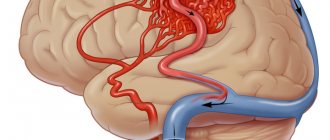
Brain contusion is a traumatic brain injury and is accompanied by focal damage to brain tissue and necrosis. The consequences of this condition seriously affect the entire body. The patient may suffer from functional and neurological disorders, and there is also a risk of falling into a vegetative state.
A brain contusion can occur when falling from a great height, due to a strong blow, or during an accident. The condition also varies in severity of consequences.
Symptoms and warning signs after a stroke
You can get a strong blow to the back of the head when practicing martial arts.
Injury to the back of the head can be accompanied by a decrease in the quality of visual function, since this area is connected to the optic nerves. In some cases, loss of consciousness or a feeling of numbness in the extremities (especially the lower ones) is provoked. This sign is explained by a possible concussion. It is not recommended to neglect a bruise of the occipital part. In medicine, there are cases where damage made itself felt after many years.
Symptoms may vary depending on the degree of injury and the exact location of the injury. With minor damage to soft tissue, a hematoma forms. A strong blow to the back of the head usually causes a concussion (ICD-10 code S06.0).
The main signs of mild damage are:
- drowsiness;
- pain;
- diplopia;
- loss of consciousness.
In case of severe trauma, a person experiences:
- loss of consciousness;
- headache;
- nausea;
- noise in ears;
- fear of light and sounds;
- nystagmus;
- asthenia;
- change in heart rate;
- sweating;
- sleep disorders.
Serious damage can be caused by hitting the back of your head against a wall or ice. The injury is characterized by clouding of consciousness, short-term loss of speech and paralysis of facial muscles. The person may feel very dizzy.
If someone hits a child on the back of the head and he has a headache, this is particularly dangerous.
Moderate brain contusions
This injury usually involves a fracture of the skull bones and is accompanied by subarachnoid hemorrhage. She shows herself:
- loss of consciousness for 1–3 hours, psychomotor agitation;
- amnesia;
- severe dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- intense headaches;
- high blood pressure, rapid heartbeat;
- increased body temperature;
- meningeal symptoms;
- severe focal neurological symptoms (changes in muscle tone, paresis, loss of sensation in the limbs, epileptic seizures, speech impairment, etc.).
Signs of moderate brain contusions persist from several weeks to 2 months. The consequence of this condition may be irreversible changes that occurred during the injury.
Diagnostic methods
The degree of damage is assessed using MRI images.
In order to diagnose damage caused by trauma to the occipital part, it is necessary to consult a neurologist. The specialist will evaluate the biomechanics of the cervical spine, determine range of motion and muscle tone.
Clinical diagnosis is based on examination results. If it is impossible to clarify it, additional procedures are carried out. MRI, CT and echoencephalography are usually prescribed.
Mild brain contusions
They are not accompanied by a threat to life and manifest themselves with the following symptoms:
- loss of consciousness, lethargy, drowsiness, memory loss;
- dizziness, vomiting;
- changes in heart function, increased blood pressure;
- neurological disorders (tremor of the eyeballs, lack of pupillary response to light, decreased muscle tone, anisocoria);
- meningeal symptoms (neck muscle tension, Brudzinski and Kernig symptoms).
There are no serious consequences for mild brain contusions. The prognosis for the patient is favorable. Symptoms disappear within 3 weeks.
Main services of Dr. Zavalishin’s clinic:
- consultation with a neurosurgeon
- treatment of spinal hernia
- brain surgery
- spine surgery
First aid
If a person hits the back of their head, it is recommended to apply a cold compress to the affected area. You can use ice wrapped in a cloth or a bottle filled with cold water. You need to keep the compress for 15-20 minutes, then take a half-hour break and repeat the procedure. It is extremely important to monitor your pulse and breathing. If blood appears, the wound should be disinfected and bandaged.
A severe concussion is accompanied by poor circulation and severe hematomas around the eyes. The injured person should be kept at rest. The victim may feel sick, so it is necessary to turn him on his right side so that the vomit can come out freely and air can enter the lungs. It is recommended to tilt your head back slightly and tilt your face closer to the floor. Limbs should be placed at an angle of 90 degrees to prevent fractures during convulsions. It is necessary to call an ambulance and not take any action until the doctor arrives.
