Today, the diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD) is being made less and less often to patients, but not because humanity has been able to completely defeat this disease, but because this formulation is outdated. Vegetative-vascular dystonia means dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system, which is not an independent disease, but is only a consequence of pathological changes in the body.
In the latest edition of ICD-10 there is no such disease as VSD. The disorders characteristic of it are called by the more modern and precise term “somatoform autonomic dysfunction of the nervous system.” But for simplicity of presentation and understanding, we will further use the more familiar concept of VSD.
general information
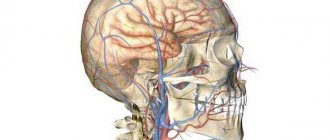
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is responsible for the unconscious regulation of the body. The movement of blood through the vessels, the digestion of food, the secretion of saliva - all these and many other processes occur automatically. The ANS itself is divided into two sections: sympathetic and parasympathetic. They are responsible for opposite processes and are in constant balance. Disturbances in this balance cause unpleasant symptoms, which form the clinical picture of NCD.
Adolescents and young women are more susceptible to the disease.
What is VSD
The autonomic nervous system, also called the autonomic nervous system, is part of the nervous system of the human body. It is responsible for controlling the activity of internal organs, metabolic processes occurring in the body, the functioning of blood and lymphatic vessels, as well as the activity of the endocrine glands. Thus, the autonomic nervous system plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis (constancy of the internal environment) and adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for the innervation of the entire body, organs and tissues. Moreover, its work is in no way subordinate to the will of a person, but is controlled independently of desires by the cerebral cortex. That is, a person cannot voluntarily stop the heart or influence the speed of intestinal peristalsis.
Autonomic nerve centers are also located in the brain stem, hypothalamus and spinal cord. Therefore, any disturbances in these organs are directly reflected in the quality of functioning of the autonomic nervous system, and can lead to the development of autonomic disorders.
Thus, all vital processes of the body are under the control of the autonomic nervous system, namely:
- heart rate;
- blood pressure level;
- thermoregulation;
- activity of salivary, sweat, endocrine glands;
- frequency and depth of breathing;
- digestion of food and intestinal motility;
- the condition of the smooth muscles of internal organs and the walls of blood vessels;
- processes of growth and reproduction;
- metabolic processes;
- urination, etc.
Anatomically and functionally, the autonomic nervous system is divided into 3 sections:
- Sympathetic - responsible for metabolism, energy consumption and mobilization of forces for active activity. Its sphere of influence includes heart function and blood pressure levels. Therefore, the sympathetic department allows the human body to prepare as much as possible for fight or active work.
- Parasympathetic - regulates the functioning of organs mainly during sleep and passive rest, and is responsible for restoring spent energy reserves. It is responsible for reducing heart rate, blood pressure and increasing peristalsis, which makes it possible to replenish energy reserves from food received.
- Metasympathetic - ensures communication between internal organs and the preservation of local autonomic reflexes.
All parts of the autonomic nervous system are in a certain relationship with each other, which ensures proper regulation of the body’s functioning. At the same time, the most important organs from the point of view of life support have double innervation with the opposite effect. But when the slightest deviation from the norm occurs, under the influence of stress, the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic departments is disrupted, which leads to the predominance of one of them over the other. The result of this is the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a syndrome that combines various disorders of autonomic functions that are the result of impaired neurogenic regulation. This occurs when the balance between the activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts of the autonomic nervous system is disturbed, which can be due to the action of a huge variety of the most disparate causes.
Thus, VSD is a multifactorial disorder that can be regarded as one of the symptoms of an existing neurological or somatic disease and consists of changes in the functioning of internal organs. Sometimes the root cause of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia cannot be established.
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is often also called cardioneurosis, dysvegetosis, neurasthenia and some other terms.
Causes
The list of causes of neurocirculatory dystonia is extensive. It includes:
- hormonal changes: puberty, pregnancy, menopause;
- acute and chronic stress;
- physical or mental fatigue;
- lack of sleep;
- bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse;
- poor nutrition and excess body weight;
- change of climate and time zones;
- hereditary predisposition;
- drinking large amounts of coffee, energy drinks, and certain medications;
- infectious diseases;
- pathology of the endocrine glands;
- mental disorders;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- chronic pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, digestive or cardiovascular systems.
