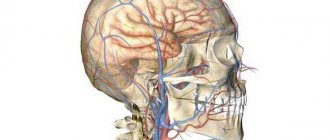
Magnetic resonance imaging combines high information content, safety and non-invasiveness. MRI of cerebral vessels is the most optimal radiation method for studying the vascular system. The contrast agent used during the study practically does not cause allergic reactions and is well tolerated.
In the absence of contraindications, the procedure is not associated with risks to the patient’s health. Electromagnetic radiation, which provides reading of information about the vascular system, has indicators that do not exceed standard values for humans in any research mode.
MRI of cerebral vessels provides detailed information for making a diagnosis in complex cases and with a confusing clinical picture - many diseases have similar symptoms. The blood supply to the head and brain comes from branches of the aorta passing through the neck. At this level, diseases or damage to the vascular system are often noted that affect cerebral circulation. To accurately determine the cause of painful conditions, an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck is performed in conjunction with a study of the brain vessels.
The examination allows you to study the condition of the main groups of cerebral vessels:
- internal carotid artery and its branches (ophthalmic, anterior and middle cerebral arteries);
- vertebral arteries located in the cervical spine, basilar, posterior cerebral arteries;
- Circle of Willis - a system of connected arteries at the base of the brain that increases the reliability of the blood supply to the brain;
- veins of the brain and venous sinuses of the dura mater.
Carrying out MRI of the vessels of the head and neck with a contrast agent allows you to visualize the smallest vessels and determine disorders of microcirculation and metabolic processes.
When is the examination carried out?
Before undergoing an MRI of the head and neck vessels, it is advisable to consult a neurologist. The doctor will assess the patient’s symptoms and condition and refer him for the most appropriate study.
The examination is usually carried out if the patient observes the following phenomena for a long time:
- prolonged headaches of unknown cause that cannot be treated with known drugs;
- periodic dizziness, loss of consciousness, fainting, darkening of the eyes, difficulty in spatial orientation;
- unstable blood pressure;
- decreased vision;
- numbness of the arms, shoulder girdle;
- actively developing osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with corresponding symptoms;
- herniated disc in the cervical region;
- subluxation, instability of the cervical vertebrae;
- traumatic brain injury, spinal injury;
- suspicion of cancer or mass formations in the brain.
The value of MRI of the head and neck vessels lies in the possibility of making an early diagnosis. The examination helps to start therapy in a timely manner and prevent the progression of the disease. Having received the necessary treatment, the patient can undergo the procedure again an unlimited number of times without risk to health. The doctor monitors the effectiveness of therapy and, if necessary, makes adjustments or changes tactics.
MRI of cerebral vessels is actively used by neurosurgeons to plan operations. Information about the location and structural features of the vascular system allows you to avoid unforeseen situations and make precise interventions. MRI is important in the postoperative period to monitor recovery processes.
What is the difference between CT and MRI of the brain?
Computed tomography is the only method that can compete with MRI. The principles of their operation differ, first of all, in the nature of the radiation: magnetic for MRI and x-ray for CT. For this reason, the first can be performed repeatedly without harm to the patient’s health, and the second can be performed no more often than a regular x-ray. At the same time, CT, unlike MRI, is not performed in a confined space, which makes it more preferable for claustrophobics.
In addition, MRI shows the chemical structure of the tissues being studied, and CT will tell us about their physical state.
Another important difference is that MRI is more effective for examining soft tissue, while CT is more effective for examining bones and joints.
The price of a brain MRI is not much different from the cost of a CT scan.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
What will the examination show?
MRI of the vessels of the head and neck is performed in angiography mode - in this case, only areas of the vascular system are visible in the images, without surrounding tissues. The examination makes it possible not only to assess the condition of the arteries and veins, but also to determine the speed of blood flow in the vessels in real time. Based on the scanning results, a three-dimensional 3-D model of the area under study is constructed.
Signs of which diseases will be shown by MRI of cerebral vessels:
- stroke - hemorrhagic (leakage of blood from the vascular system into the brain tissue or meninges) or ischemic (cessation of blood supply to a part of the brain, more common);
- arterial aneurysm - pathological expansion and thinning of the vascular wall with the risk of rupture;
- arterial dissection as a result of congenital weakness of the arterial wall or damage by a pathological process;
- thrombosis, thromboembolism;
- inflammatory diseases of the vascular system – phlebitis, arthritis, systemic vasculitis;
- vascular tumors – hemangioma, hemangioblastoma, angioreticuloma;
- atherosclerosis;
- narrowing of the lumen of the vessel due to structural features or compression from the outside by a space-occupying formation;
- congenital developmental anomalies and structural features - absence, decrease or increase in diameter, bifurcation of some parts of the vascular system, arteriovenous malformation.
MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck will show structural defects and pathological processes leading to impaired cerebral circulation:
- dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries - damage to the artery wall as a result of injury, bending, with further formation of a hematoma between the walls of the vessel, narrowing of the lumen of the artery and disruption of the blood supply to the brain;
- pathological tortuosity of the carotid artery;
- developmental anomalies and acquired lesions of the vertebral artery;
- neoplasms;
- aneurysm of a section of the vascular system;
- pathologies in the area of the carotid sinus.
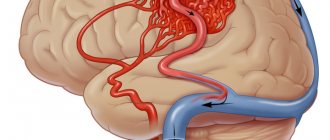
Blood supply to the brain
The normal functioning of the brain requires a large amount of energy. Nutrients and oxygen are delivered to the cells of the nervous tissue through the bloodstream. Nature has taken care to create a high degree of reliability of blood supply to the brain. It is provided by four powerful main arteries: two carotid and two vertebral. At the base of the brain, the branches of these vessels form a closed circle, called Willisian after the English physician and anatomist of the 17th century, Thomas Willis, who first described it. Thanks to this, the lack of blood supply in one of the main vessels is compensated by others. It also happens that even with serious disturbances in blood flow in three of the four main vessels, a person complains only of a slight deterioration in well-being - the compensatory capabilities of the brain are so great. Great, but, unfortunately, not unlimited. Man manages to “shatter” these perfect compensation mechanisms created by nature. It all starts with the most ordinary complaints of headache, dizziness, memory loss and fatigue.
After some time, the patient develops more serious neurological symptoms, indicating multiple brain damage. The reason for this is chronic cerebral circulatory failure, or “dyscirculatory encephalopathy.” This term was proposed in 1971 by well-known domestic scientists working at the Research Institute of Neurology of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences E.V. Shmidt and Candidate of Medical Sciences G.A. Maksudov, and it means changes in the brain associated with disturbances in its blood supply.
The main causes of the occurrence and development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy are arterial hypertension and atherosclerosis.
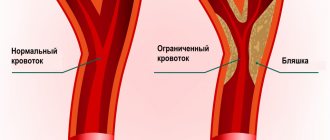
More than 40% of the adult population of Russia suffers from hypertension. Men and women, old people and young people get sick. Only in 5% of cases the cause of hypertension is clear. These may be renal failure, endocrine disorders, atherosclerosis and some other diseases. In 95% of cases, the cause of hypertension remains unclear, which is why it is called essential (literally, hypertension itself). With hypertension, the walls of blood vessels become denser, local narrowings (stenoses) and tortuosity are formed. All this leads to circulatory disorders, including blood supply to the brain. Sometimes it comes to occlusion - complete closure of the lumen of the vessel.
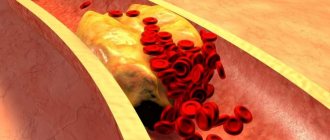
Blood clots, thrombi, develop in the area of atherosclerotic plaques that form on the inner walls of the vessel. Blood clots can completely block even large vessels, causing serious cerebrovascular accidents. (Image: Science and Life)
Unlike hypertension, the cause of atherosclerosis is known - it is a disorder of lipid metabolism. In patients with atherosclerosis, the level of fat-like substances in the blood increases - cholesterol, low-density lipoproteins, triglycerides, which are deposited on the walls of blood vessels, forming lipid stains. Then the spots grow into so-called plaques. Due to the deposition of calcium salts, the plaques become denser and ultimately narrow or even close the lumen of the blood vessels. Then they begin to disintegrate, their particles - emboli - enter the bloodstream and sometimes clog other small and large vessels.
Sometimes the development of dyscirculatory encephalopathy is facilitated by osteochondrosis, since in this disease, due to deformation of the intervertebral discs, the vertebral arteries that supply the brain with blood can be pinched.
Impaired blood supply leads to the gradual death of neurons in various parts of the brain, and the patient experiences neurological symptoms. Discirculatory encephalopathy is most characterized by emotional and personal disturbances. At the onset of the disease, asthenic conditions are noted: general weakness, irritability, poor sleep. Asthenia is often accompanied by depression. Gradually, such painful personality traits as egocentrism and periodically occurring causeless agitation begin to appear, which can be pronounced and manifest itself in inappropriate behavior. With further development of the disease, emotional reactivity decreases and gradually turns into dullness and apathy.