It is not recommended to give painkillers, as they interfere with the diagnosis of the injury.
Classification of TBI by severity
There is a special Glasgow scale. It helps determine the severity of the head injury. Experts conduct tests and evaluate:
- motor reactions;
- speech reactions;
- opening the eyes.
For each test, points are awarded and summed up:
- 14-16 - mild degree;
- 9-13 - average;
- 8 - heavy;
- 3 or less - deep coma.
Regardless of the severity of the injury, it is important to seek help promptly. Timely and adequate therapy reduces the risk of complications and improves the prognosis.
Treatment methods
Heparin ointment is used to resolve the hematoma.
Treatment at home is justified in cases of minor injury. Experts recommend the use of external agents Heparin, Traumeel gel or Dolobene gel. In accordance with the instructions, ointments are applied 2-3 times a day.
A hematoma in the occipital region is eliminated with cold compresses. If a lump forms, it is recommended to use Troxevasin or Gepatrombin ointment.
During the treatment period, it is necessary to reduce the time spent watching TV or spending time in front of a computer monitor, and avoid physical activity. This regime should be followed for a month. It is recommended to spend more time in the fresh air.
In case of a concussion, the pathology must be treated in a hospital setting under the supervision of a neurologist, surgeon and traumatologist. The duration of rehabilitation for a child is 1 month, and for an adult - 2 weeks. It is extremely important to maintain bed rest and avoid bright lights and loud sounds.
To eliminate headaches, analgesics Ibuprofen, Noofen, Nimesulide, Maxigan are prescribed.
In some cases, the patient experiences sleep disturbance or drowsiness, sudden mood swings and memory loss. To improve the general condition, sedatives Adaptol, Novopassit, Persen are prescribed, as well as drugs that help optimize blood circulation in the brain. This series includes Piracetam, Cavinton, Sermion, Trental, Cinnarizine, Instenon. Neuroprotectors Cerebrolysin, Actovegin, Gliatilin, Mexidol, Neurox are also used. To improve memory, nootropics Phezam, Selank, Phenotropil are prescribed.
In order to optimize the functionality of the nervous system, it is recommended to take B vitamins Milgamma, Neuromultivit, Benevron BF, Neurobion, as well as vitamins containing magnesium Magne B6, Magnelis B6.
For constant apathy, a course of antidepressants Tsitol, Stimuloton, Fluoxetine is recommended. Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a neurologist.
Massage
Massage helps improve blood circulation and normalize the functions of the neck and brain.
Procedures are prescribed for impaired motor functions after a severe brain injury. First of all, the back is massaged, then the limbs and abdomen. Stroking, rubbing and kneading are used. The duration of exposure is 10-20 minutes. The course includes 15-20 procedures.
For mild to moderate concussion, massage can be done 2-3 days after the injury. The back of the head, neck and forearms are warmed up while the patient is sitting. Then the back and shoulder blades are rubbed. Also, during the first 3-5 days, cryomassage is used, which involves the use of liquid nitrogen. The duration of the procedure is 5 minutes. The course includes 8-10 procedures.
Physiotherapy and spa treatment
Physiotherapeutic methods are indicated for severe bruises. They serve as an adjunct to drug treatment. Helps optimize cerebral circulation and metabolism.
Among the main procedures it should be noted:
- electrophoresis with vasodilators and cerebral circulation stimulants;
- galvanization of the brain and its segments;
- transcerebral UHF therapy;
- laser therapy;
- oxygen baths.
Patients who have suffered a mild form of concussion, after two months from the onset of the disease, can be sent to climatic and balneological resorts in Kislovodsk, Pyatigorsk, Essentuki, Solnechnogorsk.
Resort rehabilitation is not indicated in the acute phase of the disease, in the presence of contraindications and mental disorders.
Treatment with folk remedies
Ginseng root in the form of a decoction helps normalize blood circulation in the brain.
To speed up therapy, they often resort to using traditional medicine recipes. For example, it is recommended to add aloe juice to medications. Stimulation of blood circulation is facilitated by an infusion based on string, St. John's wort or ginseng. If apathy is present, taking valerian or motherwort is indicated.