Make an appointment
Symptoms
The symptoms of neurocirculatory dystonia are very diverse and form the basis for the classification of pathology. However, it is possible to identify a number of common features that are characteristic of most types of NDC:
- frequent mood changes;
- constant fatigue and drowsiness;
- lack of strength, weakness;
- feeling of a lump in the throat;
- increased sweating;
- weather sensitivity;
- anxiety;
- feeling of lack of air, etc.
An exacerbation of the disease can be triggered by any stressful situation: an excess of positive or negative emotions, lack of sleep, or even a simple change in time zones.
Types of pathology
Depending on the prevailing symptoms, several types of NCD are distinguished.
- Cardiac. Symptoms related to the heart come to the fore. A person experiences stabbing or pressing pain in the chest, which is accompanied by an increased or decreased pulse, and a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart. The pain syndrome often spreads to the left arm, completely simulating a serious pathology. At the height of an attack, a person often feels weak, dizzy, and afraid.
- NCD of hypotonic type. This type of dystonia is manifested by a periodic decrease in blood pressure. Insufficient oxygen supply to the brain leads to severe dizziness or even fainting. Against the background of low pressure, a spasm of the capillaries occurs, as a result of which the skin turns pale, the hands and feet become very cold. Lack of oxygen leads to a subjective feeling of stuffiness and shortness of breath.
- NCD of the hypertensive type. Manifests itself with periodic increases in blood pressure. During an attack, a person feels hot, his face turns red, and a severe headache appears. Vomiting often occurs during an attack. Often the trigger is a change in weather. Patients get tired quickly and experience mood swings.
- NDC of mixed type. This type of pathology is the least predictable. Blood pressure rises and falls, which is accompanied by corresponding symptoms. Often there are malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, flatulence, vomiting), and kidneys (frequent urination). The person becomes emotionally unstable and has trouble sleeping at night.
Depending on the type of flow, the following types of NDC are distinguished:
- mild: symptoms of the disease appear extremely rarely, the person leads a normal lifestyle;
- moderate: manifests itself in single crises, the frequency of attacks affects daily life;
- severe: a person experiences symptoms of NCD almost constantly; against their background, vegetative crises regularly occur.
Treatment and prognosis
In patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, treatment is carried out under the supervision of doctors of the following specializations: therapist, neurologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist. Certain prescriptions will depend on the predominant symptoms of VSD. Usually, taking into account the nature and etiology of the disease, complex long-term individual therapy is carried out.
Physical therapy classes
Special physical education is most useful in the treatment of VSD in both adults and children. Such exercises have a general strengthening effect and are an excellent way to train the whole body and improve performance. Designed for the treatment of VSD and thought out taking into account age and health status, physical therapy should also exclude jumping. In general, an active lifestyle can be an integral component of the prevention of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Undergoing physical therapy
Therapeutic massage, water treatments, and reflexology also have a positive effect in the treatment of VSD. The physiotherapeutic effect is selected depending on the type of disease: it can be electrophoresis with calcium or caffeine (in the case of vagotonia) or with magnesium, papaverine or bromine (for the treatment of sympathicotonia).
Use of drug treatment
If general strengthening and physiotherapeutic measures are insufficient for the effective treatment of VSD, the specialist individually selects drug therapy, which may include the following drugs:
- sedatives that reduce the activity of autonomic reactions, antidepressants, nootropics;
- beta-blockers and herbal psychostimulants that help reduce vegetative-vascular manifestations;
- Vitamin-mineral complexes usually have a beneficial general strengthening effect.
If necessary, to treat various forms of VSD, a course of therapy is also carried out aimed at eliminating chronic foci of infection, concomitant endocrine or somatic pathology. The doctor regularly monitors a patient with vegetative-vascular dystonia. Clinical examination may be prescribed (every 3-6 months), especially in the autumn-spring period.
Vegetative crisis
A vegetative crisis is a sudden failure in the functioning of the ANS. As a rule, it occurs in young patients. Depending on the symptoms, there are three types of crises:
- sympathoadrenal (panic attack): develops due to the release of stress hormones into the blood, as a result of which the patient’s blood pressure and pulse sharply increase, severe chills, anxiety, fear of death appear;
- vagoinsular: the opposite type of crisis, manifested by a drop in pressure and pulse, sweating and weakness; often accompanied by diarrhea;
- mixed: combines characteristics of both types.