Once it begins, the disease steadily progresses, although during its course both sharp periodic deterioration (paroxysmal course) and periods of slow increase in symptoms of the disease can be observed.
We should not forget that dyscirculatory encephalopathy increases the risk of many severe brain diseases and, above all, stroke - an acute circulatory disorder of the brain (Manvelov A., Candidate of Medical Sciences; Kadykov A., Doctor of Medical Sciences. “Stroke is a social problem and medical” // “Science and Life” 2002, No. 5.). In Russia, strokes are registered in more than 400 thousand people per year. Of these, 35% die in the first three weeks of the disease, and only half of the patients reach the annual milestone. The possibility of epileptic seizures occurring against the background of developing discirculatory encephalopathy should not be excluded.
Contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular system of the head and neck
The ban on MRI of head and neck vessels is due to the peculiarities of the interaction of electromagnetic radiation with certain metals and magnets. The examination is prescribed with caution in certain patient health conditions.
MRI of cerebral vessels is contraindicated if the patient has the following devices in the body:
- pacemaker and other stimulating implants and pacemakers, cochlear implant - implants may fail under the influence of a magnet;
- metal intravascular stents, artificial heart valves;
- endoprostheses, foreign metal bodies in the body;
- metal clips installed in the vessels of the brain after surgery - under the influence of a magnetic field they can move and cause bleeding.
Not every material prohibits MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head. Metals that react to a magnetic field by displacement and heating: stainless steel, iron, nickel, cobalt. In other cases, the procedure is not prohibited.
In some patient conditions, examination is allowed by the doctor’s decision on an individual basis:
- pregnancy up to 12 weeks - the fetus is especially sensitive to external factors;
- serious condition of the patient, severe pain;
- epilepsy, seizures, mental illness;
- body weight should not be more than 130 kg - the devices have restrictions on the patient’s weight and waist circumference.
The procedure can be performed in patients who find it difficult to maintain a stationary body position under general anesthesia or in an open-type apparatus. During the entire period of using MRI, there have been no cases of fetal pathology developing after the procedure in the first trimester of pregnancy, however, doctors are careful. If the patient suffers from a mild form of claustrophobia, he may take sedatives before the examination.
MRI of the vessels of the head and neck with the use of contrast agents is contraindicated in pregnant women at any stage, as well as in patients with renal failure.
Specialized methods
The following examination methods exist:
- Doppler ultrasound provides information about blood circulation in important vessels of the neck and brain. In this way, abnormalities of the vascular system are detected in the early stages. The effectiveness of the treatment is analyzed. Meanwhile, the day before you need to stop smoking and drinking caffeine. The above can affect vascular tone.
- Electroencephalography allows you to analyze the functional state of the brain and its irritability. In this case, even minor fluctuations are recorded. The information obtained is transferred to a special paper tape or converted into an image on a computer screen. This method makes it possible to diagnose and treat epilepsy, delayed mental and speech development, and detect the consequences of traumatic brain injuries.
- Echoencephalography diagnoses tumors and disorders of the brain structure, including after injuries. The device works by capturing a kind of echo, which is returned when ultrasonic waves are sent to the brain. The image is displayed on the screen.
- Rheoencephalography uses a weak high-frequency electric current to record fluctuations in the electrical resistance of tissues. This determines the condition of the vessels, their elasticity, blood filling and tone. The functioning of the arterial and venous systems of the brain is also established. Atherosclerosis, intracranial hypertension, subdural hematomas, and vascular dystonia are diagnosed. The effect of therapy for the listed diseases is assessed. The study is carried out using a rheograph apparatus with electrodes connected to it.
- Electroneuromyography. Using this method, brain biocurrents are recorded. The data obtained make it possible to diagnose dysfunctions of the peripheral nervous system and neuromuscular diseases. The procedure does not require lengthy and extensive preparation, and does not take much time, which makes it convenient and comfortable for those being examined.
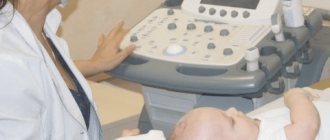
- Neurosonography allows you to study the condition of babies from birth to 12 months. Ultrasound is used, so the procedure is safe. The equipment is highly accurate, as a result of which diseases are detected at the earliest stages, right up to the overgrowth of a large fontanel in the skull.
