Epilepsy (falling disease) is a fairly common pathology of the nervous system, the main manifestation of which is an epileptic seizure. An epileptic attack can be quite frightening and is characterized by loss of consciousness, the onset of seizures and, in some isolated cases, foam at the mouth. Sometimes it may take on a reddish tint.
To provide first aid, you do not need to have specific medical knowledge or skills. In most cases, the seizure goes away on its own; it is not necessary to call an ambulance. As a rule, a person who knows about his problems carries a note with the numbers of his relatives, friends, and information about himself, which may be useful to those who happen to be close to him.
However, people who want to help the victim should carefully perform first aid procedures, since the wrong procedure can cause serious harm to the patient.
People suffering from epilepsy should be regularly examined by a doctor, as the correct prescription of medications and constant monitoring of the disease reduce the risk of epileptic seizures. The Yusupov Hospital provides medical services from the best neurologists and epileptologists in the capital, who will select individual treatment for each patient.
Epilepsy and epileptic seizures are of completely different types and can manifest themselves in different ways. However, despite the variety, the attack always occurs suddenly. There are some signs by which you can determine an impending seizure, but this is not always possible. It is important for the person providing assistance to maintain inner calm and confidently carry out all necessary actions, since a person’s life is at stake.
Rules of first aid for an epileptic attack
An attack of epilepsy is not as terrible and dangerous as failure to provide assistance to the patient at this moment.
It is necessary to remove sharp, heavy objects and those that are dangerous for the patient and others. It is advisable to find something soft (pillow, blanket, towel, folded clothes) to place under the patient’s head. Do not hold the patient by force - this will worsen the condition. You need to note for yourself the time the attack began; if it lasts more than 5 minutes, you need to call a medical ambulance. There is no need to unclench your jaws so as not to injure your tongue, teeth and oral mucosa due to muscle hypertonicity. It is necessary to fix the victim’s head between the legs, place clothes, a blanket, a pillow under it, or roll up the clothes. Tight clothing needs to be loosened. If there is excessive salivation, then the head must be turned to the side. The patient may experience spontaneous urination.
When to call an ambulance
To provide first aid for epilepsy, it is not always necessary to involve doctors. As a rule, attacks are fleeting. There are cases when compassionate citizens called the ambulance crew, but by the time they arrived they had already left the scene on their own.
In addition, for some, such situations happen several times a day. With such options, it is enough to know the basic principles of providing assistance, and if everything proceeds without complications, you can cope on your own.
In some situations, the help of medical specialists is vital for a patient with epilepsy.
The attack happened for the first time in my life
You cannot be sure how the body will react if it has not experienced such overexertion before. It is quite possible that epilepsy is manifesting itself right now (this can happen at any age). However, there is a danger that a seizure is a sign of some disease, the exacerbation of which requires the intervention of appropriately qualified specialists.
The victim is a child or elderly
The bodies of children and the elderly are most vulnerable to critical changes in health. Even if everything goes as normal, only doctors will be able to give an accurate conclusion regarding the condition of the body and further health risks.
Cramps in a pregnant woman
A neurological disease can be fatal to a child in the womb. If a woman is late in pregnancy, there is a risk of premature onset of labor.
There is a possibility of injury
During seizures, the patient may hit his head on a sharp corner or be injured during a fall. Even if it just seems to you that there is a risk of traumatic brain injury or any other injury, it is better to call specialists and keep the patient in place until the doctors arrive.
The patient remains unconscious for more than 10 minutes
It is important to check the patient’s clarity of consciousness after an attack, to find out whether he remembers his name or home address. If he does not regain consciousness on his own, there is no need to “help” him: hit him on the cheeks or splash water. It is also forbidden to try to bring people to their senses using such means as ammonia: any strong odors can provoke a second attack, which, compared to the one just suffered, can cause significant harm to health.
Epilepsy always carries the risk of irreversible changes in brain structures. If a person breathes but does not regain consciousness for more than ten minutes, it is important to organize professional medical assistance as soon as possible.
Make an appointment
What should you not do during an attack?
There is no need to restrain a person by force, try to bring him to his senses, hit him in the face, or bother him.
This will lead to greater trauma for the patient. If your teeth are clenched, there is no need to force your jaw open. Muscles are hypertonic and such actions can injure teeth, tongue and block the airways with tooth fragments. You cannot move or transfer a person to another place; such measures are necessary if the attack began in a place that threatens life. Immediately after its completion, there is no need to give the victim water or medications, because muscle function has not yet been restored and the patient may choke. You can't do chest compressions or artificial ventilation.
How is epilepsy treated?
Epileptic seizures are treated with medications. Doctors select a specific set of remedies for each specific case. Patients are usually prescribed medications of different effect groups:
- anticonvulsants
- antiepileptic drugs
- neuroleptics
- corticosteroids
- antibiotics
- anti-inflammatory and dehydrating medications
The dosage and duration of treatment is determined by the attending doctor. With improvement, the number of drugs used is reduced.
Manifestations of a grand mal seizure
An attack with loss of consciousness, severe convulsions of the body and limbs is a grand mal seizure.
Its symptoms:
- before this, the patient feels an unusual smell or hears a sound;
- pulse may be normal;
- sudden loss of consciousness, convulsive movements of the body, head, arms and legs;
- the tongue may be bitten, blue in color, pupils do not react to light;
- foam may be released from the mouth;
- respiratory arrest may occur, but quickly recovers;
- duration – from 20 seconds to several minutes.
Signs of an epileptic seizure
The mechanics of the occurrence of epilepsy has not been precisely clarified at the moment, but it is known that seizures begin against the background of intense stimulation of areas of the cerebral cortex due to increased electrical activity of nerve endings.
