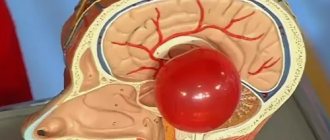
The pineal gland or pineal body (pineal) is a neuroendocrine gland located between the cerebral hemispheres and is part of the diencephalon. It got its name because of its oval shape. Weighs only 0.2 g and measures 1.5 cm x 1 cm.
Why is it considered neuroendocrine? Because it relates to both the brain and the endocrine system. This is expressed in the fact that it affects some processes in the body, and also produces hormones.
On the outside, the epiphysis is covered with a soft connective tissue membrane, from which trabeculae extend and divide it into lobules. The lobules consist of polygonal cells - pineacites. The gland has a rich blood supply.
Functional significance of the gland
The significance of the pineal gland is not fully understood; it is too small and deeply located. But the hormones that it produces have been identified: melatonin, serotonin, pinealin, adrenoglomerulotropin, dimethyltryptamine.
Serotonin is a precursor to melatonin and is involved in the regulation of circadian rhythms (sleep and wakefulness). 80% of melatonin is produced in the pineal gland. Melatonin inhibits the development of the gonads in children, affecting the gonadotropic hormone. To produce it, absolute darkness is needed, otherwise its synthesis immediately stops. Therefore, the formation of melatonin occurs during night sleep. With the end of puberty, production decreases.
The pineal gland in children affects the functioning of the entire endocrine system: the thyroid gland, adrenal glands and pituitary gland. It not only participates in the regulation of sexual development, but is also a connecting element between the tissues of the cerebral cortex. In addition, the pineal gland reduces the production of growth hormone, inhibits sexual behavior, the development of tumors, and is responsible for orientation in space and time; regulates the exchange of Ca, P, K, magnesium; regulates seasonal rhythms; has antioxidant properties, exhibits antitumor protection, and delays aging.
Serotonin is not only a precursor to melatonin, but is also considered the hormone of happiness, creates a good mood and improves emotional background. Adrenoglomerulotropin - regulates the production of adrenal hormones, stimulates the production of aldosterone, thus participating in electrolyte metabolism.
Pinealin lowers blood sugar. Little studied.
Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is responsible for dreams and clairvoyance, near-death experiences.
For centuries, the pineal gland was considered the seat of the soul, in esotericism - the third eye, determining the ability to clairvoyance and transmit information at a distance - telepathy.
Apparently, this is due to the fact that the pineal gland itself can perform rotational movements, reminiscent of the movements of the eyeball.
In addition, the structure of the gland contains rudimentary elements like a lens and some receptors reminiscent of the eyeball, but they are underdeveloped.
The pineal gland in children actively grows, but already from adolescence its growth gradually decreases. With age, it begins to involute and its activity decreases.
Pineal gland diseases
As in any other organ, developmental anomalies, inflammation, damage by parasites, trauma, neoplasms, cysts, etc. are possible here. Pineal cysts are rare - they account for only 2% of brain pathologies. But some researchers believe that the figure is greatly underestimated. There are many more cases, but it is difficult to identify them due to the lack of symptoms.
Causes of cysts
What is a pineal cyst? A cyst is a cavity filled with a liquid substance and bounded by a membrane.
A true cyst is an exclusively benign formation and does not degenerate into oncology. But neurosurgeons often encounter a parasitic cyst filled with echinococci.
Most often, such a cyst in the pineal region of the pineal gland is formed as a result of echinococci and other parasites entering the brain through the bloodstream. The larva infects the pineal gland and forms its own capsule, where the products of its vital activity accumulate.
Such a cyst is extremely toxic and dangerous. The difficulty is that this capsule is completely protected from the immune system. A cyst of this origin tends to grow.
- Other reasons for the appearance of a pineal gland cyst include: narrowing or blockage of the gland's outlet canal, in which melatonin begins to accumulate inside, gradually forming a cavity. Such changes are possible after inflammatory processes or embolism.
- Congenital anomalies of the brain in embryogenesis.
- TBI, which can lead to dystrophy and degeneration of brain tissue.
- A stroke, when a hematoma appears as a result of hemorrhage, turning into a cyst.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Untreated infections.
A cyst in the pineal region in children is often congenital in nature (due to brain hypoxia, birth injuries to the head), or occurs after infections that occur immediately after birth.
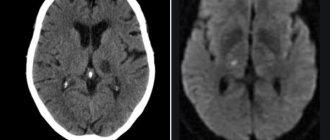
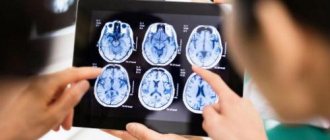
What does a cyst look like on an MRI of the brain?