Consequences and complications
Along with the classic symptoms and diseases accompanying vegetative-vascular dystonia, the patient’s condition can be worsened by frequently occurring (approximately 50%) vegetative crises - sympathoadrenal, vagoinsular and mixed (depending on the predominance of disorders of a particular part of the system).
Sympathoadrenal crisis. The development of a so-called panic attack is associated with a sharp release of adrenaline. The crisis begins with a sudden headache, rapid heartbeat, and paleness/redness of the face. Arterial hypertension, chills, tremors, numbness of the extremities, and anxiety are usually observed. The attack also ends suddenly and is accompanied by asthenia and polyuria (increased urine production).
Vagoinsular crisis. Its symptoms are almost the opposite of sympathetic manifestations. The crisis begins with the release of insulin into the blood and a sharp decrease in glucose levels. The activity of the digestive system increases, intestinal motility increases, and rumbling appears in the stomach. A vagoinsular attack is characterized by a feeling of cardiac arrest, dizziness, arrhythmia, and difficulty breathing. Blood pressure decreases, the pulse becomes rare, sweating, skin flushing, and darkening of the eyes appear. The patient feels weak throughout the body. The attack ends with a state of severe asthenia.
Mixed crises are characterized by activation of both parts of the autonomic nervous system and, consequently, all of the listed complications. As a rule, in the absence of timely treatment of VSD, rather unpleasant consequences arise. This is especially true for childhood, since psychosomatic pathologies often appear during this period of development. These consequences are quite difficult to correct. VSD is not a life-threatening disease, but over time its quality can significantly decrease. If such severe symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia persist in adulthood, poor adaptation is observed, and it becomes impossible to fully work and study.
Complications
NCD is not an independent disease, but it can cause the development of dangerous conditions. In severe dystonia and lack of adequate therapy, it can cause:
- myocardial infarction;
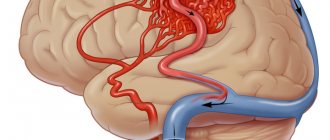
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- cholelithiasis and urolithiasis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension that does not respond to classical treatment regimens.
Malfunctions of the ANS also affect the immune system. Resistance to infections with this pathology is significantly reduced.
Treatment and monitoring of a patient with cerebral angiodystonia
Before starting treatment, it is worth determining the etiology of dystonia. Influence on the main pathogenetic link increases the chances of a complete cure.
Directions of treatment:
- Etiological treatment is correction of the underlying disease that provokes VSD;
- Normalization of vascular tone;
- Symptomatic therapy;
- Lifestyle correction, psychotherapy.
The treatment of uncomplicated angiodystonia is based on physiotherapeutic methods (therapeutic exercises, hydromassage, manual therapy, acupuncture, herbal medicine, aromatherapy), as well as the elimination of provoking factors (giving up alcohol, tobacco, reducing stress, sanitation of foci of chronic infection, if necessary, changing place work and residence). Psychotherapy with auto-training elements is quite effective.
Drug treatment of vascular dystonia of the brain is reduced to normalizing the relationship of the hypothalamic and limbic systems with other internal organs. The course of treatment is prescribed for a long period.
Drug groups:
Herbal-based sedatives - valerian, motherwort tincture, Sedavit, Persen; if ineffective - barbiturates or bromides (Elenium, Sibazon, Fenozepam, Grandaxin, Afobazol; They relieve emotional and mental stress, anxiety, fear, and normalize vegetative reactions.- Drugs that improve cerebral blood flow (neuroangiocorrectors) – Stugeron, Cinnarizine, Cavinton;
- Drugs with nootropic effect - Piracetam, Nootropil;
- Antidepressants – Amitriptyline, Fluoxetine, Paroxetine. Caffeine-based psychostimulants, antipsychotics;
- Alpha or Beta blockers (for hypertensive type) - Anaprillin, Phentolamine, Prazosin, Sotalol, Bisoprolol; ACE inhibitors – Berlipril, Enalapril; Ca2+ channel blockers – Amlodipine, Nifedipine;
- For the hypotonic type - methylxanthines (Euphylline, Theophylline), M-cholinergic blockers (Atropine);
- Vitamin complexes, antioxidants, diuretics, adaptogens with extract of eleutherococcus, lemongrass, ginseng;
- Glycine - to reduce the excitability of the autonomic nervous system, improve metabolic processes in the brain.
