This article uses excerpts from the chapter of the same name in the Face Anatomy atlas. It is of particular importance for specialists involved in the correction of age-related changes and contouring using fillers. The title “Dangerous triangle of the face” was not chosen by chance; it is in this zone that there are prerequisites of an anatomical and functional nature that can interfere with medical manipulation and cause side effects, including severe ones. Let's look at the topography of this triangle and the reasons for its danger.
Will an ultrasound of the neck vessels show a blood flow deficiency?
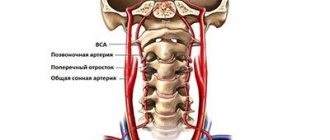
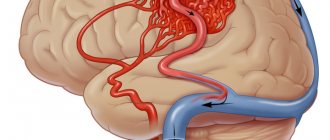
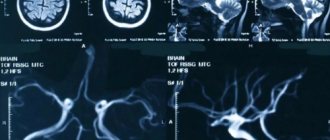
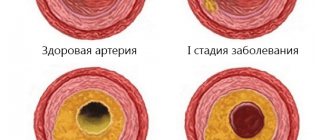
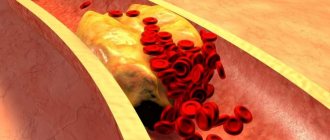
Blood flow deficiency is a very common pathology in the practice of neurologists and vestibulologists. A lot of people with headaches, constant dizziness and periodic fainting suffer from this disease. It occurs when, for one reason or another, the walls of the vessel narrow at the place where the right and left vertebral arteries inside the skull merge into one and together supply blood to the three main centers of the brain - the center of the vestibular apparatus, the center of vision, the center of hearing. Therefore, a lack of blood flow usually manifests itself as dizziness and tinnitus. Ultrasound can show the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the neck at different positions of the head. It is often important for neurologists to obtain data on the quality of blood flow in the carotid arteries. These vessels mainly supply blood to the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures. Thinking, memory, character, emotions and thought processes depend on how much oxygen the carotid arteries bring to the brain. If an ultrasound of the vessels of the neck shows a deficiency of blood flow in these arteries, the doctor must take urgent measures, since such a pathology can lead to loss of capacity. Basically, doctors encounter a deficiency of blood flow in the internal carotid arteries in post-stroke patients with one or more strokes in the past, in people who have suffered a heart attack, severe skull injury or several moderate concussions. Here, regular ultrasound of the neck vessels and MRI of the brain play an important role in assessing progress after therapy. Based on MRI and ultrasound data, the doctor can tell what and how the patient’s health has changed after treatment, and decide on a new form of therapy if the prescribed treatment is not enough and another course of other drugs is needed. In post-stroke patients, an ultrasound of the neck vessels will show how difficult the period after the stroke is, as well as how quickly or slowly the recovery is going.
| Service | price, rub. | Promotion Price |
| “Healthy Legs” program (duplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities with assessment of valves and perforating veins and duplex scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities) | 3200 rub. | 3000 rub. |
| Ultrasound triplex scanning of N/C veins with assessment of valves and perforating veins | 2500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound triplex scanning of veins of the upper extremities | 2000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound triplex scanning of the arteries of the lower extremities with measurement of the brachial-ankle index (BAI) | 2000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound triplex scanning of the arteries of the upper extremities | 2000 rub. | |
| Ultrasound duplex scanning of the arteries of the aorto-iliac segment | 1900 rub. | |
| Ultrasound duplex scanning of the abdominal aorta and visceral arteries | 1900 rub. | |
| Ultrasound duplex scanning of the inferior vena cava | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound duplex scanning of the iliac vein | 1700 rub. | |
| Ultrasound duplex scanning of the renal arteries | 1700 rub. | |
| Intracranial duplex of cerebral vessels | 2500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of neck veins | 2500 rub. | |
| Ultrasound of the brachiocerebral arteries (BCA) | 2500 rub. | |
| Heart ultrasound or echocardiography for adults | 2400 rub. | |
| Comprehensive neck diagnostics (MRI of the cervical spine, MRI of neck vessels, ultrasound examination of neck vessels, ultrasound of the thyroid gland and soft tissues of the neck, consultation with a neurologist) | 13200 rub. | 9500 rub. |
Will an ultrasound of the neck vessels show vascular compression?