Cystic structure of brain metastases on MRI
The brain is studied using high-field equipment with a power of 1.5 Tesla, which allows creating detailed and clear images. With magnetic resonance imaging, monochrome sections of the area under study are obtained in increments of 1-2 mm. On MRI images, brain cysts appear as round formations of varying diameters with clear contours. The deviation can be determined by the change in the signal. The intensity of the latter will be different compared to healthy areas. The difference is clearly visible in the photographs. Special scanning modes allow you to obtain more detailed information about the cyst and determine its type:
- Epidermoid. It is usually located in the area of the cerebellopontine angle, prepontine cistern, quadrigeminal tract, ventricles, and less commonly in the hemispheres. Growth is slow, with the risk of compression of the brain stem, entrapment of nerves and blood vessels. There are signs of inflammation around the epidermoid cyst. The intensity of the signal from the formation is usually heterogeneous, but corresponds to the cerebrospinal fluid (if there is no fat inside). On DWI and FLAIR images, the cyst appears lighter than the brain fluid. Epidermoids with fat inside T1-weighted images give a hyperintense signal, on T2 - hypointense (compared to the cerebrospinal fluid).
- Dermoid. Usually the formation is located in the midline of the skull. Due to the high lipid content, T1 imaging gives a hyperintense signal. Unlike the epidermoid, it always has a heterogeneous structure.
- Lipoma. Fatty cysts are most often located in the area of the corpus callosum, interhemispheric fissure, pituitary infundibulum and hypothalamus. MRI scans reveal clear contours of the tumor. Mass effect and swelling of surrounding tissues are not observed. On T1 WI the cyst is sharply hyperintense. On T2 VI it is the opposite (compared to cerebrospinal fluid). Calcifications and vessels look like hypointense areas in the structure of the formation.
- Ependymal. A rare type of cyst that forms under the membrane lining the brain cavity. On MR scans it looks like a formation with clear contours, the signal intensity corresponds to the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Arachnoid. It is formed as a result of the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid between the sheets of the arachnoid membrane of the brain, most often in the middle cranial fossa, interhemispheric fissure, cerebellopontine angle, at the level of the quadrigeminal. On T1, the VI looks somewhat lighter than the cerebrospinal fluid. In FLAIR mode it produces a hypointense signal.
Arachnoid cyst (indicated by arrow) on an MRI scan
- Neuroglial. Found in the cerebral parenchyma, in the area of the choroid plexus of the ventricles. In the photographs it looks like a round formation with liquor contents, often combined with anomalies of brain development.
- Colloidal. Usually located in the anterior superior part of the third ventricle, between the foramina of Monroe. It has a round shape, a fibrous capsule, and clear contours. In the presence of protein in the contents, it gives a hyperintense signal on T1 VI and a hypointense signal on T2 VI. Contrast does not accumulate.
- Rathke's pouch cyst. Rarely seen. Located in the area of the sella turcica. The signal intensity depends on the nature of the content. When serous, it gives a typical fluid response. Mucoid contents are characterized by a hyperintense signal on T1-weighted images. When contrasting, accumulation of the substance is observed in the capsule area.
Arachnoid cyst (circled in red) on MRI
An experienced radiologist knows exactly what a cyst looks like in an MRI photo. An ordinary person will not be able to independently identify and differentiate education. In doubtful cases, it makes sense to show the research results to several specialists.
Kinds
There are 5 types of cysts:
- arachnoid (the most common and most dangerous);
- colloidal;
- pineal;
- dermoid;
- epidermoid.
An arachnoid cyst of the pineal region or cerebrospinal fluid is localized in the arachnoid membranes of the brain, filled with CSF. More often diagnosed in men, it develops after inflammation and infections. Gives symptoms in case of increased ICP and compression of an area of the cerebral cortex with its increased growth.
Colloidal cysts are usually congenital and do not manifest themselves for a long time. If there are disturbances in liquorodynamics, they can cause the development of intracerebral hernias and hydrocephalus with a fatal outcome.
Dermoid and epidermoid cysts manifest themselves during embryogenesis. The contents of such cysts include fat, hair, etc.
They tend to grow rapidly, which indicates the need for urgent removal after the birth of the child.
Pineal cysts are neoplasms of the body of the gland; they are always very small and harmless.
Signs of a cyst
If the size of the cyst in the pineal region is no more than 1 cm, it does not manifest itself in any way and is not detected. Their diagnosis is most often random during studies for other reasons related to brain pathology and MRI.
The greatest danger is posed by growing cysts of the pineal region, which can cause circulatory problems in the surrounding tissues and lead to hydrocephalus.