Signs of an attack, as a rule, vary from person to person, but there is a certain set of symptoms that helps determine the stage of the attack and immediately proceed to first aid procedures. Such crises cause great pain and stress to the patient, so after the seizure the victim must be handled very carefully.
Signs of an epileptic seizure include:
- sudden loss of balance, falling to the ground;
- loss of consciousness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- heavy breathing;
- muscle hypertonicity;
- inseparable loud shouting;
- a sharp increase in blood pressure;
- blood from the nose;
- involuntary throwing of the head back;
- “glass eyes”;
- increased salivation, sometimes with foam;
- loss of sense of reality of the surrounding world;
- disruption of the thinking process, misunderstanding of words or shouts of strangers;
- involuntary bowel movements or urination;
- local convulsions or convulsions of the whole body;
- numbness of the limbs;
- pupils stop responding to light;
- bluishness or redness of the face and other skin;
- very rapid pulse or its strong decrease;
- convulsions.
It is quite difficult to prevent an attack, but by certain indicators you can understand its approach and take the patient to a safe place.
Expert opinion
Author: Olga Vladimirovna Boyko Neurologist, Doctor of Medical Sciences
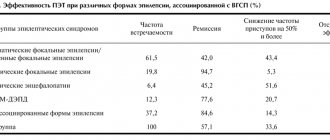
Doctors consider epilepsy one of the most dangerous neurological pathologies. This is because a seizure can occur at any time. This increases the risk of injury. Therefore, epilepsy requires timely diagnosis and treatment. The disease occupies a leading place in the structure of disability. According to statistics, 30% of patients are disabled people of group 1 or 2. In order to reduce the risk of injury during an epileptic attack, doctors have developed special first aid recommendations. Anyone can familiarize themselves with them.Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose and treat various forms of epilepsy. Modern European CT, MRI and EEG equipment are used for examination. This medical equipment allows you to quickly determine the localization of the pathological focus. The quality of treatment depends on the accuracy of the research. An individual therapeutic plan is drawn up by experienced neurologists and epileptologists. If you follow medical recommendations for the treatment and prevention of epileptic seizures, 60-70% of patients at the Yusupov Hospital achieve long-term remission.
Causes of occurrence and development
The appearance of a convulsive attack can be due to a number of reasons:
- brain tumor, meningitis, stroke;
- alcohol in high doses, drugs;
- poisoning with chemicals, poisons, paints and varnishes;
- diseases of the liver and kidneys that impair the functioning of these organs.
The occurrence of idiopathic epilepsy is associated with heredity, does not cause changes in the psyche, and most often manifests itself before the age of 25. This form of epilepsy is easily corrected with therapy.
Memo for the patient
Attack with convulsions
- Protect my head.
- Do not restrain my movements unless I am in danger.
- Don't put anything in my mouth, especially your fingers.
- When the attack is over, talk to me, put me on my side so that I can breathe easier.
- Make sure that I can completely rest and calm down after the attack ends.
- Please note there is usually no need to call the medical staff unless the attack lasts longer than usual for me, or if the seizures occur one after another.
If you have an attack without convulsions
- Do not restrain my movements unless I am in danger.
- Reassure me and stay with me during the state of confusion that may follow an attack.
- Stay with me until I fully regain consciousness and am able to talk to you.
How to spot an impending seizure
The seizure usually occurs suddenly. A person who suffers from epilepsy usually cannot accurately predict the time of an attack and the situation in which it will occur. Often, patients with epilepsy experience tension, fear that an attack will happen and that this will cause a negative reaction from others. A number of people note that they observe an aura before the onset of seizures. This may be a state of euphoria, unusual smells, sounds, a sense of taste, or a feeling that such a situation has already happened (déjà vu).
Famous epileptics
People who went down in history were also susceptible to epilepsy. Among them are Julius Caesar, Alexander the Great, Nostradamus, Dante Alighieri, Ivan the Terrible, Napoleon Bonaparte, Alfred Nobel.
For example, epilepsy was one of the diagnoses of the brilliant Ludwig van Beethoven. In addition, epilepsy was a constant companion of Nicolo Paganini and is considered one of the supposed reasons why the great composer avoided people and they were in no hurry to get closer to him.
Vincent Van Gogh suffered from epilepsy and it is believed that the order of society brought him to mental illness for this reason. There is even a version that the artist cut off his ear in a fit, unable to control his hands.
Lewis Carroll, Lord Byron, Fyodor Dostoevsky, Charles Dickens, Pyotr Tchaikovsky - all these famous writers, composers, poets and many other famous people suffered from epilepsy.
Of the living stars, Elton John, actor Hugo Weaving and many others are susceptible to epilepsy.
Treatment
Epilepsy is treated with medication.
The doctor prescribes anticonvulsants; they suppress the occurrence of pathological impulses in the brain. Additionally, psychotropic drugs (hypnotics, antidepressants, tranquilizers) are prescribed. Psychotropic medications should be taken without violating the doses prescribed by the doctor. Because they may be triggers for attacks or side effects. Therapy is not always lifelong. The doctor monitors the patient and if there is noticeable improvement and there are no recurrent attacks, then therapy can be adjusted, even to the point of discontinuation.
How can you help a patient with epilepsy?
Strictly monitor the correct intake of medications, even if this requires resorting to pedagogical pressure. Sometimes a special box with medications for the day or week helps.
The condition must be carefully recorded, i.e. keep a diary recording attacks, in which they note the time and duration of attacks, their nature, the situation with which they may be associated (high body temperature, insufficient sleep), side effects of medications.
Regularly visit the doctor and follow all his prescriptions.
Maintain a proper sleep schedule.