As rehabilitation for VSD, they use a stay in a sanatorium with the use of water procedures (swimming, body wraps, contrast showers, hydromassage), walks in the fresh air, phyto-baths (coniferous, nitrogen, valerian, iodine-bromine, hydrogen sulfide, radon, carbon dioxide). It is also recommended to take a course of electrophoresis and electrosleep.
Diagnostics
In the process of diagnosing neurocirculatory dystonia, especially of the mixed type, it is important for the doctor to exclude other causes of similar symptoms. The patient will undergo a thorough examination, including:
- collecting complaints and medical history, clarifying all details of the course of the disease;
- standard examination, including assessment of the functioning of the main body systems, including both sections of the ANS;
- general blood test to exclude inflammatory manifestations;
- general urinalysis to exclude renal pathologies;
- biochemical blood test, which necessarily includes a study of glucose and cholesterol levels, hormonal status, blood clotting and markers of autoimmune processes;
- ECG, ultrasound of the heart;
- daily monitoring of ECG and blood pressure;
- functional load tests (bicycle ergometry, treadmill) to assess the heart’s response to stress and determine the “safety margin”;
- chest x-ray, spirometry if necessary (if the patient complains of shortness of breath and a feeling of lack of air);
- rheoencephalography, Doppler ultrasound of the head and neck vessels: to assess the quality of blood supply to the brain and its structures;
- MRI of the head, x-ray of the sella turcica to visualize or exclude space-occupying formations;
- electroencephalography if one or another form of epilepsy is suspected.
During the examination, the patient also consults with a therapist, neurologist and cardiologist. If necessary, doctors of other specialties are involved: psychiatrist, endocrinologist, pulmonologist, gynecologist, nephrologist, etc.
Concomitant diseases
Violation of vascular tone is accompanied by many diseases:
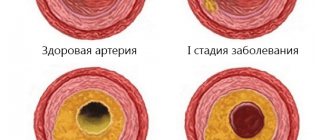
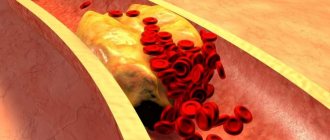
- Encephalopathy. This disease occurs due to a chronic cerebral circulation disorder, resulting in the death of brain cells. Accompanied by intellectual, vegetative and emotional disorders. At first, the disease is functional and reversible, but if atherosclerosis joins angiodystonia over time, the defect becomes irreversible.
- Hypertonic disease. The pathology is based on a sustained increase in systolic blood pressure above 140 mm Hg. Due to the increased tone of the vascular walls, the minute-by-minute volume of blood circulation in the large and small vessels of the brain decreases, which is why it suffers from ischemia and hypoxia.
- Cardiopsychoneurosis. It is characterized by pain in the heart, rhythm disturbances and fluctuations in blood pressure. Usually has a mixed type.
Treatment of neurocirculatory dystonia
Treatment of NCD has several goals:
- reduction in the strength and frequency of attacks;
- eliminating specific symptoms that cause discomfort in the patient;
- stabilization of the nervous system, in general.
The doctor’s task is to correctly select not only medications from various groups, but also non-drug treatment methods: physiotherapy, exercise therapy, massage, psychotherapy, etc.
The choice of specific medications depends on the form and severity of the disease. The patient may be prescribed:
- sedatives to eliminate excessive anxiety (Persen, valerian-based drugs, etc.);
- sleeping pills for poor sleep quality (donormil, zolpidem);
- tranquilizers in the presence of severe crises that occur like a panic attack, as well as in the ineffectiveness of softer drugs (afobazole, phenibut, atarax, etc.);
- antidepressants for excessive apatite, lethargy, depression; improve heart function, reduce pain (paroxetine, sertraline);
- nootropic drugs to improve memory, concentration and general stimulation of the body (glycine, piracetam, pantogam);
- drugs to improve metabolism in the brain (Actovegin, Cerebrolysin);
- angioprotectors to restore full blood supply to the central nervous system (Cavinton, pentoxifylline);
- antihypertensive drugs from the group of adrenergic blockers for increased pulse and blood pressure (anaprilin, bisoprolol);
- hypertensive drugs for low blood pressure (caffeine, mezaton, preparations based on ginseng and lemongrass);
- antioxidants that help strengthen the body in general (succinic acid, mexidol);
- multivitamins, as well as preparations with a high content of B vitamins to improve nerve conduction (milgamma, neuromultivit).