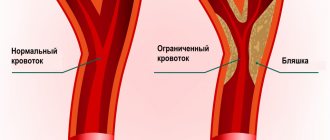
Dynamic vascular compression is the bending of a vessel from the outside at a certain position of the head or body, which leads to a temporary deficiency of blood flow. Dynamic compression of the vertebral and subclavian arteries is a common cause of regular or spontaneous fainting, as well as headaches and sudden attacks of dizziness (fainting). This pathology is closely related to osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. When the vertebrae are displaced relative to each other to some extent and their displacement presses on the outside of the vessel, this narrowing of the vessel actually leads to stenosis, but not due to an atherosclerotic plaque, but due to compression. Such compression can be either permanent or temporary. Vascular ultrasound can easily diagnose temporary compression through rotary functional tests. During an ultrasound of the vessels of the neck, the blood supply is checked in dynamics:
- with head turns;
- with a tilt of the head;
- in a lying and sitting position.
The most common location of vascular compression is the area of the vertebral arteries of the neck. They run in the bony canal of the spine and are therefore often compressed when the cervical vertebrae are misaligned relative to each other. Sometimes a person develops an abnormal bone spur that grows towards the vessel and also puts pressure on it. Such conditions can lead to sudden loss of consciousness both from childhood and in adulthood, when this situation has increased due to osteochondrosis. Diagnosis of compression of neck vessels requires an integrated approach. Typically, the neurologist prescribes the patient to undergo an ultrasound of the neck vessels and an MRI of the cervical spine. It is the ultrasound of the cervical vessels that can show hidden temporary compression of the vessel, and the MRI of the cervical spine visualizes the causes of the clamps if they are related to the condition of the intervertebral discs and vertebrae.
Previous NextCongenital anomalies of vascular development on ultrasound
Hypoplasia, that is, a small diameter of the vertebral arteries, is a fairly common finding in the practice of ultrasound diagnosticians. The most typical form of its manifestation is hypoplasia of one of the vertebral arteries with a decrease in blood flow in its basin. Often there is a high entrance of one or two arteries into the spinal canal, while part of the path of the vertebral artery is not protected by the bone canal and can be compressed when turning the neck. Less common are the absence of any of the vertebral arteries and hypoplasia of the carotid arteries. An ultrasound of the neck vessels will clearly show the presence of hypoplasia, but we will not always be able to say whether this is a congenital anomaly or an acquired narrowing of the vessel due to osteochondrosis. This pathology requires conservative vascular treatment in order to increase the general blood flow of the body so that compensation occurs at the expense of other arteries. The effectiveness of the treatment is usually monitored using a series of control ultrasounds of the neck vessels.
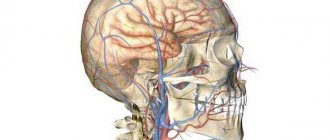
Triangle and arteries
One of the main arteries in this area is the facial artery, a branch of the external carotid artery. The facial artery, immediately after its origin, goes upward and passes to the face in front of the masticatory muscle, where its pulsation can be determined by palpation. Next, it is directed medially and towards the lips, giving off branches - the superior and inferior labial arteries, then passes under the muscle that lifts the upper lip, and reaches the wing of the nose, where its course becomes superficial and ends with two terminal branches - the arteries of the wing of the nose and the angular . Up to this point, everything is clear and clear, but in reality this is not always the case [Fig. 2].
Rice. 2. Facial artery - angular artery.
I will explain more clearly: there are many works with cadavers that emphasize the fact of the existence of frequently encountered anatomical variations and the place of origin of the facial artery, the course of this vessel and its branches. Often such variations are more the norm than the exception. Therefore, it can be argued that even with in-depth knowledge of anatomy, there is a possibility of complications due to the abnormal arrangement of blood vessels. Therefore, it is necessary to use techniques that help to avoid possible side effects as much as possible.