- Craniography. The examination is carried out using x-rays. Projections of the skull are made in profile and full face. This is how congenital or acquired bone abnormalities are detected. The value of craniography lies in the ability to quickly assess the presence of large fractures of the bones of the brain and facial skull. Craniography can be performed if there is a suspicion of a tumor of bone structures, brain structures, neuritis of the facial nerve, or if osteomyelitis is suspected.
CT scan
Diagnosis is carried out by calculating the intensity of penetration of X-rays through brain tissue. A detailed image is displayed in cross section. The accuracy of the result is guaranteed even at low levels of radiation.
The examination is used if the patient suffers:
- pain in the head and neck area;
- fainting;
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- speech and memory disorders;
- suffered a stroke;
- visual and auditory impairments.
The examination method under consideration is not applicable to pregnant women and children. If it is necessary to administer intravenously a contrast agent, the following contraindications are added:
- liver and kidney failure;
- heart defects;
- asthma;
- thyroid diseases;
- allergy to iodine;
- diabetes.
Before an examination using a contrast procedure, it is forbidden to consume food or liquid for 4 hours. Other cases do not require special preparation of patients. During the procedure, a person is moved on a moving table into a tomograph, where it is forbidden to move. At certain moments you will need to hold your breath.
In the absence of contraindications, the examination can be carried out as long as necessary to accurately establish the pathology.
Magnetic resonance imaging
MRI is very popular today. Thanks to the action of a magnetic field constantly maintained in the device, the condition of the skull is visualized. Hydrogen atoms present in the cells of the human body repulse the effects of electromagnetic waves. The data obtained is converted into images of brain tissue.
Diagnostics is effective for a wide range of pathologies: from diseases of the vascular system to tumors.
Contraindications to the examination include:
- mental disorders of the patient;
- acute pain syndrome or coma;
- metal and ferromagnetic pins, clips on blood vessels, implants in the patient’s body, permanent crowns on teeth;
- tattoos made with paint containing metallic particles.
The principle of operation is the same as that of computed tomography. The patient lies down on a moving table, the body is secured with straps, and sensory sensors are attached to the head. This is how the signal is sent and read. The table is sent to the tomograph. Duration - up to 40 minutes. The duration depends on the number of programs involved. The patient is required to lie still. The procedure is safe for children and adults.
Magnetic resonance angiography
The examinations are carried out according to the same rules as MRI. This is how pathologies of the vascular system are identified. The data is converted into a three-dimensional image of all brain vessels. The examination also allows the projection of thin sections of individual vessels and nerve trunks.
Positron emission tomography
This method examines the brain to record all ongoing functional processes. With its help, it is possible to distinguish a benign neoplasm from a malignant one in the early stages. The examination allows you to obtain information about abnormalities in the functioning of the brain, the consequences of injuries and bruises, and determine the condition of the organ after a stroke.
Patients are prohibited from eating 4-6 hours before. It is recommended to exclude foods containing protein the day before. The procedure involves intravenous administration of a radiopharmaceutical. The scan lasts 30-75 minutes.
Preparing for the study
First of all, you should make sure that there are no contraindications, and if there are any, collect all the technical documentation describing the devices and endoprostheses implanted into the body. The examination becomes possible after analyzing the composition of metal implants.
It is advisable to have with you a doctor’s referral, extracts from medical documents, expert advice, as well as the results of previous studies, if any. A patient who is scheduled to receive a contrast agent should undergo a kidney function test in advance. Women should be sure that they are not pregnant.
There is no need for special preparation for MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head. If an examination with contrast is prescribed, you must arrive on an empty stomach.
How is the examination carried out?
First of all, you need to get rid of metal items of clothing, the neck and ears should be free of jewelry. Bags, money, plastic cards, telephones, and electronic devices must be left outside the office. The patient receives disposable comfortable clothing for a comfortable procedure.
The examination without contrast agent lasts about 20 minutes; the introduction of contrast agents doubles the examination time. The patient is positioned on a table, which smoothly slides into the body of the tomograph, where the scanning will take place. During the examination, the neck and head should not make any movements. Fixation is ensured by a special coil.
When performing MRI of vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the tomograph operation is accompanied by unusual sounds, so the patient receives earplugs or headphones before the examination. The body of the tomograph is equipped with a fresh air supply system, as well as an intercom through which the doctor can give the command to hold your breath or slightly change the position of your head. If the patient becomes ill, it is possible to urgently contact the staff and stop the scan. After completing the examination, the patient changes clothes and can await the result.