With a growing cyst, its manifestations may be as follows:
- causeless cephalgia that is not relieved by analgesics;
- diplopia;
- dizziness;
- decreased vision;
- fatigue and fatigue;
- apathy;
- insomnia at night and drowsiness during the day;
- disturbances of coordination and orientation.
Parasitic cysts may present with more severe symptoms and general intoxication:
- muscle weakness;
- convulsions;
- developmental delay in children with speech delay;
- decline in information perception;
- loss of vision and hearing;
- decreased tissue sensitivity;
- extrapyramidal disorders.
They are expressed in disturbances in motor activity due to impaired muscle tone. Either complete immobility or muscle twitching may occur.
The extrapyramidal system is responsible for human postures, the accuracy of his movements and the coordination of muscle actions. With extrapyramidal syndrome, all this is disrupted.
Paranasal sinus cyst - symptoms and treatment
Treatment depends on the type of cyst, its location and size. If it is less than 1 cm and there is no discharge, then the doctor suggests conservative methods: regular examination, tablets, sprays and drops. If the cyst is large or there is purulent discharge, then surgery will be required.
Drug treatment of cysts
The method allows you to eliminate unpleasant symptoms and causes of cyst formation: swelling, inflammation and blockage of the sinus anastomosis. Drug treatment is effective and can alleviate the patient's condition in the early stages of the disease. However, it will not help when the fibrous membrane of the cyst has become too dense.
Drugs used:
- vasoconstrictor drops - quickly reduce swelling in the anastomosis area and normalize ventilation of the sinuses of the nasal cavity; medications in this group are addictive and can be safely used for no more than 5 days in a row;
- antihistamines - will help if the cyst is caused by allergies;
- mucolytics - normalize the outflow of mucus;
- antiseptics - help fight inflammation and cleanse the surface of the nasal mucosa;
- topical glucocorticosteroids are most effective in the treatment of allergic rhinosinusopathy, prolonged sinusitis, hyperplasia of the mucous membrane in the area of the anastomosis and ostiomeatal complex;
- painkillers - reduce pain caused by the pressure of the cyst on surrounding tissues [6];
- probiotics - normalize the microflora of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx, which is important in the treatment of chronic inflammation of the upper respiratory tract.
Surgery
Indications:
- cyst more than 8 mm;
- ineffectiveness of conservative treatment;
- signs of suppuration inside the cyst [7].
The most popular method of treating cysts is puncture or puncture. The surgeon pierces the wall of the cyst with a thin needle and pumps out the purulent discharge [1]. However, this method only has a temporary effect. Piercing the cyst, as well as spontaneous leakage of its contents, relieves pain for a while. But gradually the cyst grows together again and begins to accumulate purulent fluid. To remove it completely, more serious surgery will be required [8].
Maxillary sinusotomy according to Caldwell-Luke
It is performed through an incision under the upper lip in the mouth. This is a classic method for removing sinus cysts, but now it is practically not used due to its high morbidity: after the operation, scars, adhesions can form and the functioning of the sinuses can be disrupted.
Microsinusrotomy
A minimally invasive surgical technique that is performed through the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus. A 4–8 mm hole is formed in the bone, and the cyst is removed with special instruments. Performed under general anesthesia. The disadvantage is the risk of damage to the branches of the trigeminal nerve and the formation of persistent facial neuralgia.
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS surgery)
This method is considered the most gentle and effective: during the procedure, unnecessary incisions and punctures are not made on the patient’s face. It is performed through the nasal cavity under endoscopic control. Allows you to reach all paranasal sinuses, including the sphenoid, frontal sinuses and cells of the ethmoid labyrinth. The operation is performed under local and general anesthesia [17].
Additional benefits:
- can be used to treat children;
- reduce the likelihood of cyst recurrence;
- you need to stay in the hospital for no more than two days;
- the incision heals quickly;
- the operation leaves no scars;
- there is no risk that adhesions will appear [18].
Relative disadvantages: trained specialists and special equipment are required, which makes the operation expensive.
Treatment of epiphysis cyst
In most cases, treatment of pineal cysts does not require the use of drugs. The use of drugs is possible only for echinococcosis, at its earliest stage. Symptomatic treatment to eliminate the manifestations of the disease is prescribed only when they appear. And this happens when the blood vessels of the brain or its tissues are compressed by a growing cyst. Or surgical treatment is used - most often. Due to the complexity of access, operations are difficult and there is a high percentage of complications - 60-70%.
Indications for surgery:
- severe symptoms;
- parasitic nature of the cyst;
- cyst growth;
- hydrocephalus;
- influence on the cardiovascular system.