The selection of a specific combination of drugs, their dosage and regimen of administration is carried out only by a doctor, depending on the clinical situation and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body.
Non-drug treatments for NCD are used as an adjunct to medications. Their task is to strengthen the body and increase its resistance. The most popular are:
- physiotherapy: laser treatment, magnetic therapy, electro- or phonophoresis, electrosleep;
- massage of the cervical-collar area and general;
- physiotherapy;
- acupuncture;
- a variety of relaxing procedures: wraps, floating, applications, etc.;
- psychotherapy;
- Spa treatment.
It is important to remember that most of these techniques can only be used outside of an exacerbation.
Make an appointment
Symptoms of vegetative-vascular dystonia
Thus, it is already clear that vegetative-vascular dystonia can manifest itself in radically different ways. This concept “protects” various symptoms that arise in response to disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system.
In most cases, VSD occurs latently. But under the influence of overload or other unfavorable factors, an attack develops. Often they arise suddenly and unsettle a person. They are most difficult for older people, since they usually already have a number of other diseases, which aggravates the situation.
Often there are signs of other diseases that are not directly related to the autonomic nervous system or brain. But if manifestations of disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system are observed, the neurologist has good reason to assume the presence of VSD.
The most common complaints of patients who are subsequently diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia are:
- headaches of varying degrees of intensity and duration, migraines;
- attacks of dizziness;
- increased sweating;
- increased heart rate;
- severe weakness, increased fatigue;
- fluctuations in body temperature;
- noise in ears;
- darkening of the eyes, sometimes followed by fainting;
- constant drowsiness;
- increased anxiety, panic attacks;
- sudden mood swings;
- obsessive syndromes, hypochondria.
A panic attack is a strong fear of imminent death that completely grips the patient. The attack begins with the onset of anxiety, which gradually increases and turns into genuine horror. This is explained by the fact that the body sends signals of danger, but does not see options for exiting the situation. The attack lasts on average 10–15 minutes, after which the patient’s well-being gradually returns to normal.
Prevention
Prevention of NCD is important not only for healthy people who are at risk, but also for those who are already closely confronted with this pathology. Changing your lifestyle, adjusting your diet and physical activity help strengthen the body and significantly reduce the risk of unpleasant symptoms. Doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- eliminate overtime, ensure daily proper rest;
- create the most peaceful atmosphere at home and at work;
- go to bed on time (duration of sleep at night is 8 hours or more);
- do not ignore walks in the fresh air;
- choose a suitable sport that will allow you to practice for your pleasure (swimming, walking, cycling, yoga, Pilates, etc.);
- adjust nutrition: the daily diet must meet the standards for caloric content, the ratio of dietary fat, the content of vitamins and microelements;
- minimize the consumption of food stimulants: tea, coffee, fatty foods, smoked foods, alcoholic drinks;
- drink at least 2 liters of clean water daily (other drinks do not count).
Compliance with these rules is useful for the prevention of not only neurocirculatory dystonia, but also many other diseases. The body always responds gratefully to care for it and begins to cope much better with inevitable stress and physical activity.
Headache and how to deal with it during VSD
The results of research by scientists have shown that men are less likely to suffer from headaches with VSD; accordingly, this is the fate of women to a greater extent. This problem haunts them throughout the day from the moment they wake up until they go to bed (during sleep, the headache usually does not bother them). A woman constantly has to say “no” to the most pleasant and joyful moments in her life. Here is a simple example, about which so many anecdotes and jokes have already been written, a woman increasingly begins to avoid marital responsibilities, citing an illness that is debilitating her. Even close people sometimes do not understand her torment, considering her just a good actress and a liar. But this is not the case, and it’s worth looking into.
Causes of pain
We also know from the school biology curriculum that the cause of this disease is the narrowing or dilation of blood vessels in the human brain. Everything is true, but not in the case of people suffering from VSD.
Of course, first of all, it is necessary to undergo a full examination in order to certainly exclude abnormalities in the functioning of the blood flow to the brain. Today, there are many methods that will identify diseases, if any, with 100% accuracy. For example: MRI, CT, REG, EEG and ultrasound.
If studies have not revealed obvious causes, then the main source of pain can be considered a disease caused by a disorder of the central nervous system, in other words, neurosis. Thus, headache cannot be considered as an independent disease, because it is a consequence of a disorder of the nervous systems as a whole.