Causes and consequences of headaches
To get rid of headaches caused by ordinary overwork, it is enough to get a good night's sleep, adjust your lifestyle and diet. But this does not help in all cases, just like taking pills in an attempt to numb the pain. If painful sensations in the head are caused by developing pathological processes, it is necessary to identify and eliminate their causes. It can be:
- hormonal disbalance;
- vascular diseases;
- neurological disorders;
- viral diseases;
- inflammation of ENT organs;
- cranial injuries and post-traumatic pathologies;
- tumor processes.
A specially designed check-up program will help you find out what triggers your headache. Many diseases can develop for years without any symptoms. The examination results in such cases come as a complete surprise to patients.
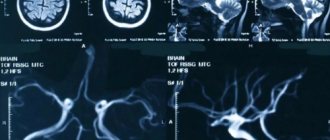
What the results look like
After performing an MRI of the vessels and arteries of the neck and head, the doctor receives layer-by-layer images of the vascular pattern with the ability to construct a three-dimensional model. The patient can pick up the images on electronic media or in printed form. The photographs are accompanied by a report from a radiologist.
Normally, the internal carotid arteries are located symmetrically, have clear contours, are not displaced, and are not compressed. The cerebral arteries arise in a typical place, the diameter is not changed, and there is no pathological tortuosity of the vessels. The cerebral veins and sinuses should be of normal diameter, without areas of blood flow disturbance, filling defects or deformations.
On MRI images of the vessels and arteries of the neck you can see signs inherent in certain diseases:
- an aneurysm is a round formation with a high signal intensity; when a thrombus attaches, a layered structure appears;
- vascular malformations appear as linear or tortuous structures with dilated vessels;
- dissection of the arterial wall is characterized by the appearance of a crescent-shaped hematoma located along the vessel, while the lumen of the artery is narrowed evenly or in the form of a rosary;
- atherosclerosis of the vascular system looks like an area of increased intensity on the vessel wall, the lumen is narrowed;
- hemangioma is a high-intensity formation with clear edges and a lobular structure.
Despite a detailed description of all identified pathological formations, the conclusion of a radiologist is not a diagnosis. The MRI result of the area of the cerebral vascular system should be shown to the doctor who ordered the study. Clinics offer the opportunity to consult with the radiologist who performed the procedure. If necessary, he will recommend contacting specialized specialists - a neurologist, oncologist or surgeon.
How to do an MRI of the brain
Only the patient’s head enters the tomograph chamber, so the feeling of enclosed space is minimized
There is no need to prepare specially for the study. The only requirement is not to wear metal or jewelry, hairpins, or watches when going for an examination (or be prepared to remove them or take them out of your pockets before placing them in the tomograph). Also, during the procedure you cannot have magnetic media (flash drives, bank cards, etc.) with you, since the information stored on them will be destroyed.
The diagnosis will take 30–40 minutes. You cannot move your head during the process, but this restriction does not apply to the facial muscles. You can even talk to your doctor while he takes sequential pictures. From time to time, the doctor himself will contact the patient to inquire about his well-being.
If you suffer from claustrophobia, but an MRI of the brain is necessary, you need to say this in advance. Then the doctor will suggest taking a sedative before starting the procedure.
Where to get a magnetic resonance imaging scan
The search for a clinical diagnostic center can be significantly speeded up if you use the help of our website. The service contains information about a large number of clinics, ranging from contact details to discount offers. If necessary, our specialist will advise you free of charge over the phone about operating hours, the availability of tomographs of the required type and the time available for making an appointment.
A patient who wants to undergo magnetic resonance imaging of the vascular system of the head and neck can independently filter the list of medical institutions by rating, cost and features of the procedure (24-hour clinics, pediatric MRI).
How often can I have a head MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging is safe for the health of patients; the number of procedures is determined by the doctor. The frequency of head MRI depends on the clinical picture and the disease being diagnosed:
- hydrocephalus requires scanning every 5 years, if necessary, dynamic monitoring is carried out, the frequency of which is determined by the attending physician;
- neoplasms are scanned up to 4 times during the first year, then 1-2 times a year if there is no tumor growth;
- for multiple sclerosis, examinations are prescribed 1-2 times a year;
- stroke - an MRI is performed to establish a diagnosis, then sent for preventive examinations every 4 years;
- Alzheimer's disease - a one-time scan is recommended to confirm the nature of the pathology;
- To monitor recovery processes after surgery, 3-4 procedures are carried out during the first year; in the future, the frequency of MRI depends on the clinical picture.
Alzheimer's disease on MRI
Scanning the brain with a magnet does not carry radiation exposure and does not have a negative effect on organs and tissues. The noise and the need to lie still during the entire examination create some inconvenience, but in general the method is painless and comfortable for the patient.