work-rest balance, and constant severe stress.
- Nutrition problems. The gastrointestinal tract makes itself known when you eat a lot of fatty, heavy foods, consume a lot of sweets and starchy foods. Poor diet is another risk factor. To avoid getting sick, you should give up frequent snacking and balance your diet.
- Past illnesses. Many viral diseases, as well as problems with the stomach and intestines, quickly provoke neurosis. The problem appears against the background of gastritis, neoplasms, ulcers and other problems.
- Negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract. The disease can manifest itself after severe poisoning, as well as during intoxication, against the background of bad habits.
Treatment of gastric neurosis: the most effective and proven methods
So, treatment of gastric neurosis is a rather long process, the course of which must be monitored by a doctor. It is necessary to start it as early as possible, because in a very advanced form this pathology leads to much more serious complications and even other diseases - problems with the esophagus and stomach.
The very first advice that can be given to a patient is to visit a competent psychotherapist. He will give all the necessary advice on avoiding emotional stress and worries, and will also prescribe certain physical activities.
Diet therapy plays a certain role. It should be selected depending on the general acidity of the patient’s stomach. The peculiarity of diet therapy is that the transition from dietary food to a regular diet occurs smoothly and also covers a long period of time. You will need to abstain from hot, spicy and salty foods during treatment. It is also necessary to completely exclude from the diet foods that are prone to fairly rapid fermentation.
The patient will benefit from baths with the addition of mint, essential oils, and any medicinal herbs. It is necessary to take herbal infusions that have a strong sedative effect. Such as infusions of oregano, motherwort and valerian. Such plants perfectly normalize the state of mind and help overcome neurosis.
Symptoms of the disease
The disease begins to manifest itself at a fairly early stage, so examination using modern diagnostic methods allows you to choose the right treatment method and get down to business.
Neurosis of the stomach and intestines is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Constant feeling of hunger. It does not disappear even after a heavy meal.
- Bloating, increased gas production. May be accompanied by colic.
- Discomfort in the abdomen. There is pain, heaviness, and a pulling sensation.
- Heartburn. It occurs in the abdomen and can spread to the sternum area.
- Belching. Sometimes a person cannot control the urges. Belching is accompanied by loud sounds and an unpleasant odor.
- Aversion to food. Often, not only the smell, but also the sight of food can cause nausea and severe psychological rejection in a person.
Psychologists also note such signs as the manifestation of a chewing reflex even when there is nothing in the mouth. Patients complain of severe nervous agitation, problems with sleep, and panic attacks. Phobias may also appear. The head begins to ache and feel dizzy, blood pressure rises, and hypochondria is observed.
Diagnosis of gastroneurosis
Many signs and symptoms of gastric neurosis are identical to those that develop with gastritis.
Therefore, to correctly diagnose this disease, it is important to pay attention to the presence of psychological symptoms, such as rapid heartbeat, headaches, overexcitation, insomnia, panic attacks, phobia, hypochondria, etc. Characteristic signs of gastric neurosis in children are nervous vomiting, not accompanied by nausea. In adults, this disease often manifests itself in the form of anorexia (complete lack of appetite) or bulimia (a condition in which a person eats too much food). Both of these pathologies are dangerous and can ultimately even lead to death.
What and how we treat
Our task is to help you in any accessible and safe way. Psychotherapy (hypnosis) is an obligatory component of therapy, and psychotherapists and gastroenterologists are specialists carrying out the treatment process.
How many hypnosis sessions are needed? Usually the first results can be seen after the first or second sessions. The general course averages 7 sessions 1-2 times a week.
Do you need a gastroenterologist? If digestion is impaired, there is an active inflammatory process, stomach or duodenal ulcers, a gastroenterologist is definitely needed.
Causes of intestinal neurosis
The causes and mechanisms of the formation of intestinal neurosis have not yet been fully studied. The following provoking factors are considered relevant:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Socio-economic status;
- Phenotypic predisposition (children whose parents suffer from functional stomach disorders are prone to the disease);
- Psychological trauma;
- Motility disorders of the digestive tract;
- Changes in the neuroendocrine system;
- Inflammation that occurs without clinical symptoms;
- Previously suffered infectious intestinal diseases;
- Diet violation.
Scientists are of the opinion that not one, but several causative factors act simultaneously, which trigger several pathophysiological mechanisms.
The most significant risk factors for the development of intestinal neurosis include:
- Belonging to the female sex (the risk is 4 times higher than for men);
- Age up to 30-40 years;
- Accommodation in large cities;
- Higher, humanitarian education.
Intestinal neurosis is more common among cultural workers and mental workers, people who have a low level of social support.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are aimed at eliminating existing gastric symptoms and correcting conditions that provoked the development of abdominal neurosis. Patients are advised to normalize their daily routine, allocate enough time for rest, establish regular nutritious meals, provide a favorable psychological atmosphere, and minimize stress. You should avoid spicy, salty, fried, smoked foods and give preference to soups and steamed main courses. The diet must be complete, ensuring the supply of all necessary substances and replenishing spent energy resources.