Before using traditional medicine, you should consult a doctor. A specialist can choose the appropriate combination of medications and herbs.
Nutrition
When restoring the nervous system, honey, potato or cabbage juice, and flax oil are useful. It is recommended to include nuts and dried fruits in your diet. Nutrition should be varied, but not heavy. You should consume more citrus fruits and drink plenty of water.
It is necessary to completely eliminate alcoholic beverages, caffeine, and nicotine.
Types of injuries due to noise in the head:
The most common form of closed TBI and the cause of noise in the head is a concussion. It can occur with a blow to the head, a fall, playing sports, or as a result of a car accident. The most traumatic sports in terms of TBI include boxing, hockey, karate, judo, football, and cycling.
Note! In most cases, after a concussion, post-concussion syndrome develops, in which the symptoms of a TBI do not go away for several weeks or even months.
With a concussion, unlike other head injuries, there are no internal pathological changes, that is, there is no damage to brain structures. With hematomas and hemorrhage, we are talking about a bruise (concussion), which is one of the more severe types of TBI. It occurs as a result of a blow to the head when falling on a hard surface (for example, hitting ice), during an accident, sports competitions, or combat.
For mild head injuries, there may be no visible signs
In the structure of TBI, brain contusion accounts for 20-25% of cases. It is characterized by crushing of nervous tissue, with the formation of a hemorrhage focus in the medulla.
Symptoms of bruises and concussions depend on the severity of the traumatic brain injury. Therefore, TBIs can be mild, moderate, or severe.
Let's take a closer look at the types of head injuries that cause noise in the head.
After a concussion
Under the influence of mechanical force, the brain shakes inside the skull, vascular spasm occurs, blood flow changes, which causes functional disorders to develop. Autonomic disorders come to the fore.
Mechanism of TBI
More often than not, after a concussion, noise in the head and other symptoms appear on the day of the injury. In severe TBI, delayed symptoms occur over several days or weeks and require special attention.
Clinical picture of concussion:
- brief confusion or loss of consciousness;
- single vomiting immediately after injury;
- retrograde amnesia;
- pale skin;
- dizziness;
- noise and ringing in the ears;
- double vision;
- constriction or slight dilatation of the pupils;
- nausea;
- weakness;
- pressing headache;
- increase in body temperature.
Immediately after a concussion, a person cannot concentrate; there are problems with coordination of movements, speech, hearing, and vision. Confusion lasts from 5 to 30 minutes.
There are 3 stages of concussion severity:
- Easy. Has the most favorable course. The person’s condition returns to normal after 20 minutes. after injury. The disturbance of consciousness is mild, slight fainting, problems with spatial orientation, headache, nausea and dizziness, and increased body temperature are possible.
- Average. Disorientation lasts more than 20 minutes, temporary memory loss is possible. The victim does not remember the events that occurred immediately before the injury.
- Heavy. A concussion is always accompanied by loss of consciousness, and retrograde amnesia develops. Dizziness, headache, noise in the ears and head persist for a long time. The victim constantly feels sick, has no appetite or strength.
Headache and dizziness may persist for several months after a TBI, but this is not normal. Regardless of the severity of the injury and clinical manifestations, it is necessary to immediately undergo a neurological examination. Comprehensive diagnostics and qualified medical care will be provided at the medical center.
With timely and correct treatment, the patient's condition returns to normal within 1-2 weeks. If the victim did not go to the hospital on time, then a month after the injury, delayed symptoms may occur:
- headache of a pressing or squeezing nature;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness during the day, sleep disturbance at night;
- fatigue, nervousness;
- increased anxiety, depression;
- decreased mental activity;
- irritability;
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- noise in ears.
Sometimes patients who have suffered a traumatic brain injury suffer not only from neurological, but also mental disorders, which include depression, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive and other disorders.
After hitting your head or falling
Hearing disorders and noises in the head are often the result of blows to the back of the head or falling on the ice while skating. It is in the occipital region that the brain regions responsible for vestibular and auditory function are located.
The severity of the consequences and symptoms depends on the type of TBI. A noise in the head after a fall may indicate the following injuries:
- brain concussion;
- fracture of the skull bones, due to which compression of the brain structures occurs, blood circulation is disrupted, and intracranial pressure increases;
- hematoma or hemorrhage, which is a sign of brain contusion;
- damage to the eardrum or inner ear.