Will an ultrasound of the neck vessels show a tumor?
With an ultrasound of the vessels of the neck, doctors sometimes detect compression of the vessels by tumors.
First of all, it may be metastases of the lymph nodes of the neck. The peculiarity of metastatic tissue is that it is rigid, so it can compress the vessel or grow into its wall and form a tumor thrombus. All this is well visualized by a comprehensive ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck and ultrasound of the soft tissues of the neck. Initial appointment with a NEUROLOGIST
ONLY 1800 rubles!
(more about prices below)
How does ultrasound show tortuosity and deformation of blood vessels?
Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head quite accurately shows changes in the shape and location of the arteries and the effect of these changes on blood flow. Most often in the practice of doctors, tortuosity of blood vessels occurs. Vascular tortuosity is an adaptation of the body to increased or unstable pressure and to various changes in the spine, which can sag in its height. This pathology is primarily associated with age-related characteristics or high blood pressure. In most hypertensive patients, ultrasound of the neck vessels will show either T-shaped or S-shaped tortuosity. Not all vascular tortuosity poses a threat to the health of patients. It is important for the neurologist to exclude loops and kinks in the arteries. The bending of the arteries at an acute angle is a kind of stenosis, which does not allow blood to pass through and requires surgical intervention. The results of the ultrasound scan will answer the question of whether this tortuosity is obstructing blood flow, since this determines the form and urgency of treatment. If the tortuosity severely deforms the vessel, when it bends at an acute angle or twists in a loop, the neurologist should refer the patient for a consultation with a vascular surgeon to decide on the need for surgical intervention.
Previous NextTherapeutic strategies to prevent and manage complications
It is obvious that it is necessary to use techniques that minimize the risk of developing these dangerous complications. The text of the atlas describes, area by area, all the precautions and manipulations that must be taken to reduce this risk: the use of a cannula, the depth of injection, the quantity and quality of filler injected, and so on. Pallor of the skin and patient complaints of sudden pain in the injection area are signs that blood flow has stopped in this area. We must be able to control this situation.
All measures are aimed at restoring blood flow: urgent dissolution of the filler (if hyaluronic acid was used), warm compresses, massage, etc. Then there are prescriptions that need to be followed at home: antibiotic therapy to prevent bacterial superinfection, antiplatelet agents, topical medications.
In the introduction to the atlas I placed the inscription
“Only non-practitioners do not make mistakes; only through practice does it become possible to reduce the risk of error.”
If all measures are carried out on time and correctly, the spread of the necrosis zone will be minimal, a large area of skin will be preserved and, therefore, the chance of restitutio ad integrum will be higher.
Nonspecific Tokayasu aortoarteritis on ultrasound of neck vessels
Tokayasu nonspecific aortoarteritis manifests itself at a young age and leads to lifelong hormone therapy. This is a systemic inflammation of blood vessels, leading to thrombosis. Diagnosis of this disease is difficult because it can develop in any part of the human vascular system. Here, it is important for doctors to use ultrasound to identify inflammatory changes in the arteries as early as possible. To do this, a comprehensive examination is carried out - ultrasound of the vessels of the whole body, which will include:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck and head;
- Ultrasound of vessels of the lower and upper extremities;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal aorta;
- Ultrasound of pelvic vessels;
- Ultrasound of renal vessels.
Author: Shogenov Ramish Kurbanovich
Neurologist with 10 years of experience
Introduction
So, a dangerous triangle of the face. We can describe this zone in this way: the apex of the triangle is located in the glabella area, its legs enclose the nasolabial folds and reach the base, which is located under the lower lip [Fig. 1].
Rice. 1. Dangerous triangle of the face.
The area within this zone is often corrected with filler: just think about glabellar lines, nasal hump correction, nasolabial folds and lip remodeling. The anatomical feature, or originality of this zone, which makes it so “insidious”, lies in its blood supply and especially in the topography of the arteries.