Psychotherapy plays a leading role. Methods are selected taking into account the nature of the identified violations. Psychoanalytic and cognitive behavioral therapy is recommended for patients with OCD and anxiety disorders. For gastroneuroses provoked by severe stress, bodily methods are effective. According to indications, psychotropic drugs are additionally prescribed. For mild symptoms, preference is given to herbal medicines. In severe cases, tranquilizers and antidepressants can be used.
Stomach pain is eliminated with the help of myotropic antispasmodics. According to indications, treatment with prokinetics is carried out. In case of exhaustion, a comprehensive correction is carried out using protein solutions, vitamins and minerals, and according to indications, the patient is transferred to parenteral nutrition. In some cases, good results are achieved by relaxing massage, electrical procedures and hydrotherapy.
With timely initiation of treatment, the absence of severe concomitant somatic diseases and chronic neurotic disorders, the prognosis is usually favorable. It should be remembered that repeated exposure to provoking factors can cause a relapse of the pathology. Primary and secondary prevention include stress prevention, proper organization of the daily routine, and balanced nutrition.
Call 8(969)060-93-93 and make an appointment.
Our offers
Our clinic treats mental disorders in Moscow.
If you have symptoms of stomach neurosis, contact us. We employ experienced psychiatrists. They specialize in the treatment of psychosomatic diseases of various internal organs caused by psychological reasons. Our doctor will examine you, perform the necessary tests, after which he will make an accurate diagnosis and provide appropriate treatment. If necessary, a psychiatrist can visit your home.
Call by phone
Nervous disorders and gastrointestinal tract
The majority of complaints to a gastroenterologist (heartburn, belching, abdominal pain, intestinal dysfunction, bloating) are based on motor disorders of the gastrointestinal tract (impaired smooth muscle function). These disorders may be associated with improper contractions/relaxations of hollow organs (stomach, intestines) and sphincters - muscle sphincters (cardiac sphincter, sphincter of Oddi, gallbladder sphincter, etc.).
Motor impairments can be either primary, functional, or secondary due to organic pathology (inflammation, erosion, ulcers, etc.).
It is in the development of functional disorders that psychogetative disorders play a large role.
How does this happen?
A short-term psycho-emotional disorder causes activation of certain brain structures (limbic system, reticular complex), these structures send signals to internal organs through special chemicals (mediators), provoking an autonomic reaction (palpitations, sweating, gastrointestinal spasms, etc.). If stress continues, the pathological chain can be fixed (cerebral cortex - hypothalamus - organ), as a result, autonomic dysfunction develops, and disorders of internal organs will become permanent.
The following signs may indirectly indicate a psychogenic etiology: multiple complaints, repeated, or, on the contrary, varied; complaints may be exaggerated, when presented they are accompanied by emotional overtones, the age of the patients is relatively young, repeated visits to doctors of different specialties, an insistent demand for numerous examinations, a skeptical attitude towards classical medicine, and often precedents for turning to alternative methods of treatment.
At the same time, during laboratory and instrumental examinations, pathological processes are not detected, or their severity does not correspond to the clinical picture.
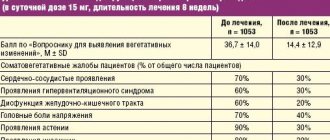
The following psychovegetative (somatoform) conditions are associated with gastroenterology:
- Anxiety. It manifests itself as a feeling of internal tension, irritability, anxiety, unjustified and groundless expectations of negative events. Sometimes it can manifest as pronounced fear, up to the development of a panic attack.
- Depression. It manifests itself as a decrease in the general background of mood, a decrease in activity, both mental and physical, and a loss of the ability to enjoy life. Additional manifestations include changes in appetite, sleep disturbances, negative thoughts, even suicidal thoughts.
- Hypochondriacal disorder. A condition in which the patient actively searches for a “hidden” “non-obvious” disease, undergoes numerous examinations, sometimes manipulates doctors and relatives, and in some cases insists on medical manipulations, including surgical interventions.
The above somatoform disorders lead to the following functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract:
- Functional esophageal disorders
- Functional dyspepsia
- Biliary dysfunction, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Functional anorectal disorders.
Treatment of somatoform disorders can be carried out by general practitioners and specialists, taking into account some prejudice of patients to visit psychiatrists. Treatment includes drugs that regulate gastrointestinal motility, as well as antidepressants, nootropic drugs, and anxiolytics.
Be healthy!
Make an appointment with a gastroenterologist
Gastroenterologist - Bakhova Anastasia Anatolyevna
You can make an appointment by calling 205−00−48 or through your personal account