An alarming signal is a severe headache after a blow or fall, which intensifies when tilting the head, does not go away the next day. If it is caused by a brain contusion, then nothing can stop it. After a few days, relief may occur, but then the patient’s condition will sharply worsen. Without treatment, the swelling will only increase, increasing the likelihood of repeated hemorrhage.
With a mild injury, the blood in the brain completely resolves within 2-3 weeks
The clinical picture of a brain contusion depends on the severity of the injury:
- Easy. The main symptoms include short-term loss of consciousness, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, increased sensitivity to loud sound and bright light, deterioration of memory and concentration.
- Average. TBI of this severity is characterized by more massive intracranial hematomas and severe neurological disorders. As a result of a brain contusion, a person loses consciousness. He is in an unconscious state from several minutes to 2-4 hours. In addition to loss of consciousness, there is a headache, sensory disorders, respiratory problems, and noise in the head and ears.
- Heavy. If the injury is severe, the person may fall into a coma. Since vital functions, which include breathing and blood circulation, are disrupted, long-term rehabilitation is required.
After a brain injury, long-term consequences are likely, which can cause noise in the head and constant headaches. These include impaired cerebral blood flow, intracranial hypertension, vasospasm, and hydrocephalus.
Post-traumatic headache
Appears within 1-2 weeks after a head and neck injury, disappears as you recover. It is a consequence of mechanical or impulse impact during falls, road accidents, bicycle collisions, fights, sports competitions, etc.
Post-traumatic headache (PTHA) occurs for the following reasons:
- cerebral edema;
- pressure on the meninges;
- damage to nerve endings;
- hemorrhages, hematomas;
- dislocation of the cerebral hemispheres;
- increased intracranial pressure.
Predisposing factors for the appearance of PTTH include stress, sleep problems, taking painkillers, impaired production of serotonin, dopamine, adrenaline, norepinephrine.
Post-traumatic headache resembles migraine or tension headache
According to the nature of the pain syndrome, it can be acute (lasts less than 3 months) and chronic (more than 3 months). Accompanied by the following accompanying symptoms:
- nausea or vomiting;
- sound and light sensitivity, intolerance to certain odors;
- hearing impairment;
- sleep disturbance;
- ringing in the head, ears;
- decreased cognitive abilities;
- dizziness;
- mood swings.
With an increase in intracranial pressure, PTTH intensifies in the morning and has a bursting character. In some patients, it spreads along the nerve fibers, affecting the area of the temple, orbit and back of the head, and intensifies with coughing, physical activity, and head movements.
Note! Noise in the head and ears, as a long-term consequence of TBI, is more common with mild degrees of damage. If the patient did not immediately call an ambulance because he considered his condition to be satisfactory, he should definitely be examined in the next few days.
Tailbone injury
Injuries to the coccygeal-sacral region are characterized by pain in this place and the lower back, varicose veins in the lower extremities, in the rectum or pelvis. So-called “bones” will form on the legs, while the feet, knees and hip joints may hurt, and the legs will constantly swell. An injured tailbone can have a negative impact on pregnancy and childbirth. Sometimes it is impossible to completely eliminate the damage. But the treatment will definitely help a woman carry a child more easily and give birth by caesarean section.
Forehead and nose injuries
Surely many people remember how they hit something with their forehead so that “sparks flew.” Of course, after a while it seems that the blow was insignificant and not harmful to health. However, frontofacial injuries are among the most insidious and can have many negative consequences.
When the forehead and nose are injured, the bones that form the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses become blocked. The result is swelling of the mucous membrane, slower mucus release and nasal congestion. Under such conditions, local immunity decreases, and the environment for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms becomes ideal. Often the most common allergic rhinitis, which is manifested by copious mucus secretion upon contact with an allergen, is a consequence of a long-standing injury. The mucous membrane, overflowing with fluid due to chronic edema, reacts inadequately to the ingress of substances that are normally familiar and safe to us, and the protective reaction becomes overly pronounced.