If pathology is identified, further treatment of a cyst in the pineal region of the brain is aimed at reducing the risk of its growth.
Treatment of pineal brain tumor
Treatment is prescribed based on the examinations performed. If the pineal region is affected, all laboratory tests and tumor markers must be taken, after which CT and MRI are prescribed. Having received the examination results, the doctor can clearly determine the sequence of actions. Most often, surgery is required, and removal is done as quickly as possible. Pineal brain tumors can be quite large, making the treatment process extremely difficult. Often it is simply impossible to remove such a lesion due to the possibility of causing irreparable harm to the patient.
When prescribing treatment, the doctor must focus on the general clinical picture, use the maximum diagnostic process, assess the general condition of the patient, and determine the possibility of eliminating the formation without causing harm. If traditional methods of therapy, in the opinion of the doctor, do not give the desired result, one should resort to the use of a surgical process in combination with chemotherapy, medications, radiotherapy, etc.
Radical treatment methods
Shunting - a drainage is installed, with the help of which the cyst is emptied, after which its walls fall off and become overgrown. But surgery can often have negative consequences for the body due to the complexity of the brain structure.
Endoscopy – the cyst is removed through a puncture in the skull. This method does not cause complications, but there are contraindications in the form of visual impairment.
Craniotomy is an effective operation where a specific area of the skull is removed to gain access to the brain. Has a high risk of brain damage.
Rehabilitation in the postoperative period
Rehabilitation after removal of a brain cyst includes a number of points that deserve special attention. For example, drinking alcohol is prohibited for a certain period of time. Air travel is not advisable for approximately 3 months. Active sports that may involve mechanical impact on the head are also prohibited. Visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or ultraviolet radiation can have negative consequences.
As a rule, rehabilitation after brain surgery is carried out according to a specially developed program, which is formed depending on the type of cyst, type of neurosurgical intervention, the presence of complications, and the postoperative condition of the patient. It is advisable to contact your doctor at the first suspicion that something is going wrong.
Symptoms of cysts in children
They are common to adults, but the development of pineal cysts in a child at an early age has its own characteristics. The child may complain of a headache, may experience vomiting and nausea, impaired motor skills, and poor coordination; complaints of blurred vision and blurred vision.
With pathology of the pineal gland, growth hormone will increase, which will lead to accelerated growth rates. Such children are superior to their peers in weight and height; puberty can also be advanced or, conversely, delayed. Perversions of sexual desire may develop in a child. What you really should be afraid of when you discover a cyst in the pineal region of the brain in a child is hydrocephalus of the brain, when CSF accumulates in its ventricles.
Hydrocephalus leads to mental retardation.
Since the fontanelles of the skull in young children are not yet overgrown and the skull bones are soft, hydrocephalus is manifested not by tissue compression, but by expansion of the subarachnoid space due to divergence of the skull bones and an increase in brain volume.
The head takes on a characteristic shape with an expansion in the frontal region, which in medicine is called the alien symptom.
This is popularly called dropsy of the brain.
Treatment
Dictate the symptoms and treatment of pineal cysts of the brain. Any surgical intervention is always risky, so surgery in children is performed only when the benefit outweighs the risk.
Monitoring a cyst means undergoing MRI diagnostics once every six months. For echinococcosis, treatment with anthelmintic drugs is used.
For hydrocephalus, a puncture of the subarachnoid space is performed with fluid suction.
If hydrocephalus recurs, a cerebro-abdominal shunt operation is performed. Its essence is that a catheter is inserted into the abdominal cavity from the skull and the liquid constantly flows there without lingering in the brain. And since fluid constantly circulates in the stomach, cerebrospinal fluid is quickly absorbed there.
Diagnosis and treatment of brain cysts
The cost of surgery to remove a brain cyst depends on the type of disease and the diagnosis.
When examining a patient, computer or magnetic resonance imaging equipment must be used. Additionally, the heart and blood vessels of the brain are examined, blood pressure is checked, blood is donated for the presence of autoimmune and infectious diseases, coagulability and cholesterol levels. After receiving all the data, the neurosurgeon prescribes a course of treatment. If the tumor is dynamic, but is not accompanied by dangerous symptoms, medication is sufficient. The cost of medications is affordable in most cases. The main task of drugs is to eliminate the causes of the disease. For example, resorption of adhesions, restoration of blood circulation, reduction of cholesterol concentrations, normalization of blood pressure.
Important points in the treatment of cysts are considered to be: providing brain cells with glucose and oxygen, increasing their resistance to intracranial pressure, and solving problems such as weakened immunity. When detecting infectious diseases, special attention is paid to this issue. If you miss this moment, you may end up paying a high price, because the situation will definitely get worse.