How to distinguish a headache with VSD from any other
- In the case of VSD, the pain is usually continuous.
- Its intensity is the same, that is, not sharp, not fading and “not shooting.”
- When you sleep, the pain usually does not bother you.
- The localization of pain can be varied; the whole head or a separate part of it can hurt. For example, the right or left half of the brain, as in hemicrania, better known to us as migraine.
- Very often there is a feeling of swelling and some kind of strange pressure in the frontal area, around the eyes and temples.
- Most importantly, head pain with VSD does not depend on blood pressure, and it cannot be relieved with symptomatic medications.
treatment of headaches in people suffering from VSD
As we have already said, the pain in the head with VSD is constant and, unfortunately, no medicine in our medicine cabinet can often curb it: not analgin, not citramon, not no-spa, etc. Some painkillers can only reduce its intensity for a short time, but cannot completely get rid of it. In this case, sedatives that cause calm or reduce emotional stress, as well as tranquilizers, come to the rescue. Among sedatives, the most popular are herbal preparations such as valerian, motherwort and mint.
Remember, a headache in the case of VSD is only one of the signs of a disorder of the nervous system. Therefore, it is necessary to treat the entire body, not just the head or another part of the body. Today, many believe that the main cause of constant headaches is osteochondrosis. They spend a huge amount of money and time on its treatment, but there is no result, the pain does not go away. The main rule that a patient suffering from VSD must learn: osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is in no way connected with the development of VSD, and, accordingly, with pain in the head.
In order to help yourself with headaches, you first need complex treatment of vegetative-vascular dystonia. And you should start by taking medications that will relieve feelings of anxiety, fear and panic (we wrote about them just above).
Well, in general, giving up bad habits, a healthy balanced diet, a positive attitude towards life, a proper work and rest schedule, moderate physical activity and just walks in the fresh air will help you avoid headaches.
Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
Treatment at the Energy of Health clinic
Doctors at the Energy of Health clinic do not downplay the significance of the symptoms of NCD. We guarantee each patient a thorough examination, including all the necessary samples and tests, as well as selection of the most gentle, but at the same time effective treatment. At your service:
- drawing up a medication correction regimen in accordance with the characteristics of the course of the disease (not only the complex of symptoms, form and stage of the disease are taken into account, but also the emotional background, chronic diseases, hormonal status, characteristics of the patient’s work, etc.);
- restorative procedures: physiotherapy, massage;
- selection of physical exercises to perform in the gym with an instructor and at home;
- acupuncture;
- help from a psychotherapist and psychiatrist;
- selection of a resort for treatment in a sanatorium, collection of necessary documents;
- detailed recommendations for correcting lifestyle, nutrition, and physical activity.
We will help keep the disease under control and will always come to the rescue in case of exacerbation.
Advantages of the clinic
The Health Energy Clinic uses an integrated approach to solving any patient’s medical problems. We offer the most complete range of services, including:
- consultations with narrow specialists, including obtaining the opinion of a foreign doctor remotely;
- all types of tests and diagnostic procedures;
- modern treatment regimens compiled on an individual basis;
- issuance of certificates and conclusions.
A healthy person can choose one of the comprehensive check-up diagnostic programs to identify hidden pathologies.
Neurocirculatory dystonia is a disease that is not recognized by all doctors, but its symptoms do not disappear. Don’t let disruptions in the nervous system ruin your life, sign up for diagnostics and treatment at the Energy of Health neurology clinic.
Rheoencephalography for angiodystonia of cerebral vessels
If there is a suspicion of angiodystonia of the cerebral vessels, rheoencephalography is performed. This method is also used when examining children. Rheoencephalography can detect circulatory disorders in the brain. This diagnostic method is safe, but it is prohibited to use it if there are wounds on the skin in the place where the electrodes need to be applied. People suffering from fungal diseases of the scalp should avoid rheoencephalography. It is not recommended to drink coffee or strong tea before the study, otherwise the accuracy of the study may decrease.
During the process of rheoencephalography, a person must be in a relaxed state: he sits comfortably on a special couch. The specialist places electrodes on the patient’s head, which are pre-treated with gel. The electrodes are fixed with a tape made of elastic material. During the procedure, special signals are sent to the brain: the monitor displays certain indicators characterizing the condition of the blood vessels. In modern devices, data is transferred directly to paper tape.