After a blow to the forehead or face, the frontal bone moves out of place and can put pressure on the speech centers of the cerebral cortex. If this happens in a child, there may be delayed speech development or stuttering. This is especially evident against the background of the initial birth trauma. When struck, the bones of the nasal septum directly transmit the impact to the main (sphenoid) bone and to the sphenobasilar symphysis. The latter is the main mechanical center of the entire body. Therefore, severe injuries to the frontal-facial region affect the entire musculoskeletal system. Blockage of the symphysis limits the mobility of the sutures of the skull. As a result, the circulation of blood and cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, and the brain does not receive proper nutrition. Therefore, adults and children who have received such trauma may experience outbursts of aggression, short temper, depression, and panic attacks.
It will heal until the wedding! How to properly care for a wound Read more
If we analyze the behavior of those who had a forehead and nose injury, we can draw a clear pattern: irritability and nervousness developed or worsened in them precisely after the injury. Of course, it also happens that such character traits are associated with upbringing, but still injuries to the frontal-facial region play a very important role.
Article on the topic
Hello from the infirmary. What injuries can you get while playing football? With severe injuries to the area between the eyebrows, usually after 4-8 years, obesity can develop, which is very difficult to combat. Women often suffer from menstrual irregularities and infertility of unknown origin. According to statistics, every third adult has a pathology of the pituitary gland. Considering the number of skull injuries, this is understandable.
Also, injuries to the forehead and nose can cause disturbances in sleep, appetite (hunger and satiety centers are located in the hypothalamus), decreased visual acuity, and vertical strabismus. Natural consequences of incidents in this area are headaches, migraines, and weather sensitivity.
Diagnosis of TBI
Even if you provided first aid, know how to treat, and have previously encountered similar injuries, do not be arrogant. Examination of the victim by a qualified physician is mandatory. If you don’t want to call an ambulance, take him to the clinic yourself. Just before doing this, make sure that the spine is damaged and the skull bones are not cracked.
The most accurate conclusion can be made using magnetic resonance therapy and computed tomography of the head. The procedures are painless. With their help, you can thoroughly study the structure of the brain, look for the presence of hemorrhages, hematomas, etc.
If it is not possible to do MRI and CT (the clinic does not have machines), diagnostics should include:
- X-ray of the skull.
- Encephalography of the head.
- Examination by an ophthalmologist.
Encephalography will also help detect hemorrhage. In this case, hospitalization cannot be avoided.
If, after an injury, the patient has liquor leaking from the ears or bruises under the eyes in the form of glasses, you should consult a doctor immediately. Self-medication or lack of help, in this case, often leads to death.
You can undergo an MRI or CT scan in Moscow at any time of the day and regardless of the day of the week. You can find a clinic with 24-hour service, close to the patient, using the service: https://msk-mrt.ru/articles/. There are hundreds of medical centers operating in different modes here. Within a few minutes you can find a clinic and make an appointment by phone. Registration through the website allows you to get a discount on the examination.
Indications for hospitalization
A doctor may refer you for hospitalization if there are the following grounds:
- post-traumatic amnesia;
- prolonged loss of consciousness;
- coma;
- epileptic seizure;
- bleeding;
- disorientation;
- obvious disorders of the nervous system;
- the patient is pregnant (even if she feels normal).
During treatment for TBI, the patient's condition may fluctuate. Periodically, the symptoms intensify and subside. Predictions can only be made after a full course of therapy. Unfortunately, the mortality rate for TBI reaches 25%. The main cause of death is inadequate first aid and reluctance to go to the hospital.
Peculiarities of manifestation of traumatic brain injuries in children
In babies under one year of age, there is a sharp increase in temperature to 38°C and above. This reaction is associated with:
- wound infection;
- inflammation;
- suffered stress;
- inappropriate use of medications.
The child is not able to clearly describe his feelings, so it is quite difficult to make a diagnosis. There is a risk of underestimating the severity of the injury. Warning signs in this case are:
- pale skin;
- lethargy, drowsiness;
- increased heart rate.
Over time, vomiting, regurgitation, tearfulness, and capricious behavior appear. The baby sleeps restlessly and often gets up at night. If it is SHM, then the symptoms go away within a week.
Please note that infants and the elderly do not experience fainting during SHM.